Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Drug Study Krizia
Uploaded by
Alexia AlbaniaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Drug Study Krizia
Uploaded by
Alexia AlbaniaCopyright:
Available Formats
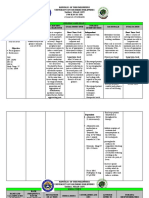
Patient Name: Arzadon, Marc Francis M.
Age: 22 Sex: M Ward/Room/Bed: Surgical Ward/Room 1/Bed 1 Diagnosis: Acute Appendicitis Date: April 14, 2023
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective: “Sumasakit po Acute pain r/t distension of After 30 minutes of Independent: After 30 minutes of
‘yung tiyan ko e, kumikirot intestinal tissues s/t nursing interventions, the 1. Determine and 1. To give appropriate nursing interventions, the
po,” as verbalized by the inflammation AEB pain patient will demonstrate document presence of intervention indicated patient demonstrated
patient. scale of 7/10 and facial use of relaxation skills and possible upon the underlying relaxation skills and
grimace. diversional activities. pathophysiological and cause of pain. diversional activities.
Objective: psychological causes of
o Facial grimace After 4 hours of nursing pain. After 4 hours of nursing
o Restlessness interventions, the patient 2. Provide accurate and 2. To decrease anxiety. interventions, the patient
o Pain scale of 7/10 will verbalize that the pain honest information verbalized that the pain is
o BP: 140/100 mmHg is controlled. regarding illness to the controlled.
o PR: 133 bpm patient.
o RR: 22 cpm 3. Keep at rest in a semi- 3. To relieve abdominal
fowler’s position. tension, therefore
relieving the pain.
4. Provide quiet 4. To promote relaxation.
environment.
5. Provide diversional 5. To refocus attention and
activities such as enhancing coping
watching and listening abilities.
to music.
Dependent:
6. Administer analgesic as 6. To relieve pain.
indicated.
Delantar, Krizia Mae C., SN
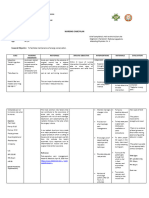
Generic Name: Side Effects/
Nursing Responsibilities
Cefuroxime Adverse Reactions
Assessment & Drug Effects
Brand Name: Zinacef Mechanism of Action
Inhibits cell wall synthesis,
• Determine history of hypersensitivity reactions to
Drug Illustration promoting osmotic instability;
cephalosporins, penicillin, and history of allergies,
usually bactericidal.
particularly to drugs, before therapy is initiated.
• Lab tests: Perform culture and sensitivity tests before
CV: Phlebitis, thrombophlebitis initiation of therapy and periodically during therapy if
indicated. Therapy may be instituted pending test results.
GI: Diarrhea, Monitor periodically BUN and creatinine clearance.
Indication pseudomembranous colitis, • Inspect IM and IV injection sites frequently for signs of
Perioperative prophylaxis nausea, anorexia, vomiting. phlebitis.
• Report onset of loose stools or diarrhea. Although
Hematologic: Hemolytic pseudomembranous colitis rarely occurs, this potentially life-
anemia, thrombocytopenia, threatening complication should be ruled out as the cause of
Contraindication
transient neutropenia, diarrhea during and after antibiotic therapy.
➢ Contraindicated in patients
eosinophilia. • Monitor for manifestations of hypersensitivity. Discontinue
Drug Classification hypersensitive to drug or
drug and report their appearance promptly.
Pharmacologic: other cephalosporins.
Skin: Maculopapular and • Monitor I&O rates and pattern: Especially important in
Second generation ➢ Use cautiously in patients
erythematous rashes, sterile severely ill patients receiving high doses. Report any
Cephalosporins hypersensitive to penicillin
abscesses, temperature elevation. significant changes.
Therapeutic: Antibiotics because of possibility of
cross-sensitivity with other
Patient & Family Education
beta-lactam antibiotics.
➢ Use cautiously in patients
Dose/Frequency/Route • Report loose stools or diarrhea promptly.
with colitis and renal
750 mg TIV q8 hrs • Report any signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity
insufficiency.
Generic Name: Side Effects/
Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities
Metronidazole Adverse Reactions
Direct-acting trichomonacide and Assessment & Drug Effects
Brand Name: Flagyl IV amebicide that works inside and
CNS: Headache, seizures, fever,
outside the intestines. It is thought
vertigo, ataxia, dizziness, • Discontinue therapy immediately if symptoms of CNS
Drug Illustration to enter the cells of microorganisms
syncope, incoordination, toxicity develop. Monitor especially for seizures and
that contain nitro reductase,
confusion, irritability, peripheral neuropathy (e.g., numbness and paresthesia of
forming unstable compounds that
depression, weakness, insomnia, extremities).
bind to DNA and inhibit synthesis,
peripheral neuropathy. • Lab tests: Obtain total and differential WBC counts before,
causing cell death. during, and after therapy, especially if a second course is
CV: Flattened T wave, edema, necessary.
Indication flushing, thrombophlebitis after • Monitor for S&S of sodium retention, especially in patients
To prevent postoperative infection IV infusion. on corticosteroid therapy or with a history of CHF.
in contaminated or potentially • Monitor patients on lithium for elevated lithium levels.
contaminated colorectal surgery. EENT: Rhinitis, sinusitis, • Report appearance of candidiasis or it’s becoming more
pharyngitis. prominent with therapy to physician promptly.
• Repeat feces examinations, usually up to 3 mo., to ensure that
Contraindication
GI: Nausea, abdominal pain, amebae have been eliminated.
➢ Contraindicated in patients
stomatitis, epigastric distress,
hypersensitive to drug or
Drug Classification vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea, Patient & Family Education
other nitroimidazole
Pharmacologic: constipation, proctitis, dry
derivatives.
Nitroimidazoles mouth, metallic taste. • Do not drink alcohol during therapy; may induce a
➢ Use cautiously in patients
Therapeutic: Antiprotozoals disulfiram-type reaction. Avoid alcohol or alcohol-containing
with history of blood
GU: Darkened urine, Genital medications for at least 48 h after treatment is completed.
dyscrasias, CNS disorder, or
Pruritus, UTI. • Urine may appear dark or reddish brown (especially with
retinal or visual field
higher than recommended doses). This appears to have no
changes.
Hematologic: Transient clinical significance.
➢ Use cautiously in patients
Leukopenia, neutropenia. • Report symptoms of candida overgrowth: Furry tongue, color
Dose/Frequency/Route who take hepatotoxic drugs
changes of tongue, glossitis, stomatitis; vaginitis, curd-like,
500 mg TIV q8 hrs or have hepatic disease,
Musculoskeletal: Transient milky vaginal discharge; proctitis. Treatment with a
alcoholism, or renal
joint pains. candidacidal agent may be indicated.
impairment.
Generic Name: Side Effects/
Nursing Responsibilities
Acetaminophen Mechanism of Action Adverse Reactions
Thought to produce analgesia by CNS: agitation, anxiety, fatigue,
Brand Name: Ofirmev inhibiting prostaglandin and other headache, insomnia, pyrexia.
substances that sensitize pain
Drug Illustration
receptors. Drug may relieve fever CV: HTN, hypotension, Assessment & Drug Effects
through central action in the peripheral edema, periorbital
hypothalamic heat-regulating edema, tachycardia. • Monitor for S&S of: hepatotoxicity, even with moderate
center. acetaminophen doses, especially in individuals with poor
GI: Oliguria nutrition or who have ingested alcohol over prolonged
periods; poisoning, usually from accidental ingestion or
Hematologic: Hemolytic suicide attempts; potential abuse from psychological
Indication anemia, leukopenia, dependence (withdrawal has been associated with restless and
For mild to moderate pain and fever neutropenia, pancytopenia, excited responses).
anemia.
Patient & Family Education
Contraindication
Hepatic: Jaundice
➢ Contraindicated in patients
• Do not take other medications (e.g., cold preparations)
hypersensitive to drug.
Metabolic: Hypoalbuminemia, containing acetaminophen without medical advice;
Drug Classification ➢ Contraindicated in patients
hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, overdosing and chronic use can cause liver damage and other
Pharmacologic: with severe hepatic
hypervolemia, hypomagnesemia. toxic effects.
Para-aminophenol derivatives impairment or severe acute
• Do not self-medicate adults for pain more than 10 d (5 d in
Therapeutic: Analgesics liver disease.
Musculoskeletal: Muscle children) without consulting a physician.
➢ Use cautiously in patients
spasms, extremity pain • Do not use this medication without medical direction for:
with G6D deficiency,
fever persisting longer than 3 d, fever over 39.5° C (103° F),
chronic malnutrition, and
Respiratory: Abnormal breath or recurrent fever.
severe hypovolemia.
sounds, dyspnea, hypoxia,
Dose/Frequency/Route ➢ Use cautiously in patients
atelectasis, pleural effusion,
600 mg TIV RTC q8 hrs with long-term alcohol use
pulmonary edema, stridor,
because therapeutic doses
wheezing
can cause hepatotoxicity.
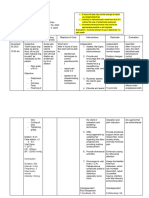
Generic Name: Side Effects/
Nursing Responsibilities
Omeprazole Adverse Reactions
Mechanism of Action
Brand Name: Losec Inhibits proton pump activity by
binding to hydrogen-potassium
Drug Illustration
adenosine triphosphatase, located at
secretory surface of gastric parietal
cells, to suppress gastric acid secretion.
Assessment & Drug Effects
CNS: Asthenia, dizziness, headache.
• Lab tests: Monitor urinalysis for hematuria and
GI: Abdominal pain, constipation, proteinuria. Periodic liver function tests with
Indication diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, prolonged use.
For eradication Helicobacter pylori vomiting, acid regurgitation.
Patient & Family Education
Musculoskeletal: Back pain,
Contraindication weakness. • Report any changes in urinary elimination such
➢ Contraindicated in patients as pain or discomfort associated with urination,
hypersensitive to drug or its Respiratory: Cough. or blood in urine.
Drug Classification components. • Report severe diarrhea; drug may need to be
Pharmacologic: ➢ Use cautiously in patients with Skin: Rash. discontinued.
Proton Pump Inhibitors hypokalemia and respiratory
Therapeutic: alkalosis an din patients on a
Gastrointestinal Agent low-sodium diet.
➢ Long-term administration of
bicarbonate with calcium or
Dose/Frequency/Route milk can cause milk-alkali
40 mg TIV OD syndrome.
You might also like
- Brain-Gut Interactions And Somatization in Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)From EverandBrain-Gut Interactions And Somatization in Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)No ratings yet
- The Journey to Pain Relief: A Hands-On Guide to Breakthroughs in Pain TreatmentFrom EverandThe Journey to Pain Relief: A Hands-On Guide to Breakthroughs in Pain TreatmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Acutepain RevisedDocument3 pagesAcutepain RevisedAndrea AutorNo ratings yet
- Final Zollinger-Ellison SyndromeDocument9 pagesFinal Zollinger-Ellison SyndromeGLYDEL CORDERONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Cervical CancerDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan for Cervical CancerAMEER MUHMIEN JALMAANI. LERIOSNo ratings yet
- Chloe Jacoba NCMA 113 BSN 1-YC-6: Subjective IndependentDocument1 pageChloe Jacoba NCMA 113 BSN 1-YC-6: Subjective IndependentPatricia ParagguaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Preoperative Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Preoperative Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveShamsa AfdalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute PainDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Acute Painunnamed person100% (1)
- Hemorrhoids N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHemorrhoids N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument2 pagesAcute PainNicole Genevie MallariNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Management for Zollinger-Ellison PatientDocument9 pagesNutrition Management for Zollinger-Ellison PatientGLYDEL CORDERONo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - SLHDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan - SLHheartyprincess54No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Clustered Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Outcome Criteria Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Clustered Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Outcome Criteria Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationCLEMENT, EUGENE CHADNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanBerlon LacsonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledJayelles Dixien JuguilonNo ratings yet
- Aiza NCPDocument6 pagesAiza NCPponponolmedoNo ratings yet
- Forro Intestinal ObstructionDocument3 pagesForro Intestinal ObstructionShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Managing Abdominal Pain from DiverticulitisDocument11 pagesManaging Abdominal Pain from DiverticulitisMa. Sofia Andrei AlcabazaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)CHRISTIE MONTANO0% (1)
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPJo Chiko FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan #1 - Acute Pain ManagementDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 - Acute Pain Managementunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Nursing Implementation FormDocument3 pagesNursing Implementation Formrosana99 ocha45No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 2: Cue Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 2: Cue Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationJIRAH MAY NAELGANo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervntion Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervntion Rationale EvaluationDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument10 pagesMyasthenia Gravisnoranhassanshams0No ratings yet
- Forro Intestinal Obstruction-2Document4 pagesForro Intestinal Obstruction-2Shiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For CholecystitisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For CholecystitisEemyaj Jaymee88% (8)
- NURSING CARE PLAN ANALYSISDocument7 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN ANALYSISCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP - Drug Study - Peptic UlcerDocument18 pagesNCP - Drug Study - Peptic UlcerEmi EspinoNo ratings yet
- Norbe COMFORT MEASURESDocument10 pagesNorbe COMFORT MEASURESMarlo Dañez NorbeNo ratings yet
- PYELONEPHRITISDocument6 pagesPYELONEPHRITISBb RabbitNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NFc CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- "My Neck Feels Stiff and There's Pain Coming From It. Every Time I Move It, It Only Gets Worse." As Stated by TheDocument4 pages"My Neck Feels Stiff and There's Pain Coming From It. Every Time I Move It, It Only Gets Worse." As Stated by TheCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Sto: Diagnostic:: Assessme NT Explanatio Nofthe Problem Planning Interven Tion Rationale Evaluati ONDocument3 pagesSubjective: Sto: Diagnostic:: Assessme NT Explanatio Nofthe Problem Planning Interven Tion Rationale Evaluati ONRona PieNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Due To Labor Process NCPDocument1 pageAcute Pain Due To Labor Process NCPRhod Vincent Jamolod TayongNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain 8thDocument2 pagesAcute Pain 8thMaze ReyesNo ratings yet
- Managing Pain and Constipation Through Targeted Nursing InterventionsDocument4 pagesManaging Pain and Constipation Through Targeted Nursing InterventionsCiara ManguiatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Western Mindanao State University College of NursingDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan: Western Mindanao State University College of NursingPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Or NCPDocument5 pagesOr NCPjelopigar921No ratings yet
- Kusain - NCP in NCM 112 RleDocument2 pagesKusain - NCP in NCM 112 Rlejay kusainNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy - NCPDocument6 pagesAppendectomy - NCPRhenzes HaraNo ratings yet
- Ms II NCPDocument2 pagesMs II NCPABIL ABU BAKARNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPKrishna Faith P. DelaraNo ratings yet
- Managing Pulmonary Hypertension Through Breathing TechniquesDocument6 pagesManaging Pulmonary Hypertension Through Breathing TechniquesJunnie Rose IsiderioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanBriana Louise HernandezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Isabella C. DomingoDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Isabella C. DomingojussNo ratings yet
- Post-Cesarean Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesPost-Cesarean Pain ManagementMillicent ComaNo ratings yet
- Post-CS Nursing Care Plan GoalsDocument7 pagesPost-CS Nursing Care Plan GoalsshinloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Labor Pain ManagementDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Labor Pain ManagementFc CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For The Patient With Burn Injury - Acute Pain Related To Tissue and Nerve InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For The Patient With Burn Injury - Acute Pain Related To Tissue and Nerve InjuryAngel Garcia67% (3)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- NCP-PAIN-1Document6 pagesNCP-PAIN-1goodemonz15No ratings yet
- 38.7°C (Fever) Pulse Rate of 87 (Normal) Respiratory Rate of 21 (Abnormal) and Blood Pressure of 130/80Mmhg (High Blood)Document3 pages38.7°C (Fever) Pulse Rate of 87 (Normal) Respiratory Rate of 21 (Abnormal) and Blood Pressure of 130/80Mmhg (High Blood)Kristine Louise JavierNo ratings yet
- Subjective Cues: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalDocument4 pagesSubjective Cues: Short Term Goal: Short Term GoalLarr SumalpongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Gallbladder StonesDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Gallbladder StonesKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- OB - NCP (Episiotomy)Document3 pagesOB - NCP (Episiotomy)eosNo ratings yet
- H-Mole NCPsDocument7 pagesH-Mole NCPsJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Actual NCP Ortho - PESCADERO 4CDocument2 pagesActual NCP Ortho - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanJan DamesNo ratings yet
- VisionIAS Monthly Current Affairs November 2023 November 2023-3-17Document15 pagesVisionIAS Monthly Current Affairs November 2023 November 2023-3-17Ved VyasNo ratings yet
- STAXI BookletDocument3 pagesSTAXI Bookletcontact.dhruvmahajanNo ratings yet
- Sovereign Order of Malta Constitutional Charter and CodeDocument148 pagesSovereign Order of Malta Constitutional Charter and CodeJuan TelloNo ratings yet
- A Prison DiaryDocument5 pagesA Prison Diarypranshu rathiNo ratings yet
- Development Bank of The Philippines vs. Sta. Ines Melale Forest Products Corporation G.R. No. 193068 - G.R No. 193099Document3 pagesDevelopment Bank of The Philippines vs. Sta. Ines Melale Forest Products Corporation G.R. No. 193068 - G.R No. 193099MikoNo ratings yet
- Last Will and Testament of Frederick DouglassDocument6 pagesLast Will and Testament of Frederick DouglassDigitalCambria.com0% (1)
- Doctrine (Rules) of PrecedentDocument9 pagesDoctrine (Rules) of PrecedentchoihwlorraineNo ratings yet
- Assignment LAW 245Document19 pagesAssignment LAW 245MsNie GeeNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH B Poetry Dreaming Black BoyDocument5 pagesENGLISH B Poetry Dreaming Black Boykavelle chuneNo ratings yet
- Sermon Notes: "The Core Value of Mission" (2 Corinthians 5:14-21)Document3 pagesSermon Notes: "The Core Value of Mission" (2 Corinthians 5:14-21)NewCityChurchCalgary0% (1)
- Bill of Rights C 4thDocument58 pagesBill of Rights C 4thDevilleres Eliza DenNo ratings yet
- Domestic Violence Prevention and Protection Act 2012Document8 pagesDomestic Violence Prevention and Protection Act 2012Xahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Moving Up Ceremony Highlights AchievementsDocument3 pagesMoving Up Ceremony Highlights AchievementsArvinNo ratings yet
- The Interesting Narrative of The Life of EquianoDocument25 pagesThe Interesting Narrative of The Life of EquianoYara SulimanNo ratings yet
- Filipinas Marble v. IACDocument4 pagesFilipinas Marble v. IACGennard Michael Angelo AngelesNo ratings yet
- Asia Lighterage and Shipping, Inc. vs. Court of Appeals PDFDocument13 pagesAsia Lighterage and Shipping, Inc. vs. Court of Appeals PDFRey Emmanuel Burgos0% (1)
- Criminal Law 2 - Mandatory Drug Test RulingDocument1 pageCriminal Law 2 - Mandatory Drug Test RulingPop CornNo ratings yet
- Petition For Correction of Entry - DeathDocument2 pagesPetition For Correction of Entry - DeathTIN GOMEZ100% (1)
- Madame Tussaud's: Marylebone Road, London, NW1 5LR. Baker StreetDocument16 pagesMadame Tussaud's: Marylebone Road, London, NW1 5LR. Baker StreetManuela Zuluaga VargasNo ratings yet
- THANTHAI PERIYAR-A MAN OF SOCIAL REFORMSDocument5 pagesTHANTHAI PERIYAR-A MAN OF SOCIAL REFORMSMannavan ThiruNo ratings yet
- Too Give or Take?: What Redburn Saw in Lanuncelott's HeyDocument5 pagesToo Give or Take?: What Redburn Saw in Lanuncelott's HeyMichael SunseriNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola Bottlers vs. Dela Cruz GR 184977 Dec 9, 2009Document8 pagesCoca Cola Bottlers vs. Dela Cruz GR 184977 Dec 9, 2009ckarla80No ratings yet
- Brouwer Compositional PeriodsDocument63 pagesBrouwer Compositional Periodskevnole100% (3)
- De Thi Giua Ki 1 Lop 11 Mon Tieng Anh Nam 2020Document5 pagesDe Thi Giua Ki 1 Lop 11 Mon Tieng Anh Nam 2020Nguyet Sao Bien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Confessions in Police CustodyDocument23 pagesConfessions in Police CustodyManDeepWarwalNo ratings yet
- English Refugees and the Varangian GuardDocument11 pagesEnglish Refugees and the Varangian GuardNicholas PappasNo ratings yet
- Kelly RD ComplaintDocument13 pagesKelly RD ComplaintWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- Global Stage 5 Revision Document InsightsDocument4 pagesGlobal Stage 5 Revision Document InsightsNguyễn Hà MyNo ratings yet
- Bell v. Union Pacific Railroad - Document No. 3Document2 pagesBell v. Union Pacific Railroad - Document No. 3Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Subcomandante Marcos - Professionals of Hope - The Selected Writings of Subcomandante Marcos-The Song Cave (2017) PDFDocument258 pagesSubcomandante Marcos - Professionals of Hope - The Selected Writings of Subcomandante Marcos-The Song Cave (2017) PDFSantiago Erazo100% (2)