Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OR Markov Analysis
Uploaded by
aisha ashraf0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThe document describes using a transition matrix to model the probabilities of moving between states over time. It gives a 2x2 transition matrix T and shows how to calculate the state probabilities M3, M6, and at steady state by raising the matrix to powers using matrix multiplication. It then sets up equations to solve for the steady state probabilities Pp and Np of being in each state.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes using a transition matrix to model the probabilities of moving between states over time. It gives a 2x2 transition matrix T and shows how to calculate the state probabilities M3, M6, and at steady state by raising the matrix to powers using matrix multiplication. It then sets up equations to solve for the steady state probabilities Pp and Np of being in each state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOR Markov Analysis
Uploaded by
aisha ashrafThe document describes using a transition matrix to model the probabilities of moving between states over time. It gives a 2x2 transition matrix T and shows how to calculate the state probabilities M3, M6, and at steady state by raising the matrix to powers using matrix multiplication. It then sets up equations to solve for the steady state probabilities Pp and Np of being in each state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Transition Matrix (T):
First Month Next Month
P N
0.
P 6 0.4
0.
N 2 0.8
M3 = M2*T
M6 = M5*T
[Pp(3) Np(3)] = [Pp(2) Np(2)]*T
[Pp(4) Np(4)] = [Pp(3) Np(3)]*T
………
[Pp(i + 1) Np(i + 1)] = [Pp(i) Np(i)]*T
Steady state is time independent
At steady state,
[Pp Np] = [Pp Np]*T
[Pp Np] = [Pp Np]*[0.6 0.4
0.2 0.8]
[Pp Np] = [0.6Pp+0.2Np 0.4Pp+0.58Np]
Pp = 0.6Pp+0.2Np === 0.4Pp – 0.2Np = 0---------(1)
Np = 0.4Pp+0.8Np=== 0.4Pp – 0.2Np = 0----------(2)
Pp + Np = 1---------(3)
Elimination Method
Substitution Method
Comparison Method
Pp = ?, Np = ? (Steady state probabilities)
Q 15: Module of Markov Analysis pdf
Its an example of 3*3 system. Above matrix is transition matrix (T)
You can find the probabilities of moving from one Spring to next Spring by applying the same concept as
we discussed in class.
S (i + 1) = S(i) * T
Like: Current Spring: S(1)
Plant Plus Crop Extra Gro-Fast
Plant Plus 1 0 1
Crop Extra 0 1 0
Gro-Fast 0 0 1
Spring 2: S(2) = S(1)*T, so answer is (see the attached excel sheet)
Next Spring 2: S(2)
Current Spring Plant Plus Crop Extra Gro-Fast
Plant Plus 0.4 0.3 0.3
Crop Extra 0.5 0.1 0.4
Gro-Fast 0.4 0.2 0.4
You might also like
- Biological Foundation of Human Development 01062022 123018pm 03102022 082939am 11032023 023436pmDocument40 pagesBiological Foundation of Human Development 01062022 123018pm 03102022 082939am 11032023 023436pmaisha ashrafNo ratings yet
- hw1Document8 pageshw1Rukhsar Neyaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Fourier Analysis: Lucas Illing 2008Document21 pagesFourier Analysis: Lucas Illing 2008alnemangiNo ratings yet
- BSpline Curves D PDFDocument210 pagesBSpline Curves D PDFsankalp meshramNo ratings yet
- Lecture On B-Spline Curves: Prof. (DR.) - Kailash Jha Dept. of Mech. EnggDocument170 pagesLecture On B-Spline Curves: Prof. (DR.) - Kailash Jha Dept. of Mech. EnggAnu SinghNo ratings yet
- Supch16 PDFDocument14 pagesSupch16 PDFvampakkNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 PDFDocument46 pagesChapter4 PDFFarahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1/ Class Test 1: 5. (MCQ Online) (Online Upload)Document8 pagesAssignment 1/ Class Test 1: 5. (MCQ Online) (Online Upload)Kgotso KgengweNo ratings yet
- 6 6 6 6 Topic Topic Topic Topic: Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms Laplace TransformsDocument23 pages6 6 6 6 Topic Topic Topic Topic: Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms Laplace Transforms Laplace TransformsManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Design A AlgorithmDocument20 pagesDesign A AlgorithmAyman AymanNo ratings yet
- Headsoln Master MethodDocument6 pagesHeadsoln Master MethodSumit DeyNo ratings yet
- System PrototypesDocument29 pagesSystem PrototypesYgor AguiarNo ratings yet
- Study of Bulk Arrival With Working VacationDocument4 pagesStudy of Bulk Arrival With Working VacationEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Catmull Rom SplineDocument4 pagesCatmull Rom SplineahimpliNo ratings yet
- IEOR 4106: Spring 2011 Solutions To Homework Assignment 7: Due On Tuesday, March 22Document5 pagesIEOR 4106: Spring 2011 Solutions To Homework Assignment 7: Due On Tuesday, March 22amyNo ratings yet
- 05 - Master's - TheoremDocument6 pages05 - Master's - Theoremrashid.shorustamov2003No ratings yet
- Tutorial No4Document1 pageTutorial No422bce546No ratings yet
- R Akne Ovningar Empirisk ModelleringDocument23 pagesR Akne Ovningar Empirisk Modelleringarafath1985No ratings yet
- Math 328 Module 1 Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesMath 328 Module 1 Fourier SeriesMelchor Jaramilla OronosNo ratings yet
- 01b-Fourier Series RevisionDocument37 pages01b-Fourier Series RevisionGeorges YoussefNo ratings yet
- Ecuatia Lui BernoulliDocument47 pagesEcuatia Lui BernoulliMihai NanNo ratings yet
- On The M-Power Free Part of An IntegerDocument4 pagesOn The M-Power Free Part of An IntegerDon HassNo ratings yet
- Assign1 2020Document4 pagesAssign1 2020Zulqarnain KhanNo ratings yet
- 11phyppuni29072022093025 0Document17 pages11phyppuni29072022093025 0Rohit Kumar MohantyNo ratings yet
- DAA Unit-2Document25 pagesDAA Unit-2Burra KotammaNo ratings yet
- Ps 1 SolDocument19 pagesPs 1 SolEmNo ratings yet
- The Method of Proton SecondsDocument30 pagesThe Method of Proton SecondsIan BeardsleyNo ratings yet
- General Renewal Processes: 0 T T T TDocument16 pagesGeneral Renewal Processes: 0 T T T TKrishnaMohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Solved Problems: Solutions To Solved Problem 4.1Document12 pagesChapter 4 - Solved Problems: Solutions To Solved Problem 4.1cilentNo ratings yet
- IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I Fall 2012, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS To Homework Assignment 7Document4 pagesIEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I Fall 2012, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS To Homework Assignment 7Songya PanNo ratings yet
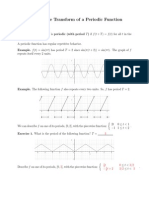
- Periodic Functions, The Unit Step Function and The Second Shifting TheoremDocument21 pagesPeriodic Functions, The Unit Step Function and The Second Shifting TheoremChristian SarmientoNo ratings yet
- MA 212 Lecture Week3 Part2Document17 pagesMA 212 Lecture Week3 Part2Andy ShawNo ratings yet
- Divide and Conquer MethodologyDocument19 pagesDivide and Conquer Methodologythe477577No ratings yet
- HW 2 SolutionDocument10 pagesHW 2 SolutionSarahBNo ratings yet
- CMPS 101 Fall 2009 Homework Assignment 4 SolutionsDocument4 pagesCMPS 101 Fall 2009 Homework Assignment 4 SolutionshoshgeldyNo ratings yet
- Laplace Periodic SolutionsDocument4 pagesLaplace Periodic SolutionsasbadgNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesTutorial1 Solutionsjohn doeNo ratings yet
- 3.4 System Response With Additional Poles: R(S) 0.2 K Y (S)Document3 pages3.4 System Response With Additional Poles: R(S) 0.2 K Y (S)Yassine DjillaliNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument25 pagesModuleYogix ThetroubleshooterNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control SystemDocument29 pagesFeedback Control SystemKelvin KongNo ratings yet
- General Forced Response: P T N B P T N A A T FDocument11 pagesGeneral Forced Response: P T N B P T N A A T FSathish Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Recurrence-Relations Time ComplexityDocument14 pagesRecurrence-Relations Time ComplexitySudharsan GVNo ratings yet
- Recurrence-Relations Time ComplexityDocument14 pagesRecurrence-Relations Time ComplexitySudharsan GVNo ratings yet
- Recurrencew Relation - Iteration MethodDocument5 pagesRecurrencew Relation - Iteration MethodMohammed Siyad BNo ratings yet
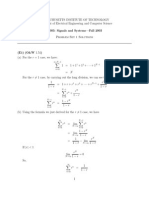
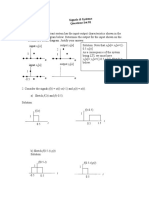
- N N N N Y: Signals & Systems Questions Set 01Document13 pagesN N N N Y: Signals & Systems Questions Set 01Sachin Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- No Textbook and Notes (Close-Book Exam) - Initial On The Top of Each PageDocument12 pagesNo Textbook and Notes (Close-Book Exam) - Initial On The Top of Each PageYaseenNo ratings yet
- Recurrence Relations PDFDocument16 pagesRecurrence Relations PDFSrinivasaRao JJ100% (1)
- P-1 Olympaid Paper - FC (AKS Sir)Document10 pagesP-1 Olympaid Paper - FC (AKS Sir)Subhankar TripathiNo ratings yet
- Lab1 Soln PDFDocument24 pagesLab1 Soln PDFJuan Carlos MerchanNo ratings yet
- First Order Linear Differential Equations: Section 2.1Document21 pagesFirst Order Linear Differential Equations: Section 2.1Mac AragonNo ratings yet
- ECEN 314: Signals and Systems: 1 CausalityDocument4 pagesECEN 314: Signals and Systems: 1 CausalityMEIVELJ 19EE025No ratings yet
- ECEN 314: Signals and Systems: 1 CausalityDocument4 pagesECEN 314: Signals and Systems: 1 CausalityMafer ValdezNo ratings yet
- 13-Substitution Method - Recursive Tree Method - Masters Theorem-17-08-2022Document32 pages13-Substitution Method - Recursive Tree Method - Masters Theorem-17-08-2022IshankNo ratings yet
- Uraian FourierDocument91 pagesUraian FourierAgus Dian PratamaNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Operational Properties IIDocument8 pages7.4 Operational Properties IIFatimah Nik MazlanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Exam Fourier - NotesDocument5 pagesFourth Exam Fourier - NotesGil Kenneth San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean Triples 3Document13 pagesPythagorean Triples 3Hiewayn ChuaNo ratings yet
- MDOF System Analysis - Direct AnalysisDocument8 pagesMDOF System Analysis - Direct AnalysisFrances Dixy AceraNo ratings yet
- hw1 SolnDocument7 pageshw1 SolnRudraraju Sai Vishnu VarmaNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- OPMDocument23 pagesOPMaisha ashrafNo ratings yet
- Life Span Development 26092022 081749am 18022023 044328pmDocument33 pagesLife Span Development 26092022 081749am 18022023 044328pmaisha ashrafNo ratings yet
- Practicum Problem Solving Report Final PDFDocument19 pagesPracticum Problem Solving Report Final PDFaisha ashrafNo ratings yet
- HRM 2Document4 pagesHRM 2aisha ashrafNo ratings yet
- Bond Valuation - Session 7Document44 pagesBond Valuation - Session 7aisha ashrafNo ratings yet
- Course: Financial Accounting Session: 2Document28 pagesCourse: Financial Accounting Session: 2aisha ashrafNo ratings yet
- Ding DongDocument20 pagesDing Dongaisha ashrafNo ratings yet
























































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1714993295?v=1)






