Professional Documents
Culture Documents
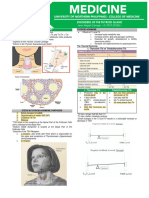
Thyroid Drugs
Thyroid Drugs
Uploaded by
CELINA WONGOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thyroid Drugs
Thyroid Drugs
Uploaded by
CELINA WONGCopyright:
Available Formats
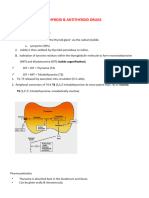
Subclass Drugs MOA Uses Pharmacokinetics ADR
"Graves disease tx MMI PTU
along with radioactive
Rapidly absorbed; 50-80 % (1st
iodine, hasten recovery Completely absorbed
pass effect)
as radiation takes time
Control disorder while Multiple oral dosing (2-3)
Mostly single oral dose Cross the placental barrier & are
needed daily
⬇️
"Contain thiourea & waiting for surgery
concentrated by the fetal thyroid
⬇️
thiocarbamide TH output Plasma t½ = 6-15 hrs, slow Plasma t½ = 2 hrs, onset 1. Urticaria rashes (most common)
(S-C-N) group" Signs & symptoms of onset faster* 2. Agranulocytosis (reversible if drug
1. Inhibit iodination of tyrosyl thyrotoxicosis"
removed)- dose related with MMI &
Thioamides/Thioureylenes/ Carbimazole, methimazole & group in thyroglobulin *Delayed clinical effects Highly bound to plasma protein
Not bound to plasma proteins older pts
Thiourea Derivatives propylthiouracil 2. Inhibit coupling of because stored (75 %)**
3. Severe liver injury & acute liver
iodotyrosine to form T3 & T4 iodinated tyrosine not
failure (PTU)
3. Inhibit peripheral affected Excreted in the urine Excreted in the urine
4. Cholestatic jaundice (MMI)
deiodination of T4 to T3 PTU: 2nd line
(propylthiouracil) 1st trimester pregnancy/ Does not inhibit T4 to T3 *Inhibits peripheral conversion 5. Headache, fever, jaundice, joint
conversion of T4 to T3 pain"
MMI allergy
Avoid in peds, unless
MMI allergy TH lowering to euthyroid 6-7
Slower, up to 16 weeks
Monitor PTU therapy for weeks
liver injury
1. Cause fetal goiter
1. Convert I to I- 1. Preparation for surgical
2. Monotherapy cause exacerbation
2. Inhibit TH release by thyroidectomy
of thyrotoxicosis in an iodine-
inhibiting thyroglobulin 2. Use with PTU/MMI for
enriched gland
proteolysis the treatment of thyroid
3. Gland escape from iodine block in
Iodine 3. May inhibit iodination of storm
2-8 weeks
thyroglobulin, possibly by 3. Prophylaxis – protect
4. Anaphylactic, rashes, swollen
⬇️
reducing H2O2 generation thyroid gland from taking
salivary gland, ulcers, conjunctivitis,
4. size & vascularity of up radioiodine
fever, rhinorrhoea, metallic taste,
gland [preoperative] after nuclear accident
Iodine bleeding disorder
131^I
Destroy fetal thyroid gland, excreted
1. Emit β radiation
Grave's disease in in breast milk
- Short ranged, absorbed by Given orally in solution as Na-I^131, single dose, t1/2=8 days
younger pts, high relapse Sore throat, salivary gland swelling,
tissue Rapidly absorbed, concentrated by thyroid & incorporated into
rate associated with mild nausea
Radioactive iodines - Exert powerful cytotoxic storage follicle
antithyroid therapy Precautions: Avoid prolonged
action on thyroid follicle cells Delayed cytotoxic effect for 1-2 month, max action for further 2
Adjunct tx in contact (11 days), sharing utensils &
(destroy tissue) months
well-differentiated CA food, Drink lots of liquid, void, flush
2. γ rays (pass through
twice
tissues)
⬇️
1. Preparation of
1. symptoms of thyrotoxic patients for
AV blockade, hypotension,
hyperthyroidism eg. surgery
bradycardia,
tachycardia, dysrhythmias, 2. Initial treatment for
β-adrenoceptor antagonist Propranolol Onset within 4-6 hours contraindicated in severe heart
tremor & agitation hyperthyroid patients while
failure and
2. Inhibit peripheral the thioamides or
asthma
conversion of T4 to T3 radioiodine take effect
3. Acute thyroid crisis tx
1. Thyroid replacement for
hypothyroidism &
Nervousness, palpitations,
cretinism 1. Long t1/2 (7days)
Levothyroxine (L-T4) tachycardia, heat intolerance &
2. TSH suppression 2. Administered once daily
unexplained weight loss
therapy in pts w thyroid
Synthetics CA, non-thyroid nodule
⬆️
1. More potent than levothyroxine,
For short-term 1. Shorter t1/2 (24hr)
risk of cardio-toxicity,
Liothyronine (L-T3) suppression of TSH and 2. Administer IV multiple time
contraindicated in cardiac ds pts
myxedema coma 3. Difficult monitoring
2. Higher cost
You might also like
- Thyroid Conversion Chart 08-13a PDFDocument1 pageThyroid Conversion Chart 08-13a PDFMichael GordanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyCourtney Dela FierraNo ratings yet
- 1-Complete Blood Count - PO1106326185-399Document8 pages1-Complete Blood Count - PO1106326185-399Arup KumarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reviewer 001Document7 pagesPharmacology Reviewer 001Kath MartinezNo ratings yet
- 4.15 DR. ROBERTO MIRASOL HYperthyroidism PSEM 2017 1 PDFDocument89 pages4.15 DR. ROBERTO MIRASOL HYperthyroidism PSEM 2017 1 PDFjackie funtanilla100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyesdaleNo ratings yet
- H-046-003249-00 TSH (CLIA) English MindrayDocument2 pagesH-046-003249-00 TSH (CLIA) English MindrayТатьяна ИсаеваNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ZOFRANDocument3 pagesDrug Study - ZOFRANKian Herrera50% (4)
- Anti-Thyroid Drugs Class Examples Indication M.O.A Side EffectsDocument2 pagesAnti-Thyroid Drugs Class Examples Indication M.O.A Side EffectsThulasi tootsieNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document4 pagesWeek 7Joanna BakNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Storm TreatmentDocument1 pageThyroid Storm TreatmentIlham NiawanNo ratings yet
- MR 4 Course Тopic10 Practical ClassesDocument7 pagesMR 4 Course Тopic10 Practical ClassesHikufe JesayaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Thyrotoxicosis (May 2014) PDFDocument30 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Thyrotoxicosis (May 2014) PDFFarman JaaferNo ratings yet
- Im-Thyroid DisordersDocument9 pagesIm-Thyroid DisordersRyan F. BernalNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Gland PRINT 2021Document9 pagesThe Thyroid Gland PRINT 2021abcde990075No ratings yet
- AngelaaDocument2 pagesAngelaaangelaamorbanco457No ratings yet
- Antithyroid Drugs: Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDocument26 pagesAntithyroid Drugs: Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityRiska PriyaniNo ratings yet
- Research Based Paper UniversityDocument2 pagesResearch Based Paper UniversitySimran SGNo ratings yet
- Temozolomide Concomitant NHSDocument4 pagesTemozolomide Concomitant NHSSyed Touseef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology: Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology: Drug StudyAkiraMamoNo ratings yet
- Nausea Movement DisorderDocument5 pagesNausea Movement DisorderoladapoNo ratings yet
- Beta-2 Adrenergic Agonist: MechanismDocument6 pagesBeta-2 Adrenergic Agonist: MechanismLola LeNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid Drugs: Dr. Novita Carolia, M.Sc. Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDocument26 pagesAntithyroid Drugs: Dr. Novita Carolia, M.Sc. Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung Universitynovita caroliaNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid Drugs: Dr. Novita Carolia, M.Sc. Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDocument26 pagesAntithyroid Drugs: Dr. Novita Carolia, M.Sc. Pharmacology and Therapy Faculty of Medicine Lampung UniversityDhita Dwi NandaNo ratings yet
- Triptorelin: A Drug NameDocument9 pagesTriptorelin: A Drug Namedavid medinaNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument43 pagesDRUG StudyNathalie Faith CotengNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland L-Thyroxine (T4) Vs Triiodothyronine (T3) : Follicular CellsDocument7 pagesThyroid Gland L-Thyroxine (T4) Vs Triiodothyronine (T3) : Follicular CellsPrincess Noreen SavellanoNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsDocument1 pageAcute Otitis Media Children and AdolescentsSreya SanilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument2 pagesDrug Study FormatLarr SumalpongNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLorence RamosNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics - EndocrineDocument6 pagesObstetrics - EndocrineJonathanNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: DosageDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: DosageGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- Bagong DrugsDocument7 pagesBagong DrugsmcensoredNo ratings yet
- Dopamine Antagonist: Generic Name: Chemical EffectDocument2 pagesDopamine Antagonist: Generic Name: Chemical EffectMajeed AlzahraniNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture 10 Anti-Thyroid Drugs (DR Thatcher Pod Pharm 2022)Document36 pages02 Lecture 10 Anti-Thyroid Drugs (DR Thatcher Pod Pharm 2022)sahilaminNo ratings yet
- Poison TableDocument12 pagesPoison TableKirk NeneriaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Cheat SheetsDocument4 pagesEndocrine Cheat Sheetsdarlington D. y ayimNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism 3.0Document2 pagesHyperthyroidism 3.0Zane ZyraNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced VomitingDocument5 pagesDrug Induced VomitingnimasNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Medication Histories of Ascities: Table 3.2aDocument9 pages3.2 Medication Histories of Ascities: Table 3.2ab_rahman2k39603No ratings yet
- Garate Aubreydrug Studyns6 01 21 23Document6 pagesGarate Aubreydrug Studyns6 01 21 23AUBREY GARATENo ratings yet
- Danzi 2013Document7 pagesDanzi 2013Ana CortezNo ratings yet
- Sruthi T (220) 11Document5 pagesSruthi T (220) 11sruthyt18No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument28 pagesLesson 6 Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugstheintrovNo ratings yet
- Medication Worksheet: Citrus College Associate Degree NursingDocument5 pagesMedication Worksheet: Citrus College Associate Degree NursingRhonnie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The ThyroidDocument18 pagesPharmacology of The ThyroidpremamoyNo ratings yet
- StrumaDocument17 pagesStruma1234ayomajuNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Antithyroid DrugsDocument27 pagesThyroid & Antithyroid DrugsjabirNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology And: Review: Endocrine and Metabolic Emergencies: Thyroid StormDocument8 pagesMetabolism Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology And: Review: Endocrine and Metabolic Emergencies: Thyroid StormibanggNo ratings yet
- Tiroiditis SubakutDocument9 pagesTiroiditis SubakutAvino Mulana FikriNo ratings yet
- PCOL - Thyroid DrugsDocument4 pagesPCOL - Thyroid DrugsTerepe CrimsonNo ratings yet
- Drugs W/ Important Action On Smooth Muscle (Autacoids)Document3 pagesDrugs W/ Important Action On Smooth Muscle (Autacoids)Liezel Dejumo Bartolata100% (1)
- Hyperthyroidism 2.0Document2 pagesHyperthyroidism 2.0Zane ZyraNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidismDocument2 pagesHyperthyroidismZane ZyraNo ratings yet
- HelminthsDocument11 pagesHelminthsTienneNo ratings yet
- Crohns Disease FinalDocument3 pagesCrohns Disease Finalapi-535481376No ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument1 pageAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Thyroid & Antithyroid Drugs - 2020Document7 pagesThyroid & Antithyroid Drugs - 2020ireneNo ratings yet
- THYROID GLAND: What Happens When Something Goes Wrong?: PIT UIDocument4 pagesTHYROID GLAND: What Happens When Something Goes Wrong?: PIT UIAnonymous HH3c17osNo ratings yet
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneAya EssamriNo ratings yet
- Oncology Cheat Sheets - 1Document5 pagesOncology Cheat Sheets - 1abdallahmaurice94No ratings yet
- Tazarotene 0.1% Cream As Monotherapy For Early-Stage Cutaneous T-Cell LymphomaDocument5 pagesTazarotene 0.1% Cream As Monotherapy For Early-Stage Cutaneous T-Cell LymphomaCassandra VérasNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsKalyx LuthenburgNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 10 Endocrine SystemJamesanne DemetriaNo ratings yet
- PD22 Hap1 L03Document33 pagesPD22 Hap1 L03Ka Yan LAUNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Group 3Document17 pagesEndocrine System Group 3arold bodoNo ratings yet
- A Successful Case Study On Ayurvedic Management of HypothyroidismDocument6 pagesA Successful Case Study On Ayurvedic Management of HypothyroidismIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Jane Bunford - 7 Feet 11 Inches (241 CM) : Jane Bunford (Also Known As Ginny Bunford or Jinny Bunford - 26 JulyDocument5 pagesJane Bunford - 7 Feet 11 Inches (241 CM) : Jane Bunford (Also Known As Ginny Bunford or Jinny Bunford - 26 JulyLukas LuconNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System & Major Organs (1-4)Document6 pagesEndocrine System & Major Organs (1-4)april lou andrea sorillaNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA Prof EvaDocument3 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA Prof EvaElsy Pramitha SariNo ratings yet
- Thyroid LectureDocument65 pagesThyroid LectureAndres TabaresNo ratings yet
- Benazir Bhutto Hospital, Surgical Unit-Ii Final Year Ward TESTDocument6 pagesBenazir Bhutto Hospital, Surgical Unit-Ii Final Year Ward TESTHassan Ahmad100% (1)
- DR Ananta Thyroid SlideDocument73 pagesDR Ananta Thyroid SlideRoshan Kumar PanditNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy & Histology of Liver: Prepared By: Anish Dhakal (Aryan) MBBS Student Patan Academy of Health SciencesDocument21 pagesGross Anatomy & Histology of Liver: Prepared By: Anish Dhakal (Aryan) MBBS Student Patan Academy of Health SciencesAjeng TunjungputriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument8 pagesChemical Coordination and IntegrationsuryababaNo ratings yet
- Nor Amira Binti Nor Azalin - 21-2373774Document2 pagesNor Amira Binti Nor Azalin - 21-2373774Nor AmiraNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response in Humans: 12.6 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesCoordination and Response in Humans: 12.6 Endocrine Systemwienna1987No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Endocrine Systemjonelllantero032No ratings yet
- Answers To Chapter 7 ExercisesDocument2 pagesAnswers To Chapter 7 ExercisessAnDrA SaNdWiChNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Equine Thyroid DysfunctionDocument15 pagesEquine Thyroid DysfunctionDirección Científica Laboratorio VitalabNo ratings yet
- Asm 2380Document2 pagesAsm 2380Aryaan LaskarNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Loop A WordDocument60 pagesActivity 1 Loop A WordPrincess AnnNo ratings yet
- Quiz EndocrineDocument16 pagesQuiz EndocrineMon DoceNo ratings yet
- Anat 1002-Anatomy Pre-Health Science Program Ch.1-Introduction To Human Anatomy Summary and WorksheetsDocument5 pagesAnat 1002-Anatomy Pre-Health Science Program Ch.1-Introduction To Human Anatomy Summary and WorksheetsAliNo ratings yet
- ThyrotoxicosisDocument16 pagesThyrotoxicosisFiorella Peña MoraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine SystemRaazia HaseebNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pendidikan Kesehatan Terhadap Pengetahuan Dan Sikap Ibu Hamil Tentang Skrining Hipotiroid Bayi Baru Lahir Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas KawalDocument10 pagesPengaruh Pendidikan Kesehatan Terhadap Pengetahuan Dan Sikap Ibu Hamil Tentang Skrining Hipotiroid Bayi Baru Lahir Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas KawalAgum Nila SariNo ratings yet
- KI 70 Therapeutic Potential in Graves Ca ThyroidDocument4 pagesKI 70 Therapeutic Potential in Graves Ca ThyroidGaurav MalhotraNo ratings yet