Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.2.7 Resistance
Uploaded by
Ishimwe Habiyakare0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages4.2.7 Resistance
Uploaded by
Ishimwe HabiyakareCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
4.2.
7 Resistance
Ohm's Law
Resistance is the opposition to current
o For a given potential difference, the higher the resistance, the lower the current
o Therefore, resistors are used in circuits to control the current
o The unit of resistance is the ohm, represented by the Greek symbol omega Ω
Ohm's Law
The definition of resistance can be given using the equation
Where
o R = resistance (ohms, Ω)
o V = potential difference (volts, V)
o I = current (amperes, A)
Ohm's Law can be stated in words:
Current is directly proportional to potential difference as long as the temperature remains constant
Use the formula triangle to help you rearrange the equation
Consequences of Ohm's Law
Resistors are used in circuits to control either
o The current in branches of the circuit (through certain components)
o The potential difference across certain components
This is due to the consequences of Ohm's Law
o The current in an electrical conductor decreases as its resistance increases (for a constant p.d.)
o The p.d. across an electrical conductor increases as its resistance increases (for a constant current)
I-V Graphs for Ohmic Resistors, Filament Lamps & Diodes
Resistance is the opposition to current
o For a given potential difference, the higher the resistance, the lower the current
o Therefore, resistors are used in circuits to control the current
o The unit of resistance is the ohm, represented by the Greek symbol omega Ω
Ohm's Law
The definition of resistance can be given using the equation
Where
o R = resistance (ohms, Ω)
o V = potential difference (volts, V)
o I = current (amperes, A)
Ohm's Law can be stated in words:
Current is directly proportional to potential difference as long as the temperature remains constant
Use the formula triangle to help you rearrange the equation
Consequences of Ohm's Law
Resistors are used in circuits to control either
o The current in branches of the circuit (through certain components)
o The potential difference across certain components
This is due to the consequences of Ohm's Law
o The current in an electrical conductor decreases as its resistance increases (for a constant p.d.)
o The p.d. across an electrical conductor increases as its resistance increases (for a constant current)
You might also like
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Electric Circuits 30 JULY 2013: Lesson DescriptionDocument4 pagesElectric Circuits 30 JULY 2013: Lesson DescriptionTosin AbiolaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Definition of Ohms LawDocument36 pagesPrinciples and Definition of Ohms LawIrfanNo ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Resistors and Resistor CircuitsDocument4 pagesResistors and Resistor CircuitsBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngDocument12 pagesOhm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngViana Celina AngNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document15 pagesModule 7Laiza GranaNo ratings yet
- Resistance FormulaDocument14 pagesResistance FormulaCarl Kristopher PeloniaNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Formula WheelDocument2 pagesOhms Law Formula WheelTesda SfistNo ratings yet
- Ohmic Vs NonOhmic DevicesDocument2 pagesOhmic Vs NonOhmic DevicesBinodNo ratings yet
- Unit Learning OutcomesDocument1 pageUnit Learning OutcomesAngelica Ulpindo BalubarNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesLecture On Ohm's LawJanxi Carlisle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Advance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsDocument5 pagesAdvance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsJoshua AsuncionNo ratings yet
- CurrentDocument10 pagesCurrentShanto NiceschoolNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDF (16-19)Document18 pagesCurrent Electricity PDF (16-19)Abhay MauryaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Current, Resistance and Ohm'S LawDocument9 pagesLesson 1 Current, Resistance and Ohm'S LawPamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- Currrent Electricity FinalDocument30 pagesCurrrent Electricity FinalSaadullah Shahid100% (1)
- IM's Practice DemoDocument32 pagesIM's Practice DemoMary Rose ManawatawNo ratings yet
- LXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 23 - Ohms Law - 05aug2014Document6 pagesLXL - Gr11PhysicalSciences - 23 - Ohms Law - 05aug2014HNo ratings yet
- Resistance and Their CircuitsDocument19 pagesResistance and Their CircuitsPrince JairoNo ratings yet
- Resistance and Ohm's LawDocument1 pageResistance and Ohm's LawSuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Electronic CircuitsDocument13 pagesElectronic CircuitsAbhisek PagadNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- Ohm LawDocument4 pagesOhm LawAnonymous jdC36sKP57No ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Parallel CircuitDocument2 pagesOhm's Law: Parallel Circuitnhie_quh29No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument15 pagesOhm's Lawpaancute8982No ratings yet
- Physics Experiment DiscussionsDocument3 pagesPhysics Experiment DiscussionsMarichelle Ann CahiligNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawBelly JoeNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's LawAdrielNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument24 pagesOhm's LawIrish de LeonNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: ElectricityDocument9 pagesElectric Circuits: ElectricityFernanda VillacísNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument27 pagesUnit IPratap VeerNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law ReportDocument8 pagesOhm's Law ReportFelicia Paya FrancisNo ratings yet
- His Article Is About The Law Related To ElectricityDocument22 pagesHis Article Is About The Law Related To ElectricitySandeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- Current, Voltage and ResistanceDocument18 pagesCurrent, Voltage and ResistanceJustine FariscalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document20 pagesChapter 17dyalatalal225No ratings yet
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2surajNo ratings yet
- Physics (5054) For Grade 11: Chapter 19: "Current Electricity"Document45 pagesPhysics (5054) For Grade 11: Chapter 19: "Current Electricity"Hammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistance: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in Physics 2-4Document21 pagesElectrical Resistance: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in Physics 2-4Sam JordanNo ratings yet
- Bee Note Ohms Law and Numericals - Pradyumna SirDocument7 pagesBee Note Ohms Law and Numericals - Pradyumna Sirniharranjanmahanta78No ratings yet
- IGCSE 24 ElectricalResistanceDocument21 pagesIGCSE 24 ElectricalResistanceHAMAD NoorNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Ohms LawDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Ohms LawnatlasNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law AnimationDocument3 pagesOhm's Law Animationholisticwarehou94No ratings yet
- What Is Ohm's Law Definition, Formula, Graph & LimitationsDocument10 pagesWhat Is Ohm's Law Definition, Formula, Graph & LimitationsjackNo ratings yet
- 3 X7 EBcf 78 Auzh Emn C5 ETDocument26 pages3 X7 EBcf 78 Auzh Emn C5 ETAnas AlamNo ratings yet
- Electric Current NotesDocument6 pagesElectric Current Notesm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument35 pagesElectricalvinomalai100% (1)
- BasicElecOhmsLawDocument16 pagesBasicElecOhmsLawRichard del RosarioNo ratings yet
- RESISTORSDocument8 pagesRESISTORSKobby BrineNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeDocument10 pagesOhm's Law: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeAditya Singh BaisNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsDocument4 pagesBasic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeDocument4 pagesElectromagnetism: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeNadya Ilmi HanifaNo ratings yet
- Aim of ProjectDocument5 pagesAim of Projectaayush sinhaNo ratings yet
- UG DocumentDocument6 pagesUG DocumentSliman 1No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Perform Mensuration and Calculation: Information Sheet 1.1 - ElectronicsDocument12 pagesLesson 5 - Perform Mensuration and Calculation: Information Sheet 1.1 - ElectronicsEscanor Lions Sin of PrideNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's Lawabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawDon't Know EverythingNo ratings yet
- 6.1.5 Gravitational Effects On OrbitsDocument6 pages6.1.5 Gravitational Effects On OrbitsIshimwe HabiyakareNo ratings yet
- 6.2.3 The Expanding UniverseDocument3 pages6.2.3 The Expanding UniverseIshimwe HabiyakareNo ratings yet
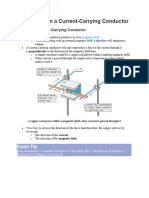
- 4.4.6 Force On A Current-Carrying ConductorDocument4 pages4.4.6 Force On A Current-Carrying ConductorIshimwe HabiyakareNo ratings yet
- 4.3.1 Circuit Diagrams & Circuit ComponentsDocument2 pages4.3.1 Circuit Diagrams & Circuit ComponentsIshimwe HabiyakareNo ratings yet
- Notes Till Lec-8 - 23135071Document80 pagesNotes Till Lec-8 - 23135071pranjal02svpslNo ratings yet
- Module 12 - Energy, Heat, and TemperatureDocument6 pagesModule 12 - Energy, Heat, and TemperatureAna Maria Millan RinconNo ratings yet
- PTS PLKR 11 (Respons)Document63 pagesPTS PLKR 11 (Respons)Ijo OjiNo ratings yet
- Matlab For Engineers 5th Edition Moore Solutions ManualDocument18 pagesMatlab For Engineers 5th Edition Moore Solutions Manualschahheelpost4ogl100% (22)
- Work Book Physics Grade 11&12Document33 pagesWork Book Physics Grade 11&12Yonatan Tolosa100% (2)
- Final Exam - 2021-FallDocument7 pagesFinal Exam - 2021-FallSrinivasa Rao DNo ratings yet
- Archimedes' Principle and Buoyancy Force ExperimentDocument9 pagesArchimedes' Principle and Buoyancy Force Experimentmohammad. 21No ratings yet
- CA01303001EDocument106 pagesCA01303001EMarlon HumbertoNo ratings yet
- Spec Sheet - GSX13 Daikin McQuayDocument40 pagesSpec Sheet - GSX13 Daikin McQuayYair FloresNo ratings yet
- Work Power EnergyDocument54 pagesWork Power EnergyfaNo ratings yet
- A Max: Field BalancingDocument18 pagesA Max: Field BalancingNanda WiratamaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of A Hybrid Gas Turbine Power Plant-Solar Photovoltaic Plant System Used in Messla Oil FieldDocument8 pagesModeling and Simulation of A Hybrid Gas Turbine Power Plant-Solar Photovoltaic Plant System Used in Messla Oil FieldBORIS KAPLANNo ratings yet
- CERTIFICATE NO 3 Diesel Welding MachineDocument2 pagesCERTIFICATE NO 3 Diesel Welding MachineOwais MalikNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios & Identities: Compound AnglesDocument44 pagesTrigonometric Ratios & Identities: Compound AnglesTanvir ShafalNo ratings yet
- Dry Type Transformer DRWDocument4 pagesDry Type Transformer DRWAli AbualsamenNo ratings yet
- Yayasan Pesantren Islam Al-Azhar: Choose The Correct Answer!Document5 pagesYayasan Pesantren Islam Al-Azhar: Choose The Correct Answer!Beny FachruriNo ratings yet
- Creative Technology 10: Pre - TestDocument4 pagesCreative Technology 10: Pre - TestAliyah RuizNo ratings yet
- HydrostaticsDocument24 pagesHydrostaticsmaria ashrafNo ratings yet
- Handheld Instrumentation: APWDocument4 pagesHandheld Instrumentation: APWMayucious MayuNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Notes by Alamgir RahimDocument66 pagesInstrumentation Notes by Alamgir RahimmersiumNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 2Document15 pagesTopic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 2burcak gecNo ratings yet
- Electrical System Layout - Group 5Document8 pagesElectrical System Layout - Group 5Darryl ArpilledaNo ratings yet
- Force Fields and Electromagnets: Summary SheetsDocument3 pagesForce Fields and Electromagnets: Summary SheetsOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Parker 1961Document7 pagesParker 1961曾帅No ratings yet
- Thermal Properties - 9-18Document25 pagesThermal Properties - 9-18Aryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Tme 213 Classwork SolutionsDocument15 pagesTme 213 Classwork SolutionsEnenamahNo ratings yet
- Gilmont RotametrosDocument15 pagesGilmont RotametrosSimon BelloNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Chapter 5Document27 pagesHydraulics Chapter 5tekalign yerangoNo ratings yet
- Smart Power Grid SystemDocument64 pagesSmart Power Grid SystemNikhil GawandeNo ratings yet
- DLP Q1 WK 8 D1 (34) Science 8Document6 pagesDLP Q1 WK 8 D1 (34) Science 8Red MarquezNo ratings yet