Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHARMA-R4.5-Thyroid, Antithyroid, Antiosteoporosis
PHARMA-R4.5-Thyroid, Antithyroid, Antiosteoporosis
Uploaded by
charmainemargaret.parreno.medOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PHARMA-R4.5-Thyroid, Antithyroid, Antiosteoporosis
PHARMA-R4.5-Thyroid, Antithyroid, Antiosteoporosis
Uploaded by
charmainemargaret.parreno.medCopyright:
Available Formats
PATHOLOGY
SHIFT
THYROID AND ANTI-THYROID
#4
DRUGS; ANTI-OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEWER #5
REVIEWER | MAY 2020
OUTLINE Metabolic clearance More
I. Thyroid III. Bone Remodeling and Biologic half life 7 days 1 day
Amount bound 99.96% 99.6%
A. Thyroid Hormone Hemostasis
Amount free 0.04% 0.4%
Biosynthesis A. Calcium and Bone Biologic potency 1 4
B. Thyroid Hormone Remodeling Oral absorption 80% 95%
II. Drugs Used in Thyroid B. Parathyroid Hormone
Disorders C. Vit D3 Formation • T3 is more widely distributed, has less stores, shorter half-life,
A. Hypothyroidism D. Calcitonin more potent, almost completely absorbed
B. Hyperthyroidism IV. Osteoporosis • T4 more bound to TBG
C. Adjunct Drugs for the A. Pharmacotherapy
Thyroid V. References General Action of Thyroid Hormone
VI. Appendices • MOA: Free T4 and T3 enters the cell, T4 is converted to T3 (via
deiodinase)
LEGEND • Regulates growth and development through protein synthesis
MUST KNOW SAMPLEX
→ Critical role in brain development
• Calorigenic effects
*hello, this is very summarized from the lecture, please study the
→ Increased oxygen consumption
powerpoint and read the book also
→ Increased BMR
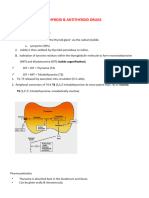
I. THYROID • Cardiovascular effects
→ Increased sensitivity to catecholamines (increased number of
A. THYROID HORMONE BIOSYNTHESIS beta-adrenergic receptors)
1. Iodide trapping → Excess catecholamines would lead to overactive expression
• Iodide is taken up Lid lags, retraction, tremors, increased sweating, anxiety,
2. Translocation of iodide nervousness
3. Oxidation of iodide to iodine • Metabolic effects
4. Iodination (Organification) → Increased metabolism leads to weight loss (in hyperthyroid
state)
• Incorporation of iodide into tyrosine residues within
thyroglobulin in colloid II. DRUGS USED IN THYROID DISORDERS
5. Conjugation B. HYPOTHYROIDISM
• Clinical features: slowing down of bodily functions
• “coupling” reaction
• Goals of treatment
• Combination of DIT+DIT = T4, DIT+MIT = T3 → Replace the thyroid hormone
6. Uptake of thyroglobulin from colloid into follicular cells by → Avoid overcorrection
endocytosis, fusion of thyroglobulin with a lysosome, proteolysis Will lead to hyperadrenergic reactions (tachycardia,
and release of T4, T3, DIT, MIT into circulation palpitations, atrial fibrillation, tremors, increased bone
• Oxidation, Iodination/Organification, Conjugation – catalyzed by resorption)
thyroid peroxidase enzyme Thyroid Preparations
• Synthetic thyroid preparation
B. THYROID HORMONE
→ Levothyroxine (T4)
• T4 is best absorbed (70 to 80%) in the duodenum and ileum.
→ Liothyronine (T3)
• T3 is almost completely absorbed (95%) → Liotrix (mix T4/T3)
• Taken 1 hour before breakfast, 4 hours after the last meal, or at • Natural hormone extracts
bedtime → Desiccated thyroid
• T4 metabolism • Indicated for hypothyroidism, simple goiter
→ Deiodination to active T3 by 5’ deiodinase enzyme Synthetic Thyroid Preparations
→ Deiodination to reverse T3 (Inactive) by 5 deiodinase enzyme • Levothyroxine T4 – preparation of choice for replacement
therapy
Thyroid Hormone Carriers
→ Long half-life (7 days), but is given 1/day
• Thyroxine binding globulin – major carrier for both T4 and T3
→ Does not have T3, but this is derived from peripheral
→ Bind more T4 than T3
conversion of T4
Free T3 is 10x more than free T4. Disease states can alter
→ Less cardiotoxic than liothyronine
this.
• Liothyronine T3 – 3-4x more potent than levothyroxine
→ Increased TBG = decreased free hormone, vice versa
→ No longer recommended
• Transthyretin binds only T4
• T3/T4 Liotrix
• Albumin
→ Good for those who lack 5’ deiodinase enzyme
Table 1. T4 vs T3
Needed to convert T4 to T3
Parameter T4 T3
Volume of distribution 10L 40L → Potentially cardiotoxic cause of T3
Extrathyroidal pool More Natural Hormone Extracts
Daily production More
• No longer recommended
Reviewer PREPARED BY: Velasco, Jacqueline 1 of 6
#4.5
PATHO REVIEWER 4.5: Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs, Antiosteoporosis 2 of 6
→ Unstable Table 2. PTU vs Methimazole
Characteristics PTU Methimazole
→ Protein antigenicity
Absorption Rapid Complete but variable
→ Hard to monitor Bioavailability 50-80% >95%
Precautions T1/2 1.5 hrs 6 hrs
Excretion Faster Slower
• Thyroid hormones are not effective and not indicated in:
Duration of action Short Long
→ Obesity Relative potency 1 10
→ Dyslipidemia Dosing 100-200 mg TID 10-30 mg OD
→ Abnormal vaginal bleeding Dose response Lower Higher
→ Depression Toxicity Idiosyncratic Agranulocytosis
Effect on liver Hepatitis Cholestatic jaundice
• Do not give levothyroxine unless proven that patient has
Albumin binding More Less
hypothyroidism Placental passage Less More (congenital
B. HYPERTHYROIDISM malformation)
Breast milk Low levels Low levels
• Acceleration of body functions
Blocks peripheral Extensive None
• Goal of treatment conversion T4 to T3
→ Eliminate excess thyroid hormone DOC 1st trimester First line
→ Prevent acute complications (thyroid storm) and long-term pregnancy, thyroid
storm
complications (thyrotoxic heart disease)
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism General Categories Iodides
• Antithyroid drugs • MOA: (if used >6mg/day)
→ Inhibit synthesis of T4 and T3 → Inhibits iodination/organification – Wolff-Chaikoff effect
• Radioactive iodine therapy Iodide in small amounts can stimulate thyroid hormone
production, but in large amounts can inhibit it
→ Iodine 131 taken up by thyroid can destroy the glands
→ Inhibits hormone release (seen in 2-7 days)
• Surgical resection
→ Decreases size and vascularity of hyperplastic gland
Antithyroid Drugs Good for preop of thyroid surgery to reduce bleeding
• Anion inhibitors • Preparation:
→ Perchlorate → Lugol’s solution or SSKI saturated solution
→ Pertechnetate • Indication:
→ Thiocyanate → Thyroid storm
• Thioamides → Preoperative prep for thyroid surgery
→ Propylthiouracil (PTU) → Protection of thyroid against fallout in nuclear accident
→ Thiamazole (Methimazole) • Disadvantages:
→ Carbimazole → If used more than 2 weeks – Jod Basedow Phenomenon
• Iodides “escape”, iodide is used for hormone synthesis
→ Lugol’s solution → Can cause fetal goiter in pregnancy
Anion Inhibitors → May delay onset of thioamide therapy
• Block iodide trapping/uptake of iodide by thyroid • Iodide toxicities
• MOA: competitive inhibition of iodide transport (Na-Iodide → Uncommon (includes acneiform rash, rhinorrhea, etc.)
symport) C. ADJUNCT DRUGS FOR THE THYROID
• Compete with iodide (effects can be overcome with large doses • Don’t directly interfere with thyroid hormones
of iodide) • Add-ons to thioamides
• Associated with aplastic anemia
Beta Blockers (Propanolol)
Thioamides • Blocks peripheral effects of thyroid hormone
• Block thyroid peroxidase • At >160 mg/day: block peripheral conversion of T4 to T3
→ Rate limiting enzyme of thyroid synthesis • For thyroid storm: dose is 40-80 mg q6
• Structure: has thiocarbamide group (essential for anti-thyroid
Lithium
activity)
• Blocks release of thyroid hormone
• MOA: Prevents hormone synthesis via inhibition of thyroid
peroxidase catalyzed reactions (oxidation, organification, • Last resort alternative to iodides and thioamides
coupling) • Toxicity: nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
→ PTU inhibits peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 Prednisone
→ Does not block uptake of iodide nor release of thyroid • Anti-inflammatory
hormones → Useful in grave’s ophthalmopathy
• Adverse reactions Swelling of orbital fat pad due to TSH receptor antibody
→ Most common: Maculopapular rash +/- fever cross reaction, lead to eye proptosis
→ Methimazole • Blocks conversion of T4 to T3
Altered sense of smell, cholestatic jaundice → Useful in thyroid storm
Agranulocytosis – most dreaded Radioactive Iodine
− Leukopenia, neutropenia can lead to severe infections • I131
Cutis aplasia birth defect
• MOA: Destroy thyroid gland through ionizing radiation beta rays
→ PTU
→ Epithelial swelling and necrosis, follicular disruption, edema,
Increase risk of severe hepatitis
and leukocyte infiltration
→ Switching from PTU to methimazole for severe reactions not
→ Thyroid gland shrinks within 6-12 weeks
recommended (has 50% cross reactivity)
• More definitive treatment but there is delay in control of
hyperthyroidism
• Pretreatment with anti-thyroid drug to achieve euthyroid state
before radioactive iodine therapy is desired
PATHO REVIEWER 4.5: Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs, Antiosteoporosis 3 of 6
• Disadvantage: develop hypothyroidism • Kidneys
• Indications: preferred treatment for those who → Increases calcium reabsorption
→ Fail to respond to drug therapy → Increases phosphorus reabsorption
→ Had ADR with other treatments D. CALCITONIN
→ Had recurrence of hyperthyroidism even after surgery • T1/2 = 10 min
→ Are poor surgical risks (elderly, cardiac, debilitated patients) • Secreted by Parafollicular C cells of Thyroid in response to
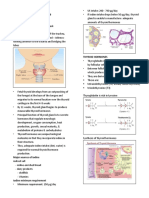
III. BONE REMODELING AND HEMOSTASIS increased calcium
A. CALCIUM AND BONE PHYSIOLOGY • Actions:
• 99% of calcium found in bone → Increase osteoclastic resorption in bone
• Bone → Increase renal Ca and PO4 excretion
→ Dynamic reservoir with constant remodeling readily → Salmon calcitonin has longer half-life
exchanges Ca with ECF Bone Remodeling Cycle
→ Disturbances lead to osteoporosis and problems in • Osteoclasts resorb lacuna, form a cavity (break bone)
coagulation • Osteoblasts deposit new bone
Calcium IV. OSTEOPOROSIS
• Functions: nerve conduction, second messengers, coagulation • Bone resorption exceeds bone formation
• Average diet: 600 to 1000 mg per day (10-25% absorbed in • Compromised bone strength
small intestine) • Increased risk of fracture
→ Enhanced by Vit D • Associated with:
→ Decreased by PPI → Menopause (loss of estrogen production)
• Preparations → Ca/Vit D deficiency
→ Calcium carbonate is the preparation of choice → Drugs: steroids
Highest elemental calcium (40%) → Inadequate peak bone mass
Give with meals to increase absorption
A. PHARMACOTHERAPY
→ Calcium citrate
• Goal: Block osteoclast, promote osteoblast
Can be taken anytime but with low elemental calcium
(21%) • Anti-resorptive agents (inhibit osteoclast)
→ Calcium gluconate → Bisphosphonates
IV form → Salmon calcitonin
For hypocalcemic tetany → Estrogen
→ SERM (Raloxifene)
B. PARATHYROID HORMONE
→ Denosumab
• Major regulator of calcium and phosphorous metabolism
• Anabolic agent (stimulate osteoblast)
• Stimulus for release: low calcium level
→ Teriparatide
• Half-life 2-5 min
• Dual effect (antiresorptive and anabolic)
• 90% clearance by liver and kidneys
→ Strontium ranelate
• PTH on Calcium Metabolism:
→ Net effect: Increase serum Ca, Decrease serum PO4 Bisphosphonates
→ PTH promotes bone reabsorption • MOA: inhibits farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase (key enzyme
→ Ca in circ, in kidney activate 1-alpha-hydroxylase enzyme to in mevalonic acid pathway needed for osteoclast survival)
convert Vitamin D into calcitriol (active form) → When embedded in bone matrix binds to hydroxyapatite
→ Active Vit D will enhance Ca and PO4 absorption in intestine → Retards dissolution of hydroxyapatite crystals within and
→ PTH also increases reabsorption of Ca and increases PO4 outside bone
excretion • Oral preparation: alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate
→ Take on empty stomach
C. VIT D3 FORMATION
• IV preparation: zoledronate, pamidronate
• Skin has 7-dehyrocholesterol, converted by UV B rays into
→ Zoledronate: retained for months or year
previtamin D3
• Excreted in kidney
• This will form cholecalciferol (not yet active)
• Drug effect:
• Cholecalciferol is acted by 25-hydroxylase (from liver), and 1a -
→ Provide greatest increase in bone mineral density
hydroxylase (from kidney) to become calcitriol (1,25
dihydrocholecalciferol; active form) → Decrease spine and hip fractures
• DOC: prevention and treatment of postmenopausal
Vitamin D and the Hydroxycholecalciferols osteoporosis, osteoporosis in men, glucocorticoid induced
• Fat soluble, absorbed from intestine osteoporosis
→ Enhanced by bile salts • Side effects:
• Bound to Vit D binding globulin in circulation → Oral: cause esophageal and gastric irritation, GERD
• 25 OH Vit D3 – storage form in adipose tissue → Contraindicated in hypocalcemia
→ Best index for Vit D sufficiency → Atypical femur fractures or subtrochanteric femoral fractures
• Calcitriol or 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol due to over suppression of bone turnover
→ Active form Solution: drug holiday after 5 years
→ Formulation needed when PTH is deficient Estrogen
Effect of Calcitriol on Calcium and Phosphorous • Estrogen receptors in bone favors bone formation
Metabolism • Safety issues: breast cancer, endometrial hyperplasia,
• Bone cardiovascular events
→ Promotes mineralization of bone • Indication: alleviation of postmenopausal vasomotor symptoms
• Gastrointestinal Tract Raloxifene
→ Increases calcium absorption
• Selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)
→ Increases phosphorus absorption
• Estrogenic in bones, antiestrogenic in breast and uterus
PATHO REVIEWER 4.5: Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs, Antiosteoporosis 4 of 6
• Uses: prevention and treatment of postmenopausal
osteoporosis
• Side effects: hot flushes, leg cramps, and a threefold increase in
the relative risk of venous thromboembolism.
→ Will not improve postmenopausal symptoms
Salmon Calcitonin
• Longer half-life than human calcitonin
• ADR: nasal irritation
• Inhibits osteoclastic resorption of bone, increase renal Ca and
PO4 excretion
• Use:
→ 2nd line treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis if unable
to tolerate the other drugs
→ Lower calcium in hypercalcemia
→ Provide pain relief in vertebral fractures
Denosumab
• Human monoclonal antibody to RANKL
• Prevents RANKL binding to its receptor = osteoclast inhibition
• Reduces bone resorption and fracture risk
• Uses:
→ Postmenopausal osteoporosis
→ Prostate CA
→ Breast CA
• No dose adjustment for renal disease
• ADR:
→ Increased risk of infection (RANKL is present in immune
system)
→ Osteonecrosis of the jaw
→ Subtrochanteric fractures
Teriparatide
• Recombinant human PTH
• 1/day subcutaneous injection 20 mcg stimulates new bone
formation on trabecular and cortical bone surfaces
• Osteoblastic activity > osteoclastic activity
• Increases serum Ca and decreases serum PO4
• Indicated for those with high risk for fracture
→ Postmenopausal osteoporosis
→ Men with primary or hypogonadal osteoporosis
→ Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis
• Treatment limited to 2 years then follow with antiresorptive
agent
• ADR: hypercalcemia, nausea, esophageal reflux, postural
hypotension, dizziness
• Osteosarcoma in rodents
Strontium Ranelate
• Inhibit osteoclast, promote osteoblast
• ADR: GI, allergic reactions
• Warning: cardiovascular events
• Take at bedtime, 2 hours after eating
REFERENCES
Dr. Jean Uy-Ho’s Powerpoint Lecture
END OF REVIEWER
Prepared by: Velasco, Jacqueline
PATHOLOGY
SHIFT
THYROID AND ANTI-THYROID
#4
DRUGS; ANTI-OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEWER #5
REVIEWER | MAY 2020
UNIVERSITY OF SANTO TOMAS
FACULTY OF MEDICINE AND SURGERY
D2022 Reviewer
Sample EXAMINATION
May 2020
Instructions:
1. There are 20 items in this questionnaire
2. CHOOSE THE BEST ANSWER.
3. Try to answer on your own (without the use of reviewers/trances)
4. Answers are given in a separate document.
5. God bless!
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHOOSE THE BEST ANSWER
TRUE OR FALSE:
1. Methimazole can inhibit peripheral conversion of T4 to T3.
A. TRUE B. FALSE
2. Human calcitonin has a longer half-life than salmon calcitonin.
A. TRUE B. FALSE
3. Iodide 4mg/day elicits the Wolff-Chaikoff effect.
A. TRUE B. FALSE
4. Absorption of thyroid hormones is affected by food.
A. TRUE B. FALSE
5. Bisphosphonates are the drug of choice for postmenopausal osteoporosis.
A. TRUE B. FALSE
MULTIPLE CHOICE.
6. Which of the following is used to treat hypothyroidism?
A. SSKI B. Perchlorate C. Lithium D. Levothyroxine
7. The most common adverse effect of thioamides is:
A. Pruritus B. Hepatitis C. Maculopapular rash D. Sore throat
8. Agranulocytosis is a dreaded adverse reaction of which drug?
A. Bisphosphonates B. Radioactive Iodine C. Liotrix D. Methimazole
9. All of the following can be used for treating thyroid storm, EXCEPT:
A. PTU B. Iodides C. Prednisone D. none of the above
10. Perchlorate inhibits __ in thyroid hormone synthesis?
A. Organification B. Conjugation C. Oxidation D. Iodide trapping
11. What drug for hyperthyroidism is the drug of choice for patients in their 1st trimester of pregnancy?
A. Methimazole B. Pertechnetate C. PTU D. SSKI
Reviewer PREPARED BY: Velasco, Jacqueline 5 of 6
#4.5
PATHO REVIEWER 4.5: Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs, Antiosteoporosis 6 of 6
12. What is the storage form of Vit D?
A. Calcitriol B. Cholecalciferol C. 25 OH Vit D3 D. 7-Dehydrocholesterol
13. What is the mechanism of action of Zoledronate?
A. Blocks farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase B. Antibody to RANKL
C. SERM D. Recombinant human PTH
14. Which of the following may provide pain relief in vertebral fractures?
A. Alendronate B. Raloxifene C. Salmon calcitonin D. Denosumab
15. Which of the following antiosteoporosis drugs has a dual effect?
A. Teriparatide B. Strontium C. Raloxifene D. Ibandronate
16. A 60-year old woman with osteoporosis will be started on an anti-resorptive drug. She requested for an IV drug
that is given once a year, which drug is it?
A. Zoledronate B. Strontium C. Ibandronate D. Calcitonin
17. The most appropriate drug for a 70-year-old male with osteoporosis that provides the greatest increase in bone
mineral density and fracture risk reduction is __?
A. Alendronate B. Calcitonin C. Teriparatide D. Cinacalcet
18. A 55-year-old female with metastatic breast cancer (to the spine and femur) and chronic kidney disease will
benefit most from this anti-resorptive agent:
A. Denosumab B. Alendronate C. Teriparatide D. Strontium
19. A hyperthyroid patient will be started on methimazole in a few days, which of the following should NOT be given
before starting the said drug?
A. Iodide B. Propranolol C. Prednisone D. Thiocyanate
20. A 15-year-old male presents with 3x4 cm anterior neck mass. Thyroid function tests revealed low TSH, elevated
free T4 and T3. The most appropriate drug to give is:
A. Methimazole B. Propranolol C. Iodides D. Perchlorate
JVLV2020
- END OF QUIZ-
GOD BLESS!
You might also like
- Substance Abuse Counseling Complete 5th EditionDocument379 pagesSubstance Abuse Counseling Complete 5th Editionnintendoagekid86% (59)
- Talking Thyroid FactsDocument6 pagesTalking Thyroid FactsVegan Future100% (4)
- Hypothyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypothyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesPhysiology of The Thyroid GlandSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormones & Anti Thyroid AgentsDocument3 pagesThyroid Hormones & Anti Thyroid AgentsJaybee SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Astropalmistry From The Cradle of AstropalmistryDocument3 pagesAstropalmistry From The Cradle of AstropalmistryANTHONY WRITERNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antithyroid Agent-VDocument60 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid Agent-VVine100% (1)
- Mycobacteria Protocol BookDocument413 pagesMycobacteria Protocol Book신정이100% (1)
- Homestay Business AgreementDocument17 pagesHomestay Business AgreementRasyidahNo ratings yet
- Correct Answer.: Science Diagnostic Test Year 6 - 2014Document16 pagesCorrect Answer.: Science Diagnostic Test Year 6 - 2014Nantha Kumar Sivaperumal67% (9)
- Thompson, Marie-2017-Beyond Unwanted Sound. Noise Affect and Aesthetic Moralism PDFDocument212 pagesThompson, Marie-2017-Beyond Unwanted Sound. Noise Affect and Aesthetic Moralism PDFTasha Ballard100% (3)
- My Family and Other Animals - Gerald DurrellDocument5 pagesMy Family and Other Animals - Gerald DurrellzubikepaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Pharmaco Part 2Document34 pagesWeek 3 Pharmaco Part 2Tiko JomidavaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Problems: Hypothyroidism, Autoimmune Thyroiditis and Thyroid HealingFrom EverandThyroid Problems: Hypothyroidism, Autoimmune Thyroiditis and Thyroid HealingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Construction Management Fundamentals 2nd Edition Knutson Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesConstruction Management Fundamentals 2nd Edition Knutson Solutions ManualTonyaJohnsonDDSrzjt100% (57)
- 5.06 Anti Thyroid Drugs 1Document9 pages5.06 Anti Thyroid Drugs 1CarmineNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Antithyroid Drugs - 2020Document7 pagesThyroid & Antithyroid Drugs - 2020ireneNo ratings yet
- Im-Thyroid DisordersDocument9 pagesIm-Thyroid DisordersRyan F. BernalNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Thyroid GlandsDocument10 pagesDisorders of The Thyroid GlandsIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.6 Thyroid Gland-Endocrinology-LmsDocument10 pagesLesson 6.6 Thyroid Gland-Endocrinology-LmsJohanna MarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 37Document6 pagesChapter 37kdayeon018No ratings yet
- 5,6-Thyroid HyperhypoDocument16 pages5,6-Thyroid Hyperhypomogesie1995No ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument9 pagesThyroid GlandZach ReyesNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology SlidesDocument344 pagesEndocrinology SlidesleanNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Thyroid Gland PDFDocument10 pagesDisorders of The Thyroid Gland PDFNadia Abdurasid100% (1)
- 3ES-2 Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs 1436Document46 pages3ES-2 Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs 1436Muath AlqarniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function and Antithyroid Drugs-PciDocument17 pagesThyroid Function and Antithyroid Drugs-PciSamad KaziNo ratings yet
- Transcript Midterms PharmacologyDocument15 pagesTranscript Midterms PharmacologyPrincess Krenzelle BañagaNo ratings yet
- Transcript MidtermsDocument15 pagesTranscript MidtermsPrincess Krenzelle BañagaNo ratings yet
- CombinedDocument40 pagesCombinedshortsmotivation87No ratings yet
- Topic3.3 Physiology Thyroid HormoneDocument7 pagesTopic3.3 Physiology Thyroid HormoneRen AlvNo ratings yet
- 2s Finals Pharma BeshyDocument60 pages2s Finals Pharma BeshyJohanei Mae PeraltaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Pharmacology - Thyroid & Antibone DrugsDocument20 pages1 - Pharmacology - Thyroid & Antibone DrugsSoc Gerren TuasonNo ratings yet
- Rene Luis F. Filarca, M.D.: February 5, 2014Document8 pagesRene Luis F. Filarca, M.D.: February 5, 2014Maikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland Clinical Chemistry 2 (Laboratory) : LessonDocument4 pagesThyroid Gland Clinical Chemistry 2 (Laboratory) : LessonCherry Ann ColechaNo ratings yet
- 14) Drugs For Thyroid DisordersDocument13 pages14) Drugs For Thyroid DisordersLatiNo ratings yet
- Class 6 (19.07.2022)Document70 pagesClass 6 (19.07.2022)Ãqûã FîggâNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Gland PRINT 2021Document9 pagesThe Thyroid Gland PRINT 2021abcde990075No ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders 1Document29 pagesThyroid Disorders 1zxcvbzaki123No ratings yet
- PEDIA Thyroid Gland DisordersDocument6 pagesPEDIA Thyroid Gland DisordersEmerson QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Hormones: - Iodine (I)Document7 pagesThyroid Hormones: - Iodine (I)lelouch_damienNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland L-Thyroxine (T4) Vs Triiodothyronine (T3) : Follicular CellsDocument7 pagesThyroid Gland L-Thyroxine (T4) Vs Triiodothyronine (T3) : Follicular CellsPrincess Noreen SavellanoNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument44 pagesThyroidHossen AliNo ratings yet
- Beta-2 Adrenergic Agonist: MechanismDocument6 pagesBeta-2 Adrenergic Agonist: MechanismLola LeNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid, Thyroid Hormone and Antithyroid DrugsDocument42 pagesParathyroid, Thyroid Hormone and Antithyroid Drugsp6hccq6jd7No ratings yet
- Enlarged Thyroid PDFDocument58 pagesEnlarged Thyroid PDFBANAWAN TRESHIA MAE D.No ratings yet
- Chapter 77Document4 pagesChapter 77Regina Ysabel SartagudaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Thyroid Drugs and Thyroid HormoneDocument7 pagesAnti-Thyroid Drugs and Thyroid Hormonemicheal1960100% (1)
- Thyroid and Antityr DrugsDocument23 pagesThyroid and Antityr Drugsmsmobile shNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism 2.0Document2 pagesHyperthyroidism 2.0Zane ZyraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders: (Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism)Document28 pagesThyroid Disorders: (Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism)Mina RoxasNo ratings yet
- Hypo BrochureDocument2 pagesHypo Brochurea604No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The ThyroidDocument18 pagesPharmacology of The ThyroidpremamoyNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland - Normal FunctionDocument34 pagesThyroid Gland - Normal FunctionjabirNo ratings yet
- Hypo Thyroid Is Mfa QDocument1 pageHypo Thyroid Is Mfa Qmariela pinedaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Drugs For Thyroid Problems2Document51 pages11 - Drugs For Thyroid Problems2nica velanoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument14 pagesThyroid DisordershaleyNo ratings yet
- Biochem ThyroidDocument42 pagesBiochem ThyroidHussein QasimNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nesrine Salah El Dine: Thyroid Gland From Pharmacology To Clinical PracticeDocument24 pagesDr. Nesrine Salah El Dine: Thyroid Gland From Pharmacology To Clinical Practiceamaal ramadanNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function and Disease: Sponsored by Department of Continuing Medical EducationDocument69 pagesThyroid Function and Disease: Sponsored by Department of Continuing Medical EducationSriman YarrarapuNo ratings yet
- 05 Endo GIT RenalDocument131 pages05 Endo GIT RenalMaria Arlyn Lacuña SagosoNo ratings yet
- 5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردDocument27 pages5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردRana Abdullah100% (1)
- PhysioLec 8 Thyroid Metabolic Hormones (Dr. Queenie)Document4 pagesPhysioLec 8 Thyroid Metabolic Hormones (Dr. Queenie)Lafayette DelantarNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument38 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid DrugsbrkbsnNo ratings yet
- Antithyroid DrugsDocument32 pagesAntithyroid DrugsLUMUMBA OluwatomisinNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DisordersDocument86 pagesThyroid DisordersJEPHTHAH KWASI DANSONo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations Management Grave's Disease / Hyperthyroidism/ ThyrotoxicosisDocument3 pagesClinical Manifestations Management Grave's Disease / Hyperthyroidism/ ThyrotoxicosisShaine_Thompso_6877100% (1)
- Lecture3-Thyroid DrugsDocument20 pagesLecture3-Thyroid DrugsPeter MaithyaNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-RATIONALE-R4.5-Thyroid, Antithyroid, AntiosteoporosisDocument2 pagesPHARMA-RATIONALE-R4.5-Thyroid, Antithyroid, Antiosteoporosischarmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-RATIONALE-R3.5-Antifungal AgentsDocument3 pagesPHARMA-RATIONALE-R3.5-Antifungal Agentscharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-RATIONALE-R4.6-Developmental PharmacologyDocument2 pagesPHARMA-RATIONALE-R4.6-Developmental Pharmacologycharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-R1.1-NSAIDs, DMARDs, Non-Opioid Analgesics and Drugs Used in GoutDocument11 pagesPHARMA-R1.1-NSAIDs, DMARDs, Non-Opioid Analgesics and Drugs Used in Goutcharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- (7 - 25) LEC 10 Gyn UltrasoundDocument61 pages(7 - 25) LEC 10 Gyn Ultrasoundcharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- (PSG) Examination 2 (06 Nov 2020)Document4 pages(PSG) Examination 2 (06 Nov 2020)charmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- Zuckerman Et Al 2017 Imaging With Synthesized 2d Mammography Differences Advantages and Pitfalls Compared With DigitalDocument8 pagesZuckerman Et Al 2017 Imaging With Synthesized 2d Mammography Differences Advantages and Pitfalls Compared With Digitalcharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- (PSG) Examination 1 (18 Sep 2020)Document6 pages(PSG) Examination 1 (18 Sep 2020)charmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- 100k Ipon ChallengeDocument1 page100k Ipon Challengecharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Improves Sputum Conversion and Chest X-Ray Severity ScoreDocument6 pagesAtorvastatin Improves Sputum Conversion and Chest X-Ray Severity Scorecharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Delhi English Edition 2018-10-15.Document15 pagesPioneer Delhi English Edition 2018-10-15.JohnDNo ratings yet
- CHEM1 Q2 M2-Lewis-StructuresDocument32 pagesCHEM1 Q2 M2-Lewis-StructuresMark TerradoNo ratings yet
- Astro ph0505128Document7 pagesAstro ph0505128anca irinaNo ratings yet
- Rights of A ChildDocument2 pagesRights of A ChildAytona Villanueva PearlNo ratings yet
- Sidebar MenuDocument23 pagesSidebar MenuDediNirtadinataAlQudsyNo ratings yet
- Utility Computing: Cost OptimizationDocument4 pagesUtility Computing: Cost Optimizationpragya pathakNo ratings yet
- Class 12th For Board ExamDocument5 pagesClass 12th For Board Examakashsadoriya5477No ratings yet
- El Método LEST, Su Aplicación Y Evaluación en Las Prácticas ErgonómicasDocument16 pagesEl Método LEST, Su Aplicación Y Evaluación en Las Prácticas ErgonómicasTorSan LuizNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument7 pagesConstitutionChiDeltaSigmaNo ratings yet
- Counselling Notice SD 9610d0f8d4Document25 pagesCounselling Notice SD 9610d0f8d4Janib Ahmad TantryNo ratings yet
- Aniceto G. Saludo v. Philippine National Bank, G.R. 193138, August 20, 2018Document14 pagesAniceto G. Saludo v. Philippine National Bank, G.R. 193138, August 20, 2018Stephen Neil Casta�oNo ratings yet
- MODEL PAPER-2 HISTORY & CULTURE AP GR-I & II English DO YOU SUCCESS TELEGRAM CHANNELDocument21 pagesMODEL PAPER-2 HISTORY & CULTURE AP GR-I & II English DO YOU SUCCESS TELEGRAM CHANNELindianap15081947No ratings yet
- Kerala: "God's Own Country"Document13 pagesKerala: "God's Own Country"Muhammed AlwaniNo ratings yet
- Aerospray Stat 7122Document97 pagesAerospray Stat 7122JanNo ratings yet
- Indian Salon Hair and Skin Products Industry ReportDocument24 pagesIndian Salon Hair and Skin Products Industry ReportReevolv Advisory Services Private LimitedNo ratings yet
- Aguias Iluminacion MexDocument46 pagesAguias Iluminacion MexIrvingNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (E) - Article 21aDocument20 pagesModule 2 (E) - Article 21aJ SNo ratings yet
- Resume Jasmine Ervin1Document2 pagesResume Jasmine Ervin1api-241347777No ratings yet
- Chapingo Autonomous University Dima English 2 Test 1 Review: Who Did You Go With?Document5 pagesChapingo Autonomous University Dima English 2 Test 1 Review: Who Did You Go With?Anonymous tlX5S51No ratings yet
- C. SGH-wall 3Document61 pagesC. SGH-wall 3MoustafaNo ratings yet
- PS-2 (Compatibility Mode)Document8 pagesPS-2 (Compatibility Mode)03ranNo ratings yet
- Econ 12 PaperDocument11 pagesEcon 12 PaperKKNo ratings yet