Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Business Cycle
Uploaded by
768balochOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Cycle
Uploaded by
768balochCopyright:
Available Formats
Powered by AI
Copilot
The business cycle is a cycle of fluctuations in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) around its long-term natural
growth rate. It explains the expansion and contraction in economic activity that an economy experiences over
time. A business cycle is completed when it goes through a single boom and a single contraction in sequence.
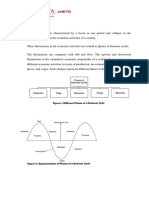
The business cycle is characterized by the alternation of the phases of expansion and contraction in aggregate
economic activity. Here are the stages of the business cycle:
1. Expansion: This is the first stage in the business cycle, where there is an increase in positive economic
indicators such as employment, income, output, wages, profits, demand, and supply of goods and services.
2. Peak: The economy then reaches a saturation point, or peak, which is the second stage of the business cycle.
The maximum limit of growth is attained.
3. Recession: The recession is the stage that follows the peak phase. The demand for goods and services starts
declining rapidly and steadily in this phase.
4. Depression: There is a commensurate rise in unemployment. The growth in the economy continues to
decline, and as this falls below the steady growth line, the stage is called a depression.
5. Trough: In the depression stage, the economy’s growth rate becomes negative. There is further decline until
the prices of factors, as well as the demand and supply of goods and services, contract to reach their lowest
point.
These stages are recurrent but not periodic. The severity of a recession is measured by the three D’s: depth,
diffusion, and duration, and the strength of an expansion by how pronounced, pervasive, and persistent it is.
You might also like
- Macro Economics PPT Notes Part 5Document6 pagesMacro Economics PPT Notes Part 5Romeo FF YTNo ratings yet
- The Business Cycle: Definition and PhasesDocument6 pagesThe Business Cycle: Definition and PhasesIbrahim Khan100% (1)
- Business CycleDocument2 pagesBusiness Cycleseul GiNo ratings yet
- 3 Whats Is A Business CycleDocument3 pages3 Whats Is A Business Cycletsiry tsiryNo ratings yet
- Economic CycleDocument3 pagesEconomic CycleimymeweourusyouNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Business Cycles - JBNDocument28 pagesTopic 6 Business Cycles - JBNleimarNo ratings yet
- Phases of Business CycleDocument2 pagesPhases of Business CycleFahima YvNo ratings yet
- Business Cycle 1 PDFDocument4 pagesBusiness Cycle 1 PDFAmina GulNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument2 pagesMicrojjpbautista.cbpaNo ratings yet
- Buisness CycleDocument8 pagesBuisness CycleyagyatiwariNo ratings yet
- Business CycleDocument4 pagesBusiness CycleNaman LadhaNo ratings yet
- Trade Cycle BBs 2nd YearDocument8 pagesTrade Cycle BBs 2nd YearSTAR Digital Arts100% (1)
- Tugas 1 Mkdu4107 Tiara AntasyaDocument3 pagesTugas 1 Mkdu4107 Tiara AntasyaTiara AntasyaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Mkdu4107 Tiara AntasyaDocument3 pagesTugas 1 Mkdu4107 Tiara AntasyaTiara AntasyaNo ratings yet
- Business Cycle and Its PhasesDocument3 pagesBusiness Cycle and Its PhasesArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Business Cycle 3Document25 pagesBusiness Cycle 3Siwani BarmaNo ratings yet
- Trade Cycle: Macro Economic Indicators: Trade Cycle, DIMAT Arjun Madan, 2005Document4 pagesTrade Cycle: Macro Economic Indicators: Trade Cycle, DIMAT Arjun Madan, 2005rudraarjunNo ratings yet
- Business Cycle The 6 Different Stages of A Business CycleDocument3 pagesBusiness Cycle The 6 Different Stages of A Business CyclevinayNo ratings yet
- Diskusi 1 BAHASA INGGRIS NIAGA NofitasariDocument2 pagesDiskusi 1 BAHASA INGGRIS NIAGA NofitasariRamadhan AzizNo ratings yet
- Trade CyclesDocument2 pagesTrade Cyclessasiforever06No ratings yet
- The Business CycleDocument6 pagesThe Business CycleoogaboogaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business CycleDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Business CycleFarhan RajaniNo ratings yet
- Economics Business CycleDocument12 pagesEconomics Business CycleYandex PrithuNo ratings yet
- Business Cycles - EconomicsDocument3 pagesBusiness Cycles - EconomicsE K VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document6 pagesChapter 10Nepali CricketNo ratings yet
- Business Cycles / Trade CyclesDocument2 pagesBusiness Cycles / Trade CyclesArpita PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Economics Sem 4 ProjectDocument12 pagesEconomics Sem 4 ProjectSakshiK ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Stages of Business CycleDocument2 pagesStages of Business CycleOkim MikoNo ratings yet
- What Is InflationDocument222 pagesWhat Is InflationAhim Raj JoshiNo ratings yet
- 4 Phases of Business Cycle in Economics With DiagramDocument3 pages4 Phases of Business Cycle in Economics With Diagrammmiguelrey100% (1)
- Business CycleDocument9 pagesBusiness CycleHarsha SekaranNo ratings yet
- Four Phases of Business CycleDocument10 pagesFour Phases of Business CyclehardyNo ratings yet
- Trade CycleDocument8 pagesTrade CyclestunningvibhaNo ratings yet
- Unit III - Business Cycles, Inflation, DeflationDocument21 pagesUnit III - Business Cycles, Inflation, DeflationKushal BagdeNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document17 pagesModule 3Neola LoboNo ratings yet
- The GDP Deflactor - IsDocument3 pagesThe GDP Deflactor - IsNetha CjNo ratings yet
- Business CycleDocument9 pagesBusiness CycleiamshijasNo ratings yet
- Eco Business CycleDocument4 pagesEco Business CycleparulkakNo ratings yet
- What Is A Business CycleDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Business CyclefelizNo ratings yet
- Hm-Hu 701Document14 pagesHm-Hu 701Prabhat RoutNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics 3Document18 pagesMacro Economics 3Baysa AlemuNo ratings yet
- Business Cycles/Trade CyclesDocument2 pagesBusiness Cycles/Trade CyclesmonuNo ratings yet
- Trade CyclesDocument22 pagesTrade CyclesTimothy ForemanNo ratings yet
- Trade Cycles: Chapter No: 04 by Mrs Paras ChannarDocument25 pagesTrade Cycles: Chapter No: 04 by Mrs Paras ChannarCafe MusicNo ratings yet
- Theories of Trade CyclesDocument13 pagesTheories of Trade CyclesSurekha NayakNo ratings yet
- MS6 Topic 2-Additional NotesDocument3 pagesMS6 Topic 2-Additional NotesYlese LopezNo ratings yet
- What Is Business CycleDocument4 pagesWhat Is Business Cyclebhagat103No ratings yet
- 5Document6 pages5sanjuladasanNo ratings yet
- L4 - Academic ScriptDocument24 pagesL4 - Academic ScriptNaomi SaldanhaNo ratings yet
- Real Business Cycle TheoryDocument7 pagesReal Business Cycle TheoryAbdul alimNo ratings yet
- Aec 675 F 4Document14 pagesAec 675 F 4RahulNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics Final Project ReportDocument12 pagesMacro Economics Final Project ReportHaseeb RehmanNo ratings yet
- The Business Cycle Describes The Rise and Fall in Production Output of Goods and Services in An EconomyDocument9 pagesThe Business Cycle Describes The Rise and Fall in Production Output of Goods and Services in An Economyqari saibNo ratings yet
- Business Cycles and Stabilization LectureDocument4 pagesBusiness Cycles and Stabilization LectureShokunbi MoyoNo ratings yet
- Economic Fluctuations: Business CycleDocument8 pagesEconomic Fluctuations: Business CycleCzarina Faye MolinaNo ratings yet
- Mb0042 Managerial EonomicsDocument7 pagesMb0042 Managerial EonomicsShobhit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Business CycleDocument10 pagesMeaning of Business CycleAAMIR IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Policy Responses to the Business CycleFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Policy Responses to the Business CycleNo ratings yet
- Project Presentation Empowering Education in GwadarDocument11 pagesProject Presentation Empowering Education in Gwadar768balochNo ratings yet
- Presentation KBDocument8 pagesPresentation KB768balochNo ratings yet
- Copilot: Powered by AIDocument1 pageCopilot: Powered by AI768balochNo ratings yet
- Trade PolicyDocument1 pageTrade Policy768balochNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument1 pageMonetary Policy768balochNo ratings yet