Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHD211 Plaster and Patches
Uploaded by
2022823764Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PHD211 Plaster and Patches
Uploaded by
2022823764Copyright:
Available Formats
PHD211
PLASTER AND PATCHES
INTRODUCTION
In medicine, plasters and patches have numerous of therapeutic uses
and purposes. It can be classified into two types which is medicated
and also unmedicated.
Medicated plaster and patches are known for their transdermal drug
delivery over an extended period of time. While unmedicated
plasters and patches are used to provide protection and
support to the affected area without addition of
any active ingredient.
It also come in various shapes, sizes and materials.
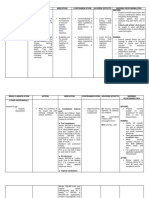
TYPES OF MEDICAL PLASTER
AND PATCHES
Common types of medical plaster and patches:
Waterproof: used for wound dressing and protection
Hydrocolloid: has soothing properties, used for blisters and burn
Nicotine: help in smoking cessation
Hormonal: used for hormonal replacement/imbalance therapy
Pain reliever: used to relieve pain
PROPERTIES COMMON USED ACTIVE
PHARMACEUTICAL
ADHESIVE INGREDIENTS (API)
Three fundamental attributes of
patch adhesion:
MENTHOL &
the ability to quickly METHYL SALICYLATE
adhere to all types of skin
Tack cause the skin to feel cool then warm,
with light pressure upon
so the feeling of pain is distracted
initial contact.
crucial for the patch to
stay strongly attached to NICOTINE
Shear the skin despite factors
like body movements and for the relief of nicotine withdrawal
rubbing symptoms
important for the patch to
be easily removable FENTANYL
Peel without causing trauma to
the skin or leaving for the relief of pain of any part of
excessive residue. the body
more efficient drug SALICYLIC ACID
THIN
delivery and higher
bioavailability help to reduce inflammation on skin
ensure proper and
FLEXIBLE ESTROGEN
comfortable fit
usually used in hormonal replacement
therapy or any hormonal imbalance
HYPOALLERGENIC treatment
minimize risk of skin irritation,
redness, or allergic reactions.
SCOPOLAMINE
contain anti-nausea substance used to
EXAMPLES prevent or reduces nausea
IN MARKET
EXCIPIENTS
HANSAPLAST NEXCARE
WATERPROOF HYDROCOLLOID
PLASTER PATCHES
Membrane and
Anti-adhesive
skeleton material
used for the
polymeric material is protection of the
selected and used. eg, adhesive layer
polyglycolic acid.
KENHANCER
NICORETTE
KETOPROFEN Pressure-sensitive
PLASTER
NICOTINE PATCHES Drug reservoir
adhesive
a single material or a
can be adhered under
paste, ointment,
slight pressure and can
hydrogel, suspension,
be easily peeled off.
or solution.
Transdermal Backing
enhancer material
NEOBUN EVRA HORMONAL
MEDICATED PATCHES increase the speed of support the drug
drug transdermally. library or pressure-
PLASTER
sensitive adhesive
PACKAGING AND STORAGE
Store in a cool place
Store below 30°C
Individual Sealed foil
sachets wrappers Keep away from children
Avoid placing plasters
and patches near
chemicals, solvents, or
Resealable Multi-plaster strong odors
pouches carton
ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
IF FAILS TO SUIT THE SKIN,
DISCREET AND EASY TO USE
THE IRRITATION CONTINUES
CAN BE CUT TO THE EXACT SIZE NEEDED DESIGNED TO BE USED ONLY ONCE AND
TO FIT THE AREA THAT HAS BEEN CANNOT BE REUSED.
AFFECTED
PRESCRIPTION PATCHES MAY COST MORE
ONE APPLICATION PROVIDES CONTINUOUS
THAN OVER-THE-COUNTER ORAL PAIN
DRUG DELIVERY IMPROVING COMPLIANCE
RELIEVERS.
EXTRA WARMING AND COOLING AGENTS, SWEAT OR WATER-RELATED ACTIVITIES
SUCH AS MENTHOL MIGHT CAUSE PATCHES TO LOOSEN.
LOSE THEIR USEFULNESS WHEN
NO PUNGENT ODOUR
MEDICATIONS ARE EXPIRED.
References: https://www.mybib.com/b/WYaxl2
Annissa Nur Dania ⟡ Nursyaidatul Irdina ⟡ Nurul Farahiyah Fathiah
REFERENCES
A guide to different types of plasters and when to use them.
(n.d.). First Aid Warehouse.
https://www.firstaidwarehouse.co.uk/blogs/news/a-guide-
to-different-types-of-plasters-and-when-to-use-them
Advantages and Disadvantages of Arthritis Drug Pain Relief
Patches. (n.d.). Www.kongdycn.com. Retrieved January 1,
2024, from https://www.kongdycn.com/news/Advantages-
and-Disadvantages-of-Arthritis-Drug-Pain-Relief-
Patches.html
All types of plaster. (n.d.). Dr. Yash Shah.
https://puneortho.com/all-types-of-plaster/
An In-Depth Guide to Transdermal Patches. (n.d.). Tapemark.
https://www.tapemark.com/transdermal-patches
Charman, H. (2022, January 18). Different Types of Medical
Plasters | Morsafe UK. Morsafe.
https://www.morsafesupplies.com/2022/01/18/different-
types-of-medical-plasters/
Different Types of Medical Plasters: A Comprehensive Guide |
Molloys Pharmacy | Ireland. (n.d.). Www.molloyspharmacy.com.
https://www.molloyspharmacy.com/c/different-types-of-
medical-plasters-a-comprehensive-guide-/1444
DRUGBANK. (2023). Nicotine. Go.drugbank.com.
https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00184
Excipients for Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems Materials
- CD Formulation. (n.d.). Www.formulationbio.com.
https://www.formulationbio.com/products/transdermal-
drug-delivery-systems-materials.html
House, L. K. (n.d.). What are Transdermal Patches and their
Different Types? Www.strouse.com.
https://www.strouse.com/blog/what-are-transdermal-
patches-types
Iliopoulos, F., Sil, B. C., & Evans, C. L. (2022). The role of
excipients in promoting topical and transdermal delivery:
Current limitations and future perspectives. Frontiers in Drug
Delivery, 2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fddev.2022.1049848
Kenhancer Plaster. (2024). Mims.com.
https://www.mims.com/malaysia/drug/info/kenhancer%20plas
ter
Kolter, K. D., & Rieker, A. D. (n.d.). Plaster for transdermal
administration. Retrieved January 9, 2024, from
https://patents.google.com/patent/EP0380989A2/en
Kummer, A., Wasner, M., & Wuestling, J.-U. (n.d.). Skin friendly
active ingredient plaster based on sbc, containing at least 34
wt % of a pharmaceutical active ingredient and production
thereof. Retrieved January 9, 2024, from
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2004019919A1/en
Methyl Salicylate-Menthol Topical: Uses, Side Effects,
Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing - WebMD. (n.d.).
Www.webmd.com. Retrieved January 1, 2024, from
https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-18536-2113/methyl-
salicylate-menthol-topical/methyl-salicylate-menthol-patch-
topical/details
Nalamachu, S., & Gudin, J. (2020). Characteristics of Analgesic
Patch Formulations. Journal of Pain Research, Volume 13,
2343–2354. https://doi.org/10.2147/jpr.s270169
NICORETTE® Invisi Transdermal Patch. (n.d.). NICORETTE®.
https://www.nicorette.com.my/products/invisipatch
Plasters: Types, Formulation, Advantages, Disadvantages.
(2023, February 17). PharMSkooL.
https://www.pharmskool.com/2023/02/plasters-types-
formulation-advantages-disadvantages.html
Salonpas Pain Relieving Patch topical Uses, Side Effects &
Warnings. (n.d.). Drugs.com. Retrieved January 7, 2024, from
https://www.drugs.com/mtm/salonpas-pain-relieving-patch-
topical.html
Versatis 700mg Medicated Plaster - Patient Information
Leaflet (PIL) - (emc). (n.d.). Www.medicines.org.uk.
https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/290/pil#gref
Weishaupt, J. (2023, May 8). What Are Hydrocolloid Patches
for Pimples? WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/skin-
problems-and-treatments/acne/what-are-hydrocolloid-
patches-for-pimples
LIST OF ROLES
ANNISSA NUR DANIA BINTI NOR HELME
in charged in searching information about:
1. PROPERTIES
2. PACKAGING AND STORAGE
3. REFERENCES
NURSYAIDATUL IRDINA BINTI ERWAN in
charged in searching information about:
1. INTRODUCTION
2. TYPES OF PLASTER AND PATCHES
3. LIST OF ROLES
and also designing the infographic
NURUL FARAHIYAH FATHIAH BINTI
ABDUL MANAF in charged in searching
information about:
1. ACTIVE PHARMACEUTICAL
INGRIDIENTS
2. EXCIPIENTS
3. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
4. EXAMPLE IN THE MARKET
PHD211 A+
You might also like
- PESTEL Analysis of MoroccoDocument2 pagesPESTEL Analysis of Moroccoethernalx67% (15)
- Devitec 11402Document1 pageDevitec 11402Shkelzen KomoniNo ratings yet
- Blues CheatDocument77 pagesBlues CheatRobbie ChambersNo ratings yet
- Ointments: Chemical Properties Physical PropertiesDocument3 pagesOintments: Chemical Properties Physical PropertiesYunoNo ratings yet
- Dosage Lab Activity 2 PDFDocument4 pagesDosage Lab Activity 2 PDFsybyl formenteraNo ratings yet
- Pharmmanuf. Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsDocument2 pagesPharmmanuf. Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsDenzyl Ann LaguitNo ratings yet
- A Review On Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films: (Reg. No. 14421S0303)Document23 pagesA Review On Fast Dissolving Oral Thin Films: (Reg. No. 14421S0303)SiriNo ratings yet
- TabletDocument80 pagesTabletParizal Very100% (4)
- LynalDocument2 pagesLynalmarianamejiarpoNo ratings yet
- Drug PhenytoinDocument11 pagesDrug PhenytoinSalmanNo ratings yet
- Suppository, Insert & StickDocument3 pagesSuppository, Insert & StickCorina Faye RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chemical ProductDocument20 pagesChemical ProductShNo ratings yet
- N.C. Thinner 113: General Description: PropertiesDocument1 pageN.C. Thinner 113: General Description: PropertiesAMIT HALDERNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug DeliveryDocument38 pagesTransdermal Drug DeliveryJhansi SattiNo ratings yet
- 426 Prism Black Max GelDocument6 pages426 Prism Black Max Gellorejaz84071127No ratings yet
- Lynal: Tissue Conditioner & Temporary RelinerDocument2 pagesLynal: Tissue Conditioner & Temporary RelinerGonzalo Urrutia ElsoNo ratings yet
- Dispersed System 1Document9 pagesDispersed System 1Chantelle MeaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Analgesia in Paediatric Population Part 2 Pharmacological Metholds of Pain ReliefDocument5 pagesEmergency Analgesia in Paediatric Population Part 2 Pharmacological Metholds of Pain Relieffuka priesleyNo ratings yet
- Semi-Solid Applications 101Document1 pageSemi-Solid Applications 101CHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- Ubber Hemicals: Flexzone 4L Antioxidant / AntiozonantDocument1 pageUbber Hemicals: Flexzone 4L Antioxidant / AntiozonantMarcos ROSSINo ratings yet
- Neoretin Ultra EmulsioDocument2 pagesNeoretin Ultra EmulsioEaH321XNo ratings yet
- Cream: Light Liquid Paraffin White Soft ParaffinDocument2 pagesCream: Light Liquid Paraffin White Soft ParaffinAshraf AlbhlaNo ratings yet
- Semi Solids FinalDocument41 pagesSemi Solids FinalLalitha Sravani100% (1)
- Seal N Flex Advance Labels 300ml FinalDocument4 pagesSeal N Flex Advance Labels 300ml Finalumer ChNo ratings yet
- 7m150-Tds-Ebecryl IbomaDocument1 page7m150-Tds-Ebecryl Ibomashahin774No ratings yet
- Surgical DressingDocument60 pagesSurgical DressingJeffri syaputraNo ratings yet
- Laxo HandDocument3 pagesLaxo HandAimon JahangirNo ratings yet
- Opthalmic Preparations Unit III Part-BDocument37 pagesOpthalmic Preparations Unit III Part-BKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sterile Products & ParenteralsDocument41 pagesSterile Products & ParenteralsRonit PoudelNo ratings yet
- Pds-Solvalux 5-30 ClearDocument1 pagePds-Solvalux 5-30 ClearvitharvanNo ratings yet
- Modern Wound Dressing - pptx-1Document32 pagesModern Wound Dressing - pptx-1puvi.mayor2104No ratings yet
- Adesivo 5181h LoctiteDocument6 pagesAdesivo 5181h LoctiteDiego S. FreitasNo ratings yet
- AntiSkin BDocument3 pagesAntiSkin BLê TiếnNo ratings yet
- Dosage Chapter 7Document6 pagesDosage Chapter 7Lena EmataNo ratings yet
- Product and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesProduct and Company Identification: Safety Data Sheetrafael_figueroa100% (1)
- Product and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesProduct and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetNikolay ZhelunicinNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Antifungal Agent BeforeDocument4 pagesDrug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Antifungal Agent BeforeElizabeth Ivory ChuaNo ratings yet
- Suppositories Vaginal Suppositories: Dosage FormsDocument5 pagesSuppositories Vaginal Suppositories: Dosage FormsRye M. BirungNo ratings yet
- Dosage - Chapter 7Document6 pagesDosage - Chapter 7Kim ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Safety Advice Sheet: Product Name: Interfine 979 Ref No: 0006Document1 pageSafety Advice Sheet: Product Name: Interfine 979 Ref No: 0006Mohamed NouzerNo ratings yet
- Clearing: Pre-Finals DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesClearing: Pre-Finals DisadvantagesIsah SittiNo ratings yet
- Pharm Chem 1 Lec PF Unit Vii - Topical Agents 092015Document6 pagesPharm Chem 1 Lec PF Unit Vii - Topical Agents 092015davenNo ratings yet
- Pil 378Document1 pagePil 378njaydopeNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System: Shirode Rahul ADocument37 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System: Shirode Rahul AFrancisco MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Product and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesProduct and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetYandell ACNo ratings yet
- Poonam PPT FinalDocument15 pagesPoonam PPT Finalpooam_rktNo ratings yet
- AU - DW02829 Intergrain Universal Timber Oil: DescriptionDocument4 pagesAU - DW02829 Intergrain Universal Timber Oil: DescriptioninezNo ratings yet
- Operating Techniques (Doc. Pascua) : ContraindicatedDocument5 pagesOperating Techniques (Doc. Pascua) : Contraindicatedjeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- Suppositories: Presented byDocument21 pagesSuppositories: Presented byVanessa PatraoNo ratings yet
- Eyes OutlineDocument7 pagesEyes OutlineNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Poster ThivyaDocument1 pagePoster ThivyaThivya ShankariNo ratings yet
- Ointments:: DefinitionDocument2 pagesOintments:: DefinitionJibran NaeemNo ratings yet
- Product and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesProduct and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetBonkNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Preparation and Evaluation of Cold CreamDocument7 pagesPharmaceutical Preparation and Evaluation of Cold CreamInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ointments: Prodi Farmasi Universitas MalahayatiDocument35 pagesOintments: Prodi Farmasi Universitas MalahayatiAulia Fitri Handayani SiregarNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Nursing PracticeDocument23 pagesFundamental Nursing PracticeChristine MagbataNo ratings yet
- Lotion Foam Soap With Moisturisers: Safety Data SheetDocument3 pagesLotion Foam Soap With Moisturisers: Safety Data SheetIgoriok911_105921426No ratings yet
- Semi Solids FinalDocument27 pagesSemi Solids FinalAubrey Monette Padilla-ItchonNo ratings yet
- Thicken ErDocument3 pagesThicken ErErnesto Vicuña IslasNo ratings yet
- Thicken ErDocument3 pagesThicken ErAmr RagabNo ratings yet
- ThickenerDocument3 pagesThickenerErnesto Vicuña IslasNo ratings yet
- Penjelasan IMRAD StructureDocument2 pagesPenjelasan IMRAD Structureaji bondesNo ratings yet
- Inter-Bank Fund Transfer: Case Study 6Document5 pagesInter-Bank Fund Transfer: Case Study 6Ravi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Boss DD-6Document28 pagesBoss DD-6Justin Alexander SanzonENo ratings yet
- Ccie DC Full Scale Labs PDFDocument185 pagesCcie DC Full Scale Labs PDFnaveedrana100% (2)
- History of Operating SystemDocument16 pagesHistory of Operating SystemBryan John BerzabalNo ratings yet
- (R) Nelson JB (2017) - Mindful Eating - The Art of Presence While You EatDocument4 pages(R) Nelson JB (2017) - Mindful Eating - The Art of Presence While You EatAnonymous CuPAgQQNo ratings yet
- Geologic Report Arches NationalDocument9 pagesGeologic Report Arches NationalJacob AndersonNo ratings yet
- Economic GrowthDocument15 pagesEconomic GrowthANJULI AGARWALNo ratings yet
- 1908 The Watchower and Herald of Christ's PresenceDocument193 pages1908 The Watchower and Herald of Christ's PresenceTimothy RichesNo ratings yet
- ExcaDrill 45A DF560L DatasheetDocument2 pagesExcaDrill 45A DF560L DatasheetИгорь ИвановNo ratings yet
- 900 MCQs Ancient IndiaDocument189 pages900 MCQs Ancient IndiaZahaab AlimNo ratings yet
- Billy Mitchel: The Fundamental Principles of Modern Monetary Economics (MMT/PDF)Document6 pagesBilly Mitchel: The Fundamental Principles of Modern Monetary Economics (MMT/PDF)mrwonkish100% (1)
- Kitimat JRP SummaryDocument17 pagesKitimat JRP SummaryNorthwest InstituteNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Rizal Morga Lifestyle: LifestyleDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Rizal Morga Lifestyle: LifestyleMarjorie GawalaNo ratings yet
- SDS - Molykote 1000Document8 pagesSDS - Molykote 1000Zarni KyawNo ratings yet
- Artificial RainfallDocument20 pagesArtificial Rainfallsurajsingh100% (3)
- PGCC 2022 HandbookDocument17 pagesPGCC 2022 HandbookhasnainNo ratings yet
- 805-Article Text-3656-1-10-20220310Document16 pages805-Article Text-3656-1-10-20220310abolfazlshamsNo ratings yet
- Free LinkDocument40 pagesFree LinkiguinhocoelhaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Identifying Author's Bias For or Against: Quarter 3 Wk-1Document4 pagesLesson: Identifying Author's Bias For or Against: Quarter 3 Wk-1Mary Cris Navarro LiboonNo ratings yet
- English Slide Un SMK 1819Document93 pagesEnglish Slide Un SMK 1819EkhaSoemarnoNo ratings yet
- FCo Research Report Debit Card and Bitcoin in MenaDocument10 pagesFCo Research Report Debit Card and Bitcoin in MenaJhimy JeanNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Series 7Document44 pagesUser Manual: Series 7Roniel ManjaresNo ratings yet
- Analogy - 10 Page - 01 PDFDocument10 pagesAnalogy - 10 Page - 01 PDFrifathasan13No ratings yet
- Economics Key WordsDocument30 pagesEconomics Key WordsJanetNo ratings yet
- TranscriptDocument1 pageTranscriptGursharanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Sow English Year 2 2023Document12 pagesSow English Year 2 2023Noramaliza GhazaliNo ratings yet