Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Purpose CIS Checklist
Uploaded by
mian UmairOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Purpose CIS Checklist
Uploaded by
mian UmairCopyright:
Available Formats
`
General Purpose CIS Checklist
Client Name: MUHAMMADI GAS COMPANY (PRIVATE) LIMITED
Period: 30 June 2021
Name Date:
Prepared by: M Usman
Reviewed by:
Approved by:: Waqar Nadeem
Computer Information Systems (CIS)
Business processes are often facilitated by computer information systems. Obtain an understanding
of the:
Level of dependence the client has on computer information systems (include a list of the
client’s computer information systems);
Computer information systems’ personnel structure and skills
Security of computer information systems; Access Controls, Backups, Disaster Recovery.
Reliability of computer information systems; Data Integrity, Processing, and Reporting
Controls.
Degree and rate of change in computer information systems;
Dependence on external computer processing; Use of Service, Organization understanding
and evaluation thereof.
The entity totally depends on CIS, Sidat Hyder Financials is the main software used by the entity
for recording and processing its day to day transactions. The entity has placed very strict controls
over its CIS which include passwords, access to authorized personnel only etc. The company also
has an effective data backup plan. According to our assessment no issues were identified regarding
data integrity, processing and reporting controls. The entity does not depend on external computer
processing.
Organization and Management Policies Objective Summary of findings
Satisfied
MUNIFF ZIAUDDIN & CO. CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
1
A MEMBER FIRM OF BKR INTERNATIONAL
1. To ensure that organizational policies and
management procedures are in place to
enable Y/N
the IT function to be properly controlled.
Yes No
IT Strategy
1.1 Is there a formal documented plan for IT
covering systems to be developed or
enhanced over the next 1 - 3 years?
1.2 Is there an IT Steering Committee?
Consider
Other, less formal, means of
establishing and communicating IT strategy
User management representation
IT Policies and Procedures
1.3 Are there formal and comprehensive IT
Policies and Procedures relating to Information
Security, User Access Management, Program
Change Management, Backup Management,
Password Management etc?
Consider
Approval at board level
Objectives
Scope and coverage
Responsibility for monitoring or update
Distribution to staff
Role of Internal Audit
1.4 Is internal audit department involved in
review of IT controls.
Consider the following:
Competence of audit personnel
Frequency of review
Matters raised in such reviews and its
Implication on audit.
IT Security Function
1.5 Is there a formal IT Security function in the
organization
Consider
Roles and responsibilities
Reporting lines (Independent of IT)
Security awareness trainings
Control Consciousness
1.6 Is the attitude of management and the
structure of the organisation conducive to control
consciousness?
Objective
Satisfied Summary
b) Segregation of Duties Y/N of findings
MUNIFF ZIAUDDIN & CO. CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
2
A MEMBER FIRM OF BKR INTERNATIONAL
To ensure there is reasonable
segregation of duties for staff, both
within the IT department and between
the IT and user functions, to prevent
and/or detect errors or irregularities.
Yes No
Comments / WP Ref.
2.1 Is there an organisation chart for the IT
department?
(Obtain a copy and review it)
2.2 Is segregation of duties within the IT
department appropriate for the size of the
organisation?
Consider
Segregation of functions e.g.
Number of IT staff
Systems programmers
Application programmers
Database administrator
IT operations
Data input
Network security
Reliance on key personnel
Reliance on contract staff
2.3 Do IT staff only have responsibilities for
functions within the IT department?
Consider
Responsibility for initiating or authorising
transactions
Amendments to master files
Correction of input errors
Objective
Satisfied Summary
(c) Logical Access Controls Y/N of findings
3. To ensure that unauthorised access
cannot be gained to sensitive data or
programs.
Yes No
Comments / WP Ref.
3.1 Have sensitive data or applications been
identified?
3.2 Have appropriate security measures been
implemented to restrict users' access to
data and programs?
Consider
User-id and passwords
Menu facilities
Management approval of menu options
Periodic review of appropriateness of access
rights
Review of security logs
MUNIFF ZIAUDDIN & CO. CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
3
A MEMBER FIRM OF BKR INTERNATIONAL
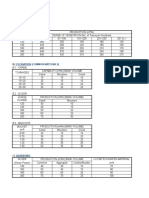
3.3 Check from the system controls relating to
passwords:
password length (e.g. 6 characters).
Password composition (e.g.alphanumeric)
Password change interval (e.g. 90days)
Account lockout (e.g. 3 invalid attempts)
Password history (e.g 5 password
remembered)
Force password change on first login
Session time out (e.g 10 min of inactivity)
Concurrent sessions allowed
3.4 Are system development staff prevented
from accessing data and software in the
live environment?
Consider
Segregation of live and test environments
Procedures for emergency changes eg
documentation
review
3.5 Is the allocation, authorization and use of
powerful user-ids (e.g. system
Administrator, database administrator etc.)
or passwords controlled and monitored?
(Note to whom these user ids are assigned)
Objective Summary
Satisfied of findings
(d) Physical Access Controls Y/N
4. To ensure that the risk of accidental or
Malicious damage to, or theft of, computer
equipment or media is minimized.
Yes No
Comments / WP Ref.
4.1 Is there adequate physical security over
computer equipment, data, media and
documentation?
Consider
Buildings (including the protection of
terminals)
Server room
Communications equipment
Fire proof storage for magnetic media
Fire prevention or detection
Off-site storage
(e) Systems Development and Program Objective
Change Controls Satisfied
Y/N Summary of findings
5. To ensure that systems development and
program changes are authorized tested,
MUNIFF ZIAUDDIN & CO. CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
4
A MEMBER FIRM OF BKR INTERNATIONAL
documented and operate as designed.
Yes No
Comments / WP Ref.
5.1 In-house developments
For in-house developed systems, is there a
formal methodology?
Consider
Formal software development methodology
adopted
Internal procedures developed by the systems
development team No In-house software is
Prototype software developed by the
Programming standards followed company
5.2 Packages
Is the business dependent on externally
supplied and maintained application
Systems?
Consider:
Maintenance agreement with the supplier
Changes and upgrades checked and
tested before installation
Source code provided
Measures to prevent unauthorised access to the
software
If the software is owned by the supplier, is
there an escrow agreement?
5.3 Are users appropriately involved in the
systems development process?
Consider
Specification of requirements
Contribution to priority setting
User sign offs
User acceptance testing
Training
Formal approval before implementation
Development of user manuals etc.
5.4 Are development staff restricted from
implementing new program versions into the
production environment?
5.5 Is comprehensive systems and program
documentation produced?
Consider
Compliance with standards
System documentation
Operating instructions
User documentation
5.6 Are there program change control
procedures?
Consider
MUNIFF ZIAUDDIN & CO. CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
5
A MEMBER FIRM OF BKR INTERNATIONAL
Program change documentation
Management authorization
Test procedures
User involvement in authorizing and testing
Objective
f) Business Continuity and Computer Satisfied Summary
Operations Y/N of findings
Yes No
Comments / WP Ref.
Back Up Procedures
6.1 Are back up copies of data files and
programs taken regularly? (Note the back up
cycle)
Consider
Data at end of day, week, month, year
Whether back up taken after changes in the
application
6.2 Are back up copies held in a secure
location remote from the computer site?
Consider
Data files
Programs
Systems software
Systems documentation
Operating procedures
User procedures
Disaster Recovery Plan
6.3 Are back up versions taken offsite regularly?
6.4 Have the back up and restoration procedures
been tested?
Consider
Time taken to restore
Completeness and accuracy of data restored
Disaster Recovery Planning
6.5 Have the business's critical systems, without
which the entity’s operations and business could
be affected, have been identified?
Consider
How long could the business operate
effectively without their critical computer
systems?
eg. hours, < 7 days, etc.
6.6 Has a disaster recovery plan been developed,
documented and tested?
Consider
Regular review and update of the
plan (Note when it was last updated)
Periodic testing
MUNIFF ZIAUDDIN & CO. CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
6
A MEMBER FIRM OF BKR INTERNATIONAL
(Note when last tested)
Insurance
6.7 Does the organisation have adequate
insurance cover relating to its IT risks?
Consider
Loss of computer equipment and data
Consequential loss
Additional cost of working
Denial of access
Exclusion clauses
Objective
(g) User Management e.g. Finance Director Satisfied Summary
/ Financial Controller / Chief Accountant Y/N of findings
7. To ensure that IT systems satisfy the
business needs.
7.1 Are users satisfied with the critical
accounting systems?
Consider
Management information
Timeliness of reporting
User friendliness
Response times
7.2 Are the systems stable?
Consider
Few modifications since, say, six months
before the start of the
accounting period
New systems planned
OVERALL CONCLUSION
Summarize the internal control weaknesses identified during our review which have an impact on the
control objectives, for consideration when planning reliance on CIS controls.
The company is currently using ready-made software (SidatHyder Financials). It is reliable software and
according to our enquiries and procedures performed, there were no major weaknesses identified in
company’s IT controls. Hence we can rely on entity’s IT controls in performing our audit.
MUNIFF ZIAUDDIN & CO. CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
7
A MEMBER FIRM OF BKR INTERNATIONAL
You might also like
- Template 23 Assessing General IT Controls and Application ControlsDocument12 pagesTemplate 23 Assessing General IT Controls and Application ControlsGreen TayengwaNo ratings yet
- 02 - AFA - PPT - Unit 5Document38 pages02 - AFA - PPT - Unit 5tfknrNo ratings yet
- IT ChecklistDocument127 pagesIT ChecklistANILNo ratings yet
- Update Intro To IT Audit Support v4Document41 pagesUpdate Intro To IT Audit Support v4Handayani Tri WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument15 pagesInformation Technologyabebe kumelaNo ratings yet
- Topic Security Issue Response: Roles & ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesTopic Security Issue Response: Roles & ResponsibilitiesAnton BriliawanNo ratings yet
- Section 302 Section 404: 1. Organizational Structure ControlDocument6 pagesSection 302 Section 404: 1. Organizational Structure Controlfathma azzahroNo ratings yet
- P: C IT D: Andemics Onsiderations For IsruptionsDocument2 pagesP: C IT D: Andemics Onsiderations For IsruptionsziftikharNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Internal Auditing Assurance and Consulting Services 2nd Edition by RedingDocument13 pagesSolution Manual For Internal Auditing Assurance and Consulting Services 2nd Edition by RedingJosephWilliamsjfyae100% (85)
- TOPIC 6 - Implication of IT On IADocument38 pagesTOPIC 6 - Implication of IT On IAHanis ZahiraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - Internal Audit Tools and Techniques 2019Document41 pagesCHAPTER 8 - Internal Audit Tools and Techniques 2019NORAZIAN HUSSINNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - Internal Audit Tools and Techniques STDTDocument39 pagesCHAPTER 8 - Internal Audit Tools and Techniques STDTNor Syahra AjinimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Illustrative Solutions PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 7 Illustrative Solutions PDFNaeemNo ratings yet
- GMP Checklist For DI AuditDocument4 pagesGMP Checklist For DI Auditshri_palaniNo ratings yet
- Mwaa Security Assessment Questionnaire: Topic Security Issue ResponseDocument4 pagesMwaa Security Assessment Questionnaire: Topic Security Issue ResponseAdil Raza SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Auditing in CIS EnvironmentBIT006WFAsystemssecurityDocument28 pagesAuditing in CIS EnvironmentBIT006WFAsystemssecurityJohn David Alfred EndicoNo ratings yet
- Auditing in CIS Environment DISCUSSION16Document5 pagesAuditing in CIS Environment DISCUSSION16Yo Han SongNo ratings yet
- MGT422Document8 pagesMGT422Uzair FarooqNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Auditing IT Governance ControlsDocument63 pagesLecture 2 Auditing IT Governance ControlsAldwin CalambaNo ratings yet
- 33254ipcc Paper7A PM Rev 2Document20 pages33254ipcc Paper7A PM Rev 2Piyush GambaniNo ratings yet
- Auditing IT Governance ControlsDocument55 pagesAuditing IT Governance ControlsLouella Vea HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Auditing IT Governance ControlsDocument63 pagesLecture 2 - Auditing IT Governance ControlsLei CasipleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Auditing It Governance ControlsDocument54 pagesChapter 2 Auditing It Governance ControlsMary Joy AlbandiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On IS AuditDocument6 pagesAssignment On IS AuditRakibul IslamNo ratings yet
- It AuditDocument15 pagesIt AuditaleeshatenetNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Computer Assisted Audit Technique and Cobit FrameworkDocument37 pagesUnit Iv Computer Assisted Audit Technique and Cobit Frameworkhot reddragon1123No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 7 QuizFitri-ssiNo ratings yet
- Ffiec Itworkprogram InformationsecurityDocument22 pagesFfiec Itworkprogram InformationsecurityfreakyneoNo ratings yet
- Best Practices Guide For IT Governance & ComplianceDocument14 pagesBest Practices Guide For IT Governance & ComplianceAnonymous 2WKRBqFlfNo ratings yet
- Supplier Security Assessment QuestionnaireDocument9 pagesSupplier Security Assessment QuestionnaireAhmed M. SOUISSI100% (1)
- Information Systems and IT Fundamentals: 2.2.1 Communication CapabilitiesDocument26 pagesInformation Systems and IT Fundamentals: 2.2.1 Communication Capabilitiesrakesh adamalaNo ratings yet
- Auditing IT Governance ControlsDocument44 pagesAuditing IT Governance ControlsEdemson NavalesNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning and Risk Assessment in A ComputerizedDocument6 pagesAudit Planning and Risk Assessment in A Computerizedalexissosing.cpaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Information Technology ItDocument63 pagesChapter 4 Information Technology It黄勇添No ratings yet
- Topic 10 - The Impact of IT On Audit ProcessDocument34 pagesTopic 10 - The Impact of IT On Audit Process2022930579No ratings yet
- Computer Base Information ControlDocument39 pagesComputer Base Information ControlAura MaghfiraNo ratings yet
- MU1 Module 7 NotesDocument48 pagesMU1 Module 7 NotesCGASTUFFNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 - Infomtion Assets Seccurity and Risk Presentation UpdatedDocument49 pagesTOPIC 3 - Infomtion Assets Seccurity and Risk Presentation UpdatedMulTechNo ratings yet
- IT Due Diligence QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesIT Due Diligence QuestionnaireSinh Trắc Vân Tay ENIXNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument11 pagesAuditingJabonJohnKennethNo ratings yet
- InfoSystemsAuditChecklist (Version 1)Document44 pagesInfoSystemsAuditChecklist (Version 1)Merrick Martin100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Upto MicsDocument49 pagesChapter 11 Upto MicsSuZan DhaMiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery Policy v1.0Document4 pagesDisaster Recovery Policy v1.0CSKNo ratings yet
- Cis - Lesson 4 Part 2Document6 pagesCis - Lesson 4 Part 2Terrence Grace EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 IscaDocument1 pageChapter-6 IscakishorejiNo ratings yet
- Management Information System MISDocument5 pagesManagement Information System MISSyeda hudaibiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction On Is AuditDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Introduction On Is AuditSteffany RoqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Auditing It Governance ControlsDocument36 pagesChapter 2: Auditing It Governance ControlsKino MarinayNo ratings yet
- Data Centre Operations Final V3Document11 pagesData Centre Operations Final V3anon_689537573No ratings yet
- ACCN 301 GROUP PRESENTATION-21 Nov 2022Document67 pagesACCN 301 GROUP PRESENTATION-21 Nov 2022Mcdonald MutsvangaNo ratings yet
- Ethics Fraud & Internal ControlwfaDocument26 pagesEthics Fraud & Internal ControlwfaRiviera MehsNo ratings yet
- Audit Management 2015 PDFDocument9 pagesAudit Management 2015 PDFRoni YunisNo ratings yet
- IT Governance Evaluation of Hotel Warehouse Section Using The COBIT 5 FrameworkDocument8 pagesIT Governance Evaluation of Hotel Warehouse Section Using The COBIT 5 FrameworkMonica WahyuningasriNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Information Security Program Maturity Assessment ToolDocument24 pagesISO27k Information Security Program Maturity Assessment ToolsashiNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument8 pagesAuditingJabonJohnKennethNo ratings yet
- RTM 1 - Kelompok 2 - Kelas XDocument17 pagesRTM 1 - Kelompok 2 - Kelas XDayatNo ratings yet
- Notes in Acctg 027 PrelimsDocument12 pagesNotes in Acctg 027 PrelimsJenny PadillaNo ratings yet
- CISA CH 4 ReviewDocument89 pagesCISA CH 4 ReviewjcantomNo ratings yet
- Student Assessment Tasks 520 FinalDocument23 pagesStudent Assessment Tasks 520 FinalYayo MirandaNo ratings yet
- Quickstart V. 1.1: A Setting of Damned Souls and Unearthly Horrors For 5 EditionDocument35 pagesQuickstart V. 1.1: A Setting of Damned Souls and Unearthly Horrors For 5 EditionÁdám Markó100% (2)
- Ppg-Gdch-Nur-45 Crash Cart Maintenance and ChecksDocument5 pagesPpg-Gdch-Nur-45 Crash Cart Maintenance and ChecksKenny JosefNo ratings yet
- SOW OutlineDocument3 pagesSOW Outlineapi-3697776100% (1)
- Financial Management: Usaid Bin Arshad BBA 182023Document10 pagesFinancial Management: Usaid Bin Arshad BBA 182023Usaid SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- 3-16-16 IndyCar Boston / Boston Grand Prix Meeting SlidesDocument30 pages3-16-16 IndyCar Boston / Boston Grand Prix Meeting SlidesThe Fort PointerNo ratings yet
- Homicide Act 1957 Section 1 - Abolition of "Constructive Malice"Document5 pagesHomicide Act 1957 Section 1 - Abolition of "Constructive Malice"Fowzia KaraniNo ratings yet
- Names of PartnerDocument7 pagesNames of PartnerDana-Zaza BajicNo ratings yet
- The District Governess & Other Stories by Miss Regina SnowDocument118 pagesThe District Governess & Other Stories by Miss Regina SnowMarianne MartindaleNo ratings yet
- TA Holdings Annual Report 2013Document100 pagesTA Holdings Annual Report 2013Kristi DuranNo ratings yet
- Psychology Essay IntroductionDocument3 pagesPsychology Essay Introductionfesegizipej2100% (2)
- AI Intelligence (Sam Charrington and Abeba Birhane)Document2 pagesAI Intelligence (Sam Charrington and Abeba Birhane)Ethel Shammah Waoulda Acleta90% (10)
- C.W.stoneking Lyric BookDocument7 pagesC.W.stoneking Lyric Bookbackch9011No ratings yet
- Accounting For Revenue and Other ReceiptsDocument4 pagesAccounting For Revenue and Other ReceiptsNelin BarandinoNo ratings yet
- Crisis Communications: Steps For Managing A Media CrisisDocument15 pagesCrisis Communications: Steps For Managing A Media Crisismargarita BelleNo ratings yet
- RPA Solutions - Step Into The FutureDocument13 pagesRPA Solutions - Step Into The FutureThe Poet Inside youNo ratings yet
- CH03 - Case1 - GE Becomes A Digital Firm The Emerging Industrial InternetDocument4 pagesCH03 - Case1 - GE Becomes A Digital Firm The Emerging Industrial Internetjas02h10% (1)
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocument4 pagesMonopolistic CompetitionAzharNo ratings yet
- Philippine Phoenix Surety vs. WoodworksDocument1 pagePhilippine Phoenix Surety vs. WoodworksSimon James SemillaNo ratings yet
- What Is OB Chapter1Document25 pagesWhat Is OB Chapter1sun_shenoy100% (1)
- EZ 220 Songbook Web PDFDocument152 pagesEZ 220 Songbook Web PDFOscar SpiritNo ratings yet
- Enochian Tablets ComparedDocument23 pagesEnochian Tablets ComparedAnonymous FmnWvIDj100% (7)
- Multan Electric Power Company: Say No To CorruptionDocument2 pagesMultan Electric Power Company: Say No To CorruptionLearnig TechniquesNo ratings yet
- A Review Essay On The European GuildsDocument11 pagesA Review Essay On The European GuildsAnonymous xDPiyENo ratings yet
- Discipline, Number of Vacancies, Educational Qualification and ExperienceDocument8 pagesDiscipline, Number of Vacancies, Educational Qualification and ExperienceMohammedBujairNo ratings yet
- Tok SB Ibdip Ch1Document16 pagesTok SB Ibdip Ch1Luis Andrés Arce SalazarNo ratings yet
- Tiktok PresentationDocument17 pagesTiktok Presentationapi-681531475No ratings yet
- Ethiopia Pulp & Paper SC: Notice NoticeDocument1 pageEthiopia Pulp & Paper SC: Notice NoticeWedi FitwiNo ratings yet
- 2.1.. Democracy As An IdealDocument12 pages2.1.. Democracy As An IdealMichel Monkam MboueNo ratings yet
- Estimating Guideline: A) Clearing & GrubbingDocument23 pagesEstimating Guideline: A) Clearing & GrubbingFreedom Love NabalNo ratings yet
- In Christ: Romans 6:4Document6 pagesIn Christ: Romans 6:4Bruce LyonNo ratings yet