Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Yeart Neet
Uploaded by
Yash KapoorCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Yeart Neet
Uploaded by
Yash KapoorCopyright:
Available Formats
FEAT: The Career Institute
IIT-JEE | NEET | Olympiads | CBSE - ICSE
PART TESTS
NEET – 2024
WEEKLY TEST-1
TEST DATE: 23-04-2023
Time Allotted: 2.5 Hours Maximum Marks: 260
General Instructions:
• Each question carries 4 marks. For each correct response, the candidate will get 4 marks.
• For every wrong response. 1 mark shall be deducted from the total score. Unanswered /
Unattempted questions will be given no marks. The maximum marks are 260.
Name of the Candidate: _________________________
Physics
Q1. One metallic sphere A is given positive charge whereas another identical metallic sphere B of exactly
same mass as of A is given equal amount of negative charge. Then,
(a) mass of A and mass of B still remain equal
(b) mass of A increases
(c) mass of B decreases
(d) mass of B increases
Q2. When1014 electrons are removed from a neutral metal sphere, then the charge on the sphere becomes
(a) 16 μC (b) −16 μC (c) 32μC (d) −32μC
Q3. Which of the following is correct regarding electric charge?
(i) If a body is having positive charge, then there is shortage of electrons.
(ii) If a body is having negative charge, then there is excess of electrons.
(iii) Minimum possible charge = ± 1.6 × 10-19C.
(iv) Charge is quantised, i.e. Q = ± ne, where n = 1, 2, 3, 4,…
(a) Both (i) and (ii) (b) Both (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii) (d) All of these
Q4. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it
(a) gains electrons from silk (b) gives electrons to silk
(c) gains protons from silk (d) gives protons to silk
Q5. Consider a neutral conducting sphere. A positive point charge is placed outside the sphere. The net
charge on the sphere is
(a) negative and distributed uniformly over the surface of the sphere
(b) negative and appears only at the point on the sphere closest to the point charge
(c) negative and distributed non-uniformly over the entire surface of the sphere
(d) zero
Q6. Two charges each equal to 2μC are 0.5 m apart. If both of them exist inside vacuum, then the force
between them is
(a) 1.89 N (b) 2.44 N (c) 0.144 N (d) 3.144 N
Q7. Two charges of equal magnitudes and at a distance r exert a force F on each other. If the charges are
halved and distance between them is doubled, then the new force acting on each charge is
(a) F/8 (c) F /4 (c) 4F (d) F/16
Q8. Two point charges placed at a certain distance r in air exert a force F on each other. Then, the distance
r’ at which these charges will exert the same force in a medium of dielectric constant K is given by
(a) r (b) r/K (c) 𝑟/√𝐾 (d) 𝑟√𝐾
Q9. Two particles of equal mass m and charge q are placed at a distance of 16 cm. They do not experience
𝑞
any force. The value of 𝑚 is
𝜋𝜀0 𝐺
(a) 𝑙 (b) √ (c) √4𝜋𝜀 (d) √4𝜋𝜀0 𝐺
𝐺 0
Q10. Electric charges of 1μC, −1μC and 2μC are placed in air at the corners A, B and C respectively of an
equilateral triangle ABC having length of each side 10 cm. The resultant force on the charge at C is
(a) 0.9 N (b) 1.8 N (c) 2.7 N (d) 3.6 N
Q11. Two charges +5 μC and +10 μC are placed 20 cm apart. The net electric field at the mid-point between
the two charges is
(a) 4.5 × 106 NC−1 directed towards +5μC
(b) 4.5 × 106 NC−1 directed towards +10 μC
(c) 13.5 × 106 NC−1 directed towards +5μC
(d) 13.5 × 106 NC−1 directed towards +10 μC
Q12. Two point charges +8q and −2q are located at x = 0 and x = L, respectively. The location of a point on
the X-axis at which the net electric field due to these two point charges is zero, is
(a) 8L (b) 4L (c) 2L (d) L / 4
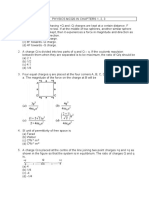
Q13. An uncharged sphere of metal is placed in between two charged plates as shown. The lines of force
look like
(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
Q14. If the electric flux entering and leaving an enclosed surface respectively is ɸ1 and ɸ2 , then the
electric charge inside the surface will be
(a) (ɸ1 + ɸ1 )𝜀0 (b) (ɸ2 − ɸ1 )𝜀0 (c) (ɸ1 + ɸ2 )/𝜀0 (d) (ɸ2 − ɸ1 )/𝜀0
Q15. Charge of 2 C is placed at the centre of a cube. What is the electric flux passing through one face?
1 1 2 3
(a) 3𝜀 (b) (4) 𝜀0 (c) 𝜀 (d) 𝜀
0 0 0
Q16. If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero, then
(i) the electric field must be zero everywhere on the surface
(ii) the electric field may be zero everywhere on the surface
(iii) the charge inside the surface must be zero
(iv) the charge in the vicinity of the surfaces must be zero
(a) (i), (ii) (b) (ii), (iii) (c) (ii), (iv) (d) (i), (iii)
Q17. An infinite line charge produces a field of18 × 104 N/C at 0.02 m. The linear charge density is
(a) 2 × 10−7 C/m (b) 10−8 C/m (c) 107 C/m (d) 10−4 C/m
Q18. A charge of 17.7 × 10−4 C is distributed uniformly over a large sheet of area 200 m2. The electric
field intensity at a distance 20 cm from it in air will be
(a) 5 × 105 N/C (b) 6 × 105 N/C (c) 7 × 105 N/C (d) 8 × 105 N/C
Q19. Consider the charge configuration and spherical Gaussian surface as shown in the figure. When
calculating the flux of the electric field over the spherical surface, the electric field will be due to
(a) q2 (b) only the positive charges
(c) all the charges (d) + q1 and − q1
Q20. q1, q2, q3 and q4 are point charges located at points as shown in the figure and S is a spherical
Gaussian surface of radius
R. Which of the following is true according to the Gauss’s law?
Chemistry
Q1. H2S, a toxic gas with rotten egg like smell, is used for the quantitative analysis. If the solubility of H2S in water at
STP is 0.2 m, then Henry’s law constant for H2S in water at 273 K is
(a) 3.6 × 108 Pa (b) 5.0 × 108 Pa
(c) 5.0 × 105 Pa (d) 2.78 × 107 Pa
Q2. The boiling points of C6H6, CH3OH, C6H5NH2 and C6H5NO2 are 80°C, 65°C, 184°C and 212°C, respectively.
Which of
the following will have the highest vapour pressure at room temperature?
(a) C6H6 (b) CH3OH (c) C6H5NH2 (d) C6H5NO2
Q3. Each of the following pair shows a positive deviation from the Raoult’s law except
(a) (C2H5)O + HCl (b) CCl4 + CH3OH (c) CHCl3 + C2H5OH (d) C2H5OH + H2O
Q4. Heptane and octane form ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the pure liquids are 106 kPa and 46
kPa, respectively. What will be the vapour pressure, in bar, of a mixture of 30.0 g of heptane and 34.2 g of
octane?
(a) 76 bar (b) 152 bar (c) 1.52 bar (d) 0.76 bar
Q5. The boiling point of an azeotropic mixture of water and ethanol is less than that of water and ethanol,
separately. The mixture shows
(a) no deviation from Raoult’s law.
(b) positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
(c) negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
(d) that the solution is unsaturated
Q6. An aqueous solution of sucrose is 0.5 molal. What is the vapour pressure of water above this solution?
The vapour pressure of pure water is 25.0 mm Hg at this temperature.
(a) 24.8 mm Hg (b) 0.45 mm Hg
(c) 2.22 mm Hg (d) 20.3 mm Hg
Q7. For an ideal solution containing two liquid components A and B, the Gibb’s free energy of mixing is minimum,
when the molar ratio of the liquids is
(a) 1 : 1 (b) 1 : 2 (c) 1 : 10 (d) 1 : 1000
Q8. An ideal solution was obtained by mixing methanol and ethanol. If the partial vapour pressures of methanol and
ethanol are 2.8 and 4.2 kPa respectively, the mole fraction of methanol in the vapour at equilibrium is
(a) 0.67 (b) 0.4 (c) 0.6 (d) 0.33
Q9. After removing the hard shell of an egg by dissolving in dilute HCl, a semipermeable membrane can be visible.
If such an egg is kept in a saturated solution of common salt, the size of egg will
(a) shrink
(b) grow
(c) remain unchanged.
(d) first shrink, then grow
Q10. If 0.1 molar solution of glucose is separated from 0.1 molar solution of cane sugar by a semipermeable
membrane, then which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Water will flow from glucose solution into cane sugar solution.
(b) Cane sugar will flow across the membrane into glucose solution.
(c) Glucose will flow across the membrane into cane sugar solution.
(d) There will be no net movement across the semipermeable membrane.
Q11. A solution having 54 g of glucose per litre has an osmotic pressure of 4.56 bar. If the osmotic pressure of a urea
solution is 1.52 bar at the same temperature, then what would be its concentration?
(a) 1.0 M (b) 0.5 M (c) 0.3 M (d) 0.1 M
Q12. The molal boiling point elevation constant of water is 0.513°C kg mol−1. When 0.1 mole of sugar is dissolved in
200 g of water, the solution boils under a pressure of 1 atm at
(a) 100.513°C (b) 102.565°C (c) 100.256°C (d) 101.025°C
Q13. An aqueous solution of a non-volatile and nonelectrolyte solute (molecular mass = 150) boils at 373.26 K.
The composition of solution, in terms of mass percent of the solute, is (Kb of water = 0.52)
(a) 50% (b) 7.5% (c) 6.98% (d) 75%
Q14. It is more convenient to obtain the molecular mass of an unknown solute by measuring the freezing point
depression than by measuring the boiling point elevation because
(a) freezing point depression is a colligative property, whereas boiling point elevation is not.
(b) freezing point depressions are larger than boiling point elevations for the same solution.
(c) freezing point depressions are smaller than boiling point elevations for the same solution.
(d) freezing point depressions depends more on the amount of solute than boiling point elevation.
Q15. g of urea is dissolved in one kg of water. Up to what temperature, the solution may be cooled before ice starts
crystallizing out? (Kf of water = 1.86)
(a) −0.310°C (b) −0.240°C (c) −0.195°C (d) −0.155°C
Q16. The van’t Hofactor for a dilute solution of K3[Fe(CN)6] is
(a) 4.0 (b) 0.25 (c) 5.0 (d) 3.0 78.
Q17. At the same temperature, each of the following solution has the same osmotic pressure except
(a) 0.140 M-sucrose (b) 0.07 M-KCl (c) 0.070 M-Ca(NO2)2 (d) 0.140 M-urea
Q18. Which of the following aqueous solution will have the lowest freezing point?
(a) 0.10 m-sucrose (b) 0.10 m-NiCl2 (c) 0.10 m-CuSO4 (d) 0.10 m-NH4NO3
Q19. The elevation in boiling point, when 13. 44 g of freshly prepared CuCl2 is added to one kg of water, is
(Some useful data: Kb of water = 0.52 K − kg/mol and molecular weight of CuCl2 = 134.4)
(a) 0.052 (b) 0.104 (c) 0.156 (d) 0.208
Q20. Maximum osmotic pressure will be shown by which of the following solution (all 90% ionized)?
(a) 0.1 M-AlCl3 (b) 0.1 M-BaCl2 (c) 0.1 M-NaCl (d) 0.1 M-sugar
Biology
1. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
a. In banana, potato, and ginger, the plantlets arise from the internodes present in the modified stem.
b. Offspring produced by asexual reproduction is called a clone
c. Water hyacinth can deplete oxygen and cause the death of fishes
d. All of the above
2. A piece of potato tuber will form a new plant if it has _____
a. Stored Food
b. Roots
c. Branches
d. Eyes
3. Clones are
a. Genetically similar
b. Morphologically similar
c. Both (a) and (b)
d. None of these
4. Name an organism where cell division is itself a mode of reproduction?
a. Euglena
b. E. coli
c. Amoeba
d. All of these
5. Vegetative propagules of Agave is
a. Runner
b. Tuber
c. Bulbil
d. Rhizome
6. Plants, animals or fungi differ in all of these aspects except
a. Pattern of sexual mode of reproduction
b. Internal structure
c. External morphology
d. Physiology
7. Which of the following flowers only once in their lifetime?
a. Neem
b. Mango
c. Bamboo
d. All of these
8. Oestrous cycle occurs in
a. Rats
b. Cows
c. Deer
d. All of the above
9. Which part of the plant bryophyllum performs vegetative reproduction?
a. Stem
b. Floral buds
c. Underground roots
d. Buds on life margin
10. Non-flagellate spores are called conidia. In which organism are they seen?
a. Penicillium
b. Hydra
c. Amoeba
d. Chlamydomonas
11. Which of the following is not a natural method of vegetative reproduction?
a. Suckers
b. Cutting
c. Runners
d. Offsets
12. Which of the following group of animals show regeneration?
a. Planaria, Hydra, Starfish
b. Starfish, Amoeba, Plasmodium
c. Amoeba, Hydra, Paramoecium
d. Amoeba, Planaria, Starfish
13. The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as
a. Distribution of pollen grains
b. Transportation of pollen grains
c. Formation of pollen grains
d. Pollination
14. In Angiosperms, which parts of the flowers wither and fall off?
a. Sepals
b. Petals
c. Stamens
d. All the three
15. In which development of zygote takes place in female is called as…….. in animals.
a. Oviparous
b. Viviparous
c. Ovoviviparous
d. None
16. Choose the correct statement from amongst the following:
a. Monoecious (hermaphrodite) organisms are seen only in animals
b. Monoecious organisms are seen only in plants
c. Monoecious organisms are seen in both plants and animals
d. Monoecious organisms are seen only in vertebrates
17. There is no natural death in single celled organisms like Amoeba and bacteria because:
a. They cannot reproduce sexually
b. They reproduce by binary fission
c. Parental body is distributed among the offspring
d. They are microscopic
18. There are various types of reproduction. The type of reproduction adopted by an organism depends on:
a. The habitat and morphology of the organism
b. Morphology of the organism
c. Morphology and physiology of the organism
d. The organism’s habitat, physiology and genetic makeup
19. Which of the following is a post-fertilisation event in flowering plants?
a. Transfer of pollen grains
b. Embryo development
c. Formation of flower
d. Formation of pollen grains
20. The number of chromosomes in the shoot tip cells of a maize plant is 20. The number of chromosomes
in the microspore mother cells of the same plant shall be:
a. 20
b. 10
c. 40
d. 15
21. Syngamy means
a. fusion of gametes
b. fusion of cytoplasms
c. fusion of two similar spores
d. fusion of two dissimilar spores
22. In ginger vegetative propagation occurs through:
a. Offsets b. Bulbils
c. Runners d. Rhizome
23. Clear cut vegetative, reproductive and senescent phases are seen in:
I. Annual plants
II. Biennial plants
III. Perennial plants
a. Only I
b. Only III
c. Only I and ii
d. I, II, III
24. In angiosperms after fertilisation:
I. The zygote develops into the embryo
II. The ovules develop into the seed.
III. The ovary develop into the fruit.
IV. A thick protective fruit wall called pericarp develops.
a. Only I, II and IV are correct
b. only II, III and IV are correct
c. Only I, II and III are correct.
d. I, II, III and IV are correct.
25. The male gametes of rice plant have 12 chromosomes in their nucleus. The chromosome number in the
female gamete, zygote and the cells of the seedling will be, respectively,
a. 12, 24, 12
b. 24, 12, 12
c. 12, 24, 24
d. 24, 12, 24.
You might also like
- IIt PaceDocument15 pagesIIt Paceabhishekjanjalkar100% (1)
- Electric Charge & Force (Physics Vision)Document4 pagesElectric Charge & Force (Physics Vision)sediy97350No ratings yet
- Elec Assign 2Document5 pagesElec Assign 2paulaNo ratings yet
- Physics - XII Preboard-1Document14 pagesPhysics - XII Preboard-1Parth SharmaNo ratings yet
- VITEEE Physics 2013Document10 pagesVITEEE Physics 2013ssjatavNo ratings yet
- Physics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BDocument39 pagesPhysics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BPi PoliNo ratings yet
- Final 2020Document4 pagesFinal 2020Ashraf WaleedNo ratings yet
- 8 Copies 3rd Sem 2k19Document7 pages8 Copies 3rd Sem 2k19Abin VargheseNo ratings yet
- DbenkricnsbejfmDocument15 pagesDbenkricnsbejfmShreshta PuppamNo ratings yet
- Wipro TestDocument16 pagesWipro TestGireesh GachchinamathNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper - 8 Term-1Document11 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - 8 Term-1JatinNo ratings yet
- CG PET 2006 Question Paper: PhysicsDocument24 pagesCG PET 2006 Question Paper: PhysicsRahul BadgujarNo ratings yet
- CUET Physics ChapterwiseDocument273 pagesCUET Physics ChapterwiseNafeesNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocument11 pagesNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIYuhua SunNo ratings yet
- Aieee 2002 QDocument18 pagesAieee 2002 Qvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- MCQ Physics 1,2,3Document10 pagesMCQ Physics 1,2,3Sugaraj SamuelNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2002 Question PaperDocument18 pagesAIEEE 2002 Question PaperDeepa LakshmiNo ratings yet
- The ReformerDocument10 pagesThe ReformerDanis LevinNo ratings yet
- 2nd PUC Physics Important MCQsDocument51 pages2nd PUC Physics Important MCQsUrav SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Ho DHHDJDHSB Hapter - TestDocument5 pagesHo DHHDJDHSB Hapter - TestRSNo ratings yet
- SsssDocument33 pagesSsssAbhishek PareekNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper - IIDocument8 pagesPhysics Paper - IIPrajwal SolankiNo ratings yet
- Innovation Tuition Class Class 12 Physics Test Q1Document3 pagesInnovation Tuition Class Class 12 Physics Test Q1Hemant HemantNo ratings yet
- QP Xii PhysicsDocument9 pagesQP Xii PhysicsSufiyan BelimNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Set-ADocument9 pagesXii Physics Set-AAshik Anamic ShimiyaNo ratings yet
- ( (Premier Batch: Problem Solving DQG ( (HuflvhsheetDocument31 pages( (Premier Batch: Problem Solving DQG ( (HuflvhsheetAYUSH GUPTANo ratings yet
- Kcet Model QP Word Document (2) 15!04!2024Document9 pagesKcet Model QP Word Document (2) 15!04!2024mahadevipatil.patil04No ratings yet
- NEET 2019 Physics Sample Question Paper IIDocument10 pagesNEET 2019 Physics Sample Question Paper IImisostudyNo ratings yet
- Innovation Tuition Class Class 12 Physics Test Q1Document3 pagesInnovation Tuition Class Class 12 Physics Test Q1Hemant HemantNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET12Document8 pagesWORKSHEET12Anfeli JamesNo ratings yet
- Test - 15 JEEDocument14 pagesTest - 15 JEEAjaykrishnaNo ratings yet
- 12 PhysicsDocument26 pages12 Physicsqadeer03038185164No ratings yet
- CUET 2022 Chapterwise Physics PYQsDocument156 pagesCUET 2022 Chapterwise Physics PYQsbro96793No ratings yet
- Physics (Question Paper)Document7 pagesPhysics (Question Paper)Jay Doshi ShashikantNo ratings yet
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2012Document30 pagesJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2012chithrasajeev100% (1)
- Aiims Mbbs Solved Papers - 2016Document54 pagesAiims Mbbs Solved Papers - 2016ravichandran0506No ratings yet
- AIEEE 2002 Paper: Physics and ChemistryDocument36 pagesAIEEE 2002 Paper: Physics and ChemistryDiyaNo ratings yet
- Upsee-2011 Model Test Paper Paper 1 ( (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics)Document14 pagesUpsee-2011 Model Test Paper Paper 1 ( (Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics)Kundan AnandNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 (Electric Charges and Fields)Document2 pagesWorksheet 5 (Electric Charges and Fields)Kingsley CalexNo ratings yet
- Btech Model QuestionsDocument22 pagesBtech Model QuestionsAkshayKannanNo ratings yet
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2007Document25 pagesJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2007chithrasajeevNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Paper 2002 PDFDocument18 pagesAIEEE Paper 2002 PDFKiran Raj RNo ratings yet
- Viteee Mock TestDocument24 pagesViteee Mock TestJanaki KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Asc Class-12 Test-1 McqsDocument3 pagesAsc Class-12 Test-1 McqsAnkit JainNo ratings yet
- Physics PapersDocument61 pagesPhysics PapersDanial Amjad ChohanNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced 2022 Set-1Document6 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced 2022 Set-1abdulhafeez mohammed100% (1)
- Eklavya (NEET) Sample Paper - 1Document58 pagesEklavya (NEET) Sample Paper - 1arja keerthanaNo ratings yet
- MCQ ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesMCQ ElectrostaticsqesuzNo ratings yet
- Physics PapersDocument61 pagesPhysics PapersDanial Amjad ChohanNo ratings yet
- Physics For All (Panda Sir)Document11 pagesPhysics For All (Panda Sir)Darshan NayakNo ratings yet
- XII Physics Summer Vacations Home WorkDocument7 pagesXII Physics Summer Vacations Home WorkVaibhav VermaNo ratings yet
- MCQ2Document9 pagesMCQ2shiviNo ratings yet
- Prashant Tutorials: MM-64. Physics Chap 1 & 2 Time1h.30min Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics McqsDocument29 pagesPrashant Tutorials: MM-64. Physics Chap 1 & 2 Time1h.30min Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics McqsRitika SinghNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series of Monographs in Natural Philosophy, Volume 2From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series of Monographs in Natural Philosophy, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryFrom EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillNo ratings yet
- 1 T KUFHz KTZT Fa 0 QB HXEaDocument3 pages1 T KUFHz KTZT Fa 0 QB HXEaYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts BDocument8 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Acids Bases Salts BYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Aldol and Canizaro ReactionsDocument15 pagesChapter - Aldol and Canizaro ReactionsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Important-Question-ICSE-2010-Class-10th - Acids-Bases-Salts-CDocument5 pagesImportant-Question-ICSE-2010-Class-10th - Acids-Bases-Salts-CYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Changes - Important Qs - Important Questions - ICSEDocument1 pageChemical Reactions and Changes - Important Qs - Important Questions - ICSEYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- 9 Oct Neet 1 Year Test - Complete Haloalkanes (Substitution and Elimination)Document7 pages9 Oct Neet 1 Year Test - Complete Haloalkanes (Substitution and Elimination)Yash KapoorNo ratings yet
- 9 Oct Neet 1 Year Test - Complete Haloalkanes (Substitution and Elimination)Document7 pages9 Oct Neet 1 Year Test - Complete Haloalkanes (Substitution and Elimination)Yash KapoorNo ratings yet
- 9 Oct Jee Mains 1 Year Test - Complete Haloalkanes (Substitution and Elimination)Document7 pages9 Oct Jee Mains 1 Year Test - Complete Haloalkanes (Substitution and Elimination)Yash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Gravitation 50 Questions 09-10-23Document9 pagesGravitation 50 Questions 09-10-23Yash KapoorNo ratings yet
- NEET TEST - Microbes in Human WelfareDocument8 pagesNEET TEST - Microbes in Human WelfareYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Neet Test - Ray - Optics - 06 10 23Document6 pagesNeet Test - Ray - Optics - 06 10 23Yash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases Salts Assignmnet 4 Basic Assignmnet 10thDocument3 pagesAcids Bases Salts Assignmnet 4 Basic Assignmnet 10thYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Neet Iv-Test Body Fluids and CirculationDocument8 pagesNeet Iv-Test Body Fluids and CirculationYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Weekly Test - JEE 2 Year Prog - 4 JuneDocument12 pagesWeekly Test - JEE 2 Year Prog - 4 JuneYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- ICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Exercise QuestionsDocument16 pagesICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 8 Exercise QuestionsYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry LaboratoryDocument56 pagesChemistry LaboratoryYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Leaf Optical PropertiesDocument23 pagesLeaf Optical PropertiesLídia SilvaNo ratings yet
- C3 PPT Anil Sir ProjectDocument40 pagesC3 PPT Anil Sir ProjectNarasimha Murthy S VNo ratings yet
- Vanilla Book 1Document14 pagesVanilla Book 1Richard Andrew ParedesNo ratings yet
- Downy Mildew of CrucifersDocument5 pagesDowny Mildew of Crucifersbinthunder100% (1)
- BIOLAB Plant Hormones Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesBIOLAB Plant Hormones Exercise PDFRaphael MontierroNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science (EVS) - Worksheet: Subject: Plants Class: 2Document4 pagesEnvironmental Science (EVS) - Worksheet: Subject: Plants Class: 2KusumaLathaNo ratings yet
- Complete Botany 111Document44 pagesComplete Botany 111Sukriti BaniyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3/Class-XI/Biology: Plant KingdomDocument6 pagesChapter-3/Class-XI/Biology: Plant KingdomraghavNo ratings yet
- Mongo Grown in The Shaded AreaDocument1 pageMongo Grown in The Shaded Areazhaicke zhaickerNo ratings yet
- Senescence Dan Absisi Lia MociDocument19 pagesSenescence Dan Absisi Lia MociNahla FaridaNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity I Lab 5: Nonvascular Plants Mosses & LiverwortsDocument27 pagesPlant Diversity I Lab 5: Nonvascular Plants Mosses & LiverwortsCaleb Thomas-AlexisNo ratings yet
- Bio 400 Lab 4Document11 pagesBio 400 Lab 4Aqilah AzmanNo ratings yet
- Doc14848765 636145787Document14 pagesDoc14848765 636145787Asal BR100% (1)
- Lecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)Document9 pagesLecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)maheen akramNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1 Seed MorphologicalDocument17 pagesLaboratory 1 Seed MorphologicalJohn Rey De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Propagation of Walnut - A Review PDFDocument22 pagesIn Vitro Propagation of Walnut - A Review PDFDoru OlarNo ratings yet
- A. Cyperus Rotundus B. Fimbristylis Littoralis C. Pistia Stratiotes D. Paspalum DistichumDocument48 pagesA. Cyperus Rotundus B. Fimbristylis Littoralis C. Pistia Stratiotes D. Paspalum Distichumshakira0% (1)
- Xi. Biology. Revision Work.-Ch.3,4,&5. 3. Plant Kingdom. 1.what Do You Mean by ? 3.why Is Algae Grouped Under Thllophyta? 4. Write TheDocument2 pagesXi. Biology. Revision Work.-Ch.3,4,&5. 3. Plant Kingdom. 1.what Do You Mean by ? 3.why Is Algae Grouped Under Thllophyta? 4. Write TheOwasisNo ratings yet
- 12th Bio Botany Important Questions English MediumDocument7 pages12th Bio Botany Important Questions English MediumMohammed FahadNo ratings yet
- Sacoila Reprint1Document22 pagesSacoila Reprint1DennisNo ratings yet
- Bragrisc - Plant Morphology and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesBragrisc - Plant Morphology and PhysiologyRica MarcialNo ratings yet
- Nama LatinDocument5 pagesNama Latinnia umniaNo ratings yet
- 01 The Living World, Biological Classification, Plant Kingdom 19 JuneDocument4 pages01 The Living World, Biological Classification, Plant Kingdom 19 JuneUV JANGRA100% (1)
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 4 Monocot and DicotDocument9 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 4 Monocot and DicotAngelica Fernandez Resabal Acot86% (7)
- The Concept MapDocument1 pageThe Concept MapTrisha Claire Gio BaylosisNo ratings yet
- Know PlantsDocument7 pagesKnow PlantshitosnapNo ratings yet
- Connec Tions: Joseph RosenbergDocument40 pagesConnec Tions: Joseph RosenbergMarc Angelo DavidNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: Chapter - 09Document15 pagesTransport in Plants: Chapter - 09Raichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Name - Roll No.Document44 pagesWorksheet: Name - Roll No.skNo ratings yet
- Common Weeds in Oil Palm PlantationDocument8 pagesCommon Weeds in Oil Palm Plantationalanzo8988% (17)