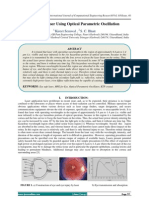
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laser Quiz
Uploaded by
Ahmed AboelataOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laser Quiz
Uploaded by
Ahmed AboelataCopyright:
Available Formats
LLE Laser Safety Quiz
Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester
NAME (Printed) DATE
LLE Group/Supervisor
SIGNATURE (Return to E. Kowaluk)
Check off “” or put an “” in the appropriate column (T=True, F=False)
T F UNDERSTANDING LASERS & LASER LIGHT
1 The laser beam’s wavelength is determined by the lasing media
2 Lasers consist of an active medium, an excitation mechanism, & an optical resonator
3 Lasers operate in the visible, ultraviolet, infrared, and audio regions
4 Different colors in the visible indicate different wavelengths
5 Light at the output of a laser is coherent, monochromatic, and non-directional
6 Ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths are part of the visible spectrum
T F UNDERSTANDING HUMAN TISSUE
7 High power lasers can cause permanent eye damage and skin burns
8 Your eye can magnify light intensity by 100,000 times
9 When light enters your eye, the first tissue affected is the lens
10 Because the skin does not magnify like the eye, lasers cannot burn the skin
T F LASER HAZARDS
11 Pulsed lasers are always less hazardous than continuous lasers
12 Class 4 lasers, like cryogenics, can cause skin burns
13 The electrical hazards associated with a laser are seldom life threatening
14 Collateral laser hazards come from the primary beam
15 Capacitors are still a danger even after the laser power is turned off
T F LASER CLASSES
16 OMEGA is a Class 1 laser
17 Class 2 laser signs use the word DANGER
18 500 mW is the upper limit for Class 3B CW lasers
19 A safe way to view a Class 4 laser beam without eyewear is by diffusely reflecting the beam
20 Class 4 laser beams are hazardous to view directly under most conditions
21 Class 2 lasers don’t emit more than 1 milliwatt
22 Class 3R (formerly Class IIIa) laser pointers can be associated with flash blindness
23 Classes 3B & 4 use the signal word CAUTION
24 High-power laser pointers are limited to the laser Class 3B
25 Class 4 lasers are only hazardous when pulsed
T F PREVENTING LASER ACCIDENTS
26 Protective eyewear allows you to view direct laser radiation safely
27 Optical systems should not be designed with laser beams at eye level.
28 Engineering controls are the most effective types of controls
29 Administrative controls include training, standard operating procedures (SOP), and warning signs
30 The most important aspect of operating lasers safely is to understand the equipment and its
associated hazards and to apply safe work practices
31 Personal protective equipment provides a second layer of defense to protect against unforeseen
events, operator error, failure of engineering or administrative controls, and equipment failures.
32 Green color laser-safety eyewear will protect you from “green” beams
33 Any laser-safety eyewear can protect you from all laser beams
34 Your blink response will protect you from a Class 4 laser
Rev. 2012.05.08
You might also like
- An Introduction to Non-Ionizing RadiationFrom EverandAn Introduction to Non-Ionizing RadiationMuhammad MaqboolNo ratings yet
- GN09 Laser SafetyDocument9 pagesGN09 Laser Safetysezgin bayramNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety Handbook-TntDocument12 pagesLaser Safety Handbook-Tnt42mhNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety ReportDocument27 pagesLaser Safety ReportGabriel Jose SabulaoNo ratings yet
- Laser SafetyDocument25 pagesLaser SafetyGeorge ShihNo ratings yet
- Laser and Fiber Optics Safety: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimDocument15 pagesLaser and Fiber Optics Safety: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimjohnNo ratings yet
- Technology White Paper: Executive SummaryDocument3 pagesTechnology White Paper: Executive SummaryAnonymous 1MjHWwNo ratings yet
- 64-Laser Safety ManualDocument12 pages64-Laser Safety ManualROSSINo ratings yet
- Ehs Laser Safety ManualDocument11 pagesEhs Laser Safety ManualSaffet BORANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Laser Safety: Ian Gillett Safety Director Imperial CollegeDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Laser Safety: Ian Gillett Safety Director Imperial CollegejamesborNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety ManualDocument9 pagesLaser Safety Manualheba.abouessaNo ratings yet
- Laser Pointer Safety 0Document2 pagesLaser Pointer Safety 0cosmofloydNo ratings yet
- Laser Welding and CuttingDocument7 pagesLaser Welding and CuttingeliiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Continuous-Wave Fiber Laser User Guide: RFL-C1500X/RFL-C2000XDocument40 pagesContinuous-Wave Fiber Laser User Guide: RFL-C1500X/RFL-C2000XNicolas2458No ratings yet
- Safe Use of LasersDocument18 pagesSafe Use of LasersSaid A AttiaNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety PDFDocument13 pagesLaser Safety PDFManoj Nehra100% (1)
- Laser safety classification and eye protectionDocument39 pagesLaser safety classification and eye protectionshaymaa alabassiNo ratings yet
- OAJDS16000156Document7 pagesOAJDS16000156Sushma DhimanNo ratings yet
- Fs19 Soldadura LaserDocument3 pagesFs19 Soldadura LaserAntonio AntezanaNo ratings yet
- 20 10 06 A3001 Cren Operational ManualDocument306 pages20 10 06 A3001 Cren Operational Manualvutrung23113163No ratings yet
- Laser Safety Training: For Users of The Pilot™ Class 4 LaserDocument42 pagesLaser Safety Training: For Users of The Pilot™ Class 4 LaserCAO Group, Inc.No ratings yet
- Factsheet Laser PointerDocument12 pagesFactsheet Laser PointerMuhanned SaeedNo ratings yet
- Fact-Sheet-No.-19-Dec-2018 LASER WELDING AND CUTTING SAFETYDocument3 pagesFact-Sheet-No.-19-Dec-2018 LASER WELDING AND CUTTING SAFETYCarlos BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Laser Module 4Document31 pagesLaser Module 4Luis Enrique B GNo ratings yet
- MedicineDocument4 pagesMedicineJyotiNo ratings yet
- Health Risks From The Use of Laser Pointers: Fact Sheet No 202 July 1998Document4 pagesHealth Risks From The Use of Laser Pointers: Fact Sheet No 202 July 1998Gayathri BhatNo ratings yet
- School Lab Safety2010Document41 pagesSchool Lab Safety2010d3mnNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On Laser Radiation: Health Sciences AuthorityDocument11 pagesShort Notes On Laser Radiation: Health Sciences Authorityloveanbu24No ratings yet
- TruDisk Laser Operating Manual PDFDocument286 pagesTruDisk Laser Operating Manual PDFjulio perez0% (2)
- Laser Module 5Document25 pagesLaser Module 5Luis Enrique B GNo ratings yet
- Physics Demonstration File 2019-2020: by P Sai Pradyumnan CLASS: - XII ScienceDocument11 pagesPhysics Demonstration File 2019-2020: by P Sai Pradyumnan CLASS: - XII ScienceSai PradyumnanNo ratings yet
- Laser ClassificationDocument2 pagesLaser ClassificationmrdangquanNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety JSP-392 - CH - 34 - Web - VersionDocument2 pagesLaser Safety JSP-392 - CH - 34 - Web - VersionFirdaus Mohd IdrisNo ratings yet
- Lase Rules 2008Document27 pagesLase Rules 2008LoveNo ratings yet
- Continuous-Wave Fiber Laser User Guide: RFL-C3000SDocument38 pagesContinuous-Wave Fiber Laser User Guide: RFL-C3000SSergej PokhilkoNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)Document7 pagesInternational Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)International Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- Laser Radiation HazardsDocument16 pagesLaser Radiation HazardsLarryKnappNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Fundamentals of Laser OperationDocument7 pagesPart 1: Fundamentals of Laser OperationadetoroadewumiNo ratings yet
- Laser Light Security System.Document9 pagesLaser Light Security System.AshrayKunnurNo ratings yet
- Basic Laser Safety Training FundamentalsDocument35 pagesBasic Laser Safety Training FundamentalsĐông PhùngNo ratings yet
- Laser safety program for eye hospitalsDocument6 pagesLaser safety program for eye hospitalsAhmedAhmedNo ratings yet
- OSHA Guide to Non-Ionizing Radiation ProtectionDocument2 pagesOSHA Guide to Non-Ionizing Radiation ProtectionJaneiro Antonio SalazarNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety Manual 9-1-2017Document36 pagesLaser Safety Manual 9-1-2017Urología GinecológicaNo ratings yet
- RFL-P200 User's Guide V1.0Document32 pagesRFL-P200 User's Guide V1.0shrusNo ratings yet
- Laser Security FinalDocument8 pagesLaser Security FinalHarsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety - Class 2 Laser Safety InformationDocument1 pageLaser Safety - Class 2 Laser Safety InformationRobert Dave AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Laser Safety CalculationsDocument8 pagesLaser Safety CalculationsGeorge ShihNo ratings yet
- Raycus 1000wDocument37 pagesRaycus 1000wGustavo BittencourtNo ratings yet
- BErtle RiskAssesmentDocument36 pagesBErtle RiskAssesmentAbd ZouhierNo ratings yet
- 27750220-1 Calculase II Maintenance and Safety Check V2011 Dec 19Document76 pages27750220-1 Calculase II Maintenance and Safety Check V2011 Dec 19Rubén Cadima BarrientosNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS PROJECT (2019-2020) : By: Name: Yogesh Class: 12thDocument17 pagesPHYSICS PROJECT (2019-2020) : By: Name: Yogesh Class: 12thria sreekumarNo ratings yet
- Laser Manual LS-2137U DESYDocument36 pagesLaser Manual LS-2137U DESYandrea0% (1)
- Tank Combat Full Tracked 105 MM Gun M1 2Document881 pagesTank Combat Full Tracked 105 MM Gun M1 2Milan PitovicNo ratings yet
- Laser Registration Form - 121619Document7 pagesLaser Registration Form - 121619BIO HPNo ratings yet
- Manual de Utilizare 1Document13 pagesManual de Utilizare 1Anunturi GratuiteNo ratings yet
- SOP Use of Lasers in Schools Part 1 Laser Pointers - 0Document5 pagesSOP Use of Lasers in Schools Part 1 Laser Pointers - 0travis harutoNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 1: Laser Safety D: Never Allow A Laser Beam To Enter The Eye!Document14 pagesEXPERIMENT 1: Laser Safety D: Never Allow A Laser Beam To Enter The Eye!Ali AmjadNo ratings yet
- Proteksi Radiasi Dari RadiografiDocument34 pagesProteksi Radiasi Dari RadiografiBachtiar Muhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Lasers in Ophthalmology: Moderator: Dr. S. Kalpana Presenter: Dr. AnjaliDocument89 pagesLasers in Ophthalmology: Moderator: Dr. S. Kalpana Presenter: Dr. AnjaliSammie PingNo ratings yet
- User Guide-Raycus-Single-Module Laser ManulDocument49 pagesUser Guide-Raycus-Single-Module Laser ManulMateusz ŻurawskiNo ratings yet
- 02 - Particle Counter - PC-2200 BrochureDocument2 pages02 - Particle Counter - PC-2200 Brochurejatin kumar panwalNo ratings yet
- The Principe Laser Diode and Amplifer PDFDocument697 pagesThe Principe Laser Diode and Amplifer PDFAlix BoubanNo ratings yet
- Lloyd S Register Sec IX 2017 Edition Key ChangesDocument38 pagesLloyd S Register Sec IX 2017 Edition Key ChangesDilip Varadharajan100% (1)
- Adaptive Optics Engineering Handbook - Robert K TysonDocument339 pagesAdaptive Optics Engineering Handbook - Robert K Tysoneverret08100% (1)
- Manual TheGrowroom SPACE10 PDFDocument24 pagesManual TheGrowroom SPACE10 PDFVan Kochkarian100% (1)
- Photography Through A Microscope PDFDocument22 pagesPhotography Through A Microscope PDFJose PerezNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Technology An Introduction To DepositionDocument7 pagesThin Film Technology An Introduction To DepositionGeetha Sokkian RammanoharNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Sensor PDFDocument36 pagesUltrasonic Sensor PDFRoberto RizaldyNo ratings yet
- HP Color Laserjet 9500 Service ManualDocument536 pagesHP Color Laserjet 9500 Service ManualJessica OrdoyneNo ratings yet
- Airbus Eurocopter wires cablesDocument12 pagesAirbus Eurocopter wires cablesrafiNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument59 pagesOpticsLucas FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Machining Processes by JainDocument112 pagesAdvanced Machining Processes by JainKali DasNo ratings yet
- Obt751 PPT 2Document13 pagesObt751 PPT 2Ryan Miller100% (1)
- Luxel Service Manual PDFDocument760 pagesLuxel Service Manual PDFreprop100% (3)
- Brushless DC MotorsDocument14 pagesBrushless DC MotorsNeroGetsu100% (1)
- An Assignment ON " Input and Output Devices": Subject Name: Computer Subject CodeDocument7 pagesAn Assignment ON " Input and Output Devices": Subject Name: Computer Subject CodeHarpreet AroraNo ratings yet
- Manual TopconDocument180 pagesManual TopconStefanescu MirceaNo ratings yet
- Scanning Electron MicrosDocument17 pagesScanning Electron MicrosVishal MishraNo ratings yet
- Optical Tweezers-The Force of Light-17slDocument17 pagesOptical Tweezers-The Force of Light-17slmanfredm6435No ratings yet
- TL90-1500M GB 01Document4 pagesTL90-1500M GB 01salamrefighNo ratings yet
- SputteringDocument17 pagesSputteringAadil WaseemNo ratings yet
- Clean Room SU-8 and PDMS RecipeDocument2 pagesClean Room SU-8 and PDMS RecipeAybüke ÇalıkoğluNo ratings yet
- High Precision, Low Force 3D Touch Probe For Measurements On Small ObjectsDocument4 pagesHigh Precision, Low Force 3D Touch Probe For Measurements On Small Objectspm089No ratings yet
- Advanced Materials & Processes - January 2015Document61 pagesAdvanced Materials & Processes - January 2015FilipNo ratings yet
- Leica Theodolite 100 Series: User Manual T105/T110Document64 pagesLeica Theodolite 100 Series: User Manual T105/T110Kurniawan Budi SantosoNo ratings yet
- Corner ShotDocument5 pagesCorner ShotKamranNo ratings yet
- Em 422 R 03 05 Macro Executor An Operation Supplement Manual For The Cincinnati CL 7a Laser System With Ge Fanuc Control PDFDocument62 pagesEm 422 R 03 05 Macro Executor An Operation Supplement Manual For The Cincinnati CL 7a Laser System With Ge Fanuc Control PDFManolo MedranoNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing:: Opportunities and ConstraintsDocument21 pagesAdditive Manufacturing:: Opportunities and ConstraintsPaolo VelcichNo ratings yet
- EOS System Data Sheet EOS P396 enDocument4 pagesEOS System Data Sheet EOS P396 enMomo PierreNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)