Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Series #5
Uploaded by
nafaamezzoudjOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Series #5
Uploaded by
nafaamezzoudjCopyright:
Available Formats
Prof. R.
AYACHE TUTORIAL SERIES N° 5 : Refraction at Spherical Surfaces February 2024
University of Batna2
Faculty of Medicine
Pharmacy Department
Module of Pharmaceutical Physics
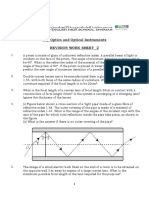
Exercise N°1:
- Is the crown glass spherical surface drawn below converging or diverging?
- What is its power if its radius of curvature is 15.00 mm?
- Locate and label F′.
Exercise N°2:
An object is located 50.00 cm to the left of a +5.00 D spherical crown glass surface (n=1.52). How
far is the image from the apex of the surface? Is the image real or virtual? Is it erect or inverted? If
the object is 3.00 cm in height, what is the height of the image?
Exercise N°3:
Show that for refraction at a concave spherical surface (separating glass-air medium), the distance
of the object should be greater than three times the radius of curvature of the refracting surface for
the image to be real.
Exercise N°4:
A convex surface of radius of curvature 40 cm separates two media of refractive indices 4/3 and
1.50. An object is kept in the first medium at a distance of 20 cm from the surface.
Calculate the position of the image.
Exercise N°5:
The eye can be regarded as a single spherical refracting surface of radius of curvature of cornea 7.8
mm, separating two media of refractive indices 1.00 and 1.34. Calculate the distance from the
refracting surface at which a parallel beam of light will come to focus.
You might also like
- Interceptive Orthodontics: A Practical Guide to Occlusal ManagementFrom EverandInterceptive Orthodontics: A Practical Guide to Occlusal ManagementNo ratings yet
- VISN1111 Geometrical and Physical Optics 2013 Tutorial-4Document1 pageVISN1111 Geometrical and Physical Optics 2013 Tutorial-4shadowosNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision On Light (Calculation) : o e o e o e o e o e o e o e o eDocument1 pagePhysics Revision On Light (Calculation) : o e o e o e o e o e o e o e o eLim JingNo ratings yet
- CH. LIGHT-MLP - 2 (2023-24) (To Take Printout For Class Discussion)Document2 pagesCH. LIGHT-MLP - 2 (2023-24) (To Take Printout For Class Discussion)DhdubNo ratings yet
- Optics Class 10 PhysicsDocument16 pagesOptics Class 10 PhysicsKumkum KumariNo ratings yet
- Phy - Wave OpticsDocument2 pagesPhy - Wave Opticsdebadrita senguptaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Term 2 Physics ActivityDocument8 pagesClass 12 Term 2 Physics Activitysuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Chap1-Geometrical Optics - ExercisesDocument3 pagesChap1-Geometrical Optics - ExercisesReema HlohNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Document7 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Saji JayarajNo ratings yet
- Class X PracticalsDocument14 pagesClass X PracticalsGopika RanaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics: Reading: OutlineDocument6 pagesPhysics 11 Chapter 18: Ray Optics: Reading: OutlinesenjicsNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics AssgnDocument3 pagesRay Optics AssgnHimanshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solution of Reflection and RefractionDocument17 pagesExercise Solution of Reflection and RefractioniTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- Light WorksheetDocument1 pageLight WorksheetKanishka ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Homework 17Document4 pagesHomework 17AngelNo ratings yet
- 10th Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-4Document4 pages10th Reflection and Refraction of Light Cbse Test Paper Solved-4ashokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Geometric OpticsDocument2 pagesChapter 25: Geometric OpticsAlarcon KendrickNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum IDocument6 pagesLaporan Praktikum IIrfan fajrulNo ratings yet
- Optical Equipment "Lup and Convex Lens ": Practicum Report General PhysicsDocument11 pagesOptical Equipment "Lup and Convex Lens ": Practicum Report General PhysicsJuwita PardedeNo ratings yet
- 7TH Week LensesDocument7 pages7TH Week LensesMira VeranoNo ratings yet
- Optics F 1 Ass 1Document11 pagesOptics F 1 Ass 1NikhilPrakashNo ratings yet
- Reflection Light 3Document31 pagesReflection Light 3api-296824694No ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction of Light (Revision Questions) : Very Short Answer Type (1 Mark)Document10 pagesReflection & Refraction of Light (Revision Questions) : Very Short Answer Type (1 Mark)Muthu KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- CbseDocument15 pagesCbseYaaroNo ratings yet
- Physics 30 Lesson 9 Optics - Thin Lenses: Refraction 2 Refraction 1Document11 pagesPhysics 30 Lesson 9 Optics - Thin Lenses: Refraction 2 Refraction 1John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Light - Intext & ExerciseDocument8 pagesLight - Intext & ExerciseTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Title Allocated Marks Marks: 15 SEPTEMBER 2015Document18 pagesTitle Allocated Marks Marks: 15 SEPTEMBER 2015AisyahNo ratings yet
- Light 1Document2 pagesLight 1SUSMIT SAHANo ratings yet
- Q.2. Srlu W3 G10Document6 pagesQ.2. Srlu W3 G10Pamela IndosoNo ratings yet
- Science Class-10th Physics 5Document7 pagesScience Class-10th Physics 5JjjjNo ratings yet
- To Study Reflection in Concave Mirror - Physics Astronomy Project TopicsDocument4 pagesTo Study Reflection in Concave Mirror - Physics Astronomy Project TopicsramNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual Science Class XDocument85 pagesLaboratory Manual Science Class Xkaviya.iseNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Series #6Document1 pageTutorial Series #6nafaamezzoudjNo ratings yet
- Exercise The MicroscopeDocument15 pagesExercise The Microscopemydiamondstar17No ratings yet
- UNIT 6: Optics - Ray Optics: Question BankDocument4 pagesUNIT 6: Optics - Ray Optics: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics Type 2 PART 2 of 2 ENGDocument27 pagesGeometrical Optics Type 2 PART 2 of 2 ENGRenu SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Compound Microscope PDFDocument9 pagesThe Compound Microscope PDFSushi LushyNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Focal-Length.Document11 pagesDetermination of The Focal-Length.mohammed1998No ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Intext QuestionsDocument8 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 10 Intext QuestionsDebsuvro RoyNo ratings yet
- All Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & RefractionDocument3 pagesAll Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & Refractionshivanshu kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument4 pagesReflection of LighthelenNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Assignment3Document3 pagesRay Optics Assignment3hsofficial910No ratings yet
- OpticsDocument27 pagesOpticsSiddharth AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesLight Reflection and RefractionShaurya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Mirror Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesMirror Worksheet PDFLadylane Carol Paras Puducay0% (1)
- 12 Physics Notes Ch09 Rayoptics and Optical InstrumentsDocument5 pages12 Physics Notes Ch09 Rayoptics and Optical InstrumentsMayank SainiNo ratings yet
- Properties of LightDocument10 pagesProperties of LightKesanam SpNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Optics 3Document1 pageWorksheet Optics 3Anagha Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Light - Class WorkDocument6 pagesLight - Class Workarunkumar0909iqNo ratings yet
- Optics 10Document24 pagesOptics 10Uday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics 2Document2 pagesRay Optics 2AryaNo ratings yet
- ph104 Exp08Document18 pagesph104 Exp08mimiikebunnaNo ratings yet
- Science Pp3 - Unit 2Document37 pagesScience Pp3 - Unit 2EmadElDinEzzatNo ratings yet
- Soal Daily Test Static Optics - 1Document3 pagesSoal Daily Test Static Optics - 1Gregorius Bryan H RNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Series #7Document1 pageTutorial Series #7nafaamezzoudjNo ratings yet
- 2224 - Physics (IIT 4)Document4 pages2224 - Physics (IIT 4)1harshikaNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 1 Micros PDFDocument4 pagesExercise No 1 Micros PDFAlthea ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Viewing the Constellations with Binoculars: 250+ Wonderful Sky Objects to See and ExploreFrom EverandViewing the Constellations with Binoculars: 250+ Wonderful Sky Objects to See and ExploreNo ratings yet