Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iom Finals Notes
Uploaded by
Katrine Siean Batoon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views5 pagesIom Finals Notes
Uploaded by
Katrine Siean BatoonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
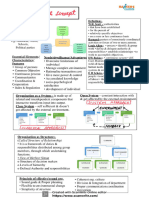
MODULE 1: PLANNING 3 CRITICAL INNOVATION STRATEGIES
Exploration, External Coordination,
10 MANAGER ROLES Entrepreneurship
INFORMATIONAL
- Monitor 3 TYPES OF CURRENT PROBLEMS OD CAN
- Disseminator SOLVE
- Spokesperson - Merger/acquisitions
INTERPERSONAL - Organizational decline
- Figurehead - Conflict management
- Leader
- Liaison OD ACTIVITIES
DECISIONAL - Team-building
- Entrepreneur - Survey
- Disturbance Handler - Large group
- Resource Allocator
- Negotiator CHANGES IN OD
- Unfreezing
LEVELS OF GOALS AND PLANS (PYRAMID) - Changing
Mission Statement - Refreezing
Strategic Goals or Plans – top managers
Tactical Goals or Plans – middle managers MODULE 3: LEADING
Operational Goals or Plans – lower levels
COMPONENTS OF ATTITUDE
6 PURPOSE OF GOALS AND PLANS - Cognitions – thoughts
- Legitimacy - Affective – feelings
- Source of motivation and commitment - Behavior
- Resource allocation
- Guides to action HIGH- PERFORMANCE WORK ATTITUDES
- Rationale for decisions - Job satisfaction
- Standard of performance - Organizational Commitment
5 ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING PROCESS 4 TYPES OF PERCEPTUAL
1. Develop the plan ERROR/DISTORTIONS
2. Translate the plan 1. Stereotyping – generalizations
3. Plan operations 2. Halo effect – one impression
4. Execute the plan 3. Projection – personal traits in other
5. Monitor and learn people
4. Perceptual defense – protect
4 MAJOR ACTIVITIES THAT MAKE MBO themselves
SUCCESSFUL
- Set goals 2 TYPES OF ATTRIBUTIONS
- Develop action plans - Internal – characteristics -> behavior
- Review progress - External – situation -> behavior
- Appraise overall performance
FACTORS AFFECTING ATTRIBUTION
2 TYPES OF DECISIONS Distinctiveness, consistency, consensus
1. Programmed
2. Non-programmed 2 ATTRIBUTION ERRORS
- Fundamental attribution errors
3 TYPES OF DECISION-MAKING MODELS (underestimate external)
Classical, Administrative, Political - Self-serving bias (overestimate internal)
MODULE 2: ORGANIZING PERCEPTION PROCESS
1. Observe
5 APPROACHES OF STRUCTURAL DESIGN 2. Screen & select
- Vertical Function 3. Organize
- Divisional Function
- Matrix BIG 5 PERSONALITY FACTORS
- Team-based Approach - Extroversion
- Virtual network - Agreeableness
- Conscientiousness
4 ROLES IN ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE - Emotional stability
1. Inventor - Openness to experience
2. Sponsor
3. Champion 4 BASIC EQ COMPONENTS
4. Critic - Self-awareness – basis
- Self-management – control
- Social awareness – understand
- Relationship management – connect
4 AREA RELATED TO PERSONALITY 2 MAJOR FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Locus of control – primary responsibility - Income statement – profit – loss
- Authoritarianism – power & status - Balance sheet – financial position
- Machiavellianism – manipulation
- Problem-solving Styles TYPES OF RATIOS
𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
Liquidity ratio =
𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑙𝑖𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑒𝑠
4 PROBLEM SOLVING STYLES 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑠𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑝𝑢𝑟𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝑜𝑟𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑠
Activity ratio = ;=
- Sensation-thinking 𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑦 𝑐𝑢𝑠𝑡𝑜𝑚𝑒𝑟 𝑖𝑛𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑟𝑖𝑒𝑠
𝑔𝑟𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝑛𝑒𝑡 𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒
- Intuitive-thinking Profitability ratio = ;=
𝑠𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
- Sensation-feeling 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑒𝑏𝑡
Leverage ratio =
- Intuitive-feeling 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠
LEARNING STYLE TYPES 2 APPROACHES TO CONTROL
1. Diverger - Hierarchical control – use of rules
2. Assimilator - Decentralization – culture, group norms
3. Converger
4. Accommodator TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
TECHNIQUES
FORMS OF STRESSORS - Quality circles – 6-12 volunteers
- Task demands - Benchmarking – continuous process
- Interpersonal demands - Six sigma – higher quality
- Reduced cycle time – steps taken
TYPES OF LEADERS - Continuous improvement – large
- Charismatic – motivate number
- Transformational – innovator
- Transactional – clarifies role NEW FINANCIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS
- Economic Value-Added (EVA) – after
TYPES OF FOLLOWERS tax
- Alienated follower – passive - Market Value-Added (MVA) – stock
- Conformist – no critical thinking market
- Pragmatic survivor – all 4 - Activity-Based Costing (ABC) – various
- Passive follower – none activities
- Effective follower – thinking, - Corporate Governance – corporate
participation owners protected
TYPES OF LEADERSHIP
- Servant – fulfill subordinate needs MODULE 5: MANAGING PRODUCT &
- Moral – right from wrong SERVICE OPERATIONS
SOURCES OF POWER 4 CATEGORIES OF COSTS OF QUALITY
Position power (traditional) (COQ)
- Legitimate – formal - Appraisal costs – conformance to ASQ
- Reward – bestow rewards - Internal failure costs – defects before
- Coercive – punish - External failure costs – defects after
Personal power (internal) - Prevention costs – prevent or avoid
- Expert – special knowledge
- Referent – respect, admiration DIMENSIONS OF PRODUCT QUALITY
Other - Performance
- Information - Features
- Network of Relationships - Reliability
- Personal Effort - Conformance
- Durability
- Serviceability
MODULE 4: CONTROLLING - Aesthetics
- Perceived Quality
STEPS OF FEEDBACK CONTROL
1. Establish standards of performance QUALITY ORGANIZATIONS
2. Measure actual performance - American Society for Quality (ASQ)
3. Compare performance to standards - International Organization for
4. Take corrective action Standardization (ISO)
- US National Institute of Standards and
BUDGETS THAT MANAGERS USE Technology (NIST)
- Expense budget – anticipated
- Revenue budget – forecasted revenue TYPE OF DEFECTS
- Cash budget – estimate cash flows - Critical defects
- Capital budget – investments - Major defects
o Top-down – middle & low - Minor defects
o Bottom-up – lower level to up
3 GENERAL INSPECTION LEVELS 5 TYPES OF MANUFACTURING PROCESSES
- Level I (reduced inspection) - Repetitive Manufacturing
- Level II (normal inspection) - Discrete Manufacturing
- Level III (tightened inspection) - Job Shop Manufacturing
- Continuous Process Manufacturing
DEMING’S 14 POINTS - Batch Process Manufacturing
1. Create “constancy of purpose” that
encourages everyone to cooperate in 10 PRINCIPLES OF FACILITIES LAYOUT
continually improving quality and 1. Minimum Movement
meeting customer needs. 2. Space Utilization
2. “Adopt the new philosophy” of defect 3. Flexibility
prevention instead of the concept of 4. Interdependence
“acceptable quality level” monitored by 5. Overall Integration
defect detection. 6. Safety
3. End dependence on mass inspection by 7. Smooth Flow
building in quality from the start. 8. Economy
4. End the practice of purchasing solely on 9. Supervision
price; develop long-term relationships 10. Satisfaction
with single suppliers based on product
quality and trust. 8 FACTORS THAT GREATLY AFFECT
5. Improve constantly and forever the FACILITY LAYOUTS
system of production and service, to - Materials
improve quality and productivity, and - Machinery
thus constantly decrease costs. - Labor
6. Institute modern methods of training in - Material Handling
the organization’s philosophy and goals - Waiting Time
as well as job performance. - Auxiliary Services
7. Institute leadership, so that supervisors - The Building
become coaches to help workers do a - Future Changes
better job.
8. Eliminate fear, which impedes employee TYPES OF FACILITIES LAYOUT
performance. - Process Layout
9. Break down barriers between - Product Layout
departments. - Cellular Layout
10. Eliminate numerical goals and - Fixed-Position Layout
slogans—they don’t work.
11. Eliminate work standards and numerical MODULE 6: MARKETING & THE ENGINEER
quotas, which emphasize quantity rather
than quality. TYPES OF MARKETING RELATIONSHIPS
12. Remove barriers that rob employees of - Transaction-based
their pride of workmanship. - More Sustained
13. Institute a vigorous program of - Highly-committed
education and training.
14. Structure the organization for quality. ENGINEERING INVOLVEMENT IN
MARKETING INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTS
4 MAIN TYPES OF SECTORS - Installations – large, durable custom
1. Primary: Raw Materials - Accessories – shorter-lived capital good
2. Secondary: Manufacturing - Raw materials – agricultural products
3. Tertiary: Service - Process materials – change form
4. Quaternary: Knowledge - Component parts – do not lose identity
- Fabricated items – custom-made
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SERVICE - Maintenance, repair, and operation
SECTOR - Services – incidental product use
- Intangibility
- Real-time and customer presence AFTER-SALES SERVICES
- Inability to be inventoried - Usage – guidance
- Challenged in staffing - Education – user training
- Assurance – guarantee, warranty
THE DIMENSIONS OF SERVICE QUALITY - Assistance – product configuration
- Tangibility - Support – online and offline support
- Relailability - Reward – loyalty rewards
- Responsiveness
- Assurance ENGINEERS ARE USED IN SERVICE DEPTS
- Empathy AS:
4 TYPES OF MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS - Backup to crews of technicians
- Custom Manufacturing Systems - Agents involved with client-related tasks
- Intermittent Manufacturing Systems after the sales transaction
- Continuous Manufacturing Systems - Trainer to extensive systems
- Flexible Manufacturing Systems
MODULE 7: ETHICS & SOCIAL MODULE 8: CONFLICT RESOLUTION &
RESPONSIBILITY NEGIOTATION SKILLS
3 DOMAINS OF HUMAN ACTION FORMS OF CONFLICT
1. Domain of Codified Law - Interpersonal
2. Domain of Ethics - Intrapersonal
3. Domain of Free Choice - Intragroup
- Intergroup
CRITERIA FOR ETHICAL DECISION-MAKING
1. Utilitarian Approach NEGOTIATION PROCESS
2. Individualism Approach 1. Investigation and preparation
3. Moral Rights Approach 2. Preparation
6 MORAL RIGHTS 3. Bargaining
a. The right to free consent 4. Agreement
b. The right to privacy
c. The right of freedom of TYPES OF CONFLICTS IN PROFESSIONAL
conscience SETTINGS
d. The right of free speech - Task Conflict
e. The right to due process - Relationship Conflict
f. The right to life and safety - Value Conflict
4. Justice Approach
TYPES OF JUSTICE SOURCES OF CONFLICT
a. Procedural - Limited Resources
b. Compensatory - Different Goals
c. Distributive - Ineffective Cooperation
- Change
3 LEVELS OF PERSONAL MORAL
DEVELOPMENT IMPACT OF UNRESOLVED CONFLICTS ON
1. Preconventional (to avoid punishment) ORGANIZATIONS
2. Conventional (lives up to expectations) - Decreased Job Satisfaction
3. Postconventional (self-chosen) - Toxic Work Environment
- Inefficiencies
PYRAMID OF CSR
NEGOTIATION MODELS
- Win-win approach
- Win-lose approach
- Lose-lose approach
- Compromise approach
STRATEGIES FOR NEGOTIATING CONFLICT
EFFECTIVELY
1. Clearly define goals
2. Consider the other party’s background
3. Be proactive
4. Use established forums for negotiating
conflicts
5. Be flexible with time
CORE VALUES OF ORGANIZATIONAL
ETHICS 6. Focus on creating value
- Responsibility
SKILLS FOR CONFLICT NEGOTIATION
- Result-oriented
- Research
- Respect
- Emotional Intelligence
- Trustworthiness
- Expectation Management
- Justice
- Empathy
- Caring
- Honour
- Persistence
THE ETHICAL ORGANIZATION
MODULE 9: BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY
4 ACTION FRAMEWORK
1. Elimate
2. Reduce
3. Raise
4. Create
6 STAGES OF THE BUYS EXPERIENCE
CYCLE
1. Purchase
2. Delivery
3. Use
4. Supplements
5. Maintenance
6. Disposal
6 KEY PRINCIPLES (THE HEART)
1. Reconstruct Market Boundaries
2. Focus on the Big Picture
3. Reach Beyond Existing Demand
4. Get the Strategic Sequence Right
5. Overcome Organizational Hurdles
6. Build Execution into Strategy
3 E PRINCIPLES OF FAIR PROCESS
Engagement, Explanation, Expectation clarity
You might also like
- Bes 3143 Lesson 1Document2 pagesBes 3143 Lesson 1yoongidotexe420No ratings yet
- Management reviewer 1- 8.docxDocument12 pagesManagement reviewer 1- 8.docxaceadiova564No ratings yet
- Action Plan - Final FrameworkDocument2 pagesAction Plan - Final FrameworkthienlcapitalNo ratings yet
- Xii BS at A GlanceDocument3 pagesXii BS at A GlancePreeti MuralidharNo ratings yet
- Principles of ManagementDocument74 pagesPrinciples of ManagementsangeshnnNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Commerce)Document9 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Commerce)Naina MalikNo ratings yet
- Midterms Entrepreneurial Mind ReviewerDocument3 pagesMidterms Entrepreneurial Mind ReviewerPrince LitchNo ratings yet
- Organization Theory - SynopsisDocument19 pagesOrganization Theory - Synopsisvv.vaishali142No ratings yet
- Sba Reviewer 2Document7 pagesSba Reviewer 2Erica FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- An Overview of OBDocument37 pagesAn Overview of OBDevrajNo ratings yet
- BNAD 302 Exam 2 Review SP22Document2 pagesBNAD 302 Exam 2 Review SP22Quế Chi Thiều NgọcNo ratings yet
- Short Grade 11 Org-Man-ReviewerDocument4 pagesShort Grade 11 Org-Man-Reviewerrica maeNo ratings yet
- 5 Dimensions of Leadership CompetencyDocument3 pages5 Dimensions of Leadership CompetencyPatty Viray100% (1)
- Industrial Organization and Management: REVIEWERDocument8 pagesIndustrial Organization and Management: REVIEWERGuian RomasantaNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Commerce)Document8 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Commerce)hussainhaiar110No ratings yet
- How Businesses Operate and Manage to Achieve ObjectivesDocument69 pagesHow Businesses Operate and Manage to Achieve Objectivesmy tràNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 1 PDFEYENNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 1 PDFEYENNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Competencies and Career OpportunitiesDocument7 pagesEntrepreneurial Competencies and Career OpportunitiesDimple MontemayorNo ratings yet
- BASIC-CONSIDERATIONS-IN-MASDocument2 pagesBASIC-CONSIDERATIONS-IN-MASmonicafrancisgarcesNo ratings yet
- Information & DMDocument4 pagesInformation & DMRatna Dwi WulandariNo ratings yet
- ORGANIZATION MANAGEMENTDocument49 pagesORGANIZATION MANAGEMENTasentsa92% (13)
- Basics of Management Functions and PrinciplesDocument40 pagesBasics of Management Functions and PrinciplesSujal GolarNo ratings yet
- Acfrogadjpwf2dlaginhz8stqbjieccjmnqsrppknerbnl2r6fueo7srlgrdglmolt K71ejsh3sywfkqwp419hd e Czadjk1a9ztqot9ui1e2yn9-Yegxmkopmoj0a9kbodzvkzin2uc6fmudxDocument13 pagesAcfrogadjpwf2dlaginhz8stqbjieccjmnqsrppknerbnl2r6fueo7srlgrdglmolt K71ejsh3sywfkqwp419hd e Czadjk1a9ztqot9ui1e2yn9-Yegxmkopmoj0a9kbodzvkzin2uc6fmudxfeteneNo ratings yet
- Part 01 The Entrepreneurial PerspectiveDocument8 pagesPart 01 The Entrepreneurial PerspectiveMohd Daud MDMSNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning ModelDocument53 pagesStrategic Planning ModelSui Yuxuan100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To ManagementDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To ManagementNur Hidayah Bustam100% (3)
- TLE 10 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument1 pageTLE 10 2nd Quarter ReviewerSchool Purpose100% (2)
- Week 1 - Chapter 1Document55 pagesWeek 1 - Chapter 1Châu GiangNo ratings yet
- Phase 1Document38 pagesPhase 1nikolas85No ratings yet
- BA NotesDocument20 pagesBA NotesTin Tin MoeNo ratings yet
- Department Manager, or Office ManagerDocument6 pagesDepartment Manager, or Office ManagerMia KingNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveNina ManginsayNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour OverviewDocument37 pagesOrganisational Behaviour Overviewsk5335No ratings yet
- Management Control Systems: Chapter-3 Designing and Evaluating MCSDocument15 pagesManagement Control Systems: Chapter-3 Designing and Evaluating MCSPUTTU GURU PRASAD SENGUNTHA MUDALIARNo ratings yet
- Mo CS 1028Document2 pagesMo CS 1028Fred CheungNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning ADocument26 pagesStrategic Planning AmelissaNo ratings yet
- Organizations DefinedDocument13 pagesOrganizations DefinedMara JavierNo ratings yet
- Management, Behavioral & Social SciencesDocument41 pagesManagement, Behavioral & Social SciencesSurangaGNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 2 NotesDocument12 pagesChap 1 2 NotesRosemenjelNo ratings yet
- Business Management Technopreneur GuideDocument5 pagesBusiness Management Technopreneur GuideVoltaire Eroy Lopez IINo ratings yet
- fundamentals of management and organisationDocument38 pagesfundamentals of management and organisationjandrewNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management Process PlanningDocument11 pagesNursing Management Process PlanningMiden AlbanoNo ratings yet
- Management Unit 1Document7 pagesManagement Unit 1surabhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Professional Attributes of Management ConsultantsDocument1 pageChapter 4 Professional Attributes of Management ConsultantsLeonilaEnriquezNo ratings yet
- Managing The ManagersDocument342 pagesManaging The ManagersAnjum MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3marisNo ratings yet
- Corporate Strategic Planning: The Complete ProcessDocument48 pagesCorporate Strategic Planning: The Complete ProcessChristian Mark PalayNo ratings yet
- MG1351 Hand OutsDocument38 pagesMG1351 Hand Outss.reeganNo ratings yet
- SBL SummaryDocument19 pagesSBL SummaryKub100% (1)
- 1 ManagementDocument7 pages1 ManagementAudrey Ann AcobNo ratings yet
- OrgMan ReviewerDocument5 pagesOrgMan ReviewerChirsten ArabejoNo ratings yet
- Module 7 PlanningDocument6 pagesModule 7 PlanningMarla Brigitte GalvanNo ratings yet
- Management & Organization: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mehmet ERÇEKDocument40 pagesManagement & Organization: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mehmet ERÇEKSerhat ÇulhalıkNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Management The Function of the Mind in Determining, Teaching and Installing Methods of Least WasteFrom EverandThe Psychology of Management The Function of the Mind in Determining, Teaching and Installing Methods of Least WasteNo ratings yet
- The "How to" of Performance ManagementFrom EverandThe "How to" of Performance ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chief Executive Team: The Transformation of LeadershipFrom EverandChief Executive Team: The Transformation of LeadershipRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ignite: The Entrepreneur's Journey: The Entrepreneur's Journey: Unleashing Entrepreneurial SuccessFrom EverandIgnite: The Entrepreneur's Journey: The Entrepreneur's Journey: Unleashing Entrepreneurial SuccessNo ratings yet
- LWR Rise of Filipino Nationalism GRP 5Document13 pagesLWR Rise of Filipino Nationalism GRP 5Katrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- Group 9Document17 pagesGroup 9Katrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- To The Young Women of MalolosDocument7 pagesTo The Young Women of MalolosKatrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- g8 The Indolence of FilipinosDocument8 pagesg8 The Indolence of FilipinosKatrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- B STS Technology Evidences - MesoamericaDocument4 pagesB STS Technology Evidences - MesoamericaKatrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- Price vs Quantity Demanded & Supplied ChartDocument2 pagesPrice vs Quantity Demanded & Supplied ChartKatrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- STS - Science, Technology, and Society (BOOK)Document141 pagesSTS - Science, Technology, and Society (BOOK)Katrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- Chemlab Final LabrportDocument6 pagesChemlab Final LabrportKatrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Monopoly & OligopolyDocument24 pagesModule 7 - Monopoly & OligopolyKatrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - The Price System and The Case For FreeDocument16 pagesModule 6 - The Price System and The Case For FreeKatrine Siean BatoonNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in English 10: Prepared By: Aira C. Mirandilla L. ObjectivesDocument11 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in English 10: Prepared By: Aira C. Mirandilla L. ObjectivesMae Mallapre100% (10)
- 2009 Bar Exam Criminal Law QuestionsDocument25 pages2009 Bar Exam Criminal Law QuestionsJonny Duppses100% (2)
- Azure Blockchain Workbench guideDocument183 pagesAzure Blockchain Workbench guideAhmed AyadNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Third Circuit, 952 F.2d 742, 3rd Cir. (1991)Document22 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Third Circuit, 952 F.2d 742, 3rd Cir. (1991)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crime and Law ClassDocument99 pagesCyber Crime and Law ClassMohd ShifanNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Drug and Substance Abuse Prevention Programs PDFDocument245 pagesEffectiveness of Drug and Substance Abuse Prevention Programs PDFjohn gooco100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Teaching English in The Elementary GradesDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Teaching English in The Elementary GradesMedz Legaspi BilaroNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Prefabricated MyofunctionalDocument10 pagesEffectiveness of Prefabricated MyofunctionalAdina SerbanNo ratings yet
- CS 401 Artificial Intelligence: Zain - Iqbal@nu - Edu.pkDocument40 pagesCS 401 Artificial Intelligence: Zain - Iqbal@nu - Edu.pkHassan RazaNo ratings yet
- Armenian Question in Tasvir-İ Efkar Between 1914 and 1918Document152 pagesArmenian Question in Tasvir-İ Efkar Between 1914 and 1918Gültekin ÖNCÜNo ratings yet
- Newsletter 9th October PDFDocument6 pagesNewsletter 9th October PDFcaseliseNo ratings yet
- Document PDFDocument16 pagesDocument PDFnelson_herreraNo ratings yet
- Midea R410A T3 50Hz Split Type Top-Dishcharge Series Technical Manual - V201707Document157 pagesMidea R410A T3 50Hz Split Type Top-Dishcharge Series Technical Manual - V201707kaleabNo ratings yet
- Juice in PakistanDocument9 pagesJuice in Pakistanrize1159100% (1)
- ĐỀ THI THỬ ĐH - Mã 129 (Smartie)Document6 pagesĐỀ THI THỬ ĐH - Mã 129 (Smartie)Hoang Huy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Advenginuse3 Ank Wbspa 16129Document32 pagesAdvenginuse3 Ank Wbspa 16129JMJPILOT75% (4)
- Exercise For FitnessDocument44 pagesExercise For FitnessSheena Mae Sube PoNo ratings yet
- Tugas B.INGGRIS ALANDocument4 pagesTugas B.INGGRIS ALANAlan GunawanNo ratings yet
- Decision Criteria For Ethical ReasoningDocument14 pagesDecision Criteria For Ethical ReasoningZara ImranNo ratings yet
- PESTLE analysis of M&S UK retail challengesDocument1 pagePESTLE analysis of M&S UK retail challengesMac Corleone0% (1)
- Statistical PhysicsDocument4 pagesStatistical PhysicsRenan ZortéaNo ratings yet
- Wayside Amenities GuidelinesDocument8 pagesWayside Amenities GuidelinesUbaid UllahNo ratings yet
- Wireless Local LoopDocument8 pagesWireless Local Loopapi-3827000100% (1)
- Meng Chen, Lan Xu, Linda Van Horn, Joann E. Manson, Katherine L. Tucker, Xihao Du, Nannan Feng, Shuang Rong, Victor W. ZhongDocument1 pageMeng Chen, Lan Xu, Linda Van Horn, Joann E. Manson, Katherine L. Tucker, Xihao Du, Nannan Feng, Shuang Rong, Victor W. ZhongTHLiewNo ratings yet
- AISD Fees Structure for 2023-24 Academic YearDocument2 pagesAISD Fees Structure for 2023-24 Academic YearKawsar AlamNo ratings yet
- Human Rights EducationDocument149 pagesHuman Rights EducationLeonard MamergaNo ratings yet
- Album China RayaDocument12 pagesAlbum China Rayaapitmelodi23No ratings yet
- German Modern Architecture Adn The Modern WomanDocument24 pagesGerman Modern Architecture Adn The Modern WomanUrsula ColemanNo ratings yet
- TQM Implementation in ToyotaDocument15 pagesTQM Implementation in ToyotaSaikat GhoshNo ratings yet
- Exam On Multiculturalism: - Acculturation Process of Immigrants From Central and Eastern Europe in SwedenDocument60 pagesExam On Multiculturalism: - Acculturation Process of Immigrants From Central and Eastern Europe in SwedenMarta santosNo ratings yet