Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Talent Management
Uploaded by
dipeshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Talent Management
Uploaded by
dipeshCopyright:
Available Formats
TALENT MANAGEMENT
Emerging Trends:
. Talent analytics and work force analytics
. Employee's training, skilling, and reskilling
. Diversity equity and inclusion
. Empathy (Connectivity, interaction, flexibility, training, opportunities, and encouragement )
. Employment strategies for nontraditional occupations
. Experiences of employees
. Physical fitness
. onboarding and retainment strategies
. Impact of Covid-19
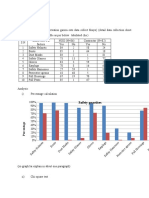
- Economy dropped: US 35%, Eurozone 12.1%, Spain 18.5%, job reduced 42% (data of 2020)
. Managing remote work force
. Evidence based TM practices
. Speedier TM processes
. Talent identification within the organization
. Multigeneration work force utilization i.e., internship and returnship
. Adaptability and socialization
Nepalese context
. Psychological preparation
. Reservation
. Review in curriculum and career system
. Qualitative workforce in domestic and international market
. strategies for Attracting talents
. Impact of covid -19
. Reducing turnover
. Efficient leadership
Answer to the Questions
Federalism concept: (Some Problems)
Principles
1. Principle of residual power
2. Principle of subsidiarity
Slow pace of law making
1. Important laws are not prepared
2. Federal Civil Service Bill
Personnel Management
1. O and M Survey
2. Full Autonomy of the governments
3. Interface with public
Successful Conditions for Federalism
1. Clear understanding
2. Effective Management
3. Visionary leaders
Provisions of FCSB
1. Review on reservation policy
2. Questions on the quality of public service delivery
3. Clustering for the promotion in secretary
4. Retirement age (differences between 2 to 5 years for women, 67 years in Australia by 2023, 65 in
Belgium by 2030, 67 in Denmark by 2022, Japan 65, Malaysia 60, average retirement age 65 in
international organization)
5. Double number recommendation to the government for the secretary level promotion
6. No open competition
7. Mandatory provision of contract to the position of project chief, office in charge and departmental
head
8. No opportunities to the existing personnel to seat in competition
9. Inter service competition
10. Civil service up to state level
11. No classless positions
12. Trade union
13. Closed provision of Foreign Service
14. Experts in PSC as an invitee
15. Adjustment up to the level of US
16. Secretary as a manager or adviser
some Knots of Civil service Bill
. Trade union
. Retirement age
. Service Contract
. Open competition
. Reservation
. clustering for secretary
. Biased provision for policy level staffs
. No provision for the locally appointed staffs
. Compatible with Constitutional spirit
Problems of Personnel Adjustment
. Leadership level
. Duration for taking decision
. Appropriate structure
. Inclusion or Positive discrimination n
. Improvements in work performance
. Strengthening of meritocracy
. Application of new technology and methods
. Identification of all sorts of personnel
. Simplification of service delivery
. Personnel with appropriate skill
. Determination of minimum standards
. Quality and quantity of existing personnel
. VRS
. Blending nature of personnel in local level
. Adocism in personnel adjustment
Answer to the question number one:
Fundamental aspects to be incorporated in the FCSB
. Open competition up to class 2
. Inter service competition
. Fully compliance of federal principles
. Foreign service needs to be open for all talents
. Logical review of reservation
. Clustering in secretary
. Civil service only in the center
. Review in retirement age
. Trade union based on ILC standard
. Multiskilled manpower
. objective evaluation
. Application of new framework and techniques
. Unequivocal provisions for different types of local level personnel adjustment
. Correction on the provision of personnel adjustment
. Provide open competition opportunities to the existing staffs
Answer to the question number 2: Integration linkages of all personnel in the federal civil service
. Inter service competition
. Open competition
. Appropriate career system compatible with federal civil service
. No adjustment of psc completed personnel to the lower level of government
. Capacity enhancement program
. Separate provision to the locally appointed personnel
Types of local level staffs
. Appointed by the representative in permanent status
. Appointed by the representative in a temporary status
. Recommended by psc for federal service
. voluntarily prepared to work in the local level
. Forcefully adjusted by the federal government in the lower level of governments
. Recommended by PSC to the local level
. Personnel on deputation to the lower level
Answer to question number 3
Recommendations for service policies, conditions, career development and personnel adjustment in
the province and local level
. Management by deputation
. Test and verification of minimum qualification of locally appointed staffs
. O and M survey directly by the concerned government
. Temporary commission to determine minimum standard of the staff
. Application of TOR to all
. Open competition up to us level
. Transfer of JS and Secretary to the lower level of government
. Objective evaluation
. Well off local government i.e., sufficient resource
. End of politicization
. Career planning and career development schemes
(Followed by action plan)
Nature of PSC Questions
. Problems and solutions based
.Related with working environment
. Most of the questions are based on Nepalese context
Techniques to answer in written exam
. Basic concepts in brief
. Major demands of the questions
. Domestic policies, strategies , Structural arrangements , legal provisions , planning and programs
. New trends , good practices , international practices ,
. Positive aspects , negative aspects and challenges
. Questions asked covering more than one area
. Time management
. Bullet or analytical techniques of answering
. Facts, figures, graphs presentations
. Never mention obsolete data ( only can be used in comparison )
. Different parts of answering (concept , analytical part and conclusion)
. Weightage of questions ( time based on given number of the question )
. Grammar and correction
. Full marks joint secretary level ( 25 + 25 + 25+ 25 = 100) , 45 minutes time for each question
. New trends , contribution of the scholars in domestic and international journals
. Google search
. Contemporary issues
. Present yourself as an academicians and perfect practitioner
Model Questions
1, Principles and its implementation status
2, Desirable recommendations and reforms
Concept
. Minimum sixty percent of the total budget is allocated in public procurement
. Procurement means the acquisition by any means of goods , construction and services ( UNO
Model Act )
. Economy, Accountability , Transparency and value of money needs to be guaranteed
Principles
. Compliance of law
. Economy , efficiency and transparency
. Healthy competition and public accountability
. open and equal participation
. Public confidence
. Priority to the domestic production
. Necessity and usefulness
. Legal Provisions
. Ethics
. Impartiality and fairness
. Skill and effective's
. Professionalism
. Environment friendly management
. Easy access in information
. Grievances handling mechanism and provision
Implementation Status
. order of the procurement of the goods
. Component of the procurement of the goods
. Pre - qualification
. Institutional arrangements
Challenges
1) Public Institutions
. Decision making capacity and low moral
. Lack of taking risks
. Culture of working in pressure
. Highly criticized performance
. Reports of constitutional bodies
. Important parts of financial planning
. Lack of master plan and annual plan
. Management of institutional memory is weak
. Tendering process is prejudiced
. Lack of uniformity in compliance
. Discouraging competition by slicing the amount of procurement
. Favor for special brand
. competency and skill of the personnel is questioned
2) Tendering process and bidders
. Code of conduct
. Undue favor
. Weak implementations
. Lack of professionalism
. Work overload
. Promotion of healthy competition
3) Public Procurement office
. organization only in the center
. Lack of monitoring capability
. Research and innovation
. Monitoring process and mechanism in federal structure
. Lack of training for different level of government
. misuse of legal loopholes
. Replication of good practices
. Procedural complication
. Retention problem of the personnel
.Resource constraints
Reforms
Policy
Capacity enhancement and utilization
You might also like
- The Wiley Blackwell Handbook of the Psychology of Recruitment, Selection and Employee RetentionFrom EverandThe Wiley Blackwell Handbook of the Psychology of Recruitment, Selection and Employee RetentionHarold W. GoldsteinNo ratings yet
- A. Austen II Recruitment and Selection PoprDocument46 pagesA. Austen II Recruitment and Selection PoprNitin JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Monitoring, Evaluating, and Improving: An Evidence-Based Approach to Achieving Development Results that Matter!From EverandMonitoring, Evaluating, and Improving: An Evidence-Based Approach to Achieving Development Results that Matter!No ratings yet
- People Management Singhania and Partners V1 0Document12 pagesPeople Management Singhania and Partners V1 0gauarv_singh13No ratings yet
- Human Resources Management: All the Information You Need to Manage Your Staff and Meet Your Business ObjectivesFrom EverandHuman Resources Management: All the Information You Need to Manage Your Staff and Meet Your Business ObjectivesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Case Analysis People Management - Singhania & Partners Group D1 Ankit Agarwal Kausik.R Meenu Rajpal Pramod Khandelwal Syed Reza Salis N AqviDocument13 pagesCase Analysis People Management - Singhania & Partners Group D1 Ankit Agarwal Kausik.R Meenu Rajpal Pramod Khandelwal Syed Reza Salis N AqviabhisekNo ratings yet
- Human Capital Management: What Really Works in GovernmentFrom EverandHuman Capital Management: What Really Works in GovernmentNo ratings yet
- Public Sector Management in Developing CountryDocument250 pagesPublic Sector Management in Developing Countrymosehuddin_khaled100% (1)
- Chapter 1 General IntroductionDocument16 pagesChapter 1 General IntroductionAneziwe ShangeNo ratings yet
- Human Resource SpecialisationDocument8 pagesHuman Resource SpecialisationSakshiNo ratings yet
- Alagh Committee ReportDocument2 pagesAlagh Committee ReportYuktesh PawarNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Staffing Candidate Screening and Interviewing HandbookFrom EverandHealthcare Staffing Candidate Screening and Interviewing HandbookNo ratings yet
- MPP Research PaperDocument10 pagesMPP Research PaperSayak RayNo ratings yet
- Employment Security Placement Trainee: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandEmployment Security Placement Trainee: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Recruitment and Selection PracticesDocument4 pagesThesis On Recruitment and Selection Practicestjgyhvjef100% (2)
- VA-088 ICLA Technical Assistant Lashio 28th Sep 2020 PDFDocument3 pagesVA-088 ICLA Technical Assistant Lashio 28th Sep 2020 PDFsaw thomasNo ratings yet
- AB Unit 3 HRM Semester - Jan2021Document13 pagesAB Unit 3 HRM Semester - Jan2021Fahmina AhmedNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Strategic Objectives and Action Plan 2012-2016 Appendix 1 Strategic Recruitment & SelectionDocument12 pagesHuman Resources Strategic Objectives and Action Plan 2012-2016 Appendix 1 Strategic Recruitment & SelectionDominicSavioNo ratings yet
- Job Description of HR ManagerDocument4 pagesJob Description of HR ManagerMShoaibShakeel100% (5)
- Research Report On EmployabilityDocument17 pagesResearch Report On EmployabilityFizza KhanNo ratings yet
- TOR - Employers Perception Survey - ApprovedDocument16 pagesTOR - Employers Perception Survey - ApprovedAyaz Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Human Resourse ManagementDocument7 pagesHuman Resourse ManagementKutty KausyNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Public Service DeliveryDocument8 pagesDissertation On Public Service DeliveryPaperWritingServicesReviewsSiouxFalls100% (1)
- Presentation On Summer Training Report: Topic: " Grievance Handling Procedure at NHPC"Document15 pagesPresentation On Summer Training Report: Topic: " Grievance Handling Procedure at NHPC"swarna1989No ratings yet
- Talent Management Dissertation TopicsDocument5 pagesTalent Management Dissertation TopicsBestPaperWritingServiceSingapore100% (1)
- Quality ManagementDocument6 pagesQuality ManagementMikmik BanalaNo ratings yet
- Job Specification and Job DescriptionDocument14 pagesJob Specification and Job DescriptionAtul GuptaNo ratings yet
- IRIIE - 248Dr - AbdulRahmanDocument1 pageIRIIE - 248Dr - AbdulRahmanHairuddin MyhsiiumNo ratings yet
- Biotech 1Document26 pagesBiotech 1nanmun_17No ratings yet
- Strategic Management in The Public Sector of Pakistan: Presented To: Prof. Abu Zar WajidiDocument13 pagesStrategic Management in The Public Sector of Pakistan: Presented To: Prof. Abu Zar WajidiMohammad Anas KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument9 pagesChapter IIDr.P. Siva RamakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Research 1Document20 pagesResearch 1barijigoNo ratings yet
- People and Culture Manager Position Description: Department/UnitDocument7 pagesPeople and Culture Manager Position Description: Department/UnitDesty Lilian Rosana PutriNo ratings yet
- HRM Revision2014Document110 pagesHRM Revision2014Robert WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Acc 606 Topic 6 Lecture SlidesDocument11 pagesAcc 606 Topic 6 Lecture SlidesVika GasauduaNo ratings yet
- 01 7HRC HRM in ContextDocument4 pages01 7HRC HRM in ContextBVC BonnyNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and EvaluationDocument5 pagesMonitoring and EvaluationCzar EyanNo ratings yet
- HR Strategy 12Document105 pagesHR Strategy 12renu09guptaNo ratings yet
- Civil ServiceDocument35 pagesCivil ServiceAli Ibrahim AbdoulayeNo ratings yet
- HRM of LICDocument6 pagesHRM of LICsampathkishoreNo ratings yet
- Office System MamanagementDocument45 pagesOffice System MamanagementVincent BernardoNo ratings yet
- Name: Maha Israr Paper: Leading Managing The Project Teams Submitted To: Sir Abbas RazaDocument7 pagesName: Maha Israr Paper: Leading Managing The Project Teams Submitted To: Sir Abbas RazaMaha IsrarNo ratings yet
- Recruitment StrategiesDocument24 pagesRecruitment StrategiesJatinder ghumanNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics in Public AdministrationDocument8 pagesDissertation Topics in Public AdministrationSomeoneWriteMyPaperForMeUK100% (1)
- PHD EditedDocument243 pagesPHD EditedAnna DawoodNo ratings yet
- Developing The Profile of A Civil Servant v10Document76 pagesDeveloping The Profile of A Civil Servant v10Gina BawitNo ratings yet
- Recritment and Selection Midterm Review.Document6 pagesRecritment and Selection Midterm Review.Angelique ManningNo ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus For GDMM/PGDMM: Indian Institute of Materials ManagementDocument91 pagesRevised Syllabus For GDMM/PGDMM: Indian Institute of Materials ManagementVanita GanthadeNo ratings yet
- Upp 3Document53 pagesUpp 3Kai Shi CheeNo ratings yet
- Exam Summary PUB Comp Graduate July 2020Document24 pagesExam Summary PUB Comp Graduate July 2020ajrevillaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledAlemseged DeduNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document6 pagesLesson 3Roselyn IgartaNo ratings yet
- Harambee University CollegeDocument6 pagesHarambee University Collegetolossa assefaNo ratings yet
- Mainstreaming Ethics and Professionalism in The Civil Service Week 6 SlidesDocument50 pagesMainstreaming Ethics and Professionalism in The Civil Service Week 6 Slidestilahunthm100% (1)
- PMS (Provincial Managemnet Service) As A CAREERDocument35 pagesPMS (Provincial Managemnet Service) As A CAREERMudassar Nawaz100% (1)
- Project Report On Recruitment and Selection by AEGISDocument82 pagesProject Report On Recruitment and Selection by AEGISChandan Srivastava100% (1)
- Meet The High Labour TurnoverDocument9 pagesMeet The High Labour Turnoveryes1nthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 1-3 PDFdipeshNo ratings yet
- Phase I ResultDocument2 pagesPhase I ResultdipeshNo ratings yet
- BE Civil - PurU/1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4thDocument6 pagesBE Civil - PurU/1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4thdipeshNo ratings yet
- Phase I ResultDocument2 pagesPhase I ResultdipeshNo ratings yet
- Energy at Q 45 (4 Months Dry and 6 Month Dry Both Scenario)Document2 pagesEnergy at Q 45 (4 Months Dry and 6 Month Dry Both Scenario)dipeshNo ratings yet
- Project Management Maturity in The Construction Industry of Developing CountriesDocument299 pagesProject Management Maturity in The Construction Industry of Developing CountriesArun PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dam StabilityDocument3 pagesGravity Dam StabilitydipeshNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dam StabilityDocument4 pagesGravity Dam StabilitydipeshNo ratings yet
- Nepal Electricity Authority ROR PROR and Storage TarrifDocument3 pagesNepal Electricity Authority ROR PROR and Storage TarrifPujan NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Nea Ppa FactsDocument4 pagesNea Ppa FactsdipeshNo ratings yet
- Slope WDocument3 pagesSlope WdipeshNo ratings yet
- 20 Census 2011 District SindhuliDocument128 pages20 Census 2011 District SindhulidipeshNo ratings yet
- Slope PatanDocument1 pageSlope PatandipeshNo ratings yet
- 921-Article Text-3419-1-10-20220131Document11 pages921-Article Text-3419-1-10-20220131Irfan ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- What Is Talent ManagementDocument12 pagesWhat Is Talent ManagementShivangi PatelNo ratings yet
- Job Description HR ManagerDocument2 pagesJob Description HR ManagerTalha AamirNo ratings yet
- Succession Planning Practices and Their Impact On Employee RetentionDocument80 pagesSuccession Planning Practices and Their Impact On Employee RetentionOUSMAN SEIDNo ratings yet
- NFCC Talent Management Toolkit Interactive Document V2.Feb24 3Document12 pagesNFCC Talent Management Toolkit Interactive Document V2.Feb24 3gegeomar123No ratings yet
- Succession Planning in The Government SectorDocument17 pagesSuccession Planning in The Government Sectorpramodtiwari1989100% (1)
- Ey The Call For A More Strategic HRDocument12 pagesEy The Call For A More Strategic HRRamakrishnan KrNo ratings yet
- Talent Management - A Strategic PriorityDocument7 pagesTalent Management - A Strategic Prioritytaqui tazwarNo ratings yet
- Talent Identification Development ToolsDocument18 pagesTalent Identification Development ToolsshaleniNo ratings yet
- 02 2200 FinalDocument13 pages02 2200 FinalTaarikNo ratings yet
- VP EB AIESEC Stockholm Application Booklet 2014 - 2015Document14 pagesVP EB AIESEC Stockholm Application Booklet 2014 - 2015AIESECstockholmNo ratings yet
- Udemy 2023 TrendingSkillsGuide ENDocument17 pagesUdemy 2023 TrendingSkillsGuide ENAjay Patel100% (1)
- Talent Attraction and SelectionDocument52 pagesTalent Attraction and SelectionArggie Roy BusallaNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and Remuneration As Main Dimensions of Talent ManagementDocument10 pagesPerformance Management and Remuneration As Main Dimensions of Talent ManagementZIDANENo ratings yet
- Dave Ulrich On Whats Next For HRDocument21 pagesDave Ulrich On Whats Next For HRRachna MehraNo ratings yet
- HRM Talent ManagementDocument19 pagesHRM Talent ManagementJugal Shah100% (2)
- Csod WP Nonexistent TM Costing Money 022015Document25 pagesCsod WP Nonexistent TM Costing Money 022015spirit571No ratings yet
- Workday Hewlett Packard Company Case StudyDocument3 pagesWorkday Hewlett Packard Company Case Studynyi naingNo ratings yet
- SHRM at NestleDocument23 pagesSHRM at NestlesamreenNo ratings yet
- Best Workplaces 2012: Case Studies On HR Best PracticesDocument50 pagesBest Workplaces 2012: Case Studies On HR Best PracticesAnuja BhakuniNo ratings yet
- MBA 405: Talent Management: Faculty Name: Ms. Neetu Deptt. of MGMT StudiesDocument264 pagesMBA 405: Talent Management: Faculty Name: Ms. Neetu Deptt. of MGMT StudiesSongs Punjabi Share100% (6)
- Assessment Brief - 5HR02Document11 pagesAssessment Brief - 5HR02IBRAHIM ALQUHAYZ0% (1)
- Talent Management: Self-Assessment Questions & AnswersDocument7 pagesTalent Management: Self-Assessment Questions & AnswersImran BashirNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in BusinessDocument11 pagesAssignment 1 Front Sheet: Qualification BTEC Level 5 HND Diploma in BusinessQuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BBPB2103 OUM Human Resource Management May 2023Document17 pagesBBPB2103 OUM Human Resource Management May 2023KogiNo ratings yet
- David M. Alper: Learning and Development LeaderDocument2 pagesDavid M. Alper: Learning and Development LeaderDavidNo ratings yet
- High-Impact Succession Management: Executive SummaryDocument18 pagesHigh-Impact Succession Management: Executive SummaryLorena Garcia100% (1)
- CDHX and Bootcamp Calendar 2024newDocument6 pagesCDHX and Bootcamp Calendar 2024newtheresaNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument9 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionNikhita KrishnaiahNo ratings yet
- Compensation and Benefits - EbookDocument194 pagesCompensation and Benefits - EbookAnubha TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceFrom EverandThe Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (22)
- The 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleFrom EverandThe 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- The Way of the Shepherd: Seven Secrets to Managing Productive PeopleFrom EverandThe Way of the Shepherd: Seven Secrets to Managing Productive PeopleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (112)
- Organizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementFrom EverandOrganizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementNo ratings yet
- 12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerFrom Everand12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerNo ratings yet
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Five Dysfunctions of a Team SummaryFrom EverandThe Five Dysfunctions of a Team SummaryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (59)
- Coaching and Mentoring: Practical Techniques for Developing Learning and PerformanceFrom EverandCoaching and Mentoring: Practical Techniques for Developing Learning and PerformanceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Powerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesFrom EverandPowerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Goal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsFrom EverandGoal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Getting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)From EverandGetting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeFrom EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (99)
- The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthFrom EverandThe Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (101)
- 50 Top Tools for Coaching, 3rd Edition: A Complete Toolkit for Developing and Empowering PeopleFrom Everand50 Top Tools for Coaching, 3rd Edition: A Complete Toolkit for Developing and Empowering PeopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Hire With Your Head: Using Performance-Based Hiring to Build Outstanding Diverse TeamsFrom EverandHire With Your Head: Using Performance-Based Hiring to Build Outstanding Diverse TeamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- The Art of Active Listening: How People at Work Feel Heard, Valued, and UnderstoodFrom EverandThe Art of Active Listening: How People at Work Feel Heard, Valued, and UnderstoodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Summary: Who Moved My Cheese?: An A-Mazing Way to Deal with Change in Your Work and in Your Life by Spencer Johnson M.D. and Kenneth Blanchard: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Who Moved My Cheese?: An A-Mazing Way to Deal with Change in Your Work and in Your Life by Spencer Johnson M.D. and Kenneth Blanchard: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Inspiring Accountability in the Workplace: Unlocking the brain's secrets to employee engagement, accountability, and resultsFrom EverandInspiring Accountability in the Workplace: Unlocking the brain's secrets to employee engagement, accountability, and resultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Leadership's Perfect Storm: What Millennials Are Teaching Us About Possibilities, Passion and PurposeFrom EverandLeadership's Perfect Storm: What Millennials Are Teaching Us About Possibilities, Passion and PurposeNo ratings yet
- 101 Tough Conversations to Have with Employees: A Manager's Guide to Addressing Performance, Conduct, and Discipline ChallengesFrom Everand101 Tough Conversations to Have with Employees: A Manager's Guide to Addressing Performance, Conduct, and Discipline ChallengesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Working with AI: Real Stories of Human-Machine Collaboration (Management on the Cutting Edge)From EverandWorking with AI: Real Stories of Human-Machine Collaboration (Management on the Cutting Edge)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Essential HR Handbook, 10th Anniversary Edition: A Quick and Handy Resource for Any Manager or HR ProfessionalFrom EverandThe Essential HR Handbook, 10th Anniversary Edition: A Quick and Handy Resource for Any Manager or HR ProfessionalRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Irresistible: The Seven Secrets of the World's Most Enduring, Employee-Focused OrganizationsFrom EverandIrresistible: The Seven Secrets of the World's Most Enduring, Employee-Focused OrganizationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Profit Works: Unravel the Complexity of Incentive Plans to Increase Employee Productivity, Cultivate an Engaged Workforce, and Maximize Your Company's PotentialFrom EverandProfit Works: Unravel the Complexity of Incentive Plans to Increase Employee Productivity, Cultivate an Engaged Workforce, and Maximize Your Company's PotentialRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Founder & The Force Multiplier: How Entrepreneurs and Executive Assistants Achieve More TogetherFrom EverandThe Founder & The Force Multiplier: How Entrepreneurs and Executive Assistants Achieve More TogetherNo ratings yet