Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Replication of DNA
Uploaded by
zibnehuqCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Replication of DNA
Uploaded by
zibnehuqCopyright:
Available Formats
Replication of DNA
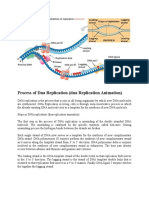
It is the process of producing two identical copies from One Original DNA molecule
Including 3 different types such as—
1. Semiconservative replication 2.Conservative replication 3. Dispersive
replication
Semiconservative replication
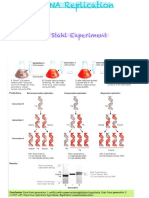
It was proposed by Watson and Crick in 1953. In this process, Produce to copies
contains one Original and one new strand.It is completed by three consecutive
stages,
a) Separation of strands:
• First of all the DNA is relaxed from its super coiling nature by topoisomerase
enzyme.
• Replication begins at the origin of replication along a DNA molecule where
DNA is unzipped and nitrogen bases separate from each other by helicase
enzyme forming replication bubbles leading to Y shaped replication fork at
both ends.
• SSBP ( single strand binding protein) binds to separated DNA strands and
prevents them from reannealing after unwinding.
b)Creation of complementary strands:
• Separated each strand of DNA serps as a template for synthesis of
complementary DNA strand
• Among them one runs from 5’ to 3’ end called leading strand and other runs
from 3’ to 5’end is called lagging strand .
• RNA primer made by RNA Primase binds at the end of leading strand and
various points of lagging strand acting as starting point for DNA synthesis.
• By the help of DNA Polymerase and magnesium ion several nucleotides are
attached at the free 3’ end of the leading strand in 5’ to 3’ direction only y the
help of phosphodiester bond.\
• In the lagging strand there are discontinuous small fragments of synthesized
DNA called Okazaki fragments. Later these fragments are joined together by
DNA Ligase enzyme.In both strands RNA primase adds more RNA primers .
c) Creation of new DNA:
• After matching up all the bases an enzyme called exonuclease removes the
primers then the new strands are proofread to DNA mismatch repair (MMR) in
the new DNA sequence.
• Finally DNA Ligase seals the sequence of DNA into two continuous double
strands.
You might also like
- Chapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)Document36 pagesChapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)abdullaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument12 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDibyakNo ratings yet
- Replication Transcription and TranslationDocument16 pagesReplication Transcription and TranslationBalangat Regine L.No ratings yet
- 6.4 - DNA Replication and Repair (Text RefDocument2 pages6.4 - DNA Replication and Repair (Text RefReeNo ratings yet
- MB 2Document76 pagesMB 2ahkrabNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument21 pagesDNA ReplicationP Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- DnaDocument68 pagesDnaArif Setiawansyah100% (2)
- Submitted By: Fatima Parvez 13/117Document24 pagesSubmitted By: Fatima Parvez 13/117Eng CirroNo ratings yet
- 2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationDocument32 pages2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationALEXANDRA MARIE BUNQUINNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument45 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyEirla Kneriz Trinidad67% (3)
- Prokaryotic Dna ReplicationDocument53 pagesProkaryotic Dna ReplicationRININo ratings yet
- All DNADocument69 pagesAll DNAkeerthiNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument13 pagesZoologydvdmegaNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesLearning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationSphesihle ThekoNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument34 pagesMolecular BiologyMega XtericsNo ratings yet
- DNA - The Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument38 pagesDNA - The Molecular Basis of InheritanceEgi JhonoNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument26 pagesDna ReplicationJerric Cristobal100% (3)
- DNA in Brief PDFDocument5 pagesDNA in Brief PDFayushfmNo ratings yet
- Assignment General MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesAssignment General Microbiology05 Jawad ZahoorNo ratings yet
- Packaging of DNA Into ChromosomeDocument13 pagesPackaging of DNA Into ChromosomeShashank AppuNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: DefinitionDocument6 pagesDNA Replication: DefinitionZEE zeeNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplDocument40 pagesDNA ReplnunutsehaynuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (DNA Replication)Document37 pagesLecture 2 (DNA Replication)M Luqman Hakim100% (1)
- Dna Replication Lecture Notes 2011Document70 pagesDna Replication Lecture Notes 2011براءة أحمد السلامات100% (1)
- Dna Replication and Repair #4Document76 pagesDna Replication and Repair #4Len ArellanoNo ratings yet
- HLF Dna ReplicationDocument8 pagesHLF Dna ReplicationPriyanka ChughNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument13 pagesDNA Replication: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleTaufik AhmadNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesDNA ReplicationAsim Bin Arshad 58-FBAS/BSBIO/S19100% (1)
- Replication Modified Mark-UpDocument26 pagesReplication Modified Mark-UpRandom personNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument27 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentationarunpandey1686No ratings yet
- Replication PDFDocument12 pagesReplication PDFYi LingNo ratings yet
- Zoology DNA ReplicationDocument22 pagesZoology DNA ReplicationbiswassjpNo ratings yet
- The Flow of Genetic InformationDocument34 pagesThe Flow of Genetic InformationOdaiNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and RepairDocument11 pagesDNA Replication and RepairCiroanneNo ratings yet
- BPH 2203, Bio-Molecular Pharmacy: Topic: DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesBPH 2203, Bio-Molecular Pharmacy: Topic: DNA ReplicationNazninNo ratings yet
- MB Chapter 4 - DNA-Replication-IDocument27 pagesMB Chapter 4 - DNA-Replication-IMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Bio Dna Replication - Transcription and TranslationDocument6 pagesBio Dna Replication - Transcription and TranslationXie YuJiaNo ratings yet
- BCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUDocument35 pagesBCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUidriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- Process of Dna Replication, Transcription, TranslationDocument8 pagesProcess of Dna Replication, Transcription, TranslationBenedictus YohanesNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication (Prokaryotes) 1 2 PDFDocument54 pagesDNA Replication (Prokaryotes) 1 2 PDFItni Si Baat HyNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationAkss ShauryaNo ratings yet
- 6.2: Dna ReplicationDocument43 pages6.2: Dna Replicationa200812No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Molecular Biology IDocument12 pagesLecture 5 - Molecular Biology IbesillysillyNo ratings yet
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument38 pagesBacterial Geneticsfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- Composed of A BaseDocument23 pagesComposed of A Basetanvi bhallaNo ratings yet
- 7th Cytogenetics Lecture 20121 1Document37 pages7th Cytogenetics Lecture 20121 1RC SILVESTRENo ratings yet
- 4 DnaDocument6 pages4 Dnadr_47839666No ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaCahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta20.020 Cahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaCahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Plant Genetics Resume: 1. DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesPlant Genetics Resume: 1. DNA ReplicationEbri Yosia ManikNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationYSOBELLATHERESE BILOLONo ratings yet
- DNA RepilicationDocument57 pagesDNA RepilicationJeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- 6.2 DNA Replication Full NoteDocument44 pages6.2 DNA Replication Full NotejiaenNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesDNA ReplicationApril Marie100% (3)
- DNA ReplicationDocument24 pagesDNA ReplicationAkhtar MuneerNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication With Video LinksDocument15 pagesDNA Replication With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)