Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathfit Reviewer
Uploaded by
micahaalliyahazores0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesPATHFIT: Movement Competency Training
Original Title
pathfit_reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPATHFIT: Movement Competency Training
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesPathfit Reviewer
Uploaded by
micahaalliyahazoresPATHFIT: Movement Competency Training
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
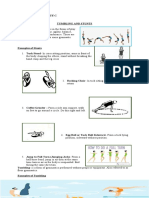
12 DIRECTIONAL AND MOVEMENT TERMS
1. Flexion and Extension
-flex is another term for bend
-to flex your shoulders it must be forward only
Hyperextension means that there's been excessive movement of a joint in one direction (straightening). In other
words, the joint has been forced to move beyond its normal range of motion.
2. Abduction and Adduction
- When we say Abduction we are moving away from your midline
-and Adduction is moving towards your midline
3. Rotation and Circumduction
-When we say Rotation it is to rotate and it’s either inversion or eversion motion
-Circumduction your movements form a circle
4. Plantar extension and Dorsiflexion
-Plantar extension meaning to say your feet are hill up and toes are down
- Dorsiflexion backward-bending motion of your foot then toe-up
5. Ipsi and Contralateral
- When we say Ipsi or Ipsilateral you are moving on the same sides
- Contralateral moving on the opposite sides
6. Pronation and Supination
- Prone is lying face down with a palm up and dorsiflex position
- the supine position, the individual is lying on their back, with their face and abdomen facing upwards. with
palm down and dorsiflex position
7. Protraction and Retraction
- When we say Protract it is a movement that results in a portion of the body being moved forward on a plane
parallel to the ground.
- (the reverse of protraction): the movement that results in the protracted portion of the body being moved
on a
parallel plane, back to its original position.
8. Inversion and Eversion
- Inversion involves the movement of the sole towards the median plane – so that the sole faces in a medial
direction.
- Eversion involves the movement of the sole away from the median plane – so that the sole faces in a lateral
direction.
9. Progression and regression
- Regression requires less effort
The preparatory position of regression has one leg dropped in a dorsiflex position
- Meanwhile progression requires effort
Parts of Your Abdomen
Abdominal bracing is the process of quickly activating all of your core muscles and sucking in your stomach. You
then hold this tightness while you perform a particular exercise motion. This action creates a lot of pressure in
your abdomen and prevents you from loosely moving this part of your body.
It helps strengthen your abdominal and back muscles, which can support more comfortable sitting and standing
positions, reduce back pain, and improve your balance.
Each exercise and activity you must always brace your core.
Non-locomotor and locomotor skills
Non-locomotor
1. Dead bug
- Standard position in dead bug you must flex your hip together with your knees and your shoulders.
2. Bird Dog
- in a prone position with a standard position called the “Quadruped position”
- spine must be neutral meaning straight
3. Hip bridge
4. Plank
- Lock your elbows and lift your knees
5. Downward Dog
6. Squat Series
7. Press-up
- In a prone position extend your arms then chess while locking your elbows
8. YTW
Locomotor
1. Baby crawl
- standard position Quadruped position
- Contralateral
- Consistent neutral spine
2. Bear Crawl
3. Gorilla Walk
4. Crab Walk
-Dorsiflex and contralateral
5. Jumping and landing
6. Walking
-heel to toe
Minimum of Warm-ups is 5 to 15 minutes
You might also like
- Pathfit ReviewerDocument3 pagesPathfit Reviewerwidafo7816No ratings yet
- Activity 8 - GYMNASTICS: PositionsDocument4 pagesActivity 8 - GYMNASTICS: PositionsJewel SkyNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1 Chapter 4Document12 pagesPathfit 1 Chapter 4Marjorie Tocoyo legaspiNo ratings yet
- FitnessDocument31 pagesFitnessjmNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document22 pagesUnit 3RUTH PARILLANo ratings yet
- Module 3 Rhythmic AcitivitiesDocument4 pagesModule 3 Rhythmic AcitivitiesAdonna Mari D. MATUTINONo ratings yet
- Pathfit 2 Module 1Document27 pagesPathfit 2 Module 1kaitlynzeaaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Movement PatternDocument12 pagesFundamental Movement PatternMa Evangelynne CondeNo ratings yet
- Med. P.E Module - Group 5 FinalDocument23 pagesMed. P.E Module - Group 5 FinalJamaica VilloNo ratings yet
- Exercises and Movements For Physical ActivitiesDocument2 pagesExercises and Movements For Physical ActivitiesMylz MendozaNo ratings yet
- "Movement Is The Song of The Body." - Vanda Scaravelli: Midterm Coverage GymnasticsDocument8 pages"Movement Is The Song of The Body." - Vanda Scaravelli: Midterm Coverage Gymnasticscristinemacababbad1No ratings yet
- PE MidtermDocument10 pagesPE MidtermReida DelmasNo ratings yet
- Basic Position Where The Most Exercises BeginDocument4 pagesBasic Position Where The Most Exercises Beginhiraeth.naharaNo ratings yet
- Skills 116 Finals ROM Assistive Devices PDFDocument64 pagesSkills 116 Finals ROM Assistive Devices PDFMae Arra Gilbao Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Notes - Body MovementsDocument7 pagesPhysical Education Notes - Body MovementsRiarene CorrelinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 FUNDAMENTAL MOVEMENT PATTERNSDocument7 pagesChapter 5 FUNDAMENTAL MOVEMENT PATTERNSJan Allyson Biag100% (1)
- LocomotorvsgagaDocument30 pagesLocomotorvsgagaShalyn Lanciso ZarsaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Training SSCDocument12 pagesCircuit Training SSCAzham Jaafar100% (1)
- Fundamental Movement PatternsDocument14 pagesFundamental Movement PatternsAnna Imaysay100% (1)
- Dry Land Workout PlanDocument2 pagesDry Land Workout PlanMaryvan AbellaNo ratings yet
- Sushibala Assignment 02Document5 pagesSushibala Assignment 02Ananda NgangomNo ratings yet
- Range of Motion Exercises: in HealthDocument8 pagesRange of Motion Exercises: in HealthCagabcab Canibel Melany100% (1)
- Lower Body Exercises For Muscular Strength and EnduranceDocument8 pagesLower Body Exercises For Muscular Strength and EnduranceLovelyNo ratings yet
- LOCOMOTOR SKILLS First SemDocument13 pagesLOCOMOTOR SKILLS First Semyhana belingonNo ratings yet
- 3 Definitions of FlexibilityDocument2 pages3 Definitions of FlexibilityChristian Rey Alexis GalonNo ratings yet
- CONCEPTS OF MOVEMENtDocument40 pagesCONCEPTS OF MOVEMENtCliff LentoNo ratings yet
- FINAL COVERAGE Fitness and WellnessDocument4 pagesFINAL COVERAGE Fitness and WellnessAngelic CabanadaNo ratings yet
- Functional Foundations by SET FOR SETDocument36 pagesFunctional Foundations by SET FOR SETdinos99hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Body Movement Movement Is Any Change in The Body Position in Space Which May Be Stationary or Dynamic. It Is A Way ofDocument2 pagesBody Movement Movement Is Any Change in The Body Position in Space Which May Be Stationary or Dynamic. It Is A Way ofRothNo ratings yet
- Movement Movement Is The Act or Process of Moving: Especially Change of Place or Position or PostureDocument13 pagesMovement Movement Is The Act or Process of Moving: Especially Change of Place or Position or PostureMark Earn AnchetaNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem PE Reviewerpart2Document3 pages1st Sem PE Reviewerpart2Charles Dominic BuñoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Body Mechanics:: Rom& Isometric ExercisesDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Body Mechanics:: Rom& Isometric ExercisesRose Antonette BenitoNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up & Stretch Ex For SwimmersDocument18 pagesWarm-Up & Stretch Ex For SwimmerskirancshetNo ratings yet
- Functional Re-Education BasicsDocument3 pagesFunctional Re-Education BasicsShreevidya IyerNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document5 pagesNotes 1john paul CompayanNo ratings yet
- Movement Enchancement-Lesson 1Document4 pagesMovement Enchancement-Lesson 1Axl TorrilloNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Dance Steps BasicDocument8 pagesMapeh Dance Steps Basicsci PantallanoNo ratings yet
- MCT Chapter 2Document8 pagesMCT Chapter 2Kenneth BocterNo ratings yet
- pathfit-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagespathfit-WPS OfficeEphrem MedallaNo ratings yet
- Exercise PilatesDocument11 pagesExercise PilatesYusuf WildanNo ratings yet
- PE Q4 ReviewerDocument2 pagesPE Q4 ReviewerAlma TatelNo ratings yet
- Rolling & Crawling/CreepingDocument17 pagesRolling & Crawling/CreepingChris EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Tumbling and Stunts STUNT-These Are Activities in The Forms of PlayDocument2 pagesTumbling and Stunts STUNT-These Are Activities in The Forms of PlayNoelle Faye MendozaNo ratings yet
- University of Caloocan City: A Research Report Presented To Physical Education Instructor Mr. VinluanDocument8 pagesUniversity of Caloocan City: A Research Report Presented To Physical Education Instructor Mr. VinluanAnz Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- PATHFITDocument1 pagePATHFITdatohenri0No ratings yet
- PE1 Introduction To MovementsDocument4 pagesPE1 Introduction To MovementsDaniela AnsayNo ratings yet
- Warm Up SessionDocument7 pagesWarm Up SessionDIABLA FFNo ratings yet
- TSF Flexibility & MobilityDocument17 pagesTSF Flexibility & MobilityChristopher Dustin100% (1)
- Group 7 Mapeh ReportDocument16 pagesGroup 7 Mapeh Reportdator.carlos3No ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Body Mechanics and Posture EducationDocument26 pagesLesson 3: Body Mechanics and Posture EducationAngel Grace Asuncion100% (1)
- Fundamental PositionsDocument35 pagesFundamental PositionsVinod Kumar50% (4)
- Basic Positions Where Most Exercises BeginDocument70 pagesBasic Positions Where Most Exercises BeginBARRIENTOS, BERNADETTE H.No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PATHFIT 1Document11 pagesChapter 5 PATHFIT 1Gerald ElaugosNo ratings yet
- Physical Education I: Lower Body Exercises For Muscular Strength and Endurance Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesPhysical Education I: Lower Body Exercises For Muscular Strength and Endurance Learning OutcomesKarl MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1 Lesson 4 6Document26 pagesPathfit 1 Lesson 4 6Ann Margaret BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Training PortfolioDocument12 pagesCircuit Training PortfolioAustin AndersonNo ratings yet
- PathFit ReviewerDocument4 pagesPathFit Reviewerchaengchong95No ratings yet
- 2-Fundamental and Derived PositionsDocument50 pages2-Fundamental and Derived Positionsphysical therapy channel ptNo ratings yet
- Pathfit Unit1 2Document51 pagesPathfit Unit1 2LeeleeNo ratings yet
- Neurodevelopmental AssessmentDocument11 pagesNeurodevelopmental AssessmentReem SaNo ratings yet
- 1.01. - Anatomical Position and MovementsDocument20 pages1.01. - Anatomical Position and MovementsAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cebu Doctors' University College of Nursing NCM 103 Fundamentals in Nursing Practice RLE Range of MotionDocument4 pagesCebu Doctors' University College of Nursing NCM 103 Fundamentals in Nursing Practice RLE Range of Motionc.No ratings yet
- Master Reg-Modul Human-Integrated Systems 2020.2Document82 pagesMaster Reg-Modul Human-Integrated Systems 2020.2eirinneNo ratings yet
- PATHFITDocument8 pagesPATHFITfrenzvincentvillasis26No ratings yet
- Case AclDocument15 pagesCase AclRashi JainNo ratings yet
- Birth Injury... Pedia Seminar1Document13 pagesBirth Injury... Pedia Seminar1BHARTI SINGHNo ratings yet
- SOAL Rehab 2010 Kak NelfiDocument5 pagesSOAL Rehab 2010 Kak Nelfifarid akbarNo ratings yet
- Head Massage TherapyDocument169 pagesHead Massage TherapyAnonymous vaQaeG15f100% (1)
- The Bobath LectureDocument4 pagesThe Bobath LectureAlessa LachicaNo ratings yet
- Dermatomes+Myotomes Lower Limb Lecture SlidesDocument13 pagesDermatomes+Myotomes Lower Limb Lecture SlidesAnelisiwe DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Motor System ExaminationDocument57 pagesMotor System ExaminationSoma wahidNo ratings yet
- A Linguistic Perspective On The Notation of FormsDocument20 pagesA Linguistic Perspective On The Notation of FormsYulia NikolaevaNo ratings yet
- Wrist and Hand ComplexDocument6 pagesWrist and Hand ComplexAlyssa Mae CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Positioning and DrapingDocument6 pagesPositioning and DrapingCraigyyNo ratings yet
- Missed Monteggia FXDocument16 pagesMissed Monteggia FXEric RothNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Practice Guideline For Physical Therapy in Patients With Hip or Knee OsteoarthritisDocument21 pagesA Clinical Practice Guideline For Physical Therapy in Patients With Hip or Knee OsteoarthritisalonsoNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Medical TermsDocument518 pagesDictionary of Medical TermsĐặng Duy100% (1)
- Futura Primus Flexible Great Toe FinalDocument12 pagesFutura Primus Flexible Great Toe FinalNasfikurNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Program: /full BodyDocument19 pagesFundamentals Program: /full Bodyscribsikici29% (17)
- Biomechanics of Ankle and FootDocument15 pagesBiomechanics of Ankle and FootJaime Aguilera100% (1)
- Frog MusclesDocument4 pagesFrog MusclesMacy MarianNo ratings yet
- Arthroscopic-SAD Neer DCE MumfordDocument5 pagesArthroscopic-SAD Neer DCE MumfordAbdul Wahid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Joint MobilityDocument5 pagesJoint MobilityIgor RadosavljevicNo ratings yet
- The Swimming Strokes BookDocument127 pagesThe Swimming Strokes BookDejan JovanovNo ratings yet
- A Case Study in Ergonomics by Using REBA, RULA and NIOSH Methods: Logistics Warehouse Sector in TurkeyDocument9 pagesA Case Study in Ergonomics by Using REBA, RULA and NIOSH Methods: Logistics Warehouse Sector in TurkeyHoàng TriềuNo ratings yet
- Terminology: Basic Terms of RelationsDocument11 pagesTerminology: Basic Terms of RelationsAzkia InayahNo ratings yet
- Warm-Up Exercise and Physical Training For Handball PlayersDocument30 pagesWarm-Up Exercise and Physical Training For Handball PlayersSano Sanoj67% (3)
- Ventral Suspension PositionDocument3 pagesVentral Suspension PositionyangNo ratings yet
- Exoskeleton Power and Torque Requirements Based On Human BiomechanicsDocument54 pagesExoskeleton Power and Torque Requirements Based On Human Biomechanicsja2ja1No ratings yet