Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HRLB
Uploaded by
Noorul ameenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HRLB
Uploaded by
Noorul ameenCopyright:
Available Formats
Configuring Hierarchical Radio Link
Bonding (hRLB)
MINI-LINK 6600
Operating Instructions
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N
Copyright
© Ericsson AB 2020-2022. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be
reproduced in any form without the written permission of the copyright owner.
Disclaimer
The contents of this document are subject to revision without notice due to
continued progress in methodology, design and manufacturing. Ericsson shall
have no liability for any error or damage of any kind resulting from the use of this
document.
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24
Contents
Contents
1 Overview 1
2 Planning and Preparing 2
2.1 Prerequisites 2
2.2 Limitations 2
2.3 Planning Advice 3
2.4 Required Documentation 4
2.5 Safety Information 5
3 Configuring hRLB Using CLI 6
3.1 Configure an hRLB Interface 6
3.2 Remove an hRLB Interface 7
4 Configuring hRLB Using MINI-LINK Node GUI 8
4.1 Configure an hRLB Interface 8
4.2 Remove an hRLB Interface 9
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24
Configuring Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24
Overview
1 Overview
This document describes how to configure Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding
(hRLB) using CLI or MINI-LINK Node GUI.
hRLB is a Layer 1 (L1) technology used for bonding of separately configured
Radio Link Terminals (RLTs) into one hRLB interface to achieve a higher radio
link capacity.
Different hRLB configurations are available for the MINI-LINK 6600 and MINI-
LINK 6200 family. The supported hRLB configurations for MINI-LINK 6600 are
listed in MINI-LINK 6600 R1 Compatibility. The supported hRLB configurations
for MINI-LINK 6200 are listed in MINI-LINK 6200 R1 Compatibility. The
supported hRLB configurations for MINI-LINK 6300 are listed in MINI-LINK
6300 R1 Compatibility. Maximum two hRLB groups are supported. The available
total capacity is 10 Gbps on NPU 1005 and MMU 1005, 17Gbps on ML6651/4
and ML6371. If one hRLB group is used, then four members can be configured for
that group. On NPU 1005 if two hRLB groups are used, each group can contain
two members with an aggregated capacity of 5 Gbps per group.
On NPU 1005 in case of one group there is one 10 Gbps and four 2.5 Gbps
links and in case of two groups there are four 2.5 Gbps links available for hRLB
members. On ML6651/4 and ML6371 there are two 10 Gbps and two 2.5 Gbps
links available for hRLB members. On MMU 1005 there are two 10 Gbps and one
2.5 Gbps links available for hRLB members, only the local links on the board can
be used as hRLB members. LAN interfaces can be added as 10 Gbps or 2.5 Gbps
capacity members.
hRLB requires a dedicated resource to bond RLTs. In case of NPU 1005, RLTs
are configured separately on the Modem Unit (MMU) and the hRLB interface is
configured on the NPU. Existing RLT configurations, such as Radio Link Bonding,
Radio Link Protection, or Equipment Protection (EQP) can be used as members.
For how to configure RLTs, see Configuring Radio Link.
This document describes how to configure hRLB through the example of an hRLB
group (4+0 hRLB) configured from two RLTs (2+0 RLB), which are already set up
on the modem.
hRLB members in the radio link modes 1+0, 2+0 RLB, 2+0 RLB EQP, 4+0 RLB
EQP can also be configured for AES Encryption Over-the-Hop, when the node
is equipped with either MMU 1002 or MMU 1004. This is only applicable for
MINI-LINK 6600, not for MINI-LINK 6200.
hRLB members in the radio link modes 1+0, or 2+0 RLB, can also be configured
for AES Encryption Over-the-Hop, when the node is equipped with MMU 1005.
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24 1
Configuring Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
2 Planning and Preparing
2.1 Prerequisites
— hRLB requires an NPU 1005, an MMU 1005, a MINI-LINK 6651/4 or a
MINI-LINK 6371.
— Since hRLB uses existing RLTs, previously configured RLTs are needed.
— hRLB requires a bonding license.
— To access an NE remotely through MINI-LINK Node GUI, a MINI-LINK Node
GUI license is required on that specific NE.
2.2 Limitations
— The supported hRLB configurations are listed in MINI-LINK 6600 R1
Compatibility, MINI-LINK 6200 R1 Compatibility, and MINI-LINK 6300 R1
Compatibility.
— The group capacity can be up to 10 Gbps. However, this capacity is not
guaranteed when using small frame sizes. In case of one group configured
the hRLB packet processing capacity is 7.5 Mpps. For example, with an
RFC 2544 throughput test that uses 64-byte or 128-byte frames, it is
not expected to reach the 10 Gbps capacity. . In case of two groups are
configured the hRLB capacity is 4 Mpps per group. Considering RFC2544
throughput test with 64, 128, 256 bytes frames the 10Gbps capacity should
not be expected.
— The maximum supported frame size over an hRLB link is 9212 bytes.
— Traffic Aware Power Save (TAPS) is not supported with hRLB. Therefore
TAPS must be disabled on all radio carriers involved in an hRLB group.
— Multi-Layer Header Compression (MLHC) is not supported with hRLB.
Therefore MLHC must be disabled on all radio carriers involved in an hRLB
group.
— Adding and removing hRLB members on MINI-LINK 6651/4 and on MINI-
LINK 6371 can result in a short traffic disturbance on that interface and
other connected interfaces as well. A short outage in DCN connectivity is also
possible.
— A LAN interface only with 10 Gbps line speed can be added as a member. It
can be added to an hRLB group as either a 10 Gbps or a 2.5 Gbps capacity
member.
— RLT ports are allowed only as 2.5 Gbps capacity members, except on MMU
1005 where RLT can be added as 10Gbps capacity member.
2 911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24
Planning and Preparing
— On NPU1005 the second hRLB group can only be configured if the first has
no 10Gbps capacity members.
— HRLB has a total capacity of 17 Gbps on ML6651/4 and on ML6371.
2.3 Planning Advice
To ensure proper node and network function, all configuration activities must be
planned in advance by skilled personnel. Before taking any actions, make sure
that only authorized persons have access to the NE.
When using CLI commands, the configuration can be prepared offline and
transferred to the node in the form of a CLI script, either remotely (when
modifying the configuration for an installed node) or on site (when installing
a new node).
When using MINI-LINK Node GUI, the configuration can also be performed
either remotely or on site.
Planning Considerations for Configuring hRLB
hRLB is recommended to use only in those scenarios when traditional Radio Link
Bonding is not suitable. For example, in case of a (4+0) RLT scenario, when the
aggregated capacity exceeds 2.5 Gbps or there are more than four radio link
carriers.
It is recommended to use hRLB only with low latency frame formats. The
recommended low latency frame IDs are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Low Latency Frame IDs for MINI-LINK 6600
ETSI mode Channel Spacing Frame ID (SISO) Frame ID (XPIC)
14 (13.75) 357 1357
28 (27.5) 358 1358
40 359 1359
56 (55) 360 1360
80 403 1403
112 (110) 361 1361
ANSI mode Channel Spacing Frame ID (SISO) Frame ID (XPIC)
20 363 1363
30 364 1364
40 365 1365
50 366 1366
60 367 1367
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24 3
Configuring Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
ANSI mode Channel Spacing Frame ID (SISO) Frame ID (XPIC)
80 368 1368
Channel Spacing (CS) 7 MHz is not supported in ETSI mode.
CS 10 MHz is not supported in ANSI mode.
hRLB provides hitless fading so radio link degradation or even fading out can be
handled without traffic loss if there is sufficient aggregated capacity, otherwise
the traffic is handled according to the priorities. However, traffic loss is expected
in case of any kind of radio link related failure or repair events.
To support hitless fading, the minimum configured ACM for every CT included
in an hRLB member is used as a safety zone in case of fading. This means
that when all carriers have a degraded performance in either direction, Ethernet
traffic will be transferred to another hRLB member as well as handled by the
QoS rules in case of a saturated hop. The safety zone should be considered when
planning the capacity of the link. Note that static modulation is still supported
but if any CT in an hRLB member is configured with static modulation, the traffic
might not be hitless in case of fading.
hRLB is not recommended to use as a backup solution, for example, where one of
the members are in a stand-by mode. All hRLB members are recommended to be
active and transmitting data.
To achieve good performance, ensure that the same software version is used on
the near-end and the far-end nodes. Note that backward compatibility provides
the possibility to upgrade the nodes in two steps.
To achieve good performance, when only RLTs are used as hRLB members,
ensure that the speed ratio between the highest capacity and lowest capacity
hRLB members does not reach 10. This 1:10 speed ratio is not likely to be
exceeded during normal operation, when hRLB is used as intended and the
highest modulation levels are used on all carriers.
2.4 Required Documentation
Read through this document. Make sure that referenced documentation is
available during the configuration process.
— Finding Information in the CPI Library
— Accessing a Network Element
— Naming Principles for Rack, Slots, and Ports
— CLI User Guide
— CLI Tool User Guide
4 911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24
Planning and Preparing
— CLI Descriptions
— MINI-LINK Node GUI User Guide
— MINI-LINK Node GUI Descriptions
2.5 Safety Information
Make sure that the information in the following documents have been
understood by the persons performing the procedures:
— Personal Health and Safety Information
— System Safety Information
— Supplementary Safety Information for MINI-LINK
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24 5
Configuring Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
3 Configuring hRLB Using CLI
3.1 Configure an hRLB Interface
1. Use this example script to configure an hRLB group (4+0 hRLB) configured
from two RLTs (2+0 RLB), which are already set up on the modem:
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, create an hRLB group
! and change to hRLB Configuration submode:
! (config)#[no] hrlb <RSP>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! The following example creates an hRLB group on 1/7/50:
hrlb 1/7/50
! Add member interfaces to an hRLB group:
! (config-hrlb)#add-member <RSP>[<CAPACITY>]
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! Capacity is optional, it can be 10G or 2500M.
! The following example adds the first RLT to the hRLB group:
add-member 1/1/1
! Add member interfaces to an hRLB group:
! (config-hrlb)#add-member <RSP>[<CAPACITY>]
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! Capacity is optional, it can be 10G or 2500M.
! The following example adds the second RLT to the hRLB group:
add-member 1/2/1
! Optionally, enable the Degraded Service alarm:
! (config-hrlb)#[no] alarm-enable-degraded-service
! The following example enables the Degraded Service alarm:
alarm-enable-degraded-service
! Optionally, enable the No Traffic alarm:
! (config-hrlb)#[no] alarm-enable-no-traffic
! The following example enables the No Traffic alarm:
alarm-enable-no-traffic
! Exit to Global Configuration mode:
! (config-hrlb)#exit
exit
2. Use this example script to confirm the configuration:
Example
! Exit Global Configuration mode:
! (config)#exit
6 911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24
Configuring hRLB Using CLI
exit
! In Privileged Exec mode, display information about hRLB groups:
! #show hrlb {<RSP> | group-info}
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! The following example displays information about hRLB group 1/7/50:
show hrlb 1/7/50
Output example:
ML66#show hrlb 1/7/50
hrlb 1/7/50
add-member 1/1/1 2500M
add-member 1/2/1 2500M
alarm-enable-degraded-service
alarm-enable-no-traffic
exit
! Display information about hRLB groups:
! #show hrlb {<RSP> | group-info}
! The following example displays information about all hRLB groups:
show hrlb group-info
Output example:
ML66#show hrlb group-info
hrlb 1/7/50
capacity of group: 10000 Mbps
speed of group: 1104 Mbps
member port:1/1/1, max capacity:552 Mbps
member port:1/2/1, max capacity:552 Mbps
! Change to Global Configuration mode:
! #configure
configure
3.2 Remove an hRLB Interface
1. Use this example script to remove an hRLB group:
Example
! In Global Configuration mode, create an hRLB group
! and change to hRLB Configuration submode:
! (config)#[no] hrlb <RSP>
! Make sure that the correct R/S/P values are used.
! The following example deletes hRLB group 1/7/50:
no hrlb 1/7/50
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24 7
Configuring Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding (hRLB)
4 Configuring hRLB Using MINI-LINK Node
GUI
4.1 Configure an hRLB Interface
1. In the Management tree, on the Packet tab, expand Packet.
2. Right-click , point to Configure, and click Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding
MINI-LINK Node GUI displays the Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding page.
3. On the Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Groups tab, in the General panel,
select the member interfaces from the 10G Members and 2.5G Members
drop-down lists for each hRLB interface.
4. Click Save to apply changes.
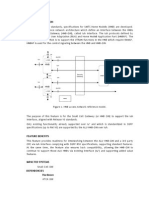
Result: The hRLB interfaces are displayed:
Figure 1 Example hRLB Configuration
5. Optionally, disable No Traffic alarm or Degraded Service alarm by selecting
the No traffic alarm or Degraded service alarm check box and click Save.
8 911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24
Configuring hRLB Using MINI-LINK Node GUI
4.2 Remove an hRLB Interface
1. In the Management tree, on the Packet tab, expand Packet.
2. Right-click Ethernet, point to Configure, and click Hierarchical Radio Link
Bonding
MINI-LINK Node GUI displays the Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding page.
3. On the Hierarchical Radio Link Bonding Groups tab, in the General panel,
click Clear next to the hRLB interface to be deleted.
4. Click OK in the pop-up window to confirm.
911/1543-HRA 901 20/11 Uen N | 2022-11-24 9
You might also like
- World Unlock Code Calculator v4.4Document1 pageWorld Unlock Code Calculator v4.4Allen Oret100% (1)
- RBS 6402 FundamentalsDocument45 pagesRBS 6402 FundamentalsNadira ChikhNo ratings yet
- 7362 - DF16 - 3 - GPON ConfigurationDocument7 pages7362 - DF16 - 3 - GPON ConfigurationDony Nurmi S100% (2)
- MPLS Interview QuestionsDocument17 pagesMPLS Interview QuestionsSyed100% (1)
- Huawei - eRAN8 1 - CA Feature ImplementationDocument28 pagesHuawei - eRAN8 1 - CA Feature ImplementationAnonymous ENqRzQeNo ratings yet
- Alcatel Gpon (I-241W-S) Troubleshooting Manual: Provided By: Nayatel NocDocument4 pagesAlcatel Gpon (I-241W-S) Troubleshooting Manual: Provided By: Nayatel NocNam Khúc NgọcNo ratings yet
- Mpls NSN Training Day 3 OspfDocument65 pagesMpls NSN Training Day 3 OspfDJRashDownloadNo ratings yet
- HRLB With Multi Band BoosterDocument33 pagesHRLB With Multi Band BoosterNoorul ameenNo ratings yet
- HPE Virtual Connect SE 100Gb F32 Module For SynergyDocument21 pagesHPE Virtual Connect SE 100Gb F32 Module For SynergyТимур КрыкпаевNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: The Industry Drives Toward Converged Xhaul Transport NetworksDocument6 pagesData Sheet: The Industry Drives Toward Converged Xhaul Transport NetworkstanashibaNo ratings yet
- CCNP Route QA EIGRPDocument196 pagesCCNP Route QA EIGRP秋山貴史No ratings yet
- R1 NokiaDocument6 pagesR1 Nokia李易No ratings yet
- SSE-F3548S - Supermicro Layer 3 Ethernet Networking SwitchDocument4 pagesSSE-F3548S - Supermicro Layer 3 Ethernet Networking SwitchValentin AtanassovNo ratings yet
- Agenda Item: 7.2.1.1.3 Source: Sony Title: Considerations On Multi Nb-Iot Carriers Document For: Discussion / DecisionDocument3 pagesAgenda Item: 7.2.1.1.3 Source: Sony Title: Considerations On Multi Nb-Iot Carriers Document For: Discussion / Decision李易No ratings yet
- Basic MPLS ConfigurationDocument48 pagesBasic MPLS Configurationsatyvan2003No ratings yet
- Ericsson Microwave-MobilisDocument33 pagesEricsson Microwave-Mobilisyacine bouazniNo ratings yet
- MPLS Traffic Engineering Fast Reroute - Link Protection: Feature OverviewDocument24 pagesMPLS Traffic Engineering Fast Reroute - Link Protection: Feature OverviewilialisseNo ratings yet
- Supported Capacity and Configuration LTEDocument19 pagesSupported Capacity and Configuration LTENadira Chikh100% (1)
- NC - NH Xe4202m 10g Epon R-Olt Data SheetDocument5 pagesNC - NH Xe4202m 10g Epon R-Olt Data SheetEllen BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Litespan 1540Document52 pagesLitespan 1540jabadNo ratings yet
- ASR9000/XR - BNG Deployment GuideDocument53 pagesASR9000/XR - BNG Deployment GuideGabriel SilvaNo ratings yet
- SW HSRPDocument13 pagesSW HSRPEmerson Barros RivasNo ratings yet
- 400G SR8 For Data Center Interconnect: January 20, 2018 Zuowei Shen GoogleDocument7 pages400G SR8 For Data Center Interconnect: January 20, 2018 Zuowei Shen GoogleSam GuapoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Wiconnect CompanyDocument14 pagesKingdom of Saudi Arabia: Wiconnect CompanymogahedNo ratings yet
- cx25 PDFDocument52 pagescx25 PDFBotnaru AurelNo ratings yet
- D2s 2.intelligent Bridging PDFDocument120 pagesD2s 2.intelligent Bridging PDFSiêuThịHoaDalatNo ratings yet
- Cisco Srv6 PPT PDFDocument80 pagesCisco Srv6 PPT PDFallPurpose myallNo ratings yet
- Red Hat, Inc. Global Professional Services BOND/VLAN/Xen Network ConfigurationDocument10 pagesRed Hat, Inc. Global Professional Services BOND/VLAN/Xen Network ConfigurationdarthjuananNo ratings yet
- Unified MPLS Functionality, Features, and Configuration ExampleDocument16 pagesUnified MPLS Functionality, Features, and Configuration ExampleAndy BrogerNo ratings yet
- Wireless Train BackboneDocument9 pagesWireless Train BackboneRicardo Escudero Vinas100% (1)
- Ericsson MINI-LINK 6600 DatasheetDocument2 pagesEricsson MINI-LINK 6600 DatasheetIboro PeterNo ratings yet
- Datasheet MINI-LINK 6600Document2 pagesDatasheet MINI-LINK 6600abdullahNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Understanding of CFP Transceiver Modules - FS CommunityDocument5 pagesA Comprehensive Understanding of CFP Transceiver Modules - FS CommunityNaser KhoshbakhtNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Ran12.0 New Hspa Features-20091230-B-1.0Document33 pagesWcdma Ran12.0 New Hspa Features-20091230-B-1.0Habib BaleNo ratings yet
- 2019 Commercial Products Update PDFDocument142 pages2019 Commercial Products Update PDFVăn HảiNo ratings yet
- Mpls NSN Training Day 3 Ospf PDFDocument65 pagesMpls NSN Training Day 3 Ospf PDFluisNo ratings yet
- Metro - Core Inter AsDocument17 pagesMetro - Core Inter AsapammmmmNo ratings yet
- Link Aggregation - Part 4 (LAG Configuration On Alcatel-Lucent Devices) - WWW - IpciscoDocument8 pagesLink Aggregation - Part 4 (LAG Configuration On Alcatel-Lucent Devices) - WWW - IpciscoDAGNUXNo ratings yet
- Technical Configuration Guide For Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) 802.3ad and VLACPDocument43 pagesTechnical Configuration Guide For Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) 802.3ad and VLACPLives KaiNo ratings yet
- Integrating The MCRNC To The Ran and CN PDFDocument114 pagesIntegrating The MCRNC To The Ran and CN PDFАлексей МихайловичNo ratings yet
- Nokia CAT-M V1.4 20220929Document20 pagesNokia CAT-M V1.4 20220929Adil MuradNo ratings yet
- Brocade® 16Gb/s LWL (10 KM) SFP+: Optimized, Certified Optical Transceivers For Extending Data-Center FabricsDocument2 pagesBrocade® 16Gb/s LWL (10 KM) SFP+: Optimized, Certified Optical Transceivers For Extending Data-Center FabricsAlex JinNo ratings yet
- MPLSDocument716 pagesMPLSarjantonio6118No ratings yet
- MT - All CHP - Telecom MGMT - Question BankDocument10 pagesMT - All CHP - Telecom MGMT - Question Bankseshu_baluNo ratings yet
- SLTA Users GuideDocument159 pagesSLTA Users GuideEbuzer GÜLHANNo ratings yet
- rfc8663 (MPLS Segment Routing Over Ip)Document17 pagesrfc8663 (MPLS Segment Routing Over Ip)cgnet techNo ratings yet
- Config Unified Mpls 00Document13 pagesConfig Unified Mpls 00Sơn ĐàoNo ratings yet
- RLC in Unacknowledged Mode: Improved Real Time Service User ExperienceDocument77 pagesRLC in Unacknowledged Mode: Improved Real Time Service User ExperienceManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Ceragon IP 10 - LAGDocument28 pagesCeragon IP 10 - LAGdenny100% (1)
- Ekinops PM - Lc2-Mp2-B: 200G Line Module For ETS Compact ChassisDocument2 pagesEkinops PM - Lc2-Mp2-B: 200G Line Module For ETS Compact ChassisBhargav SomepalliNo ratings yet
- Ccnpv7 Switch Lab 6-2 Hsrpv6 StudentDocument11 pagesCcnpv7 Switch Lab 6-2 Hsrpv6 StudentVishal Avhad50% (2)
- Alcatel-Lucent in Iuh R9 PDFDocument2 pagesAlcatel-Lucent in Iuh R9 PDFRZNo ratings yet
- IUPS Over IP IUCS Over IP: (UA6 - PM33363)Document97 pagesIUPS Over IP IUCS Over IP: (UA6 - PM33363)rdtiwari123100% (2)
- Difference Between XFP SFPDocument7 pagesDifference Between XFP SFPĐặng Trung AnhNo ratings yet
- Iub TX Configuration Recommendation - IP RAN15Document80 pagesIub TX Configuration Recommendation - IP RAN15Heidi Moore100% (3)
- Carrier Aggregation FDD-TDD: Feature DescriptionDocument18 pagesCarrier Aggregation FDD-TDD: Feature DescriptionKun Panda100% (1)
- LTE Advanced ProDocument21 pagesLTE Advanced Protareq_blay100% (2)
- Confused by 10GbE Optics ModulesDocument6 pagesConfused by 10GbE Optics ModulesCentaur ArcherNo ratings yet
- AOS 8.5.5 ReleaseNotes-RevADocument6 pagesAOS 8.5.5 ReleaseNotes-RevAAlejandro AcuñaNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNo ratings yet
- Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSFrom EverandVersatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSNo ratings yet
- 220308-002001 - 357160651650542 - Main Board SwappedDocument2 pages220308-002001 - 357160651650542 - Main Board SwappedShannon GibbsNo ratings yet
- CSE 324 - Lab-3Document8 pagesCSE 324 - Lab-3Masud SarkerNo ratings yet
- Bloq It OS: The Smart Locker Operating SystemDocument15 pagesBloq It OS: The Smart Locker Operating SystemKevin FoadingNo ratings yet
- Alcatel and Lucent MergerDocument19 pagesAlcatel and Lucent MergerRajesh JainNo ratings yet
- zNID 2400A Series Indoor GPON ONT: ZNID-GPON-2402A, 2403A, 2424A, 2425A, 2426A & 2427ADocument4 pageszNID 2400A Series Indoor GPON ONT: ZNID-GPON-2402A, 2403A, 2424A, 2425A, 2426A & 2427AAhmed SakrNo ratings yet
- Telephone Number Amount Payable Due Date: Pay NowDocument3 pagesTelephone Number Amount Payable Due Date: Pay NowDFNo ratings yet
- An Overview of FMCW Systems in MATLABDocument7 pagesAn Overview of FMCW Systems in MATLABHenry TangNo ratings yet
- Beam Management (5G RAN3.1 - 02)Document49 pagesBeam Management (5G RAN3.1 - 02)VVL100% (1)
- Chapter 21: Introduction To Data Communications and Networking - Review NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 21: Introduction To Data Communications and Networking - Review NotesRichster LofrancoNo ratings yet
- Company Profile - NMS NmsDocument4 pagesCompany Profile - NMS NmsJai AnandNo ratings yet
- Anti Collision DeviceDocument23 pagesAnti Collision Devicechetan_gupta_36100% (1)
- XT-4700 Series User Guide v1.1Document12 pagesXT-4700 Series User Guide v1.1Jay MannNo ratings yet
- ALL - EMY.P.2.03 Safety Message (GMDSS)Document2 pagesALL - EMY.P.2.03 Safety Message (GMDSS)Robin TetreNo ratings yet
- Domain Name SystemDocument5 pagesDomain Name SystemAmit Rashmi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tems Discovery Network 11.0 Presentation 2testDocument147 pagesTems Discovery Network 11.0 Presentation 2testanon_429007357No ratings yet
- 07Document15 pages07vinodNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Drive Test AnalysisDocument61 pagesWCDMA Drive Test AnalysisJagdamba Pal100% (1)
- Fortinac Poc: A Guide To Poc SuccessDocument32 pagesFortinac Poc: A Guide To Poc SuccessstiteufNo ratings yet
- PCI Express Form FactorsDocument71 pagesPCI Express Form Factorsrazvan_nNo ratings yet
- System Input-Output Guide NN43001-712 PDFDocument2,446 pagesSystem Input-Output Guide NN43001-712 PDFTomNo ratings yet
- OSN 9800 V100R001C01 Product Overview 01 REVISADO PDFDocument52 pagesOSN 9800 V100R001C01 Product Overview 01 REVISADO PDFplinio_de_paulaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On PTCLDocument25 pagesInternship Report On PTCLterylay919350% (2)
- Artica Web DocumentationDocument30 pagesArtica Web Documentationsnake972No ratings yet
- Form 4 HSP LKDocument3 pagesForm 4 HSP LKAhmad TechsNo ratings yet
- 31.parametric Study of Vivaldi AntennaDocument4 pages31.parametric Study of Vivaldi AntennaAlteea MareNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2.finaleDocument27 pagesCHAPTER 2.finaleapi-19731397No ratings yet
- Direct-Detection 25 GB/S Pon: Pros and Cons of Digital Signal Processing at The Transmitter SideDocument4 pagesDirect-Detection 25 GB/S Pon: Pros and Cons of Digital Signal Processing at The Transmitter SideElsaid SayedAhmedNo ratings yet
- Antena Satelital 1244 Ku BasebandDocument1 pageAntena Satelital 1244 Ku BasebandJaime Araya ArosNo ratings yet