Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Literature Review Process
Uploaded by
Anisa LabibaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Literature Review Process
Uploaded by
Anisa LabibaCopyright:
Available Formats
Powered by AI
Bing
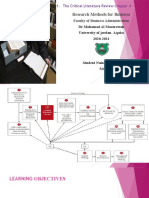
Sure, let's delve deeper into each of these steps in the literature review
process:
1. Select a Topic: This is the initial step where you choose a specific area
of interest. The topic should be narrow, focused, and researchable. The
selection of the topic is crucial as it guides the subsequent stages of the
literature review. It's important to choose a topic that is not only of
interest to you, but also contributes to the field of study.
2. Search and Choose Literature: This step involves searching for existing
literature related to the selected topic. Various sources like academic
journals, books, conference papers, and online databases can be
explored. The aim is to gather as much relevant information as possible
to gain insights into previous research and findings. It's important to use
a systematic approach to search for literature to ensure that all relevant
studies are included.
3. Analyze and Interpret Literature: In this phase, the collected literature
is evaluated critically for quality and relevance. It involves assessing the
methodologies used in previous studies, findings obtained, gaps
identified, and contradictions or consensus in the literature. This step is
crucial for understanding the current state of knowledge on the topic
and identifying areas that need further research.
4. Review Writing: This final step entails compiling all analyzed
information into a well-structured document. The literature review
should provide an overview of existing literature, methodologies
employed, findings obtained, gaps identified (if any), and your
interpretations or perspectives on them. It's important to present the
information in a coherent and logical manner, and to cite all sources
accurately to avoid plagiarism.
Remember, the literature review process is iterative and may require you to
revisit these steps multiple times as you gain a deeper understanding of the
topic. It's a critical part of any research project as it helps to establish the
context of your study and justify its relevance and significance.
You might also like
- Chapter 3 - Review or Related Literature-1Document3 pagesChapter 3 - Review or Related Literature-1Robelyn Serot NortezNo ratings yet
- Final Module in Practical Research 1 With ActivitiesDocument9 pagesFinal Module in Practical Research 1 With ActivitiesJaja Cabatic100% (1)
- PR1 Wlas Q3-W5-6Document17 pagesPR1 Wlas Q3-W5-6Ervie AuguisNo ratings yet
- Bayad Utang TasksDocument6 pagesBayad Utang Tasksjoefuertes19No ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument40 pagesLiterature ReviewKrishna Kumari BathumalaiNo ratings yet
- Learning From Others and Reviewing The Literature: Practical Research 1 Quarter 3 - Week 5Document4 pagesLearning From Others and Reviewing The Literature: Practical Research 1 Quarter 3 - Week 5Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 2015Document25 pagesChapter - 3 2015Yona TsegayeNo ratings yet
- What Is The Purpose of Literature Review in Research MethodologyDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of Literature Review in Research Methodologyc5rn3sbrNo ratings yet
- Hand Out pr1Document6 pagesHand Out pr1Maryfhel LeyteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Review of Literature)Document51 pagesChapter 4 (Review of Literature)natnael haileNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 Review of Related LiteratureDocument44 pagesWEEK 2 Review of Related LiteratureCamille Precious LalagunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lesson 1Document17 pagesChapter 4 Lesson 1Delvie BaldozaNo ratings yet
- CH II. Theoretical Framework - IIDocument40 pagesCH II. Theoretical Framework - IIBandana SigdelNo ratings yet
- PracticalResearch1 Q3 Week5 v4Document17 pagesPracticalResearch1 Q3 Week5 v4Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Business and Management LRDocument56 pagesUnit 2 Business and Management LRMonika ChandelNo ratings yet
- Describe The Process of Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesDescribe The Process of Literature Reviewelrurbrif100% (1)
- Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureDocument14 pagesLearning From Others and Reviewing The LiteraturemariacieloNo ratings yet
- Conducting A Literature ReviewDocument19 pagesConducting A Literature ReviewHainam Le100% (1)
- Week 5 - Ihlp-Las - Practical Research 1Document4 pagesWeek 5 - Ihlp-Las - Practical Research 1Tristan Genesis AmistadNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewBijay NagNo ratings yet
- RRL CapstoneDocument3 pagesRRL CapstoneAkala ko Ikaw ay akinNo ratings yet
- Res 1 Mod 2Document20 pagesRes 1 Mod 2mikaela perezNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Literature Review and Secondary ResearchDocument5 pagesDifference Between Literature Review and Secondary ResearchaflsqyljmNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document26 pagesModule 2Dr. Vignesh Nayak UllalNo ratings yet
- RMIP-21RMI56-Module 2Document24 pagesRMIP-21RMI56-Module 2Bhagyavant RajapureNo ratings yet
- Review of LiteratureDocument25 pagesReview of LiteratureGerald CorralesNo ratings yet
- Literature Review CategoriesDocument7 pagesLiterature Review Categoriesafmzslnxmqrjom100% (1)
- PR2 Notes RRLDocument6 pagesPR2 Notes RRLsofhiabiancagolezNo ratings yet
- Process of Conducting Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesProcess of Conducting Literature Reviewifqaerbnd100% (1)
- Different Types of Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Literature Reviewwqbdxbvkg100% (1)
- Final Task in Research in Daily Life 1Document8 pagesFinal Task in Research in Daily Life 1Charisse Dianne PanayNo ratings yet
- Research CA1 - PROPOSALDocument5 pagesResearch CA1 - PROPOSALtiny seboniNo ratings yet
- Literature Review vs. Research ArticleDocument4 pagesLiterature Review vs. Research Articleafmzwrhwrwohfn100% (1)
- The Critical Literature Review Chapter4Document39 pagesThe Critical Literature Review Chapter4HBH100% (1)
- ITSU3010 Research Methodology: Tutorial - 4 of Lesson - 4Document13 pagesITSU3010 Research Methodology: Tutorial - 4 of Lesson - 4Fatmayyy 9No ratings yet
- Reviewing The LiteratureDocument7 pagesReviewing The LiteratureBustamin KhaldunNo ratings yet
- III Reviewer MidtermsDocument4 pagesIII Reviewer MidtermsjkierstencvergaraNo ratings yet
- Advance ResearchDocument8 pagesAdvance ResearchroyNo ratings yet
- What Is Literature Review in A Research Paper PDFDocument8 pagesWhat Is Literature Review in A Research Paper PDFixevojrifNo ratings yet
- Module7 - Scholarly CommDocument14 pagesModule7 - Scholarly CommwajfaNo ratings yet
- Six Step Process of Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesSix Step Process of Literature Reviewhyz0tiwezif3100% (1)
- Types of Literature Review in Research MethodsDocument4 pagesTypes of Literature Review in Research Methodsc5pgpgqk100% (1)
- How Do I Do A Literature Review For A DissertationDocument8 pagesHow Do I Do A Literature Review For A DissertationmgojgerifNo ratings yet
- Components of Research - ITR - Dini Laetitia - 1209619002Document5 pagesComponents of Research - ITR - Dini Laetitia - 1209619002Dini LaetitiaNo ratings yet
- Types of Literature Review in Research MethodologyDocument7 pagesTypes of Literature Review in Research Methodologygw0935a9No ratings yet
- Steps Followed in Conducting Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesSteps Followed in Conducting Literature Reviewafdtrtrwe100% (1)
- Research Paper Sample Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesResearch Paper Sample Literature Reviewdhjiiorif100% (1)
- Learning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureDocument26 pagesLearning From Others and Reviewing The LiteratureMarianne GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04 - Chapter 2 (Literature Review) PDFDocument5 pagesLesson 04 - Chapter 2 (Literature Review) PDFlasithNo ratings yet
- Process Mapping Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesProcess Mapping Literature Reviewgatewivojez3100% (1)
- Steps To Writing A Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesSteps To Writing A Literature Reviewgw1qjeww100% (1)
- Research As Q2 W2Document6 pagesResearch As Q2 W2Zuriel GenturoNo ratings yet
- How To Write Literature Review ObjectivesDocument8 pagesHow To Write Literature Review Objectivesfvgcaatd100% (1)
- Literature ReviewDocument26 pagesLiterature ReviewKin Adonis TogononNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Literature Review On A Research PaperDocument10 pagesHow To Write A Literature Review On A Research PaperafdtbwkhbNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Literature Searching & Theoretical FrameworkDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Literature Searching & Theoretical FrameworkSmarika SubediNo ratings yet
- What Should Include in Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesWhat Should Include in Literature Reviewwtdcxtbnd100% (1)
- Advance ResearchDocument7 pagesAdvance ResearchUsman UmarNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Simplified: The Checklist Edition: A Checklist Guide to Literature ReviewFrom EverandLiterature Review Simplified: The Checklist Edition: A Checklist Guide to Literature ReviewNo ratings yet
- Types of Experimental Research DesignDocument3 pagesTypes of Experimental Research DesignAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Research Process IssuesDocument2 pagesResearch Process IssuesAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Conducting Experimental ResearchDocument1 pageConducting Experimental ResearchAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- How Intelligent Systems Work For KONE Elevators and Escalators CompanyDocument1 pageHow Intelligent Systems Work For KONE Elevators and Escalators CompanyAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- MethodologyDocument3 pagesMethodologyAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument2 pagesResearch ProposalAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Team Eternals IB Term PaperDocument8 pagesTeam Eternals IB Term PaperAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between RAM & ROMDocument2 pagesDifference Between RAM & ROMAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 02-15-2022 18.06Document32 pagesCamScanner 02-15-2022 18.06Anisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper AnisaDocument4 pagesTerm Paper AnisaAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Anisa Labiba - Class-BBA - Section-B - Roll 029-15-006Document65 pagesLab Report - Anisa Labiba - Class-BBA - Section-B - Roll 029-15-006Anisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- How Do The Components of Revenues and Expenses Differ Between A Merchandising Company and A Service CompanyDocument2 pagesHow Do The Components of Revenues and Expenses Differ Between A Merchandising Company and A Service CompanyAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Department of Management Information SystemDocument3 pagesAssignment: Department of Management Information SystemAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- N.M.Mufrad Ahsan - Term PaperDocument19 pagesN.M.Mufrad Ahsan - Term PaperAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- List Recruiting ADocument6 pagesList Recruiting AAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Characteristics of Financial StatementDocument1 pageQualitative Characteristics of Financial StatementAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Financial & Managerial AccountingDocument3 pagesDifference Between Financial & Managerial AccountingAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Twitter A/C Opening and Screen Shot of Profile: Personality Test ReportDocument19 pagesTwitter A/C Opening and Screen Shot of Profile: Personality Test ReportAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Trial BalanceDocument1 pageImportance of Trial BalanceAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of The Elements of Financial StatementsDocument1 pageMeasurement of The Elements of Financial StatementsAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper AnisaDocument19 pagesTerm Paper AnisaAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Career Test Result - Free Career Test Taking Online atDocument6 pagesCareer Test Result - Free Career Test Taking Online atAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- 1noushin Tabassum Term PaperDocument18 pages1noushin Tabassum Term PaperAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Group8 006 068 120 124 128Document174 pagesGroup8 006 068 120 124 128Anisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Case SolvingDocument20 pagesChapter 8: Case SolvingAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Nafisa - Termpaper - Individual TasksDocument19 pagesNafisa - Termpaper - Individual TasksAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7: Case 3Document9 pagesChapter-7: Case 3Anisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Subject: About The "Leave Donation Program" of ABC CompanyDocument3 pagesChapter 7: Subject: About The "Leave Donation Program" of ABC CompanyAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Case SolvingDocument14 pagesChapter 7: Case SolvingAnisa LabibaNo ratings yet
- Case SolutionsDocument12 pagesCase SolutionsAnisa Labiba100% (1)