Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biosignal Sheets 4
Uploaded by
workomar97Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biosignal Sheets 4
Uploaded by
workomar97Copyright:
Available Formats
Course Name: Biomedical Signals and Systems
Course Code : BME 371
برنامج الهندسة الطبية الحيوية Year : 2022/2023 كلية الهندسة
))ساعات معتمدة Time :2H
Sheet 4
Answer the following questions.
1; 𝑡 ≥ 0
1. If 𝑢(𝑡) = { , and 𝑟(𝑡) = 𝑡𝑢(𝑡) , Express the following signals in terms of 𝑟(𝑡)
0; 𝑡 < 0
and 𝑢(𝑡).
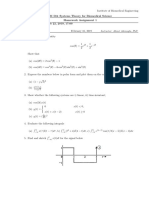
2. Compute the following.
2
a. ∫1 (3𝑡 + 1)𝛿(𝑡)𝑑𝑡
∞
b. ∫−∞( 𝑡 2 + cos(𝜋𝑡) )𝛿(𝑡)𝑑𝑡
∞
c. ∫−∞ 𝑒 −𝑡 𝛿(2𝑡 − 2)𝑑𝑡
𝑑𝑥(𝑡)
3. If 𝑥(𝑡) = 𝑠𝑔𝑛(𝑡), prove that = 2𝛿(𝑡).
𝑑𝑡
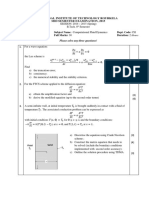
4. In the opposite circuit if 𝑥(𝑡) = 𝑖(𝑡) and y(t) = vc (t), then
a. Fin the relationship of input x(t) and output y(t),
b. Determine whether the system is (i) memoryless, (ii)
causal, iii ) linear, (iv) time-invariant, or (v) stable.
5. If 𝑦(𝑡) = 𝑥(𝑡) cos(𝜔𝑐 𝑡), determine whether it is (a) memoryless, (b) causal, (c) linear, (d)
time-invariant, or (e) stable.
6. Compute the output 𝑦(𝑡) for a continuous-time LTI-system whose impulse response ℎ(𝑡) =
𝑒 −𝑎𝑡 𝑢(𝑡) and the input 𝑥(𝑡) = 𝑒 𝑎𝑡 𝑢(−𝑡), 𝑎 > 0.
Biosignals and Systems
Course Name: Biomedical Signals and Systems
Course Code : BME 371
برنامج الهندسة الطبية الحيوية Year : 2022/2023 كلية الهندسة
))ساعات معتمدة Time :2H
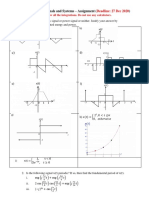
7. Evaluate 𝑦(𝑡) = 𝑥(𝑡) ∗ ℎ(𝑡), where 𝑥(𝑡) and ℎ(𝑡) are shown in the below figures. (a) by an
analytical technique, and (b) by a graphical method.
8. Evaluate 𝑦(𝑡) = 𝑥(𝑡) ∗ ℎ(𝑡), where 𝑥(𝑡) = 𝛿𝑇 (𝑡) and ℎ(𝑡) are shown in the below figures, for
the following values of T: (a) T = 3, (b) T= 2, (c) T = 1.5.
Biosignals and Systems
You might also like
- SAT-2 Math2Document15 pagesSAT-2 Math2Henry C. LiuNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6Document1 pageSheet 6workomar97No ratings yet
- Biosignal Sheet 3Document2 pagesBiosignal Sheet 3workomar97No ratings yet
- Cherrybrook 2023 AT3 Mathematics Advanced SolutionsDocument42 pagesCherrybrook 2023 AT3 Mathematics Advanced Solutionsmujtabaibrahim39No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Jiit Discrete MathsDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 Jiit Discrete Mathsvivek patelNo ratings yet
- 15EECC204: and Any ONE Full Question From UNIT-IIIDocument6 pages15EECC204: and Any ONE Full Question From UNIT-IIIAkshay ArksaliNo ratings yet
- EEE243/ECE243 Signals and Systems - Assignment : Please Show All The Integrations. Do Not Use Any CalculatorsDocument5 pagesEEE243/ECE243 Signals and Systems - Assignment : Please Show All The Integrations. Do Not Use Any CalculatorsRedwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Question (EEE 303) PDFDocument2 pagesMid Term Question (EEE 303) PDFIstiaq Ahmed AurkoNo ratings yet
- WB - Set 2022 PH PaperDocument27 pagesWB - Set 2022 PH PaperSaheli DeyNo ratings yet
- Digital Signals Processing ﺔﯿﻤﻗﺮﻟا تارﺎﺷﻻا ﺔﺠﻟﺎﻌﻣ: Lectures (Five and Six)Document12 pagesDigital Signals Processing ﺔﯿﻤﻗﺮﻟا تارﺎﺷﻻا ﺔﺠﻟﺎﻌﻣ: Lectures (Five and Six)AwadhNo ratings yet
- Ee8591 DSP Model 1Document3 pagesEe8591 DSP Model 1Ece DeptNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems Mid Sem Sig&sys PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial Problems Mid Sem Sig&sys PDFsaurabhNo ratings yet
- EE301 FINAL Fall22 Allquestions Ver5Document7 pagesEE301 FINAL Fall22 Allquestions Ver5hasan MD. ShazidNo ratings yet
- CCDocument4 pagesCCferdi tayfunNo ratings yet
- EC2601Document2 pagesEC2601Kartik GvrNo ratings yet
- EE223-Signals & Systems: Remote Final Exam Total Time: 03 Hours Total Marks: 100 Course InstructorDocument5 pagesEE223-Signals & Systems: Remote Final Exam Total Time: 03 Hours Total Marks: 100 Course InstructorMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Be Winter 2022Document2 pagesBe Winter 2022avinashlimje0No ratings yet
- Sample Test 1-2 For Calculus 1Document2 pagesSample Test 1-2 For Calculus 1Teodora MihaiNo ratings yet
- 203 EEE 2301 Assignment 1Document2 pages203 EEE 2301 Assignment 1Faizur Rahman PaponNo ratings yet
- Day 4 SolutionsDocument5 pagesDay 4 SolutionsLiz KiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Safety Engineering Assignment 0Document3 pagesIndustrial Safety Engineering Assignment 0aleemNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Questions 2023Document3 pagesTutorial 2 Questions 2023j2yshjzzsxNo ratings yet
- Parul University: Yn XN XT TDocument2 pagesParul University: Yn XN XT THarshraj MahidaNo ratings yet
- MAC 2021 Questions ESEDocument2 pagesMAC 2021 Questions ESEHarshita SinghNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Class X Maths Basic Question Paper Solutions 2023Document35 pagesCBSE Board Class X Maths Basic Question Paper Solutions 2023sarojgiri1976No ratings yet
- Determine and Sketch: The Even and Odd Parts of The Signals Depicted in Figures. Label Your Sketches CarefullyDocument5 pagesDetermine and Sketch: The Even and Odd Parts of The Signals Depicted in Figures. Label Your Sketches Carefullyyaswanth rNo ratings yet
- GROUP TASK Chapter 1 & 2 - XXX VersionDocument2 pagesGROUP TASK Chapter 1 & 2 - XXX Versionsilent spritsNo ratings yet
- United International University (Uiu)Document2 pagesUnited International University (Uiu)Faizur Rahman PaponNo ratings yet
- Kulliyyah of Engineering: End-Of-Semester Examination SEMESTER 2, 2019/2020 SESSIONDocument8 pagesKulliyyah of Engineering: End-Of-Semester Examination SEMESTER 2, 2019/2020 SESSIONMu'adzAzriNo ratings yet
- DSP - 2utc503 - Nov-Dec 2021Document4 pagesDSP - 2utc503 - Nov-Dec 2021devansh chotaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1Document2 pagesAssignment #1Hlopm YueNo ratings yet
- MidTermQuestion Paper PDFDocument5 pagesMidTermQuestion Paper PDFUsama khanNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityM.k. PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Mat351 Final Exam Fall 2018Document7 pagesMat351 Final Exam Fall 2018Lamees ElghazolyNo ratings yet
- Ap Exam Supplement: Specifically Developed For This Year's AP ExamDocument7 pagesAp Exam Supplement: Specifically Developed For This Year's AP ExamGan PentonNo ratings yet
- Ch.02 Modeling in Frequency Domain - AssignmentDocument5 pagesCh.02 Modeling in Frequency Domain - AssignmentThảo Đặng Ngọc ThanhNo ratings yet
- 5500icbteg - Am WeDocument5 pages5500icbteg - Am WeKamal SurenNo ratings yet
- Midterm-Math 211fall 2023Document7 pagesMidterm-Math 211fall 2023aalrjl08No ratings yet
- Class 11 Maths HyDocument4 pagesClass 11 Maths HyIshuNo ratings yet
- Gs2017 QP CssDocument18 pagesGs2017 QP Cssprince_1994No ratings yet
- Assignment Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesAssignment Linear AlgebraDEBOJIT CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering and Survey: Semester Ii Examinations, September 2021 B.Eng/Electrical Egineering IiDocument6 pagesFaculty of Engineering and Survey: Semester Ii Examinations, September 2021 B.Eng/Electrical Egineering IiGanja mnNo ratings yet
- 15ece204 - I Ass Jan 2018Document2 pages15ece204 - I Ass Jan 2018mahamaniNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Rourkela Mid Semester Examination, 2015Document2 pagesNational Institute of Technology Rourkela Mid Semester Examination, 2015AratrikaNo ratings yet
- AE383 Fall2020 HW1Document1 pageAE383 Fall2020 HW1eniNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics and Philosophy of Engineering MHZ3552 Engineering Mathematics II Assignment No.03Document4 pagesDepartment of Mathematics and Philosophy of Engineering MHZ3552 Engineering Mathematics II Assignment No.03kasunkNo ratings yet
- 239392769phys 2101Document5 pages239392769phys 2101080Zaid MallickNo ratings yet
- Final Question Fall 2014Document4 pagesFinal Question Fall 2014Muntasir AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document3 pagesDay 4m mmNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions - 2 Pts Each: Calculus AB Unit 4 Test 2020Document5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions - 2 Pts Each: Calculus AB Unit 4 Test 2020Joseph sNo ratings yet
- Class XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With SolutionDocument128 pagesClass XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With Solutionanushkabisht2006No ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis MCQDocument15 pagesNumerical Analysis MCQmansoormani20167% (9)
- EE39203 Aut2022 Exp2Document6 pagesEE39203 Aut2022 Exp2Bharat UdayNo ratings yet
- Corona Break Advanced p1 Exam 's-8011-1Document4 pagesCorona Break Advanced p1 Exam 's-8011-1nassorussi9No ratings yet
- Unit: 5-Curve Fitting by Numerical MethodsDocument34 pagesUnit: 5-Curve Fitting by Numerical MethodsBHAVESHNo ratings yet
- SCI101SC - PHA101SC - (B) - Assessment - 202101 - Joy and FisherDocument6 pagesSCI101SC - PHA101SC - (B) - Assessment - 202101 - Joy and FisherAhmed Sami YounisNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03 LINEAR ONLINEDocument22 pagesAssignment 03 LINEAR ONLINERupam dasNo ratings yet