Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Movement Enchancement-Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Axl TorrilloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Movement Enchancement-Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Axl TorrilloCopyright:
Available Formats
MOVEMENT ENHANCEMENT: LESSON 1
Movement is a keystone of a physical education it may be affected by:
1. Physiological factors - is physical fitness and bodybuilding.
2. Biomechanical factors - it's all about teaching movement skills effectively.
3. Sociological factors - it's always about dealing with your competitors or teammates.
4. Psychological factors - it's all about fear, anxiety and self-concept.
movement education is originated in the year 1970s by Rudolf Laban he is a dancer and the
founder of this type of education. He established that the body is the mechanism through
which people moved.
“You only get one body; it is the temple of your soul.” – Samuel Aunweor
-if you truly treat your body like a temple, it would serve you well for decades, if you abused it,
you must be prepared for poor health and a lack of energy. Our body is very important so
better to have enough knowledge and understanding of different movements that you will be
doing every day.
Movement has 4 different concepts:
1. Body Awareness
- Identification and location of body parts.
- Body shapes and position
In each person and they have their own body shapes because everybody have
different structure and it depends on the genes, in terms of position it depends
on your body shapes like for example if you are too fat there are some positions
that you cannot do if you have a big stomach or tummy's it's very difficult for you
to bend over or to get up easily if you are to lean so you cannot lift some heavy
loads so it is a case to case basis.
- Awareness of body movements
It is important also to be aware of what you will be doing with your body
because our body movement have also limitation. So be careful not to injure
yourself.
- Body as a communicator to express feelings.
To express your feelings, we can't deny that action speaks louder than words
even if you can’t tell you can use your body to express your feelings like in
Dancing.
- Awareness of muscle tension and relaxation
In this statement, our body needs a massage to release the tension and to relax
the muscles especially if you are an athlete and to all the people who feel muscle
tension needs a good massage.
2. Spatial Awareness
- To move within general space safely
It is very important to know the safety protocols in all means.
- Recognize different directions and how to change directions
There are some people who are not good at directions, so if you are one of them
you need to practice your sense of direction.
- To understand the different levels of movement
To avoid a future injuries or accident
- To travel through different pathways and the pathways that different objects
move in. Adjusting range of movements according to the task and situation.
Like in playing basketball or any kind of sports you must practice on how to avoid
some obstacles during a game and to adopt the changes of some unexpected
situation like when you bump into your crush or Yung pinaguutangan mo.
3. Qualities of movement - this concept tells you how the body moves
- Balance: Nature of Static and Dynamic balance and role of balance in movement.
Static balance - refers to the ability of stationary movement like squats, two
leg stances and one leg stance.
Dynamic balance - it's a standing and moving about or stepping from one
place to place like walking in a parallel bars and stair climbing.
- Time: differentiate among speeds and to increase or decrease the speed of
movement.
Ex: walking and running
- Force: to be able to create and modify one's force to meet the demands of the
task.
Ex: throwing some objects
- Flow: to combine movements smoothly and to perform movements within a
restricted time or space.
4. Relationships - it tells with whom and what does the body move.
- To understand the association of body parts to one another and the body.
- To move effectively relative to other individuals and/or within a group.
- To be aware of the relationship between the body and its parts to objects.
Fundamental Motor Skills - these skills are the basis for all physical activity that we
do in sports, gymnastics and other physical recreation activities. If you can't develop
these skills, you are more likely to be continued to be involved in physical activity in
later life.
3 categories of Motor Skills:
1. Locomotor Movements - these are the movements where the body travels through
space from one location to another.
Ex:
Walk - the walk is a transfer of weight from 1 foot to the other. Usually, the heel
touches first, it is a heel to toe movement.
Jog - is a form of running at a slow pace.
Run - is a transfer of weight from 1 foot to the other however, the body is propelled into
the air and suspended between run steps. Heels are almost not touching the
ground.
Jump - is performed by a 2 foot take off and 2-foot landing.
Leap - is performed by pushing off from 1 foot and landing on the other foot. can be
combined with a run or walk approach.
Gallop - a forward movement where 1-foot leads to Gallop while the other foot follows.
The lead footsteps with a bent knee and pushes off into the air and landing on
the trailing foot. The rhythm is uneven, long to short. Long (the step) and Short
(The landing).
Slide - is like a gallop but performed in sideways movement. The rhythm is uneven, long
to short. Long (the step) and Short (thee landing).
Hop - is performed by springing or pushing off from 1 foot and landing on the same foot.
Skip - a combination of a step and a hop on the same foot followed by a step and hop
on the other foot. The rhythm is uneven, long to short. Long (the step) and Short
(the hop).
2. Non- Locomotor movements - our actions and movements that we perform in our spot.
Ex:
Twisting - to rotate the part of the body around an axis.
Bending - to move from a straight position into a curved position.
Rotating - to turn about an axis or a center.
Swaying – shifting weight from one side to the other side smoothly.
Swinging - moving a body part side to side.
Turning - to face a new direction or turning the whole body.
Stretching - to extend the body parts vertically or horizontally.
3. Manipulative skills - is one in which a child handles an object with the hands, feet, or
other body parts. manipulative skills are basic to the development of sports skills.
Ex:
Throwing – involves propelling a ball away from the body and is a target skill. these skills
are difficult to practice in isolation from each other.
Catching - a performer must gain possession or control open object by reaching to
intercept a moving object or stopping it with an implement.
Kicking - to hit someone or something with the foot or to move the feet and legs
suddenly and violently.
Dribbling - is maneuvering a ball by one player while moving in each direction, avoiding
defenders attempt to intercept the ball.
Volleying - to propel (an object) while in the air and before touching the ground
especially. To
hit (a ball) on the valley or to discharge in or as if in a volley.
Hitting - to deal a blow or stroke. To come against with an impact or collision. Heating
an object with force.
Passing - the action of throwing, kicking or hitting a ball or puck to another team
member during a sports match.
Punting – punting first arose to describe kicking a ball dropped from the hands before it
hits the ground.
You might also like
- AniMotion, Energy of the four animals: Fitness & Power WorkoutFrom EverandAniMotion, Energy of the four animals: Fitness & Power WorkoutNo ratings yet
- PE MidtermDocument10 pagesPE MidtermReida DelmasNo ratings yet
- P e 2-Midterm-PupDocument7 pagesP e 2-Midterm-PupFuzz FizzNo ratings yet
- Locomotor and Non - Locomotor MovementDocument8 pagesLocomotor and Non - Locomotor MovementLee Eun JiNo ratings yet
- Movement and Body MechanicsDocument13 pagesMovement and Body MechanicsMark Earn AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Topic 1: Locomotor and Non - Locomotor Movements The Fundamental Body MovementsDocument1 pageModule 2 Topic 1: Locomotor and Non - Locomotor Movements The Fundamental Body MovementsLee Eun JiNo ratings yet
- Locomotor Movements & Non-Locomotor MovementsDocument6 pagesLocomotor Movements & Non-Locomotor MovementsNnleinomNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Movement SkillsDocument21 pagesFundamentals of Movement SkillsJanfel TVNo ratings yet
- PE 2. Meaning and Nature of MovementDocument86 pagesPE 2. Meaning and Nature of MovementDanna Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PE1 PrelimDocument8 pagesPE1 PrelimLeomar OmpadNo ratings yet
- PE 11 Module 2 Fundamental Movement SkillsDocument4 pagesPE 11 Module 2 Fundamental Movement SkillsEricka joy conarcoNo ratings yet
- Body Movement Movement Is Any Change in The Body Position in Space Which May Be Stationary or Dynamic. It Is A Way ofDocument2 pagesBody Movement Movement Is Any Change in The Body Position in Space Which May Be Stationary or Dynamic. It Is A Way ofRothNo ratings yet
- Locomotor & Non LocomotorDocument1 pageLocomotor & Non LocomotorMhin SarandiNo ratings yet
- Locomotor movements overviewDocument6 pagesLocomotor movements overviewKristy Veyna BautistaNo ratings yet
- Locomotor MovementsDocument3 pagesLocomotor MovementsAldrin CabangbangNo ratings yet
- Mov Ed L8Document6 pagesMov Ed L8Jerone RoqueroNo ratings yet
- PE 1 (1st Topic)Document27 pagesPE 1 (1st Topic)Shane Patrick PanilagNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT-2-MODULE-1Document27 pagesPATHFIT-2-MODULE-1kaitlynzeaaNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem PE Reviewerpart2Document3 pages1st Sem PE Reviewerpart2Charles Dominic BuñoNo ratings yet
- Movement Competency TrainingDocument50 pagesMovement Competency TrainingPrincess Meth Catubigan SarominesNo ratings yet
- LocomotorvsgagaDocument30 pagesLocomotorvsgagaShalyn Lanciso ZarsaNo ratings yet
- PATHfit1 - M1Document4 pagesPATHfit1 - M1clatowedNo ratings yet
- Locomotor MovementDocument4 pagesLocomotor MovementCenizal Shine100% (1)
- Fundamental Rhythms and Dance MovementsDocument2 pagesFundamental Rhythms and Dance MovementsNnayduj DgdgNo ratings yet
- Posture and Core Stability: Non-Locomotor SkillsDocument4 pagesPosture and Core Stability: Non-Locomotor SkillsJessami OrgeNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 (Locomotor Movements)Document13 pagesGrade 1 (Locomotor Movements)maryhope canete100% (3)
- Fundamental Movement Skills ExplainedDocument4 pagesFundamental Movement Skills ExplainedSebastian Vincent Pulga PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Locomotor Non-LocomotorDocument2 pagesPhysical Education Locomotor Non-LocomotorJoshua RecintoNo ratings yet
- Movement EnhancementsDocument40 pagesMovement EnhancementsLawrence YorongNo ratings yet
- Saint Michael College: Learning Module PE 1-Self - Testing ActivitiesDocument5 pagesSaint Michael College: Learning Module PE 1-Self - Testing ActivitiesApollos Jason S. OjaoNo ratings yet
- Study Guide EOC 9th Sem IIDocument3 pagesStudy Guide EOC 9th Sem IIADREAN ZEPEDANo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Space in Relation To MovementsDocument7 pagesLesson 2 Space in Relation To MovementsJhanin BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Space in Relation To MovementsDocument7 pagesLesson 2 Space in Relation To MovementsJhanin BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- Pe 1 Module College 2022 First SemDocument2 pagesPe 1 Module College 2022 First SemAnalyn AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Loco Non Loco PdfmovementDocument20 pagesLoco Non Loco PdfmovementIvy AvisoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Body Movements Are The Building Blocks Necessary For Physical Activities Like Sports and DanceDocument2 pagesFundamental Body Movements Are The Building Blocks Necessary For Physical Activities Like Sports and Dancerichmond ponsica100% (1)
- Fundamental Body Movements Are The Building Blocks Necessary For Physical Activities Like Sports and DanceDocument2 pagesFundamental Body Movements Are The Building Blocks Necessary For Physical Activities Like Sports and Dancerichmond ponsicaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Body Movements Are The Building Blocks Necessary For Physical Activities Like Sports and DanceDocument2 pagesFundamental Body Movements Are The Building Blocks Necessary For Physical Activities Like Sports and DanceFrancisNo ratings yet
- Pehealth 12 Q1 Module 12Document6 pagesPehealth 12 Q1 Module 12Rea Mae Josefa TarocNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: To Identify The Physical Activities During PandemicDocument4 pagesTopic 1: To Identify The Physical Activities During PandemicSISAS PEETSNo ratings yet
- Physical education fundamentalsDocument2 pagesPhysical education fundamentalsmae ann joy ducaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Movement and Movement Space in Relation To DanceDocument4 pagesThe Concept of Movement and Movement Space in Relation To DanceAngelo Gabriel LarionNo ratings yet
- PE 103 - Physical Activities Towards Health and Fitness (Dance)Document5 pagesPE 103 - Physical Activities Towards Health and Fitness (Dance)Franz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- MOVEMENT MAPDocument7 pagesMOVEMENT MAPFrances Camille LunaNo ratings yet
- Discover your cultural roots through local dancesDocument12 pagesDiscover your cultural roots through local dancesJANE ONGNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lesson 1Document4 pagesModule 3 Lesson 1Rickie Marx RonamoNo ratings yet
- Week 13Document7 pagesWeek 13chiiyuslayerNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Rhythmic AcitivitiesDocument4 pagesModule 3 Rhythmic AcitivitiesAdonna Mari D. MATUTINONo ratings yet
- Basic Movement 3Document4 pagesBasic Movement 3Miles AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1 Chapter 4Document12 pagesPathfit 1 Chapter 4Marjorie Tocoyo legaspiNo ratings yet
- Project in Movement Competency Training (Pathfit1)Document6 pagesProject in Movement Competency Training (Pathfit1)Christine ToledoNo ratings yet
- Pathfit 1 Lesson 4 6Document26 pagesPathfit 1 Lesson 4 6Ann Margaret BalajadiaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Body MovementsDocument2 pagesFundamental Body MovementsDji OrtizNo ratings yet
- Folkdance 8Document19 pagesFolkdance 8MaryGrace Cruz-MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Power Point For P.E. 103Document51 pagesUnit 2 Power Point For P.E. 103reymark estopaNo ratings yet
- Movement AnalysisDocument1 pageMovement AnalysisCristyNo ratings yet
- Pathfit ReviewerDocument2 pagesPathfit ReviewermicahaalliyahazoresNo ratings yet
- What I Know: Quarter 4 - Week No. 5 - 8Document6 pagesWhat I Know: Quarter 4 - Week No. 5 - 8Dianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Movement Skills Unit PlanDocument15 pagesFundamental Movement Skills Unit PlanJoeceph NarvaezNo ratings yet
- CONCEPTS OF MOVEMENtDocument40 pagesCONCEPTS OF MOVEMENtCliff LentoNo ratings yet
- WHO HIS SDS 2015.2 Eng PDFDocument1 pageWHO HIS SDS 2015.2 Eng PDFPuput Puji AstutyNo ratings yet
- IB MATH PORTFOLIO 1 - Infinite SummationDocument27 pagesIB MATH PORTFOLIO 1 - Infinite Summationmykiri790% (1)
- We Are The ChampionsDocument1 pageWe Are The ChampionsElena CopaceanuNo ratings yet
- Sakuting DanceDocument10 pagesSakuting DanceAxel Kzar AlejoNo ratings yet
- 2013 WDC General Zone 2 ResultsDocument3 pages2013 WDC General Zone 2 ResultsPuertoRicoEcuestreNo ratings yet
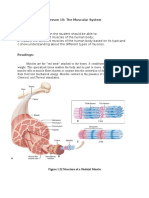
- Lesson 10: The Muscular System Lesson Objectives:: Chemical, and Thermal StimulationDocument3 pagesLesson 10: The Muscular System Lesson Objectives:: Chemical, and Thermal StimulationRichee LunnayNo ratings yet
- Astorga National High SchoolDocument2 pagesAstorga National High SchoolRuffa May OlayaNo ratings yet
- Rolf HingesDocument8 pagesRolf Hingeswalterego58100% (3)
- Lee Asher - Diving Board DoubleDocument51 pagesLee Asher - Diving Board Doublemagojuank100% (1)
- Axle, Rear - Hub, Planetary - Prior To P.I.N. N8F203816Document2 pagesAxle, Rear - Hub, Planetary - Prior To P.I.N. N8F203816AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Renal Function Assessment & Failure CausesDocument4 pagesRenal Function Assessment & Failure CausesKeserovic AdmirNo ratings yet
- Young 1995 Lab Tests For StrengthDocument8 pagesYoung 1995 Lab Tests For Strengthmike.charlick3632100% (1)
- Speed, Distance WKSTDocument3 pagesSpeed, Distance WKSTBryanne MiethNo ratings yet
- Ariana's Reasearch PaperDocument8 pagesAriana's Reasearch Paperapi-281014657No ratings yet
- Valve Body Honda CR-V 2Document9 pagesValve Body Honda CR-V 2Timur TOT100% (1)
- Tomb - of - Horrors - Гробница ужасов RUDocument42 pagesTomb - of - Horrors - Гробница ужасов RUАртём100% (1)
- Lgpro We 9431 2Document232 pagesLgpro We 9431 2Daniel Diaz0% (1)
- Gazette A 2009-IIIDocument500 pagesGazette A 2009-IIIarslanjamil_jamilNo ratings yet
- Muscle-Up RDocument8 pagesMuscle-Up Rسما سما العمرNo ratings yet
- Cabrinha Crossbow 3 ManualDocument30 pagesCabrinha Crossbow 3 Manualstef_stef_stef100% (1)
- Chess Time TableDocument2 pagesChess Time Tablechess masterNo ratings yet
- #1010 Jessica A0 Copy Shop-UnlockedDocument2 pages#1010 Jessica A0 Copy Shop-UnlockedalyakNo ratings yet
- Standard One Holiday Package Series O3Document38 pagesStandard One Holiday Package Series O3Trump DonaldNo ratings yet
- Isuzu 4le2: 52.4 Horsepower Industrial DieselDocument1 pageIsuzu 4le2: 52.4 Horsepower Industrial DieselmarkNo ratings yet
- Make Music CardsDocument20 pagesMake Music CardsShannon SmithNo ratings yet
- Everrain ExpandedOrderListDocument1 pageEverrain ExpandedOrderListrichard leonardoNo ratings yet
- RSU PE 213 Module on Fundamentals of Games and SportsDocument87 pagesRSU PE 213 Module on Fundamentals of Games and SportsJhon Salazar Madalang60% (5)
- Hypertrophy Execution Mastery - Module 4 Workouts - Hams Glutes & Calves PDFDocument24 pagesHypertrophy Execution Mastery - Module 4 Workouts - Hams Glutes & Calves PDFMarvinNo ratings yet
- Tennis Grip Guide PDFDocument4 pagesTennis Grip Guide PDFKelvin YewNo ratings yet
- WoodpeckerMethod ExcerptDocument15 pagesWoodpeckerMethod ExcerptAlejandro Magno100% (1)
- Body by Science: A Research Based Program for Strength Training, Body building, and Complete Fitness in 12 Minutes a WeekFrom EverandBody by Science: A Research Based Program for Strength Training, Body building, and Complete Fitness in 12 Minutes a WeekRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (84)
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouFrom EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindFrom EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- Chakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.From EverandChakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingFrom EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (66)
- Relentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableFrom EverandRelentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (780)
- Power of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionFrom EverandPower of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- SAS Training Manual: How to get fit enough to pass a special forces selection courseFrom EverandSAS Training Manual: How to get fit enough to pass a special forces selection courseRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerFrom EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessFrom EverandThe Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- Peak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsFrom EverandPeak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (95)
- Wall Pilates: Quick-and-Simple to Lose Weight and Stay Healthy. A 30-Day Journey with + 100 ExercisesFrom EverandWall Pilates: Quick-and-Simple to Lose Weight and Stay Healthy. A 30-Day Journey with + 100 ExercisesNo ratings yet
- Endure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceFrom EverandEndure: Mind, Body, and the Curiously Elastic Limits of Human PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (237)
- Muscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!From EverandMuscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- The Calisthenics Codex: Fifty Exercises for Functional FitnessFrom EverandThe Calisthenics Codex: Fifty Exercises for Functional FitnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Hero Maker: 12 Weeks to Superhero Fit: A Hollywood Trainer's REAL Guide to Getting the Body You've Always WantedFrom EverandHero Maker: 12 Weeks to Superhero Fit: A Hollywood Trainer's REAL Guide to Getting the Body You've Always WantedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Yamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeFrom EverandYamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- If You Like Exercise … Chances Are You’Re Doing It Wrong: Proper Strength Training for Maximum ResultsFrom EverandIf You Like Exercise … Chances Are You’Re Doing It Wrong: Proper Strength Training for Maximum ResultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- 7 Weeks to 50 Pull-Ups: Strengthen and Sculpt Your Arms, Shoulders, Back, and Abs by Training to Do 50 Consecutive Pull-UpsFrom Everand7 Weeks to 50 Pull-Ups: Strengthen and Sculpt Your Arms, Shoulders, Back, and Abs by Training to Do 50 Consecutive Pull-UpsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 7 Weeks to 10 Pounds of Muscle: The Complete Day-by-Day Program to Pack on Lean, Healthy Muscle MassFrom Everand7 Weeks to 10 Pounds of Muscle: The Complete Day-by-Day Program to Pack on Lean, Healthy Muscle MassRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Calisthenics: Guide for Bodyweight Exercise, Build your Dream Body in 30 MinutesFrom EverandCalisthenics: Guide for Bodyweight Exercise, Build your Dream Body in 30 MinutesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Calisthenics: 12 Effective Exercises to Build Calisthenics Body in 14 DaysFrom EverandCalisthenics: 12 Effective Exercises to Build Calisthenics Body in 14 DaysRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Meat Is for Pussies: A How-To Guide for Dudes Who Want to Get Fit, Kick Ass, and Take NamesFrom EverandMeat Is for Pussies: A How-To Guide for Dudes Who Want to Get Fit, Kick Ass, and Take NamesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Depression Hates a Moving Target: How Running With My Dog Brought Me Back From the BrinkFrom EverandDepression Hates a Moving Target: How Running With My Dog Brought Me Back From the BrinkRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (35)
- Deezify's Epic Workout Handbook: An Illustrated Guide to Getting SwoleFrom EverandDeezify's Epic Workout Handbook: An Illustrated Guide to Getting SwoleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)