Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Septal Nephridia
Septal Nephridia
Uploaded by
riddhiii2861Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Septal Nephridia
Septal Nephridia
Uploaded by
riddhiii2861Copyright:
Available Formats
A.
Septal nephridia (Typical nephridia):
A. Sepal nephridium consists of 3 main parts.
a.Nephrostome: Nephrostome is a funnel shaped and ciliated structure which helps to collect the
metabolic wastes from the coelom. Nephrostome is followed by a short tubular and ciliated neck.
b. Body: Body is the main part of nephridium and consists of
i. A short straight lobe and
ii. A long twisted loop with a narrow apical lobe.
The twisted loop is formed by two limbs namely a proximal and a distal limb which
are spirally coiled upon each other. The number of coils varies from 9 to 13.
There are 4 nephridial canals or tubules in the straight lobe, 3 in the twisted lobe, 2 in
the apical lobe and 1 each in the neck and the terminal duct.
c. Terminal duct: One of the nephridial canals of proximal limb then forms a short and straight
terminal duct.
Each segment from 16 segment, consists of 80-100 septal nephridia and the terminal
th
duct of all those septal nephridia then open into a septal excretory duct. Two septal excretory
ducts lying on either side of the intestine then open into a separate supra- intestinal excretory
duct lying just above the gut (alimentary canal). The supra intestinal excretory duct then opens
into the intestine at each segment.
Septal nephridia open into the intestine, such nephridia is called enteronephric or
endonephric nephridia.
B. Integumentary nephridia: They are found in all segments except first three segments. About
200-250 nephridia occurs in 4 to 13 and 17 to last. About 2000-2500 integumentary nephridia
th th th
are found in the clitellum. So, clitellum is called forest of nephridia. Integumentary nephridia is
v- shaped nephridia that has no nephrostome ant it opens outside of the body through
nephridiopores and not into the intestine. They are exonephric nephridia due to directly opening
outside the body.
C.Pharyngeal nephridia: They are found in three pairs of groups located in the 4 , 5 and 6
th th th
segments. The two ducts of nephridia of segment 4 and 5 open in the pharynx and one
th th
paired ducts of nephridia of segment 6 open into the buccal cavity. A pharyngeal nephridia
th
is also similar to septal nephridia but it too lacks nephrostome. They are enteronephric
nephridia due to directly open into gut (alimentary canal).
Physiology of excretion:
The metabolic wastes mainly urea and little amount of ammonia and amino acids
present in the coelomic fluid/coelom is collected by nephrostome and are then passed to the neck
and body and then to terminal duct from where they are passed to septal excretory canal, supra-
intestinal excretory duct and finally into the intestine. The wastes are then eventually removed
out through the anus.
You might also like
- Pneumonia Case StudyDocument49 pagesPneumonia Case StudyJohn Paul Farofil Reproto100% (3)
- Wiring Diagram-Split System Air ConditionerDocument1 pageWiring Diagram-Split System Air ConditionerSohail Ejaz Mirza85% (13)
- 3.excretory System of EarthwormDocument2 pages3.excretory System of Earthwormarjab acharyaNo ratings yet
- Excretion in AnnelidaDocument21 pagesExcretion in AnnelidaSubhashree satapathyNo ratings yet
- Development of Body Cavities and Diaphragm: Pleuro-Pericardial and Pleuro-Peritoneal MembraneDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Body Cavities and Diaphragm: Pleuro-Pericardial and Pleuro-Peritoneal MembraneÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pharynx and Esophagus 2012Document44 pagesAnatomy of The Pharynx and Esophagus 2012Syahmi IeskandarNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE 9 - 10 MM Pig Embryo - Endodermal DerivativesDocument5 pagesLAB EXERCISE 9 - 10 MM Pig Embryo - Endodermal DerivativesGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- Special Embryology-Norhan Ahmed Ahmed Hassan El-MeniawyDocument67 pagesSpecial Embryology-Norhan Ahmed Ahmed Hassan El-MeniawyNorhan Ahmed Ahmed Hassan El-MeniawyNo ratings yet
- Embryo Development Ofthe UG SystemDocument16 pagesEmbryo Development Ofthe UG SystemKingNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract AnatomyDocument61 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Anatomyيحيى اسماعيل الجميليNo ratings yet
- Airway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2Document49 pagesAirway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2agatakassaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Intern: Iris Parcon Clerks: Karen Bianca Espinola Anna Sophia Lim Leo Salvador VedanaDocument50 pagesCase Presentation: Intern: Iris Parcon Clerks: Karen Bianca Espinola Anna Sophia Lim Leo Salvador VedanaKaren Bianca Matampale EspinolaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument62 pagesUntitledManaye MamuyeNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY ReviewerDocument18 pagesBIOLOGY ReviewerAngela Nicole ManasNo ratings yet
- 4 RSDocument16 pages4 RSzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- 3-Embryology of Respiratory SystemDocument25 pages3-Embryology of Respiratory SystemNur HikmahNo ratings yet
- 4 AnatomyDocument10 pages4 AnatomyRam NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 1 1Document24 pagesRespiratory System 1 1mmaccidobadamasiNo ratings yet
- Zoo 1 PPT 10 Respiratory (2015)Document17 pagesZoo 1 PPT 10 Respiratory (2015)Zucc mahnutNo ratings yet
- Urogenital System DevelopmentDocument40 pagesUrogenital System DevelopmentAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Diaphragm Group-TDocument42 pagesThoracic Diaphragm Group-TVivev JatNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Annelida:: (A) NephridiaDocument3 pagesExcretion in Annelida:: (A) NephridiaSubhashree satapathyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemPal SedNo ratings yet
- 7th-The Alimentary SystemDocument25 pages7th-The Alimentary Systemprasun_v100% (1)
- Scenario 4Document9 pagesScenario 4Syaema MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument54 pagesRespiratory SystemEndin Nokik StujannaNo ratings yet
- Urogenital System DevelopmentDocument107 pagesUrogenital System DevelopmentTadesse MuhammedNo ratings yet
- The PharynxDocument67 pagesThe PharynxArvindhanNo ratings yet
- Ana Print 3Document12 pagesAna Print 3Ade AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Var 29 - 30Document4 pagesVar 29 - 30Honey BabaNo ratings yet
- San Beda Respiratory System 9-15Document68 pagesSan Beda Respiratory System 9-15conyxzNo ratings yet
- 156 P18ZC101 2020120606191995Document15 pages156 P18ZC101 2020120606191995prachiteegoregaonkarNo ratings yet
- RuchhhhiiDocument1 pageRuchhhhiiAnish bhandariNo ratings yet
- Abdomen CAP Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesAbdomen CAP Questions and AnswersRathnaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledANNE MARGUERITE BARETENo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Pharyngeal Lining Mucosa Is Continuous With TheDocument5 pagesPharynx: Pharyngeal Lining Mucosa Is Continuous With Themaya_fitrianaNo ratings yet
- DiaphragmDocument18 pagesDiaphragmAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- PELVIS, Student FileDocument52 pagesPELVIS, Student FileShawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- Abdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyDocument29 pagesAbdomen OSPE Charts Questions OnlyRathnaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of Urinary SystemDocument34 pagesEmbryology of Urinary SystemFatimaNo ratings yet
- Development of Pharyngeal ApparatusDocument50 pagesDevelopment of Pharyngeal ApparatusPapadoveNo ratings yet
- Prof. DR - Mohamed Talaat ElghonemyDocument49 pagesProf. DR - Mohamed Talaat Elghonemyadel madanyNo ratings yet
- Embryologi OF The Respiratory System: Arti Rosaria Dewi, DRDocument60 pagesEmbryologi OF The Respiratory System: Arti Rosaria Dewi, DRAsti NuriatiNo ratings yet
- The Oesophagus: DR M Idris SiddiquiDocument40 pagesThe Oesophagus: DR M Idris SiddiquiIdris Siddiqui100% (1)
- Abdomen (Repaired)Document174 pagesAbdomen (Repaired)Merellyn Hurtado PachecoNo ratings yet
- Rectumanalcanal 221008135814 55d691e6Document42 pagesRectumanalcanal 221008135814 55d691e6Emmanuel AdemoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ESophagusDocument28 pagesAnatomy of ESophagusAbdur RaqibNo ratings yet
- Development of Urogenital System PDFDocument112 pagesDevelopment of Urogenital System PDFLugembe MasolaNo ratings yet
- NOSEDocument6 pagesNOSEAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- Embryology of Body Cavities, Mesenteries and DiaphragmDocument35 pagesEmbryology of Body Cavities, Mesenteries and DiaphragmKankomba MuleyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemLiza Marie Cayetano AdarneNo ratings yet
- Paranasal Sinuses: By: Student at Faculty of Dentistry Ahram Canadian UniversityDocument20 pagesParanasal Sinuses: By: Student at Faculty of Dentistry Ahram Canadian Universityمحمد نعيمNo ratings yet
- Anatomy PharynxDocument15 pagesAnatomy PharynxNina ZabrinaNo ratings yet
- PlenaryDocument31 pagesPlenaryIsmail AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument71 pagesRespiratory SystemmarygracetamborlnhsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Digestive System PHARYNX OesphagusDocument31 pagesLecture 3-Digestive System PHARYNX Oesphagussamiiikhan5264No ratings yet
- Esophagus AnatomyDocument5 pagesEsophagus AnatomyJinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Respiratory System: The Respiratory Tract Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Principal BronchiDocument47 pagesChapter 3 The Respiratory System: The Respiratory Tract Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Principal Bronchisomebody_maNo ratings yet
- My Anatomy Ticket 10Document10 pagesMy Anatomy Ticket 10Aastha BhatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument42 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- Digestive System - Kelompok A4Document102 pagesDigestive System - Kelompok A4Fathoni akbarNo ratings yet
- Treatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsFrom EverandTreatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsNo ratings yet
- Microbes in Human WelfareDocument8 pagesMicrobes in Human WelfareJeevika shanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Participation in Decision Making QuestionnaireDocument21 pagesParticipation in Decision Making QuestionnaireMorrison Omokiniovo Jessa SnrNo ratings yet
- Iecex Sir 12.0100XDocument17 pagesIecex Sir 12.0100XFrancesco_CNo ratings yet
- Icd 10 CodeDocument9 pagesIcd 10 CodeFloriPuspaHumaniNo ratings yet
- Visualization of Magnetic Field Generated by PortaDocument6 pagesVisualization of Magnetic Field Generated by PortajuanNo ratings yet
- Quality AssuaranceDocument150 pagesQuality Assuarancebhatta_ashu3672No ratings yet
- Rapid Diagnostic Testing in Microbiology: Adeleke Olaide.A. 17/1078Document18 pagesRapid Diagnostic Testing in Microbiology: Adeleke Olaide.A. 17/1078Ay GlassesNo ratings yet
- Line Conductors and Supporting Structures OriginalDocument80 pagesLine Conductors and Supporting Structures OriginalRida100% (1)
- Soudure Plastique Ultra Son PDFDocument30 pagesSoudure Plastique Ultra Son PDFamr_akram_2No ratings yet
- AcuPulse Versatility SupplementDocument16 pagesAcuPulse Versatility SupplementSD DSNo ratings yet
- Food Product Recall ProcedureDocument11 pagesFood Product Recall Procedureadhe hildaNo ratings yet
- One Touch Alarm System For Women's SAFETY USING GSMDocument4 pagesOne Touch Alarm System For Women's SAFETY USING GSMBabaThakorNo ratings yet
- Subaru Generators Commercial sgx3500 sgx5000 Sgx7500e OwnersDocument35 pagesSubaru Generators Commercial sgx3500 sgx5000 Sgx7500e OwnersAdrián Verduzco OronaNo ratings yet
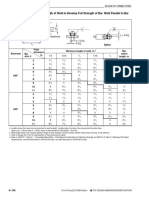
- Design Aid 6.15.3 Minimum Length of Weld To Develop Full Strength of Bar. Weld Parallel To Bar LengthDocument1 pageDesign Aid 6.15.3 Minimum Length of Weld To Develop Full Strength of Bar. Weld Parallel To Bar LengthbrettNo ratings yet
- Mini Fellowship Program OutlineDocument4 pagesMini Fellowship Program OutlineVijayraj GohilNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Dry FractionationDocument10 pagesExp 2 Dry Fractionationtusen krishNo ratings yet
- Zesc or Deq V2Document18 pagesZesc or Deq V2mungagungadinNo ratings yet
- DaburDocument27 pagesDaburKeshav KalaniNo ratings yet
- Soal Ulangan Tengah SemesterDocument9 pagesSoal Ulangan Tengah SemesterAgus MopedaNo ratings yet
- LR Guidance Note WebDocument8 pagesLR Guidance Note WebOscar Marino Campo BonellNo ratings yet
- How To Perform Criticality Analysis To Prioritize Asset MaintenanceDocument22 pagesHow To Perform Criticality Analysis To Prioritize Asset MaintenanceSreekanthMylavarapuNo ratings yet
- Goldberg 422S-422D - Datasheet, 422 LTDocument3 pagesGoldberg 422S-422D - Datasheet, 422 LTYounes ODMNo ratings yet
- Pbs 1 DatDocument2 pagesPbs 1 DatJaya LekhwaniNo ratings yet
- Salaries & Wages - Regular Payroll PERA . Due To BIRDocument7 pagesSalaries & Wages - Regular Payroll PERA . Due To BIRAyie RomeroNo ratings yet
- GRH D 16 00001 ManuscriptDocument224 pagesGRH D 16 00001 ManuscriptsrividyargNo ratings yet
- Basf Masterseal 610 614 615 PDFDocument4 pagesBasf Masterseal 610 614 615 PDFdostjanNo ratings yet
- The NWA 8159 Martian Augite Basalt Possible EruptiDocument3 pagesThe NWA 8159 Martian Augite Basalt Possible EruptiAlberto RSNo ratings yet
- Product Technical Application Guide: Volvo RemanDocument49 pagesProduct Technical Application Guide: Volvo RemanJonah RagleNo ratings yet