Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Por Qué Los Ortodoncistas Necesitan Saber Sobre La Hipomineralización de Los Incisivos Molares
Uploaded by
miriancoguevargasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Por Qué Los Ortodoncistas Necesitan Saber Sobre La Hipomineralización de Los Incisivos Molares
Uploaded by
miriancoguevargasCopyright:
Available Formats
THESIS ABSTRACTS
Book reviews and article abstracts
Alex Jacobson, Associate Editor, Birmingham, Ala
THESIS ABSTRACTS heights, and widths in patients with high-, average-, and low-
angle facial types. A total of 113 scanned patients were deemed
Craniofacial effects of alendronate acceptable. Of these subjects, 44 were included in the average
treatment in growing osteogenesis facial angle group, 35 in the high group, and 34 in the low group.
Computerized tracings of lateral cephalometric films evaluated
imperfecta mice the facial height index and the mandibular plane angle. Cross-
Jonathan E. Britton sectional slices of the mandible were rendered between the
University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada dentition at 13 locations. Each section was then measured in 8
areas including 1 height, 2 width, and 5 cortical plate thick-
Introduction: Bisphosphonates have shown promise in nesses. An ANOVA with a post-hoc Bonferroni statistical
reducing fractures in children with osteogenesis imperfecta analysis was used with a significance level of P ⬍.0167.
(OI). To date, the effects of these drugs on the growing Results and Conclusions: Although few thicknesses of
craniofacial skeleton have not been investigated. the cortical plates were statistically significant among the
Methods: To address this, alendronate (ALN) was eval- facial vertical dimension groups, nearly all measurements for
uated in the growing oim/oim mouse, a model of moderate- the low-angle subjects were greater than those in the high-
to-severe OI. Wildtype (⫹/⫹) and oim/oim mice received angle group. Mandibular height in the high-angle group was
saline solution or ALN at a dosage of 26 IJg ALN per shorter posteriorly than in the other groups, and became even
kilogram per day from 6 to 12 weeks of age. Skulls (n ⫽ 49) greater toward the symphysis. Width measurements in the
were scanned at 12 weeks with microCT to create 3-dimen- brachyfacial group were greater than in the dolicofacial
sional reconstructions. Cranial and mandibular landmarks subjects. No differences were found in cortical plate thickness
were digitized, and statistical shape analysis methods com- between the sexes, although mandibular height and upper
pared cranial and mandibular sizes and shapes between the width were greater in males. There was a trend for subjects
groups. Back-scattered electron imaging of the spheno-occip- aged 10 to 20 years and over 50 years of age to have smaller
ital synchondrosis evaluated drug effects on bone quality. cortical bone thicknesses.
Results and Conclusions: The oim/oim mice exhibited
Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2007;132:126
significant skull dysmorphology with parallels to human OI. 0889-5406/$32.00
The antiresorptive activity of ALN does not appear to Copyright © 2007 by the American Association of Orthodontists.
compromise craniofacial growth. ALN treatment normalized doi:10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.09.018
FM morphology in oim/oim mice through improvements in
skull bone quality.
Comparison of treatment result and
Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2007;132:126
0889-5406/$32.00 compliance between private practice
Copyright © 2007 by the American Association of Orthodontists.
doi:10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.09.017
Medicaid and non-Medicaid
orthodontic patients
Cross-sectional mandibular morphology Steven Dickens
University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
in high, average, and low angle subjects
Denise C. Brown Treatment results and compliance for orthodontic Medicaid
University of California, San Francisco patients were assessed and compared with non-Medicaid pa-
tients of similar initial severity. All 55 practices providing
Introduction: A common concept in orthodontics is that orthodontic treatment covered by Medicaid were asked to submit
brachyfacial patients have shorter, thicker muscles of masti- their last 5 Medicaid patients and 5 non-Medicaid patients of
cation and denser cortical bone in the mandible compared similar initial treatment complexity. Nine practices agreed to
with their dolicofacial counterparts. The goal of this study participate. Initial models, final models, and progress notes were
was to look at retrospective data acquired from live patients obtained for all subjects. Casts were scored by using the peer
by using the CB MercuRay and iCAT cone-beam computer- assessment rating (PAR) index to obtain treatment result data.
ized tomography (CBCT) systems. Progress notes were reviewed for compliance data. No signifi-
Methods: The collected CBCT scans were used to deter- cant differences were seen between the Medicaid and the
mine differences in cortical plate thicknesses, mandibular non-Medicaid groups based on initial PAR, final PAR, or
126
You might also like
- Handbook of Lower Extremity Reconstruction: Clinical Case-Based Review and Flap AtlasFrom EverandHandbook of Lower Extremity Reconstruction: Clinical Case-Based Review and Flap AtlasScott T. HollenbeckNo ratings yet
- Abstract 2004Document45 pagesAbstract 2004MOHD ISYRAFUDDIN ISMAILNo ratings yet
- Prognosis of Dental Implants in Patients With Low Bone Density: A Systemic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument10 pagesPrognosis of Dental Implants in Patients With Low Bone Density: A Systemic Review and Meta-AnalysisNathan LouisNo ratings yet
- Book Reviews and Article Abstracts: Treatment Timing: Orthodontics in Four DimensionsDocument2 pagesBook Reviews and Article Abstracts: Treatment Timing: Orthodontics in Four DimensionsmeghaNo ratings yet
- Alhammadi 2019Document9 pagesAlhammadi 2019Dela MedinaNo ratings yet
- Ortopedia Dentofacial Una Vision MultidisciplinariaDocument1 pageOrtopedia Dentofacial Una Vision MultidisciplinariaFrancisco Javier GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Craniofacial Morphology in Women With Class I Occlusion and Severe Maxillary Anterior CrowdingDocument10 pagesCraniofacial Morphology in Women With Class I Occlusion and Severe Maxillary Anterior CrowdingMonojit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Asymmetry of The Face in Orthodontic PatientsDocument6 pagesAsymmetry of The Face in Orthodontic PatientsplsssssNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Medial Epicondyle Fracture Without Associated Elbow Dislocation in Older Children and AdolescentsDocument7 pagesTreatment of Medial Epicondyle Fracture Without Associated Elbow Dislocation in Older Children and AdolescentsRahma HanifaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S027823911501438XDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S027823911501438Xhyl776210No ratings yet
- Tibial Derotational Osteotomies in Two Neuromuscular PopulationsDocument6 pagesTibial Derotational Osteotomies in Two Neuromuscular PopulationsJuan Agustin Valcarce LeonNo ratings yet
- 17-Potential Medicolegal RisksDocument1 page17-Potential Medicolegal RisksSUSANNo ratings yet
- Susarla 2020Document8 pagesSusarla 2020MarcelaGutiérrezCarranzaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Case Western Reserve University's Transverse Analysis On The Quality of Orthodontic TreatmentDocument15 pagesEffects of Case Western Reserve University's Transverse Analysis On The Quality of Orthodontic TreatmentIsmaelLouGomezNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Occlusal Vertical Dimention in Eduntulos Patients Using Lateral CephalograamsDocument7 pagesDetermination of The Occlusal Vertical Dimention in Eduntulos Patients Using Lateral CephalograamsLeenMash'anNo ratings yet
- kim 2014Document8 pageskim 2014Dela MedinaNo ratings yet
- Cambio Esqueletal Asociado A Clases LL ArticuloDocument7 pagesCambio Esqueletal Asociado A Clases LL ArticuloDavid DíazNo ratings yet
- Changes in dentition from finger-sucking therapyDocument5 pagesChanges in dentition from finger-sucking therapyIsabel Escobar MinotasNo ratings yet
- ASIMETRIA3Document10 pagesASIMETRIA3CATALINA VASQUEZ LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Follow Up of 103 Ankylosed Permanent Incisors Surgically Treated With Decoronation - A Retrospective Cohort StudyDocument7 pagesLong-Term Follow Up of 103 Ankylosed Permanent Incisors Surgically Treated With Decoronation - A Retrospective Cohort StudyAnaMariaCastroNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Mandibular First Molars' Axial Inclination and Alveolar Morphology in Different Facial Patterns: A CBCT StudyDocument10 pagesEvaluation of Mandibular First Molars' Axial Inclination and Alveolar Morphology in Different Facial Patterns: A CBCT StudyPututu PatataNo ratings yet
- 3D CT Evaluation of Craniofacial Deformity in Patients with Untreated TorticollisDocument10 pages3D CT Evaluation of Craniofacial Deformity in Patients with Untreated TorticollisLaidetNo ratings yet
- Clinical and RadiographicDocument2 pagesClinical and RadiographicJose IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Incidence of Developing Contralateral M Enie're's Disease in Patients Undergoing Transmastoid Labyrinthectomy For Unilateral M Enie're's DiseaseDocument4 pagesIncidence of Developing Contralateral M Enie're's Disease in Patients Undergoing Transmastoid Labyrinthectomy For Unilateral M Enie're's DiseaseNoviTrianaNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Treatment Results of Adult Deep-Bite Cases Treated With Lingual and Labial Fixed AppliancesDocument7 pagesA Comparison of Treatment Results of Adult Deep-Bite Cases Treated With Lingual and Labial Fixed AppliancesScribd AccountNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Radiologic Pulp Evaluation After Partial Pulpotomy in Young Permanent MolarsDocument9 pagesLong-Term Radiologic Pulp Evaluation After Partial Pulpotomy in Young Permanent MolarsAbdul Rahman AlmishhdanyNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Lip Soft Tissue Thicknesses Differ in Relation To Age and SexDocument7 pagesUpper and Lower Lip Soft Tissue Thicknesses Differ in Relation To Age and SexAly OsmanNo ratings yet
- Incisor Position and Alveolar Bone Thickness: A Comparative Analysis of Two Untreated Samples Using Lateral CephalogramsDocument8 pagesIncisor Position and Alveolar Bone Thickness: A Comparative Analysis of Two Untreated Samples Using Lateral CephalogramsLuis SanchezNo ratings yet
- Effect of Lip Bumpers On Mandibular Arch DimensionsDocument4 pagesEffect of Lip Bumpers On Mandibular Arch DimensionsLuz Maria AristizabalNo ratings yet
- 1999 115 1 29 38 ChangDocument10 pages1999 115 1 29 38 ChangAlla MushkeyNo ratings yet
- Referensi Tesis Spesialis ChoDocument6 pagesReferensi Tesis Spesialis ChoflorensiaNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Posttreatment Changes in Patients With Class II, Division 1 Malocclusion After Extraction and Nonextraction TreatmentDocument10 pagesTreatment and Posttreatment Changes in Patients With Class II, Division 1 Malocclusion After Extraction and Nonextraction TreatmentNeeraj AroraNo ratings yet
- Andrade Et Al-2009-Clinical Anatomy PDFDocument7 pagesAndrade Et Al-2009-Clinical Anatomy PDFJakeCrNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Dentoalveolar Changes After Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion in Young Adults A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study.Document11 pagesSkeletal and Dentoalveolar Changes After Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion in Young Adults A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study.Natan GussNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Suture Nonsyndromic Craniosynostosis: Early and Effective Management Using Endoscopic TechniquesDocument9 pagesMultiple-Suture Nonsyndromic Craniosynostosis: Early and Effective Management Using Endoscopic TechniquesKiky Martha A.No ratings yet
- Wheeler2002Document9 pagesWheeler2002Juliana ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Retrospective Study of Maxillary Sinus Dimensions and Pneumatization in Adult Patients With An Anterior Open BiteDocument6 pagesRetrospective Study of Maxillary Sinus Dimensions and Pneumatization in Adult Patients With An Anterior Open BiteAntonio Pizarroso GonzaloNo ratings yet
- CJN 079Document199 pagesCJN 079SelvaArockiamNo ratings yet
- 1. 1-s2.0-S0278239119305518-mainDocument15 pages1. 1-s2.0-S0278239119305518-mainALEJANDRA INÉS NIETO ARIASNo ratings yet
- Morphologic Characteristics Unilateral Condylar HyperplasiaDocument8 pagesMorphologic Characteristics Unilateral Condylar HyperplasiaSumano Guzmán Itandehui V.No ratings yet
- PatelDocument8 pagesPatelVi LinhNo ratings yet
- 8 MC Guire ANDNunn Jop 2003Document16 pages8 MC Guire ANDNunn Jop 2003Mirela1612No ratings yet
- AJODO-2013 Hodges 143 5 665Document10 pagesAJODO-2013 Hodges 143 5 665player osamaNo ratings yet
- AJODO-2013 Bradley 143 5 599Document3 pagesAJODO-2013 Bradley 143 5 599player osamaNo ratings yet
- Residentes AbrilDocument3 pagesResidentes AbrilLuis Zegarra SalinasNo ratings yet
- Wurgaft R, Rappoport K, Soler C, Ponce C, Flores-Mir CDocument16 pagesWurgaft R, Rappoport K, Soler C, Ponce C, Flores-Mir CCatalina Soler LioiNo ratings yet
- 2012-X - Relationship Between Dental Arch Dimensions AndveDocument9 pages2012-X - Relationship Between Dental Arch Dimensions AndveAnaFlaviaMedinaNo ratings yet
- Ferreira 2020Document10 pagesFerreira 2020Dela MedinaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Free-Flap Transfer Reconstruction in Elderly Patients and Oral Intake FunctionDocument3 pagesInvestigation of Free-Flap Transfer Reconstruction in Elderly Patients and Oral Intake Functioncusom34No ratings yet
- 190 Disc Repositioning Does It Really WorkDocument23 pages190 Disc Repositioning Does It Really WorkAngélica Valenzuela AndrighiNo ratings yet
- Apical Root Resorption of Incisors After Orthodontic Treatment of Impacted Maxillary Canines, Radiographic StudyDocument9 pagesApical Root Resorption of Incisors After Orthodontic Treatment of Impacted Maxillary Canines, Radiographic StudyJose CollazosNo ratings yet
- Ni Hms 565367Document25 pagesNi Hms 565367Ana Maria Tineo HuaytallaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PfnaDocument10 pagesJurnal PfnaDhea Amalia WibowoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Occlusal Appliance For The Reposition of Temporomandibular Joint Anterior Disc Displacement With ReductionDocument4 pagesAssessment of Occlusal Appliance For The Reposition of Temporomandibular Joint Anterior Disc Displacement With ReductionSTEPHANIE JARAMILLONo ratings yet
- Role of cephalometry in evaluating vertical dimensionDocument4 pagesRole of cephalometry in evaluating vertical dimensionAhmad ShoeibNo ratings yet
- Long Term Vertical ChangesDocument5 pagesLong Term Vertical ChangesthganooNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Facet Block in Lumbar Facet Joint Syndrome PatientsDocument6 pagesEfficacy of Facet Block in Lumbar Facet Joint Syndrome PatientsthiagoNo ratings yet
- Differences in Finished Case Quality Between Invisalign and Traditional Fixed ApplianceDocument7 pagesDifferences in Finished Case Quality Between Invisalign and Traditional Fixed Applianceluthfi fernandaNo ratings yet
- KJO2057Document10 pagesKJO2057강북다인치과No ratings yet
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation ORIF of ComplDocument6 pagesOpen Reduction and Internal Fixation ORIF of ComplAnnisa AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Clase Practica 6t0 (1) (Reparado)Document3 pagesClase Practica 6t0 (1) (Reparado)Sarita Chavarria CentenoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Practices and Physiological EffectsDocument9 pagesElectrical Safety Practices and Physiological EffectsSmr OnlyNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument16 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Chapter 1 IntroductionJaylen CayNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Clinical Pharmacists PDFDocument29 pagesCritical Care Clinical Pharmacists PDFMariana RibeiroNo ratings yet
- PGH GUIDELINES for SPECIALTY REFERRALSDocument2 pagesPGH GUIDELINES for SPECIALTY REFERRALSRocaya Lucman100% (1)
- Heart Cardiovasc Chap12Document69 pagesHeart Cardiovasc Chap12Thea GornezNo ratings yet
- Court Finds Surgeon, Anesthesiologist and Hospital Liable for Patient's ComaDocument2 pagesCourt Finds Surgeon, Anesthesiologist and Hospital Liable for Patient's ComaTina TinsNo ratings yet
- PWD All Outline 130819Document114 pagesPWD All Outline 130819Francis KaikumbaNo ratings yet
- 4A. Endocrine Case Studies - Student Handout-3Document11 pages4A. Endocrine Case Studies - Student Handout-3Ola0% (9)
- Hematology 1 Laboratory SheetDocument3 pagesHematology 1 Laboratory SheetNatsuki MiyajiNo ratings yet
- Policy of Retention & DestructionDocument6 pagesPolicy of Retention & Destructionumeshbharti0% (1)
- Simultaneous UV Method Estimates Pain and Anti-Inflammatory DrugsDocument4 pagesSimultaneous UV Method Estimates Pain and Anti-Inflammatory DrugsBolgam PradeepNo ratings yet
- 101 Ways To Raise A Happy BabyDocument185 pages101 Ways To Raise A Happy BabyTripti KhoslaNo ratings yet
- Medical ProjectDocument50 pagesMedical Projectharshavardhana00078No ratings yet
- ALCOOLISM TREATMENT EVIDENCEDocument12 pagesALCOOLISM TREATMENT EVIDENCEvioletaNo ratings yet
- Reducing Dental Anxiety in ChildrenDocument4 pagesReducing Dental Anxiety in Childrenapi-613602134No ratings yet
- GSK Annual Report 2006 PDFDocument71 pagesGSK Annual Report 2006 PDFslantyyNo ratings yet
- Patients' Willingness To Pay For Dental Services in A Population With Limited Restorative ServicesDocument6 pagesPatients' Willingness To Pay For Dental Services in A Population With Limited Restorative ServicesMuhamad RamadanNo ratings yet
- Language and The BrainDocument8 pagesLanguage and The BrainAntonio GoqueNo ratings yet
- Ryan Martin Ko, M.DDocument54 pagesRyan Martin Ko, M.DDhaval Makwana100% (2)
- Human Digestion PresentationDocument35 pagesHuman Digestion PresentationYamyang Galay-BañoNo ratings yet
- Drug Distribution Channels and FunctionsDocument3 pagesDrug Distribution Channels and FunctionsPaul Michael Joules SaliseNo ratings yet
- XMSDS Calcium Hydroxide 9927122Document7 pagesXMSDS Calcium Hydroxide 9927122Thameem786No ratings yet
- McIntyre Et Al-2002-European Journal of NeuroscienceDocument4 pagesMcIntyre Et Al-2002-European Journal of NeuroscienceLaura Elena Amaya DuránNo ratings yet
- A Case Report On Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Version2Document20 pagesA Case Report On Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Version2Aiko EscobidoNo ratings yet
- 85800-131 ERBE EN Application Brochure of Gastroenterology D064045Document24 pages85800-131 ERBE EN Application Brochure of Gastroenterology D064045GREYSON QCNo ratings yet
- Norton Presure Sore Risk Assessment Scale PDFDocument1 pageNorton Presure Sore Risk Assessment Scale PDFchrisyenNo ratings yet
- Louha MaranaDocument9 pagesLouha MaranaSundara VeerrajuNo ratings yet
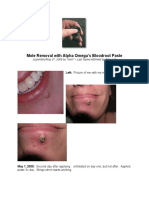
- Alpha Blood Root Paste ResultsDocument5 pagesAlpha Blood Root Paste ResultsJeNo ratings yet
- Endo MotorDocument28 pagesEndo MotorCarlos Canedo HNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (15)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)