Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Information Security Assement
Uploaded by
Dilip Ranjan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Information Security Assement
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesInformation Security Assement
Uploaded by
Dilip RanjanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Notes on Information Security
1. Definition of Information Security:
Information security, often abbreviated as InfoSec, is the practice of protecting
information assets from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification,
or destruction. It encompasses a range of strategies, technologies, and processes to
safeguard sensitive data and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of
information.
2. Core Principles of Information Security:
Confidentiality: Ensuring that information is accessible only to authorized
individuals or entities.
Integrity: Safeguarding the accuracy and completeness of information and protecting
it from unauthorized modification.
Availability: Ensuring that information and information systems are accessible and
usable when needed by authorized users.
Authenticity: Verifying the identity of users and ensuring that data, transactions, and
communications are genuine and trustworthy.
Non-Repudiation: Preventing individuals from denying the validity of their actions
or transactions.
3. Components of Information Security:
Physical Security: Measures to protect physical assets such as servers, computers,
networking equipment, and data centers from unauthorized access, theft, or damage.
Cybersecurity: Techniques, technologies, and practices to protect digital information
assets from cyber threats such as malware, phishing, ransomware, and hacking.
Access Control: Implementing controls to manage and restrict access to information
systems, applications, and data based on user roles, permissions, and authentication
mechanisms.
Encryption: Using cryptographic techniques to encode information and protect it
from unauthorized access or interception.
Security Policies and Procedures: Establishing guidelines, standards, and protocols
to govern the secure handling, storage, transmission, and disposal of information
assets.
4. Threats to Information Security:
Malware: Malicious software such as viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware
designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems or data.
Phishing: Fraudulent attempts to deceive individuals into disclosing sensitive
information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or personal data by posing as
trustworthy entities.
Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals through psychological tactics to gain
unauthorized access to information or perform fraudulent activities.
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data resulting in its exposure, theft,
or disclosure to unauthorized parties.
Insider Threats: Security risks posed by individuals within an organization, such as
employees, contractors, or partners, who misuse their access privileges or
intentionally compromise information security.
5. Information Security Controls:
Preventive Controls: Measures designed to prevent security incidents from
occurring, such as firewalls, antivirus software, access controls, and encryption.
Detective Controls: Measures to identify and detect security incidents or breaches in
real-time, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), security monitoring tools, and
log analysis.
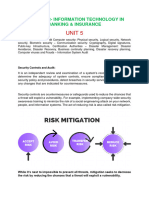
Corrective Controls: Measures to mitigate the impact of security incidents and
restore systems to a secure state, such as incident response plans, data backups, and
disaster recovery procedures.
6. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements:
Organizations may be subject to various laws, regulations, and industry standards
related to information security and data protection, such as the General Data
Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
(HIPAA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and Sarbanes-
Oxley Act (SOX).
7. Security Awareness and Training:
Promoting a culture of security awareness among employees through training,
education, and awareness programs is essential for mitigating human-related security
risks and fostering a security-conscious workforce.
8. Emerging Trends in Information Security:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Leveraging AI and ML technologies
for threat detection, anomaly detection, and automated response to security incidents.
Zero Trust Security: Adopting a security model based on the principle of "never
trust, always verify," which assumes that threats may exist both outside and inside the
network perimeter.
Cloud Security: Implementing security controls and best practices to protect data and
applications hosted in cloud environments from unauthorized access, data breaches,
and other cyber threats.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security: Addressing security challenges associated with
the proliferation of IoT devices, such as insecure configurations, vulnerabilities, and
privacy concerns.
9. Conclusion:
Information security is a critical aspect of modern organizations, requiring a proactive
and multi-layered approach to protect valuable information assets from a diverse
range of threats. By implementing robust security measures, adhering to best
practices, and staying informed about emerging threats and technologies,
organizations can effectively mitigate risks and safeguard their sensitive data.
You might also like
- Cyber SecurityDocument2 pagesCyber SecurityGedion KiptanuiNo ratings yet
- 200 IT Security Job Interview Questions-1Document188 pages200 IT Security Job Interview Questions-1yasmine ayedNo ratings yet
- Cyber Sec Assignment 1Document4 pagesCyber Sec Assignment 1swalehemmary8991No ratings yet
- CYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-1: Hacking the Hackers: Unraveling the World of CybersecurityFrom EverandCYBER SECURITY HANDBOOK Part-1: Hacking the Hackers: Unraveling the World of CybersecurityNo ratings yet
- Group - 1it Security ContentDocument5 pagesGroup - 1it Security ContentJud J VeluntaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document3 pagesChapter 15omar anwarNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking: Exploring the Dark Art of Ethical Hacking and Penetration TestingFrom EverandCybersecurity and Ethical Hacking: Exploring the Dark Art of Ethical Hacking and Penetration TestingNo ratings yet
- Lesson One IasDocument6 pagesLesson One IasRicHArdNo ratings yet
- Computer SafetyDocument7 pagesComputer SafetyKim Elfa CabalteraNo ratings yet
- Stay Safe!: A Basic Guide to Information Technology SecurityFrom EverandStay Safe!: A Basic Guide to Information Technology SecurityNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument3 pagesCyber SecurityBae BaeNo ratings yet
- Ias MR1Document7 pagesIas MR1kipper gamingNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Information Security-2Document10 pagesEnterprise Information Security-2Guillermo ValdèsNo ratings yet
- Name: D.Vijay Abhishek Roll No: 20CA231 Register No: 212000263 Topic: Cyper SecurityDocument12 pagesName: D.Vijay Abhishek Roll No: 20CA231 Register No: 212000263 Topic: Cyper SecurityST DOORSNo ratings yet
- What Is Cyber SecurityDocument9 pagesWhat Is Cyber SecurityAye Nyein MyintNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy MGT TERMPAPER PART 5Document2 pagesCybersecurity and Data Privacy MGT TERMPAPER PART 5SABERA AMVNo ratings yet
- IAS MReviewerDocument12 pagesIAS MReviewerkipper gamingNo ratings yet
- It SecurityDocument33 pagesIt Securityrenuparte5No ratings yet
- Information Security MaintenanceDocument14 pagesInformation Security MaintenanceHamza AliNo ratings yet
- Securing InformationDocument57 pagesSecuring Informationleanna hoyteNo ratings yet
- Information Assurance and Security II Lectures Quizzes and Activities Compress 1Document26 pagesInformation Assurance and Security II Lectures Quizzes and Activities Compress 1Jireh SalinasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document75 pagesChapter 1desalewminaleNo ratings yet
- CS1014 Information Security 3 0 0 100 AIMDocument19 pagesCS1014 Information Security 3 0 0 100 AIMMuthu SaanaNo ratings yet
- 5 6111596633797954468Document7 pages5 6111596633797954468jethroanthony.deitaNo ratings yet
- Cit 101Document22 pagesCit 101agapenunmi16No ratings yet
- Section 2 Security-PolicyDocument18 pagesSection 2 Security-Policyahmadjoe04No ratings yet
- Lec 1 ISDocument39 pagesLec 1 ISAffan KhawajaNo ratings yet
- MODULE-1 PART-1 Information Security FundamentalsDocument16 pagesMODULE-1 PART-1 Information Security FundamentalsRahulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 and 2Document10 pagesLecture 1 and 2Dessa Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- KrushynDV11мпDocument8 pagesKrushynDV11мпМикола КрушинNo ratings yet
- PrintoutDocument14 pagesPrintoutShalini ChintalaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Digital Forensics WorkDocument6 pagesCyber Security Digital Forensics Workokware brianNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - Juan Estevan Gomez HincapieDocument5 pagesTask 1 - Juan Estevan Gomez Hincapiejuan estevan gomez hincapieNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument12 pagesNetworkingwakgarielias4No ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument11 pagesCyber SecurityFaryal AftabNo ratings yet
- Incident Response Plan For Fictional Company - Delta Force Solutions IncDocument6 pagesIncident Response Plan For Fictional Company - Delta Force Solutions Incthazni kassimNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity ProjectDocument19 pagesCybersecurity ProjectRudra PatelNo ratings yet
- ISM UNIT 1 NotesDocument44 pagesISM UNIT 1 NotessreenidhiNo ratings yet
- MGT115R02 - Information Technology in Banking 0 Insurance - Unit 5Document34 pagesMGT115R02 - Information Technology in Banking 0 Insurance - Unit 5arunvklplmNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: (Prof. Ashok K. Bhateja, IIT Delhi)Document10 pagesCyber Security: (Prof. Ashok K. Bhateja, IIT Delhi)Jatin GoyalNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity 2024Document13 pagesCybersecurity 2024vijay52254No ratings yet
- Managing Security of InformationDocument4 pagesManaging Security of InformationredNo ratings yet
- Information Security All ChapterDocument73 pagesInformation Security All ChapterbilisummaaNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Introduction To Information SecurityDocument14 pagesChap1 Introduction To Information SecurityNitish LokhandeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document37 pagesPresentation 1Evehn KadusaleNo ratings yet
- Information Assurance and SecurityDocument3 pagesInformation Assurance and Securitympcivpacademics.nfjpia2324No ratings yet
- Cyber Security 3 - 3066Document9 pagesCyber Security 3 - 3066mehak3066.bbaa21No ratings yet
- Information SecurityDocument33 pagesInformation SecuritygashawNo ratings yet
- Information Security All Chapter1Document72 pagesInformation Security All Chapter1bilisummaaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Definitions & Challenges of Security, Attacks & ServicesDocument31 pages1 - Definitions & Challenges of Security, Attacks & ServicesNilaa RaghunathanNo ratings yet
- Session 1 - Information System Security Over ViewDocument7 pagesSession 1 - Information System Security Over ViewmunyakatimNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Intro CSDocument32 pagesUnit1 Intro CSdhirtitalrejaNo ratings yet
- Module 4b Security PDFDocument72 pagesModule 4b Security PDFAngella Chisomo MagomboNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction To Information Assurance and Security (ITEC4143)Document19 pagesChapter One: Introduction To Information Assurance and Security (ITEC4143)Dires NegashNo ratings yet
- INFORMATION SECURITY HandoutsDocument63 pagesINFORMATION SECURITY HandoutsKumkumo Kussia KossaNo ratings yet
- CC7178 Cyber Security Management: Presenter: Kiran Kumar ShahDocument20 pagesCC7178 Cyber Security Management: Presenter: Kiran Kumar ShahManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Notes IOTDocument2 pagesNotes IOTDilip RanjanNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems and Application Environments AssementDocument2 pagesOperating Systems and Application Environments AssementDilip RanjanNo ratings yet
- Maths NotesDocument1 pageMaths NotesDilip RanjanNo ratings yet
- Nformation Systems and Data Modeling (IT 1090)Document2 pagesNformation Systems and Data Modeling (IT 1090)Dilip RanjanNo ratings yet
- PeaceDocument6 pagesPeaceJinny Rose RadoNo ratings yet
- Note From Steve Clemons:confidential PDFDocument1 pageNote From Steve Clemons:confidential PDFB50% (2)
- S. Harrison OIS Determination (Saginaw County Prosecutor's Office)Document2 pagesS. Harrison OIS Determination (Saginaw County Prosecutor's Office)Caleb HollowayNo ratings yet
- Letter To AG Loretta Lynch RE Dakota Access 10-24-16Document3 pagesLetter To AG Loretta Lynch RE Dakota Access 10-24-16inforumdocs100% (1)
- GMT - COIN - Cuba Libre Rules 2015Document20 pagesGMT - COIN - Cuba Libre Rules 2015Lorenzo BeattieNo ratings yet
- Dr. Zafar Nawaz JaspalDocument15 pagesDr. Zafar Nawaz Jaspalsaad khanNo ratings yet
- T He BL A C KV A Ul TDocument12 pagesT He BL A C KV A Ul TSuoTanNo ratings yet
- Sanchez V DemetriouDocument2 pagesSanchez V DemetriouDannaIngaran71% (7)
- BSWJ202101Document11 pagesBSWJ202101Sir Wolenard50% (2)
- Tier-I Result PDFDocument28 pagesTier-I Result PDFRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Intelligence BureauDocument9 pagesIntelligence BureauVeerababu BarlaNo ratings yet
- Annexure-Vii Certificate To Be Submitted by The Candidate Claiming Reservation Under Cap CategoryDocument3 pagesAnnexure-Vii Certificate To Be Submitted by The Candidate Claiming Reservation Under Cap CategoryminiNo ratings yet
- InglesDocument6 pagesInglesLuis emanuel ChávezNo ratings yet
- Case of Nicodemo v. USADocument13 pagesCase of Nicodemo v. USAArif Zina100% (3)
- The Airpower Advantage in The Future WarfareDocument50 pagesThe Airpower Advantage in The Future WarfareaircombatNo ratings yet
- White Supremacist CoronaDocument2 pagesWhite Supremacist CoronaYahoo News84% (19)
- Osama Bin Laden Pronounced Dead For The Ninth TimeDocument13 pagesOsama Bin Laden Pronounced Dead For The Ninth TimeBharatChutiyaNo ratings yet
- Leak Site DirectoryDocument8 pagesLeak Site DirectoryEyemanProphetNo ratings yet
- (Lea 3) Police Patrol Operations With Police Communications SystemDocument23 pages(Lea 3) Police Patrol Operations With Police Communications SystemGina Cambongga100% (2)
- Jesus Rivera FL US Capitol RiotsDocument9 pagesJesus Rivera FL US Capitol RiotsWCTV Digital TeamNo ratings yet
- Spain in Flames 20 Sep 19Document15 pagesSpain in Flames 20 Sep 19Vinny CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Pressure Cooker BombsDocument17 pagesPressure Cooker BombsStewart BellNo ratings yet
- Police Custody and Judicial CustodyDocument14 pagesPolice Custody and Judicial Custodyjyotak vatsNo ratings yet
- Force ContinuumDocument13 pagesForce ContinuumDerek Punes100% (1)
- Icrc 002 0962Document1,278 pagesIcrc 002 0962nezz_8100% (1)
- Contoh Surat Sponsor Jepang - Unt AnakDocument2 pagesContoh Surat Sponsor Jepang - Unt AnakgeraldusgervanNo ratings yet
- Korean Peninsula ClashesDocument16 pagesKorean Peninsula ClashesPaul LeeNo ratings yet
- Horan Arrest ReportDocument2 pagesHoran Arrest ReportJacob EngelsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Criminal Investigation TextBookDocument84 pagesFundamentals of Criminal Investigation TextBookMae Anthonette B. Cacho93% (45)
- People vs. AdlawanDocument5 pagesPeople vs. AdlawanReniel EdaNo ratings yet