Professional Documents
Culture Documents
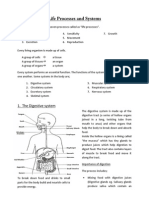
Our Body
Uploaded by
aleyisverycooCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Our Body
Uploaded by
aleyisverycooCopyright:
Available Formats
Our Body
Understanding the Human Body
The human body is an incredibly complex and intricate system, one that fascinates
scientists and medical professionals alike. It is made up of numerous cells, tissues,
organs, and systems, each with a specific function crucial for maintaining overall
health and vitality. This narrative aims to explore the fundamental aspects of the
human body, including its structure, major organ systems, and the significance of
maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
The Body's Structure
The human body can be broadly divided into several levels of organization:
Cells: The basic unit of life. Human bodies are comprised of trillions of cells, each
specialized to perform unique functions.
Tissues: Groups of similar cells that perform a common function. There are four
basic types of tissue in the body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
Organs: Structures made up of different types of tissues that work together to
perform a specific activity. Examples include the heart, lungs, and liver.
Systems: Groups of organs that work together to carry out complex functions.
The human body contains several systems, including the circulatory, respiratory,
digestive, and nervous systems, among others.
Major Organ Systems:
The Circulatory System:
This system is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, delivering
oxygen and nutrients to cells, and removing waste products. The heart, blood, and
blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries) make up the circulatory system.
The Respiratory System:
The respiratory system facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
between the body and the environment. It includes the nose, throat (pharynx),
windpipe (trachea), and lungs.
The Digestive System:
This system breaks down food into nutrients, which the body uses for energy,
growth, and cell repair. The digestive system includes the mouth, esophagus,
stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder.
The Nervous System:
The nervous system controls both voluntary actions (like walking) and involuntary
actions (like breathing) and sends signals to different parts of the body. It
comprises the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
The Musculoskeletal System:
This system provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body. It
consists of bones, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and other connective
tissues.
The Immune System:
The immune system defends against pathogens and disease. It includes white blood
cells, the spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, and antibodies.
The Endocrine System:
The endocrine system produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and
development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, and mood, among
other things. It includes glands such as the thyroid, pancreas, and adrenal glands.
Maintaining a Healthy Body:
Maintaining a healthy body is crucial for ensuring all these systems work together
harmoniously. Key components of a healthy lifestyle include:
Nutrition: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and
lean proteins.
Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart, improves muscle
strength, and enhances flexibility.
Hydration: Drinking enough water is essential for the proper functioning of every
system in the body.
Sleep: Adequate sleep allows the body to repair itself and is crucial for overall
health.
Stress: Management: Reducing stress through techniques such as meditation,
yoga, or deep breathing can improve physical and mental health.
Conclusion
The human body is a marvel of nature, capable of incredible feats and remarkable
resilience. Understanding the basics of how our body functions and the importance
of taking care of it can lead to a healthier, happier life. By nourishing our body
with proper nutrition, engaging in regular physical activity, ensuring restful sleep,
and managing stress, we can support our body's natural functions and maintain our
well-being.
You might also like
- GB Fat Loss GuideDocument124 pagesGB Fat Loss GuideMharia Almeida97% (31)
- Animal Nutrition and DigestionDocument16 pagesAnimal Nutrition and DigestiongabrielwerneckNo ratings yet
- The 11 Human Body Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument79 pagesThe 11 Human Body Organ System and Their FunctionsXin Ssai XaveraNo ratings yet
- Human Organ Systems. 2021 22Document4 pagesHuman Organ Systems. 2021 22BABU ANo ratings yet
- Organic Total Body Reboot 1 RebootDocument24 pagesOrganic Total Body Reboot 1 RebootArelis RomeroNo ratings yet
- Main Anatomical FeaturesDocument12 pagesMain Anatomical FeaturesAdelinaPredescuNo ratings yet
- Eat Carbs Lose Weight!: +stillDocument100 pagesEat Carbs Lose Weight!: +stillJoanJeannette Nieves100% (1)
- Organ SystemDocument2 pagesOrgan SystemCristina RamirezNo ratings yet
- NHS Summative Test Covers Key COVID-19 TopicsDocument4 pagesNHS Summative Test Covers Key COVID-19 Topicsrozzeille jyne geraldez100% (2)
- The Human Body Systems Power PointDocument16 pagesThe Human Body Systems Power PointElyzza Wye Albao100% (1)
- Hbs Unit 1 Summary OutlineDocument39 pagesHbs Unit 1 Summary Outlineapi-277771710No ratings yet
- Sample CopywritingDocument5 pagesSample CopywritingSleeptalker CullenNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- Ccypi 3.0Document76 pagesCcypi 3.0GirishNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy and FunctionDocument24 pagesBrain Anatomy and FunctionAdamu GudinaNo ratings yet
- Part of Human BodyDocument3 pagesPart of Human BodySasi KalaNo ratings yet
- Hbs Unite 1 Summary FinalDocument45 pagesHbs Unite 1 Summary Finalapi-277775953No ratings yet
- Co2 Lesson 1.1 Human Anatomy Week 4Document10 pagesCo2 Lesson 1.1 Human Anatomy Week 4accfor everythingNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument27 pagesBiology Projectswatipatel200816No ratings yet
- Week 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsDocument30 pagesWeek 3 - Basic Human Anatomy, Physiology & Fitness ConceptsJohn Cailen Barceñas IINo ratings yet
- Tingkat Organisasi Tubuh Sistem OrganDocument19 pagesTingkat Organisasi Tubuh Sistem OrgansanoizuNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems OverviewDocument5 pagesHuman Body Systems OverviewJohn Niño CasuelaNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: A Guide to Systems & OrgansDocument14 pagesThe Human Body: A Guide to Systems & OrgansdanielcustodioNo ratings yet
- Movement Enhancement 1 LESSON 1Document53 pagesMovement Enhancement 1 LESSON 1Marckim DangoNo ratings yet
- The Human Body A Complex and Remarkable SystemDocument1 pageThe Human Body A Complex and Remarkable Systemurushadzelazare1No ratings yet
- Dokumentum 24Document1 pageDokumentum 24szlizi06No ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument116 pagesBody SystemskarunaNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemDocument7 pagesOrgan SystemAR JAY FRANCONo ratings yet
- Systems of Human BodyDocument13 pagesSystems of Human BodyMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemsDocument3 pagesSkeletal Systemsemmanuel richardNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Eleven Body Organ SystemsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding The Eleven Body Organ SystemsReinan Ezekiel Sotto LlagasNo ratings yet
- 9th. INTRODUCTION TO TERMINOLOGY AND BODYDocument2 pages9th. INTRODUCTION TO TERMINOLOGY AND BODYOwusu ProsperNo ratings yet
- Human Body EssayDocument1 pageHuman Body EssayAtlas CruxNo ratings yet
- Body Systems: CirculatoryDocument5 pagesBody Systems: CirculatoryFasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- Discuss and Elaborate The Relationship of The Different Systems Found in The Animal BodyDocument3 pagesDiscuss and Elaborate The Relationship of The Different Systems Found in The Animal BodyJenny V. BajoNo ratings yet
- Factsheet Organ SystemsDocument2 pagesFactsheet Organ SystemsJulia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- How Inactivity Affects Human System: MEPE 115 Reporter: Enrico T. PasinaboDocument20 pagesHow Inactivity Affects Human System: MEPE 115 Reporter: Enrico T. PasinaboENRICONo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology OverviewDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology OverviewSumiati FranNo ratings yet
- Human Organs (3)Document4 pagesHuman Organs (3)Tishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Ch. 13 Human Body Final 1Document16 pagesCh. 13 Human Body Final 1RANJAN RAJNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemDocument2 pagesOrgan SystemB Dela Pena, Paul M.No ratings yet
- Human ScienceDocument8 pagesHuman ScienceOscar MasindeNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument6 pagesHuman AnatomyRazel PiñeroNo ratings yet
- Visit The Human BodyDocument7 pagesVisit The Human BodyAnonymous lSTzdU8PgNo ratings yet
- Human Body, Cells, TissuesDocument6 pagesHuman Body, Cells, Tissuesjaspreetsinghmehrok100% (1)
- Directions: Answer The Following Questions. Write Down You Answers On The Space ProvidedDocument2 pagesDirections: Answer The Following Questions. Write Down You Answers On The Space ProvidedTrisha Joyce AsisNo ratings yet
- The PartsDocument37 pagesThe PartsRachel Anne TapangNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemsDocument2 pagesOrgan SystemsArnel LaspinasNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 4 Week1 - Lesson1 - The Major Organs of The BodyDocument62 pagesSCIENCE 4 Week1 - Lesson1 - The Major Organs of The BodyARLENE PINERANo ratings yet
- Vince Ford N. Marquez Grade 6 - RutherfordDocument15 pagesVince Ford N. Marquez Grade 6 - RutherfordfordmayNo ratings yet
- Health TuteDocument6 pagesHealth TuteN GunaratneNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Pre LimDocument13 pagesAnaphy Pre LimKyle M. BayangosNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyArif HidyawanNo ratings yet
- Human Body Terms ExplainedDocument5 pagesHuman Body Terms ExplainedRed DemonNo ratings yet
- Body System ChecklistDocument8 pagesBody System Checklistapi-421876369No ratings yet
- Activity Number 1 Organization of The BodyDocument4 pagesActivity Number 1 Organization of The Bodyjmiavaldez CañasNo ratings yet
- Ahmad Zajuli E2214401059 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEM-1Document2 pagesAhmad Zajuli E2214401059 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEM-1AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument15 pagesThe Skeletal SystemOCCIDENTAL BERNADETH O.No ratings yet
- The Human Body: Anatomy, Facts & FunctionsDocument3 pagesThe Human Body: Anatomy, Facts & FunctionsJass BawaNo ratings yet
- Elc590 PS Template Sugar (030919)Document6 pagesElc590 PS Template Sugar (030919)FATIMAH MOHAMAD ISANo ratings yet
- ITP and Diet Foods To Avoid, Eat, and MoreDocument1 pageITP and Diet Foods To Avoid, Eat, and MoreBlanca MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- In The Loop Teacher S Book Starter Level PDFDocument10 pagesIn The Loop Teacher S Book Starter Level PDFDamaris SosaNo ratings yet
- BNS FormsDocument25 pagesBNS FormsShery Ann Fabreag Fesalbon100% (1)
- Diet Brain Health Guide Single Pages 12.08.22Document66 pagesDiet Brain Health Guide Single Pages 12.08.22nurip67No ratings yet
- Weightloss Questionnaire 1Document3 pagesWeightloss Questionnaire 1j.j0% (2)
- Bai Tap Tieng Anh 7 I Learn Smart World Unit 2Document4 pagesBai Tap Tieng Anh 7 I Learn Smart World Unit 2TrizzyPhuongThaoNo ratings yet
- Undernutrition and Its Associated FactorsDocument19 pagesUndernutrition and Its Associated Factorsrezky_tdNo ratings yet
- KHAMISDocument3 pagesKHAMISyouvarajNo ratings yet
- Garden Betty's Chicken Feed CalculatorDocument6 pagesGarden Betty's Chicken Feed CalculatorWutNo ratings yet
- Spasmophilia: VitaminsDocument5 pagesSpasmophilia: VitaminsVictoria NatashaNo ratings yet
- Foreword: Food Services ManualDocument650 pagesForeword: Food Services ManualmableyNo ratings yet
- Feeding Stray DogsDocument4 pagesFeeding Stray DogsRohan SinghNo ratings yet
- PUTYODocument5 pagesPUTYORiwaj LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Motivational Role of Free Mid-Day Meals On Learning Process in Basic Community Schools of Western NepalDocument7 pagesMotivational Role of Free Mid-Day Meals On Learning Process in Basic Community Schools of Western NepalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (2)
- Operations Management Sept 2019 LastestDocument16 pagesOperations Management Sept 2019 LastestAnas TawfiqNo ratings yet
- Psychia Reviewer 1Document8 pagesPsychia Reviewer 1Gesta, Van Gerard T.No ratings yet
- BBDO WORKS - Presentation To SH TeamDocument147 pagesBBDO WORKS - Presentation To SH TeamtonecheungNo ratings yet
- Arepa With EggDocument6 pagesArepa With EggYony GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Class 4 InsectsDocument4 pagesClass 4 Insectsbimal sao100% (1)
- 9870 20072021Document2 pages9870 20072021priya swathiNo ratings yet
- Understanding: Breastfeeding & Diaper LogDocument4 pagesUnderstanding: Breastfeeding & Diaper LogFayrouz EssawiNo ratings yet
- Seqota Declaration Roadmap For Expansion and Scaleup Phases - PrintDocument73 pagesSeqota Declaration Roadmap For Expansion and Scaleup Phases - PrintFiraol Bekele100% (1)
- FiberDocument51 pagesFiberJasmineFirdaArijaNo ratings yet
- 3222 6515 1 SMDocument6 pages3222 6515 1 SMPanggil PopoNo ratings yet