Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RHCSA Exam Preparation
Uploaded by
Mehul SolankiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RHCSA Exam Preparation
Uploaded by
Mehul SolankiCopyright:
Available Formats
RHCSA EXAM PREPARATION
Author: Mehul Solanki
Date: 19-Jan-2024
Version: 3.0
Document History
Author Date Comments
Mehul Solanki 19-Jan-2024 RHCSA Exam preparation only.
Contact Details
Name : Mehul Solanki
Phone : +919879729795
Email : er.mehulsolanki1887@gmail.com
LinkedIn : https://in.linkedin.com/in/mehulsolanki1887
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 1 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
Table of Contents
1. Configure Network. .................................................................................................................... 5
2. Configure YUM repos.................................................................................................................. 5
3. Debug SELinux. ........................................................................................................................... 6
4. Create user accounts with supplementary group. ........................................................................ 7
5. Set the permission. ..................................................................................................................... 8
6. Set the password expire date. ..................................................................................................... 8
7. Assign Sudo Privileges. ............................................................................................................... 8
8. Configure a cron job. .................................................................................................................. 9
8.1 logger "EX200 in progress” as the user natasha ............................................................................................. 9
8.2 logger "EX200 in progress" as the user natasha ............................................................................................. 9
9. Create a collaborative Directory................................................................................................ 10
10. Configure NTP. ......................................................................................................................... 11
11. Configure AutoFS...................................................................................................................... 12
12. ACL. ......................................................................................................................................... 13
13. Create user and password......................................................................................................... 14
14. Locate all files owned by user "harry " and copy UNDER /root/harry-files. ................................. 14
15. Find a string 'ich' FROM “/usr/share/dict/words “AND put it into /root/lines file. ...................... 15
16. Create an archive '/root/backup.tar.bz2' of /usr/local directory and compress it with bzip2 ....... 15
17. Create container image ............................................................................................................ 15
18. Create container as a service. ................................................................................................... 16
19. Container Creation Method-2. .................................................................................................. 17
20. Create the script file. ................................................................................................................ 18
21. Break the password. ................................................................................................................. 18
22. Yum repository configuration. .................................................................................................. 19
23. Add a swap partition. ............................................................................................................... 19
24. Resize a logical Volume. ........................................................................................................... 20
25. Create a logical volume and mount it permanently. .................................................................. 20
26. Configure system tuning. .......................................................................................................... 21
27. Create a VDO volume. .............................................................................................................. 21
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 2 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 3 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
Table of Figures
No table of figures entries found.
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 4 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
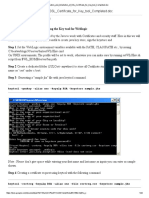
1. CONFIGURE NETWORK.
● Configure Network.
Step 1 : Log in root with the password as per the instructions.
Step 2 : systemctl set-default graphical.target
Step 3 : reboot
Step 4 : configure ip and all as per below from graphical.
IP ADDRESS = 172.25.250.10
NETMASK = 255.255.255.0
GATEWAY = 172.25.250.254
DNS/NameServer = 172.25.250.254 (Auto Off)
hostname = servera.lab.example.com
OR
Step 1 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection show
Step 2 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection delete ens160
Step 3 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-
name ens160 ifname ens160
Step 4 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection modify "ens160"
ipv4.addresses 172.25.250.10/24
Step 5 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection modify "ens160"
ipv4.gateway 172.25.250.254
Step 6 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection modify "ens160"
ipv4.dns 172.25.250.254
Step 7 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection modify "ens160"
ipv4.method static
Step 8 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection modify ethernet-ens160
ipv4.method auto
Step 9 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli connection up ens160
Step 10 : [root@servera ~]# nmcli device status
Step 11 : [root@servera ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname
servera.lab.example.com
2. CONFIGURE YUM REPOS.
● Configure YUM repos with the given link (2 repos: 1st is Base and 2nd is AppStream).
● Base_url= http://content.example.com/rhel8.0/x86_64/dvd/BaseOS.
● AppSterm_url= http://content.example.com/rhel8.0/x86_64/dvd/AppStream.
Step 1 : vim /etc/yum.repos.d/sky.repo (reponame with extension.
repo)
[BaseOS]
name = BaseOS
baseurl = http://content.example.com/rhel8.0/x86_64/dvd/BaseOS
enabled = 1
gpgcheck = 0
[AppStream]
name = AppStream
baseurl = http://content.example.com/rhel8.0/x86_64/dvd/AppStream
enabled = 1
gpgcheck = 0
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 5 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
3. DEBUG SELINUX.
● A web server running on non-standard port 82 is having issues serving content. Debug and
fix issues.
● The web server on your system can server all the existing HTML files from
/var/www/html (NOTE: Do not make any changes to these files).
● Web service should automatically start at boot time.
Step 1 : yum install httpd
Step 2 : systemctl enable httpd
Step 3 : systemctl start httpd
Step 4 : systemctl status httpd
Step 5 : vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Step 1 : semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 82
Step 2 : semanage port -l | grep http
Step 3 : yum install firewalld
Step 4 : systemctl enable firewalld
Step 5 : systemctl start firewalld
Step 6 : systemctl status firewalld
Step 7 : firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=82/tcp
Step 8 : firewall-cmd --reload
Step 9 : firewall-cmd --list-all
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 6 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
Step 10 : systemctl restart httpd
Step 11 : systemctl enable httpd
Step 12 : systemctl start httpd
Step 13 : systemctl status httpd
Step 14 : curl 172.25.250.10:82
4. CREATE USER ACCOUNTS WITH SUPPLEMENTARY GROUP.
● Create the group a named "sysadms".
● Create users as named "natasha" and "harry", will be the supplementary group "sysadms".
● Create a user as named "sarah", should have non-interactive shell and it should be not the
member of "sysadms".
● Password for all users should be "trootent”.
Step 1 : groupadd sysadms
Step 2 : cat /etc/group (Check group add or not)
Step 3 : adduser -G sysadms natasha
Step 4 : useradd -G sysadms harry
Step 5 : useradd -s /sbin/nologin sarah
Step 6 : passwd --stdin natasha
Step 7 : passwd --stdin harry
Step 8 : passwd --stdin sarah
Step 9 : vim /etc/passwd (for checking user is added or not)
Step 10 : vim /etc/group (for checking group added or not)
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 7 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
5. SET THE PERMISSION.
● (a)All new creating files for user natasha as -r-------- as default permission.
● (b) All new creating directories for user natasha as dr-x------ as default permission.
Step 1 : echo “umask 277” >> /home/natasha/.bashrc
Step 2 : su - natasha
Step 3 : umask
Step 4 : mkdir dir1
Step 5 : ls -l ( o/p directory should have dr-x------ permissions)
Step 6 : touch file1
Step 7 : ls -l ( o/p file should have -r-------- permissions)
Step 8 : exit
umask octal value permission
(0=rwx,1=rw-,2=r-x,3=r--,4=-wx,5=-w-,6=--x,7=---)
6. SET THE PASSWORD EXPIRE DATE.
● (a)The password for all new users in serverb.lab.example.com should expires after 20 days.
Step 1 : vim /etc/login.defs
PASS_MAX_DAYS 20
Step 2 : esc:wq
7. ASSIGN SUDO PRIVILEGES.
● (a)Assign the Sudo Privilege.
(For Group)
Step 1 : vim /etc/sudoers
%admin ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
Step 2 : esc
Step 3 : :wq!
(For User)
Step 1 : vim /etc/sudoers
harry ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
Step 1 : esc
Step 2 : :wq!
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 8 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
8. CONFIGURE A CRON JOB.
● CONFIGURE A CRON JOB THAT RUNS EVERY 1 MINUTES AND EXECUTES.
8.1 LOGGER "EX200 IN PROGRESS” AS THE USER NATASHA
Step 1 : which logger (To check the directory of logger)
Step 2 : crontab -eu natasha
Step 3 : crontab -lu natasha (To Check crontab)
● Configure a cron job that runs every day at 12:23 and executes.
8.2 LOGGER "EX200 IN PROGRESS" AS THE USER NATASHA
Step 1 : which logger (To check the directory of logger)
Step 2 : crontab -eu natasha
Step 3 : crontab -lu natasha (To Check crontab)
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 9 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
9. CREATE A COLLABORATIVE DIRECTORY.
● Create the Directory "/home/manager " with the following characteristics.
● Group ownership of "/home/manager" should go to "sysadms" group.
● The directory should have full permission for all members of "sysadms" group but not to
the other users except "root". files created in future under "/home/manager" should get the
same group ownership.
Step 1 : mkdir -p /home/manager
Step 2 : chgrp sysadms /home/manager
Step 3 : ls -ld /home/manager
Step 4 : chmod 770 /home/manager
Step 5 : chmod g+s /home/manager
Step 6 : ls -ld /home/manager
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 10 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
10. CONFIGURE NTP.
● Synchronize time of your system with the server classroom.example.com.
Step 1 : vim /etc/chrony.conf
(Server/pool) classroom.example.com iburst (you have to
type this line in server or pool as you saw upper line you
should have to comment the upper line)
Step 2 : dnf install chrony
Step 3 : systemctl enable chronyd.service
Step 4 : systemctl start chronyd.service
Step 5 : systemctl status chronyd.service
Step 6 : timedatectl set-ntp true
Step 7 : timedatectl
Step 8 : systemctl restart chronyd.service
Step 9 : chronyc sources -v
Step 10 : timedatectl
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 11 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
11. CONFIGURE AUTOFS.
● All Ldapuser2 home directory is exported via NFS, which is available on
classroom.example.com (172.25.254.254) and your NFS-exports directory is /home/guests for
Ldapuser2.
● Ldapuser2's home directory is classroom.example.com:/home/guests/ldapuser2.
● Ldapuser2's home directory should be automount autofs service.
● Home directories must be writable by their users.
● while you are able to log in as any of the user ldapuser1 through ldapuser20, the only home
directory that is accessible from your system is ldapsuser2.
Step 1 : yum install autofs -y
Step 2 : getent passwd ldapuser2 (Check user added or not)
Step 3 : systemctl enable autofs
Step 4 : systemctl start autofs
Step 5 : systemctl status autofs
Step 6 : vim /etc/auto.master (Put it in the file as per below).
Step 7 : vim /etc/auto.misc
Step 8 : su ldapuser2 (for checking useradded or not)
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 12 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
12. ACL.
● Copy the file /etc/fstab to /var/tmp/ and configure the "ACL" as mentioned following.
● The file /var/tmp/fstab should be owned by the "root".
● The file /var/tmp/fstab should belong to the group "root".
● The file /var/tmp/fstab should not be executable by anyone.
● The user "natasha" should be able to read and write to the file.
● The user “sarah" can neither read nor write to the file.
● Other users (future and current) should be able to read /var/tmp/fstab.
Step 1 : cp -rvf /etc/fstab /var/tmp (User should be root for
copy).
Step 2 : ls -ld /var/tmp/fstab
Step 3 : setfacl -m u:natasha:rw- /var/tmp/fstab
Step 4 : getfacl /var/tmp/fstab
Step 5 : setfacl -m u:sarah:--- /var/tmp/fstab
Step 6 : getfacl /var/tmp/fstab
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 13 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
13. CREATE USER AND PASSWORD.
• Create user 'bob' with 2112 uid and set the password 'trootent.
Step 1 : useradd -u 2112 bob
Step 2 : passwd --stdin bob
14. LOCATE ALL FILES OWNED BY USER "HARRY " AND COPY
UNDER /ROOT/HARRY-FILES.
• Locate all files owned by user "harry " and copy it under /root/harry-files.
Step 1 : mkdir /root/harry-files
Step 2 : find / -user harry -exec cp -arvf {} /root/harry-files \;
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 14 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
15. FIND A STRING 'ICH' FROM “/USR/SHARE/DICT/WORDS “AND
PUT IT INTO /ROOT/LINES FILE.
• Find a string 'ich' from " /usr/share/dict/words " and put it into /root/lines file.
Step 1 : grep ich /usr/share/dict/words > /root/lines
16. CREATE AN ARCHIVE '/ROOT/BACKUP.TAR.BZ2' OF /USR/LOCAL
DIRECTORY AND COMPRESS IT WITH BZIP2
• Create an archive '/root/backup.tar.bz2' of /usr/local directory and compress it with bzip2.
Step 1 : tar -cjf /root/backup.tar.bz2 /usr/local (bzip)
OR
Step 1 : tar -cJf /root/backup.tar.xz /usr/local (xz)
OR
Step 1 : tar -czf /root/backup.tar.gz /usr/local (gzip)
17. CREATE CONTAINER IMAGE
• Get the Containerfile from the existing user “seshat” and create an image.
Image name should be "monitor". Dont change anythings in Containerfile.
Step 1 : [root@servera ~]# ssh seshat@servera.example.com
Step 2 : [seshat@servera ~]$ podman login
username : (Redhat container registry user)
password : (As per the instructions)
Step 3 : [seshat@servera ~]$ wget
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Mehul-
Redhat/rsyslog/main/Containerfile
Step 4 : [seshat@servera ~]$ ls (To check Containerfile is download or
not)
Step 5 : [seshat@servera ~]$ podman build -t monitor .
Step 6 : [seshat@servera ~]$ podman images (To Check images)
Step 7 : [seshat@servera ~]$ exit (to logout seshat)
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 15 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
18. CREATE CONTAINER AS A SERVICE.
• Configure the container with systemd services by an existing user “seshat”. The
storage directories become persistent of /opt/files with the container directory
/opt/incoming and /opt/processed with the container directory /opt/outgoing.
• Container Name : asaii2pdf
• Services Name : container-asaii2pdf
Step 1 : Make sure user should be a root.
Step 2 : [root@servera ~]# loginctl enable-linger seshat
Step 3 : [root@servera ~]# loginctl list-users
Step 4 : [root@servera ~]# mkdir -p /opt/files
Step 5 : [root@servera ~]# mkdir -p /opt/processed
Step 6 : [root@servera ~]# chown seshat /opt/files/
Step 7 : [root@servera ~]# chown seshat /opt/processed/
Step 8 : [root@servera ~]# ssh seshat@servera.example.com
Step 9 : [seshat@servera ~]$ mkdir -p .config/systemd/user
Step 10 : [seshat@servera ~]$ podman images (To verify images)
Step 11 : [seshat@servera ~]$ podman run -dit –-name asaii2pdf -v
/opt/files/:/opt/incoming:Z -v
/opt/processed/:/opt/outgoing:Z monitor:latest
Step 12 : [seshat@servera ~]$ podman ps (To check container created or
not)
Step 13 : [seshat@servera ~]$ podman generate systemd asaii2pdf >>
.config/systemd/user/container-asaii2pdf.service (Service
name should be container.asaii2pdf.service. it’s must)
Step 14 : [seshat@servera ~]$ cat .config/systemd/user/container-
asaii2pdf.service
Step 15 : [seshat@servera ~]$ systemctl --user daemon-reload
[seshat@servera ~]$ systemctl --user enable container-
asaii2pdf.service
Step 16 : [seshat@servera ~]$ systemctl --user start container-
asaii2pdf.service (Run this command two times, first time you
will getting an error).
Step 17 : [seshat@servera ~]$ systemctl --user status container-
asaii2pdf.service
Step 18 : [seshat@servera ~]$ exit
Step 19 : [root@servera ~]# reboot
Step 20 : After reboot, login again with the seshat(with SSH) user and
make sure service is started or not.
Step 21 : [root@servera ~]# ssh seshat@servera.example.com
Step 22 : [seshat@servera ~]$ systemctl --user status container-
asaii2pdf.service
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 16 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
19. CONTAINER CREATION METHOD-2.
Step 1 : [root@servera ~]# yum install podman container-tools -y
Step 2 : [root@servera ~]# podman --version
Step 1 : [root@servera ~]# systemctl enable podman
Step 2 : [root@servera ~]# systemctl start podman
Step 3 : [root@servera ~]# systemctl status podman
Step 4 : [root@servera ~]# useradd rhel
Step 5 : [root@servera ~]# loginctl enable-linger rhel
Step 6 : [root@servera ~]# loginctl list-users
Step 7 : [root@servera ~]# mkdir /opt/files/
Step 8 : [root@servera ~]# mkdir /opt/processed/
Step 9 : [root@servera ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t container_file_t
/opt/files/
Step 10 : [root@servera ~]# semanage fcontext -a -t container_file_t
/opt/processed/
Step 11 : [root@servera ~]# restorecon -vRF /opt/files/
Step 12 : [root@servera ~]# restorecon -vRF /opt/processed/
Step 13 : [root@servera ~]# ssh rhel@localhost
Step 14 : [rhel@servera ~]$ mkdir -p .config/systemd/user
Step 15 : [rhel@servera ~]$ podman login
Step 16 : [rhel@servera ~]$ username (as given in instructions)
Step 17 : [rhel@servera ~]$ password (as given in instruction)
Step 18 : [rhel@servera ~]$ wget
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mehul-
redhat/rsyslog/main/Containerfile
Step 19 : [rhel@servera ~]$ podman build -t rsyslog .
Step 20 : [rhel@servera ~]$ podman image ls
Step 21 : [rhel@servera ~]$ podman run -dit --name logserver -v
/opt/files/:/opt/incoming:Z -v
/opt/processed/:/opt/outgoing:Z rsyslog (imagename)
Step 22 : [rhel@servera ~]$ podman generate systemd logserver >>
.config/systemd/user/container-logserver.service
Step 23 : [rhel@servera ~]$ cat .config/systemd/user/container-
logserver.service
Step 24 : [rhel@servera ~]$ systemctl --user daemon-reload
Step 25 : [rhel@servera ~]$ systemctl --user enable container-
logserver.service
Step 26 : [rhel@servera ~]$ systemctl --user start container-
logserver.service
Step 27 : [rhel@servera ~]$ systemctl --user status container-
logserver.service
Step 28 : [rhel@servera ~]$ reboot
Step 29 : [rhel@servera ~]$ systemctl --user status container-
logserver.service
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 17 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
20. CREATE THE SCRIPT FILE.
• Example -1
Step 1 : vim script.sh
!/bin/bash
if [ “$1” = “GM” ]; then
echo “good morning”
elif [ “$!” = “GN” ]; then
echo “good night”
else
echo “enter GM/GN for output”
fi
Step 2 : chmod 755 script.sh
Step 3 : ./script.sh GM
Step 4 : ./script.sh GN
• Example -2
Step 1 : vim script.sh
#!/bin/bash
[/data/k it's a directory]
mkdir -p /data/k
find / -type f -size +30M -size -50M -exec cp -
v {} /data/k \;
Step 2 : chmod 755 script.sh
Step 3 : ./script.sh
Step 4 : ./script.sh
21. BREAK THE PASSWORD.
• Break the password of root user and set password tootrent.
Step 1 : reboot
Step 2 : press “e” at kernel option (On Rescue Mode)
Step 3 : type rd.break at last of the line which is start with
linux
Step 4 : Ctrl + x
Step 5 : mount -o remount,rw /sysroot
Step 6 : chroot /sysroot
Step 7 : passwd root
Step 8 : type passwd
Step 9 : touch /.autorelabel
Step 10 : ctrl + d (press twice) OR exit (press two time)
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 18 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
22. YUM REPOSITORY CONFIGURATION.
• Configure YUM repos with the given link ( 2 repos: 1st is Base and 2nd is AppStream).
• Base_url= http://content.example.com/rhel8.0/x86_64/dvd/BaseOS
• AppSterm_url= http://content.example.com/rhel8.0/x86_64/dvd/AppStream
Step 1 : vim /etc/yum.repos.d/sky.repo (reponame with extension
.repo)
[BaseOS]
name = BaseOS
baseurl= http://content.example.com/rhel8.0/x86_64/dvd/BaseOS
enabled = 1
gpgcheck = 0
[AppStream]
name = AppStream
baseurl = http://content.example.com/rhel8.0/x86_64/dvd/AppStream
enabled = 1
gpgcheck = 0
23. ADD A SWAP PARTITION.
• Add a swap partition of 512 MB and mount it permanently.
Step 1 : lsblk
Step 2 : fdisk /dev/vdb
Step 3 : press “n” for new partition
Step 4 : press “p” for primary partition
Step 5 : choose partition default “1”
Step 6 : press enter in first sector
Step 7 : enter size in last sector +512M
Step 8 : press t for assigning type in of partition
Step 9 : press 82 for swap
Step 10 : press “w” for write and save
Step 11 : lsblk (To check created partition)
Step 12 : partprobe /dev/vdb1
Step 13 : mkswap /dev/vdb1
Step 14 : swapon /dev/vdb1
Step 15 : blkid /dev/vdb1 >> /etc/fstab
Step 16 : vim /etc/fstab
UUID=0b9f9c46-35fb-49d5-9f59-8c2e40a6139d swap
swap defaults0 0 (edit entry like this)
Step 17 : mount -a
Step 18 : lsblk (check partition added or not)
└─rhel-swap 253:1 0 1.5G 0 part [SWAP]
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 19 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
24. RESIZE A LOGICAL VOLUME.
• Resize the logical volume "mylv " so that after reboot the size should be in between 200
MB to 300MB.
Step 1 : df -h
Step 2 : lvdisplay
Step 3 : lsblk
Step 4 : lvextend -r -L 250M /dev/mapper-myvol-mylv
OR
lvextend -r -L +50M /dev/mapper-myvol-mylv
OR
resize2fs /dev/myvg/lv (if fstype is xfs then use
xfs_growfs [options] mountpoint)
25. CREATE A LOGICAL VOLUME AND MOUNT IT PERMANENTLY.
• Create the logical volume with the name "wshare" by using 50PE's from the volume group
"wgroup".
• Consider each PE size of the volume group as "8 MB".
• Mount it on /mnt/wshare with file system vfat.
Step 1 : fdisk /dev/vdb
Step 2 : press “n” for new partition
Step 3 : press “p” for primary partition
Step 4 : choose partition default “2”
Step 5 : press enter in first sector
Step 6 : enter size in last sector +408M (lv extent multiply by vg
extent size add 1 vg extent).
Step 7 : press t for assigning type in of partition
Step 8 : press 8e for lvm partition type
Step 9 : press “w” for write and save
Step 10 : partprobe /dev/vdb2
Step 11 : pvcreate /dev/vdb2
Step 12 : vgcreate wgroup -s 8m /dev/vdb2 (i.e. wgroup is group
name).
Step 13 : lvcreate -n wshare (for lv name) -l 50 wgroup.
Step 14 : mkfs.vfat /dev/wgroup/wshare (for attaching file system)
Step 15 : blkid /dev/wgroup/wshare >> /etc/fstab
Step 16 : vim /etc/fstab
UUID=0b9f9c46-35fb-49d5-9f59-8c2e40a6139d /mnt/wshare
vfat defaults 0 0(edit entry like this)
Step 17 : systemctl daemon-reload
Step 18 : mount -a
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 20 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
26. CONFIGURE SYSTEM TUNING.
• Choose the recommended 'tuned' profile for your system and set it as the default.
Step 1 : yum install tuned
Step 2 : systemctl start tuned
Step 3 : systemctl enable tuned
Step 4 : tuned-adm recommend (below you show recommended profile).
virtual-guest
Step 5 : tuned-adm profile virtual-guest (type recommended profile
name) (for setting up recommended profile).
Step 6 : tuned-adm active (for showing activated profile).
Step 7 : systemctl restart tuned
Step 8 : systemctl enable tuned
Step 9 : systemctl start tuned
Step 10 : systemctl status tuned
27. CREATE A VDO VOLUME.
• Create the vectra volume using the VDO with the logical size 50GB and mount under test
directory.
Step 1 : yum install vdo kmod-kvdo -y
Step 2 : systemctl enable vdo
Step 3 : systemctl start vdo
Step 4 : systemctl status vdo
Step 5 : lsblk
Step 6 : vdo create --name=vectra --device=/dev/vdc --
vdoLogicalSize=50G
Step 7 : mkfs.xfs /dev/mapper/vectra
Step 8 : blkid /dev/mapper/vectra >> /etc/fstab
Step 9 : mkdir /mnt/vdo01
Step 10 : vi /etc/fstab
UUID=3393-846F /mnt/vdo01 vfat defaults 0 0
(edit entry like this)
Step 11 : systemctl daemon-reload
Step 12 : mount –a
Step 13 : df -hT
Step 14 : lsblk
sda 8:0 0 10G 0 disk
└─vdo01 253:0 0 50G 0 vdo /mnt/vdo01
Step 15 : systemctl restart vdo
Step 16 : systemctl enable vdo
Step 17 : systemctl status vdo
Step 18 : reboot
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 21 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
Author: Mehul Solanki Page 22 of 22
Printed: 14 Mar 24
You might also like
- Exdump 3Document5 pagesExdump 3chalapathiraoNo ratings yet
- DB SchedulerDocument6 pagesDB Schedulersandeep.srivastava00100% (1)
- Progress Test 4 Units 10 12 Ingls de La Escuela 2011 Pearson Longman EltDocument11 pagesProgress Test 4 Units 10 12 Ingls de La Escuela 2011 Pearson Longman EltNines TicóNo ratings yet
- Buyer Keywords Guide PDFDocument15 pagesBuyer Keywords Guide PDFTauseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- RHCSA ExamsPreparationFInalDocument22 pagesRHCSA ExamsPreparationFInalprajapatkaushik3No ratings yet
- Rhcsa Paper HaDocument6 pagesRhcsa Paper Haapoorvaguptaspn27No ratings yet
- RHCSA MockpaperpracticeDocument4 pagesRHCSA Mockpaperpracticesureshchaudhary200702No ratings yet
- RhcsaDocument11 pagesRhcsaabusiddiksumon2202No ratings yet
- RHCSA v9-DUMPSDocument10 pagesRHCSA v9-DUMPSJeevan Mallik SNo ratings yet
- Exam Rhel 9Document12 pagesExam Rhel 9Qammar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Transcender Ex200 Study Guide 2024-Feb-04 by Lou 84q VceDocument16 pagesRed Hat Transcender Ex200 Study Guide 2024-Feb-04 by Lou 84q VceZero RainNo ratings yet
- Sample Rhcsa QuestionsDocument2 pagesSample Rhcsa QuestionsSantoshSangroulaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Enterprise Manager 12c Agent Installation GuideDocument39 pagesOracle Enterprise Manager 12c Agent Installation GuideKoszufNo ratings yet
- R12 (12.1.1) Installation Oel5 PDFDocument15 pagesR12 (12.1.1) Installation Oel5 PDFsherif adfNo ratings yet
- Installing and Configuring Oracle OEM 10g Grid Control On SolarisDocument75 pagesInstalling and Configuring Oracle OEM 10g Grid Control On SolarisSethunath.U100% (1)
- VXVMDocument64 pagesVXVMThimmarayan KrishnappaNo ratings yet
- RHEL-9 RHCE EXAM MODEL PAPERDocument18 pagesRHEL-9 RHCE EXAM MODEL PAPERbedoui marwenNo ratings yet
- Ex180 April22 Day1Document3 pagesEx180 April22 Day1smile2me2012No ratings yet
- AIX TipsDocument16 pagesAIX TipsClaudio RafaelNo ratings yet
- Netbackup Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesNetbackup Interview QuestionsSanthosh KumNo ratings yet
- RMANDocument13 pagesRMANTaoqir KhosaNo ratings yet
- Uninstall NetBackup from Solaris ServerDocument4 pagesUninstall NetBackup from Solaris ServerMarioNo ratings yet
- Redirected Oracle restoresDocument6 pagesRedirected Oracle restoresjoefromdaytonNo ratings yet
- Legato Interview QuestionsDocument6 pagesLegato Interview QuestionsVinesh Pandit75% (4)
- Netbackup Advanced TroubleshootingDocument58 pagesNetbackup Advanced Troubleshootingapi-19652305No ratings yet
- RHCSAv 9Document4 pagesRHCSAv 9apoorvaguptaspn27No ratings yet
- Configure sudo for a functional account on AIXDocument3 pagesConfigure sudo for a functional account on AIXMohammed Amer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Netbackup ManualDocument2 pagesNetbackup ManualJohn MckinNo ratings yet
- LabsDocument5 pagesLabsAlex EnriquezNo ratings yet
- An Advanced Guide to the Powerful vim Text EditorDocument14 pagesAn Advanced Guide to the Powerful vim Text EditorBadi Ul ZamanNo ratings yet
- Creation and Installation of SSL Certificate For Key Tool CompletedDocument22 pagesCreation and Installation of SSL Certificate For Key Tool CompletedpraveenNo ratings yet
- LiveLessons RHCSADocument14 pagesLiveLessons RHCSAmoskytNo ratings yet
- Weblogic Trouble Shooting GuideDocument3 pagesWeblogic Trouble Shooting GuiderockineverNo ratings yet
- Code 23Document12 pagesCode 23subhrajitm47No ratings yet
- Veeam Data Protection Oracle EnvironmentsDocument29 pagesVeeam Data Protection Oracle Environmentsanhtuan206No ratings yet
- Samba On AIXDocument14 pagesSamba On AIXChristian FisherNo ratings yet
- Ubuntu SSL 2048 ByteDocument5 pagesUbuntu SSL 2048 ByteIrfan Irawan CbnNo ratings yet
- How To Debug and Fix Common Docker IssuesDocument17 pagesHow To Debug and Fix Common Docker Issueskamakom78No ratings yet
- Practice Test: Microsoft 70-647Document132 pagesPractice Test: Microsoft 70-647Kasha Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- CSE390a Shell Scripting LectureDocument22 pagesCSE390a Shell Scripting LectureRajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- NBU Snapshot 1Document2 pagesNBU Snapshot 1liuylNo ratings yet
- LFS272 - Labs - 7.17.2019Document67 pagesLFS272 - Labs - 7.17.2019Jagi SarcillaNo ratings yet
- Rhel 8 Mock Paper IDocument5 pagesRhel 8 Mock Paper Idhc14301No ratings yet
- Setup FTP Server for File DownloadsDocument5 pagesSetup FTP Server for File DownloadsPriyanka GuptaNo ratings yet
- Backup Types and Methods in NetbackupDocument9 pagesBackup Types and Methods in NetbackupSrinivas KumarNo ratings yet
- Veritas Status Codes and MessagesDocument62 pagesVeritas Status Codes and MessagesamsreekuNo ratings yet
- Mount RHEL ISO & Upgrade to 7.6Document9 pagesMount RHEL ISO & Upgrade to 7.6Abdallah AttiaNo ratings yet
- Chmod666 NIM Cheat Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesChmod666 NIM Cheat Sheet PDFhosnitmiNo ratings yet
- Tivoli Storage Manager Client Commands (DSMC Commands) - TarDocument4 pagesTivoli Storage Manager Client Commands (DSMC Commands) - Tarb.henriqNo ratings yet
- NetBackup812 AdminGuide AzureStackDocument25 pagesNetBackup812 AdminGuide AzureStackNavneetMishraNo ratings yet
- List of Legato Networker Commands and TipsDocument4 pagesList of Legato Networker Commands and TipsSai100No ratings yet
- NetBackup 7.7 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesNetBackup 7.7 Cheat SheetsparctusharNo ratings yet
- Netbackup Upgrade 6.5.4 To 7.0.1 v1.0Document44 pagesNetbackup Upgrade 6.5.4 To 7.0.1 v1.0Mahek AroraNo ratings yet
- How To Install and Activate RAID 1 Ubuntu (Server) 14.04 LTS Step-by-StepDocument42 pagesHow To Install and Activate RAID 1 Ubuntu (Server) 14.04 LTS Step-by-StepMusa FathonyNo ratings yet
- Cloning Oracle Apps 11i With Rapid CloneDocument7 pagesCloning Oracle Apps 11i With Rapid ClonekrishnanaamdasNo ratings yet
- Veritas Netbackup ™ Enterprise Server and Server 8.2 - 8.X.X Hardware and Cloud Storage Compatibility List (HCL)Document325 pagesVeritas Netbackup ™ Enterprise Server and Server 8.2 - 8.X.X Hardware and Cloud Storage Compatibility List (HCL)AviNo ratings yet
- Upgrade Data Protector 7.0x to 9.0x in 38 StepsDocument9 pagesUpgrade Data Protector 7.0x to 9.0x in 38 StepsVikram ReddyNo ratings yet
- Oracle Restore Using RMAN With AvamarDocument2 pagesOracle Restore Using RMAN With AvamardoostabadNo ratings yet
- RHCSASolved PDFDocument5 pagesRHCSASolved PDFDuluth MarketsNo ratings yet
- Elective Paper - APRIL 2022Document3 pagesElective Paper - APRIL 2022rajamanickam selva vinayagamNo ratings yet
- Arduino Playground - ShiftOutX LibraryDocument4 pagesArduino Playground - ShiftOutX LibraryWinexNo ratings yet
- Safe Assign OverviewDocument10 pagesSafe Assign OverviewCETLNo ratings yet
- Freescale-FRS iMX53 - Mentor Inflexion Quick Start Board Training FINALDocument37 pagesFreescale-FRS iMX53 - Mentor Inflexion Quick Start Board Training FINALprova34No ratings yet
- Dimming AC lamps with Arduino using TRIAC phase angle controlDocument21 pagesDimming AC lamps with Arduino using TRIAC phase angle controlrodolfos_8No ratings yet
- DOC-12-85006-AK - Environmental Monitoring Solution Overview 2022Document2 pagesDOC-12-85006-AK - Environmental Monitoring Solution Overview 2022AbbaNo ratings yet
- Dok Fly Mra4e Mra4Document4 pagesDok Fly Mra4e Mra4Sorin NicuNo ratings yet
- Beginner Guide To VIIRS Imagery DataDocument33 pagesBeginner Guide To VIIRS Imagery Datavnh01No ratings yet
- General SpecificationsDocument24 pagesGeneral Specificationsabirahnaz99No ratings yet
- ERP Study Material Explains Benefits of Integrated Resource ManagementDocument7 pagesERP Study Material Explains Benefits of Integrated Resource Managementswathi krishnaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Premiere Pro CC 2017 TutorialDocument38 pagesAdobe Premiere Pro CC 2017 TutorialPoornima DineshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Endpoint Security and Analysis: Instructor MaterialsDocument48 pagesChapter 10: Endpoint Security and Analysis: Instructor MaterialsH BurtonNo ratings yet
- Stata GLLAMM Companion for Multilevel Modeling BookDocument44 pagesStata GLLAMM Companion for Multilevel Modeling BookWerner KraushaarNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking 12-SeptDocument13 pagesEthical Hacking 12-SeptArun KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Subject: Information Technology Chapter 2 Introduction To It - Ites IndustryDocument10 pagesClass Ix Subject: Information Technology Chapter 2 Introduction To It - Ites IndustryChinna SamyNo ratings yet
- Wastewater Treatment Plant SCADA ApplicationDocument6 pagesWastewater Treatment Plant SCADA ApplicationDaniel Elmer Parado SosaNo ratings yet
- FS-8700-64 ATMI ACM: Driver ManualDocument22 pagesFS-8700-64 ATMI ACM: Driver ManualEric DunnNo ratings yet
- UK website page ID and news article URLsDocument10 pagesUK website page ID and news article URLsJoshua SackeyNo ratings yet
- New Features in PLANBAR 2019-0-1Document81 pagesNew Features in PLANBAR 2019-0-1Koresh KhalpariNo ratings yet
- Check and configure 3G network cells, nodes, alarmsDocument2 pagesCheck and configure 3G network cells, nodes, alarmsYasser El-sammak100% (1)
- KJHKJHKJDocument6 pagesKJHKJHKJjscansinoNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: Branch: Computer Science & EngineeringDocument10 pagesJntuworld: Branch: Computer Science & EngineeringventhiiNo ratings yet
- Documentum D2 4.2 Installation GuideDocument135 pagesDocumentum D2 4.2 Installation GuideHariprasad ManchiNo ratings yet
- ErrorDocument477 pagesErrormantenimiento crc100% (1)
- West Bengal SSC Computer Application SyllabusDocument2 pagesWest Bengal SSC Computer Application SyllabusDiptimoy MandalNo ratings yet
- CLIRefVOSS 8.4 CRGDocument1,755 pagesCLIRefVOSS 8.4 CRGJosé BerenguerNo ratings yet
- Palawan Electric CooperativeDocument4 pagesPalawan Electric CooperativeDemz PalmerasNo ratings yet