Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Changes in Equilibrium Price and Output
Changes in Equilibrium Price and Output
Uploaded by
Johndhel CaumeranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Changes in Equilibrium Price and Output
Changes in Equilibrium Price and Output
Uploaded by
Johndhel CaumeranCopyright:
Available Formats
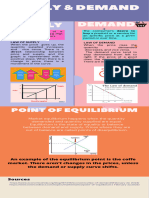
CHANGES IN EQUILIBRIUM PRICE AND OUTPUT SIMULTANEOUS CHANGES IN EQUILIBRIUM OF DEMAND AND SUPPLY
AND SIMULTANEOUS CHANGES IN DEMAND AND SUPPLY (EQUAL PROPORTION)
CHANGES IN THE EQUILIBRIUM PRICE AND OUTPUT
It means the increase or decrease in Demand or Supply. A situation when both demand and supply increase or decrease at the
It occurs due to a change in factors other than the price of a commodity same time
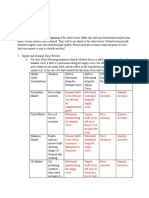
1. SHIFT IN SUPPLY ONLY (DEMAND REMAINS CONSTANT) A. Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Demand Curve to the right and
Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Supply curve to the Right ex. Due to Shift of the Supply Curve to the Right (Equal Proportion)
technological improvements When increase in Demand is equal to increase in Supply:
Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Supply curve to the Left ex. Due to Equilibrium price remains the same; equilibrium quantity increases
the effects of typhoon
2. SHIFT IN DEMAND ONLY (SUPPLY REMAINS CONSTANT)
Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Demand curve to the Right ex. Due
to Increase In Income
Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Demand curve to the Left ex. Due to
Change of Preference/Taste
1. SHIFT IN SUPPLY ONLY
Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Supply curve to the Right
Supply for a commodity increases while Demand remains Constant.
Decrease in Equilibrium Price but increase In Quantity
B. Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Demand Curve to the Right and
Shift of the Supply Curve to the Left (Equal Proportion)
When increase in Demand is equal to decrease in Supply:
Equilibrium price increases; equilibrium quantity remains the same
1. SHIFT IN SUPPLY ONLY
B. Market equilibrium with shift of the supply curve to the left
Supply for a commodity decreases while Demand remains Constant.
-Increase in Equilibrium Price but decrease in Quantity.
C. Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Demand Curve to the Left and
Shift of the Supply Curve to the Right (Equal Proportion)
When decrease in demand is equal to increase in supply:
Equilibrium price decreases; equilibrium quantity remains the same
2. SHIFT IN DEMAND ONLY
A. Market equilibrium with shift of the demand curve to the right
Demand for a commodity increases while supply is Constant.
-Equilibrium Price and Quantity Increases
D. Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Demand Curve to the Left and
Shift of the Supply Curve to the Left (Equal Proportion)
When decrease in demand is equal to decrease in supply:
Equilibrium price remains the same; equilibrium quantity decreases.
2. SHIFT IN DEMAND ONLY
B. Market Equilibrium with Shift of the Demand curve to the Left
Demand for a commodity decreases while
Supply is constant.
-Equilibrium Price and Quantity Decreases
A. Decrease in Demand > Decrease in Supply
When decrease in demand is proportionately more than decrease in
supply, then leftward shift in demand curve and supply curve:
equilibrium price falls/decreases and equilibrium quantity falls/
decreases
B. Decrease in Demand < Decrease in Supply F. Decrease in Demand < Increase in Supply
When decrease in demand is proportionately less than decrease in When decrease in demand is proportionately less than increase in
supply, then leftward shift in demand curve and supply curve: supply, then leftward shift in demand curve is proportionately less than
Equilibrium price rises/increases whereas, equilibrium quantity rightward shift in supply curve
falls/decreases Equilibrium price falls/decreases; equilibrium quantity rises/increases
G. Increase in Demand > Decrease in Supply
When increase in demand is proportionately more than decrease in
C. Increase in Demand > Increase in Supply
supply, then rightward shift in demand curve is proportionately more
When increase in demand is proportionately more than increase in
than leftward shift in supply curve:
supply then rightward shift in demand curve:
equilibrium price rises/increases; equilibrium quantity rises/ increases
Equilibrium price rises/increases and equilibrium quantity
rises/increases
H. Increase in Demand < Decrease in Supply
When increase in demand is proportionately less than decrease in
D. Increase in Demand < Increase in Supply supply then rightward shift in demand curve is proportionately less than
When increase in demand is proportionately less than increase in supply leftward shift in supply curve
then rightward shift in demand curve and supply curve equilibrium price rises/increases; equilibrium quantity falls/decreases
Equilibrium price falls/ decreases whereas, equilibrium quantity
rises/increases
E. Decrease in Demand > Increase in Supply
When decrease in demand is proportionately more than increase in
supply then leftward shift in demand curve is proportionately more than
rightward shift in supply curve:
equilibrium price falls; equilibrium quantity falls
You might also like
- Economics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4From EverandEconomics for CFA level 1 in just one week: CFA level 1, #4Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Applied Assessment. Demand and Supply BumanglagDocument4 pagesApplied Assessment. Demand and Supply BumanglagClinton John BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Notes On Demand, Supply, Single Shifts, and Double Shifts Principle of Microeconomics Notes On DemandDocument7 pagesNotes On Demand, Supply, Single Shifts, and Double Shifts Principle of Microeconomics Notes On DemandJoel C. BaccayNo ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Mumbai CxoDocument9 pagesMumbai CxopoonamNo ratings yet
- The Binary PlanDocument3 pagesThe Binary PlanShashikant MadkaikerNo ratings yet
- The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDocument3 pagesThe Market Forces of Supply and DemandAlba De Castro RísquezNo ratings yet
- Microecnomics PresentationDocument24 pagesMicroecnomics PresentationMinahil GMNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - Applied Economics - MarkeT EquilibriumDocument10 pagesChapter2 - Applied Economics - MarkeT EquilibriumArven DulayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Demand and Supply)Document18 pagesChapter 3 (Demand and Supply)Sharif HassanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Topic 1 Demand and Supply Theories and DeterminantsDocument50 pagesLesson 3 - Topic 1 Demand and Supply Theories and DeterminantsMarianne Jade HonorarioNo ratings yet
- Handout Market EquilibriumDocument10 pagesHandout Market Equilibriumagarwalapratham123No ratings yet
- Notes EptDocument9 pagesNotes Ept223109No ratings yet
- Market Equilibrium Chapter ThreeDocument20 pagesMarket Equilibrium Chapter ThreeAli TreeshNo ratings yet
- Extra Credit - Supply and Demand Infographic - Answer KeyDocument6 pagesExtra Credit - Supply and Demand Infographic - Answer Keyrowena vocesNo ratings yet
- Changes in DD & SSDocument20 pagesChanges in DD & SSJasmine JeganNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Demand and SupplyDocument2 pages1.1 Demand and SupplyKrish MonparaNo ratings yet
- Supply, Elasticity of SupplyDocument4 pagesSupply, Elasticity of SupplySaurabhNo ratings yet
- By Consumers at Various PricesDocument9 pagesBy Consumers at Various PricesJanhavi SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Movement-Shift in Demand Curve and Market Equilibrium by Gregorius TurangDocument3 pagesMovement-Shift in Demand Curve and Market Equilibrium by Gregorius TurangGregory TurangNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply Session SummaryDocument8 pagesDemand and Supply Session SummarySonu KumarNo ratings yet
- Business Economic: Dr. Dina YousriDocument36 pagesBusiness Economic: Dr. Dina YousriLilian MichelNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Reflects The Perfect Balance of Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesEquilibrium Reflects The Perfect Balance of Supply and DemandGözde GürlerNo ratings yet
- CLASS - XI (SESSION 2022-23) Subject: Economics (030) Chapter 11:-Price DeterminationDocument6 pagesCLASS - XI (SESSION 2022-23) Subject: Economics (030) Chapter 11:-Price Determination123saanvisinha6dNo ratings yet
- Economics Chapter 4Document14 pagesEconomics Chapter 4Sharif HassanNo ratings yet
- Activity5 Tema 5Document1 pageActivity5 Tema 5Erick VillagranNo ratings yet
- Bravo - John Venedick - Market EquilibriumDocument31 pagesBravo - John Venedick - Market EquilibriumJV BravoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Shift of Demand: When The Demand Curve ShiftsDocument7 pagesFactors Affecting Shift of Demand: When The Demand Curve ShiftsKirthi RkNo ratings yet
- Market MechanismDocument23 pagesMarket MechanismGokul KSNo ratings yet
- Be Stu - Tutorial 2Document18 pagesBe Stu - Tutorial 2Gia LinhNo ratings yet
- 12 Supply GiffengoodsDocument10 pages12 Supply GiffengoodsSurya Prakash Reddy PutluruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Market Equilibrium Equilibrium PriceDocument4 pagesChapter 11 - Market Equilibrium Equilibrium PriceTraining & Development GWCNo ratings yet
- DollyDocument2 pagesDollyyagyarthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Price DeterminationDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Price DeterminationNeelabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Market ForcesDocument30 pagesMarket ForcesamorrisNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Questions: (3 / 4 Marks)Document16 pagesShort Answer Questions: (3 / 4 Marks)sridharvchinni_21769100% (2)
- Module - 2Document66 pagesModule - 2AST TROLLINGNo ratings yet
- The Price System PDFDocument5 pagesThe Price System PDFCommerce LineNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandDocument7 pagesSupply and DemandManoj K100% (1)
- Economics 14: Lecture 5: Supply and Demand, Part 2Document7 pagesEconomics 14: Lecture 5: Supply and Demand, Part 2Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2i Demand and SupplyDocument5 pagesChapter 2i Demand and Supplychuojx-jb23No ratings yet
- Answerstohomework 2 Summer 2010Document10 pagesAnswerstohomework 2 Summer 2010Abul KashemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Markets - AS Business StudiesDocument1 pageChapter 6: Markets - AS Business StudiesHR purposes 2006No ratings yet
- Goods X and Y Are Compliments WhileDocument48 pagesGoods X and Y Are Compliments Whilem-amirNo ratings yet
- Chapter (Eng. Eco) 002Document23 pagesChapter (Eng. Eco) 002dsbsabirkhanNo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply EquilibriumDocument4 pagesDemand and Supply EquilibriumMuhammad Yasir GondalNo ratings yet
- Market Equilibrium (Students)Document23 pagesMarket Equilibrium (Students)Melroy PereiraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document59 pagesLecture 4Zong Zheng SunNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument21 pagesDemandYatharth GroverNo ratings yet
- Supply: - A Particular Price For The Good - All Other Constraints On The FirmDocument23 pagesSupply: - A Particular Price For The Good - All Other Constraints On The Firmkamalyadav73373No ratings yet
- Price Determination in A Perfectly Competitive Market With Fixed Number of FirmsDocument10 pagesPrice Determination in A Perfectly Competitive Market With Fixed Number of FirmsSamruddhi DoshettyNo ratings yet
- Eco CH 12 Starting FinalDocument21 pagesEco CH 12 Starting Finaldeep_lath2180No ratings yet
- Effect of Changes in SupplyDocument6 pagesEffect of Changes in SupplyohhiNo ratings yet
- The Working of Competitive Markets and Demand and The ConsumerDocument19 pagesThe Working of Competitive Markets and Demand and The ConsumerStivon LayNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230920 180146 0000Document19 pagesPDF 20230920 180146 0000Dina MonikaNo ratings yet
- Infography. NoadepouplanaDocument1 pageInfography. NoadepouplananoapoureyNo ratings yet
- Oferta y DemandaDocument9 pagesOferta y DemandaRosario Rivera NegrónNo ratings yet
- Micro Assignment 1Document2 pagesMicro Assignment 1Hamza KhalidNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Opportunity Cost and Marginal Analysis Vocab:: Equations and Quick Summaries by ChapterDocument29 pagesCh. 1 Opportunity Cost and Marginal Analysis Vocab:: Equations and Quick Summaries by ChapterSpencer AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Cheat Sheet - CompressDocument2 pagesTest 1 Cheat Sheet - CompressThe TwitterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Performance Measurement Evaluation Nov2020 1Document113 pagesChapter 8 Performance Measurement Evaluation Nov2020 1Question BankNo ratings yet
- 20230123-20230124-Sandeep Kumar Sahu-Njp-Rnc TicketDocument1 page20230123-20230124-Sandeep Kumar Sahu-Njp-Rnc TicketSandy SandyNo ratings yet
- Bank Quest October - December 2022Document68 pagesBank Quest October - December 2022Naveen Kumar PoosalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 618Document25 pagesChapter 618Pranav GargNo ratings yet
- SPWP 61Document34 pagesSPWP 61Loo Lik HoNo ratings yet
- SCM Mod3Document25 pagesSCM Mod3Amir RajaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-Intro & Cost ClassificationDocument8 pagesTopic 1-Intro & Cost ClassificationMuhammad Alif100% (2)
- EconomicsDocument14 pagesEconomicsravenNo ratings yet
- Example of Management Consultant ResumeDocument1 pageExample of Management Consultant ResumeRoberto PeñaNo ratings yet
- Account STMTDocument27 pagesAccount STMTsrinivas rao kNo ratings yet
- Lease 1Document5 pagesLease 1richard kayNo ratings yet
- Global Trade Law PPT IDocument15 pagesGlobal Trade Law PPT Ismkamran.mbaNo ratings yet
- Bouys SinkersDocument5 pagesBouys SinkersJohn Devin SatoNo ratings yet
- Fin 444Document38 pagesFin 444mrinmoy royNo ratings yet
- TakonDocument28 pagesTakonBasovi Wahyu AdytamaNo ratings yet
- Task 01 - PresentationDocument54 pagesTask 01 - PresentationRomali KeerthisingheNo ratings yet
- MBA5014 Assessment1-1Document8 pagesMBA5014 Assessment1-1AA TsolScholarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - Industrial Building AllowanceDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 - Industrial Building AllowanceChan YingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 TestbankDocument26 pagesChapter 10 TestbankBruce ChenNo ratings yet
- Data PegawaiDocument14 pagesData Pegawaitimdiklat.rsialikhlaspemalangNo ratings yet
- Gokongwei V SEC DigestDocument8 pagesGokongwei V SEC DigestKrissy PepsNo ratings yet
- Ohio Lottery Sports Gaming ReportDocument1 pageOhio Lottery Sports Gaming ReportWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Financing And: Business ModelsDocument9 pagesInfrastructure Financing And: Business ModelsAbhijeet JhaNo ratings yet
- ICICI FASTag - Closure Form - NewDocument2 pagesICICI FASTag - Closure Form - NewMadan ShivashankarNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment - 02Document5 pagesSummative Assessment - 02Joris YapNo ratings yet
- Organizational PlanDocument4 pagesOrganizational PlanCheradee EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Dividend PolicyDocument10 pagesDividend PolicyMoguche CollinsNo ratings yet
- Daftar Isi Manajemen StrategikDocument3 pagesDaftar Isi Manajemen StrategikbudiNo ratings yet