Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug-Study and NCP Fracture
Uploaded by
Carl Simon Calingacion0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Drug-study and Ncp Fracture
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views6 pagesDrug-Study and NCP Fracture
Uploaded by
Carl Simon CalingacionCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
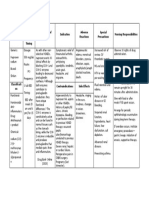
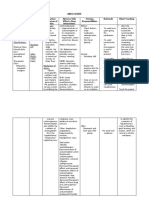
DRUG STUDY FOR FAMOTIDINE
MECHANISM CONTRAINDICATIO ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG NAME CLASSIFICATION INDICATION
OF ACTION N EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: Pharmacologic A competitive It is commonly used Famotidine has CNS (Central
Famotidine class: H2 blockers inhibitor of histamine for the management contraindications that Nervous o Perform a focused physical
H2-receptors, leading of benign gastric and include System): Adjusting assessment of the patient's
Dosage/ Therapeutic to the inhibition of duodenal ulcers, hypersensitivity to the dosage of abdomen through
Route class: gastric acid providing relief by famotidine or other famotidine may be inspection, palpation, and
/Frequency: Histamine H2 secretion. This reducing stomach H2-receptor necessary to minimize auscultation of bowel
10 mg IV q12 receptor medication primarily acid production. antagonists, which CNS adverse effects, sounds to confirm the
antagonists works by blocking the Additionally, can lead to adverse such as dizziness and indication for famotidine
effects of histamine, famotidine is reactions like headaches .
reducing the prescribed for GERD anaphylaxis, GI o Monitor for adverse effects,
production of (gastroesophageal Stevens-Johnson (Gastrointestinal): Fa such as abdominal pain,
stomach ac reflux disease) syndrome, motidine can lead to and assess the patient's
angioedema, side effects like response to the medication
leukopenia, toxic constipation and .
epidermal necrolysis, vomiting o Administer famotidine at
agranulocytosis, Hepatic (Liver): Some bedtime if using one dose a
thrombocytopenia, adverse effects on the day, and decrease doses
and pancytopenia liver associated with with renal failure
famotidine include .
changes in liver o Arrange for the
function, hepatitis, and administration of concurrent
abnormalities in liver antacids if needed
enzymes .
Cardio o Monitor for hypersensitivity
(Cardiovascular): Sp reactions
ecific cardiovascular
adverse effects of
famotidine were not
explicitly mentioned in
the provided search
results.
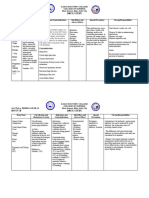
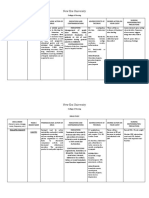
DRUG STUDY FOR AMPIMAX
MECHANISM ADVERSE NURSING
DRUG NAME CLASSIFICATION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION
OF ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: Pharmacologic Inhibition of bacterial cell Ampimax is a Individuals with a Central Nervous System o Monitoring Vital Signs:
Sultamicillin Class: wall formation. Ampicillin, medication used known hypersensitivity (CNS): Regularly monitor the patient's
Antibiotics a key component of for the treatment to Ampimax or any of Headache blood pressure and pulse to
Brand Name: Ampimax, inhibits the of various its components should Gastrointestinal (GI): assess their response to the
Ampimax biosynthesis of the cell bacterial not take this Diarrhea medication
wall mucopeptide, infections. Its medication due to the Nausea o Fluid Intake Monitoring: levels
Dosage/Route Therapeutic exerting bactericidal indications risk of severe allergic Vomiting are maintained
/Frequency: Class: activity against a wide include reactions like Candidiasis o Administration Instructions:
750 mg IV q8 ANST Beta-lactamase range of gram-positive infections where anaphylaxis or Fatigue Instruct patients to take the
inhibitor and gram-negative beta-lactamase Stevens-Johnson Malaise oral medication on an empty
aerobic and anaerobic producing syndrome. Secondly, Flatulence stomach, either 1 hour before
bacteria organisms might patients diagnosed Abdominal or 2 hours after meals
occur. with infectious distension o Medication Stability:
mononucleosis should Glossitis
avoid Ampimax Urine retention
Cardiovascular
(CARDIO):
Chest pain or
tightness
Substernal pain
Hepatic (HEPATIC):
Abnormal liver
function, including
yellowing of the
skin
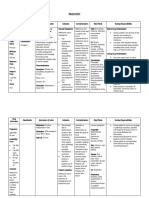
DRUG STUDY FOR KETEROLAC
DRUG NAME CLASSIFICATION MECHANISM INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING
OF ACTION EFFECTS RESPONSIBILITES
Generic Name: Pharmacologic Ketorolac exerts its Ketorolac is Individuals with a CNS: Check for allergies to ketorolac
ketorolac Class: effects by inhibiting the primarily known hypersensitivity Headache, dizziness, or NSAIDs, previous reactions,
tromethamine Nonsteroidal anti- enzymes cyclooxygenase indicated for the to ketorolac or other drowsiness, fatigue current medications, and
inflammatory drug (COX)-1 and COX-2. short-term NSAIDs. Patients with relevant medical conditions.
Brand Name: (NSAID) These enzymes are management of a history of peptic ulcer GI: Ensure the right drug, right
crucial for the production moderate to disease or Nausea, diarrhea, dose, right patient, right route,
of prostaglandins, which severe pain. This gastrointestinal (GI) heartburn, abdominal and right time are followed.
Dosage/Route/ Therapeutic play a key role in pain, can include pain bleeding. Individuals pain, constipation, Explain the medication's
Frequency: Class: inflammation, and fever. following surgery, with severe heart indigestion (dyspepsia) purpose, potential side effects,
10 mg IV q8 ANST Analgesic By blocking these injuries, or other failure, kidney disease, and any precautions to take
pathways, ketorolac medical or liver disease. Cardiovascular: Record the medication, dose,
reduces the production of procedures. Due Fluid retention, edema route, time, and any observed
prostaglandins, leading to to potential side (swelling), high blood responses in the patient's
decreased pain, effects, its use is pressure medical record.
inflammation, and fever. generally limited Assess for side effects like
to less than 5 Renal (Kidney): nausea, diarrhea, stomach
days. Acute kidney injury, pain, headache, or dizziness.
especially with prolonged Document and report any
use or high doses concerning symptoms to the
health care provider.
Skin:
Hives
Itching
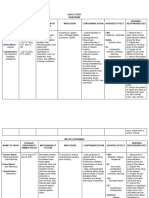
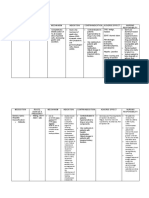
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR ACUTE PAIN
IMPLEMENTATION
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING EVALUATION
INTERVENTION RATIONALE
Subjective Data: Acute pain related Within 15 minutes of Independent: Goal Met.
The patient has stated pain to Physical trauma nursing After 15 minutes of
in her arms as she secondary to interventions, the 1. Evaluated the patient’s overall To determine a proper and efficient nursing interventions,
verbalized “masakit po yung vehicular accident as patient is expected condition. Assessed the health care necessary for the the patient was able to
mga sugat ko” evidenced by to experience location of incision, and noted patient’s condition. experience alleviation of
presence of alleviation of any presence of redness and symptoms and reported
Objective Data: abrasions symptoms and inflammation. reduced levels of pain
Facial grimacing reports reduced To ensure patient’s concerns are as evidenced by a pain
Pain scale of 8 out of levels of pain. 2. Monitored the patient’s being heard and addressed as well scale of 3/10.
10 response to pain, and as to determine if current treatment
encourage patient to plan is providing adequate relief.
communicate their pain
levels.
Helps redirect patient’s attention
away from pain to other things,
3. Instructed patient to perform reducing their pain perception and
deep breathing techniques, discomfort.
distraction methods and
guided imagery.
Prevents or minimize exacerbation
4. Educated the patient about of pain and changes in lifestyle
the aggravating factors that promote lower chances of triggers.
should be avoided.
To address the symptoms of the
Dependent: disease process and alleviate pain.
5. Ketorolac 10 mg IV q8 ANST
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR SLEEP DEPRIVATION
IMPLEMENTATION
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING EVALUATION
INTERVENTION RATIONALE
Subjective Data: Sleep Deprivation Within 8 hours of Independent: Goal Met.
The patient stated difficulty in related to pain and nursing interventions, 1. Assessed and evaluated Helps in identifying factors After 8 hours of nursing
sleeping and decreased discomfort secondary the patient will able to patient’s sleeping pattern and affecting patient’s sleep ensuring interventions, the patient
quality as she verbalized to Abrasions develop a regular potential causes contributing to formulation of patient centered was able to develop a
“Masakit po kasi yung sugat sleep pattern, and sleep deprivation. care and addressing patient’s regular sleep pattern, as
ko pag nadadaganan ko” verbalize experience sleeping problems and concerns. the S.O verbalized “Mas
of comfort during mahaba na po ang tulog
sleep. 2. Provided a calm and supportive Reduces levels of stress and niya ngayon kumpara
Objective Data: environment to create anxiety, promoting relaxation, nung nakaraan”
Presence of eyebags conducive sleeping which helps in enhancing sleep
environment. and overall health.
3. Instructed client to perform Helps patient to relax and loose
relaxation techniques such as tense muscles which makes the
deep breathing exercises before patient fall asleep easier.
sleeping.
Ensures that patient is able to
4. Educated the patient to correct find comfortable sleeping
and comfortable positioning of positions tailored to his condition.
the body when sleeping.
Dependent: Promote alleviation of pain to the
5. Ketorolac 10mg IV q8 ANST patient
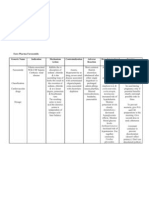
NURSING CARE PLAN FOR RISK FOR INFECTION
IMPLEMENTATION
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING EVALUATION
INTERVENTION RATIONALE
Objective Data: Risk for Infection Within 8 hours of Independent: Elevated temperature can Goal Met.
- Presence of Abrasions and related to presence of nursing interventions, 1. Monitored the patient’s vital indicates inflammatory response After 8 hours of nursing
Laceration Presence of Abrasion the patient will signs, and laboratory results. and is an early indication of interventions, the patient
- HGB 10.1 and laceration remain free from infection. has remained free from
Risk Factors: secondary to infection, and the SO infection, and the SO was
- Low levels of Hemoglobin decreased levels of will be able to 2. Assessed the patient’s wound Presence of edema, discharge, able to demonstrate and
hemoglobin. demonstrate and appearance. swelling, skin discoloration and identify methods to prevent
identify methods to odor is an indication of infection. and reduce risk of
prevent and reduce infection.
risk of infection. 3. Promoted clean and sterile Reduces the chance of entry of
environment, and used microorganisms when performing
appropriate aseptic techniques wound care and change of
during procedures and dressing dressings.
changes.
Proper nutrition enhances,
4. Encouraged and assisted the maintains, and strengthens
patient to have proper nutrition. immune functions and promote
faster wound healing and
recovery.
5. Educated the SO, the
importance of hand hygiene Destroys microorganisms in our
before and after performing hands and prevents entry of
wound care. bacteria in open wounds when
performing wound care.
6. Educated SO about different
methods to prevent the risk of Knowledge of risk factors
infection. encourages patients to prevent
the onset and occurrence of the
disease.
You might also like
- Thyroid Function TestDocument28 pagesThyroid Function TestDhinesh Muthusamy100% (1)
- MICROBILOGYDocument13 pagesMICROBILOGYDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- HLTINF001 Student Assessment Task 1 - Questioning...Document10 pagesHLTINF001 Student Assessment Task 1 - Questioning...Muskan SohalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetoclopramideDocument2 pagesDrug Study MetoclopramidePrince Rupee Gonzales100% (2)
- BORLAND Douglas Infuluenza PDFDocument18 pagesBORLAND Douglas Infuluenza PDFJxson GomezNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument7 pagesAntibioticsCeleste Largo Arayan-LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Death Anxiety: A Cognitive-Behavioral Approach: Patricia Furer, PHD John R. Walker, PHDDocument17 pagesDeath Anxiety: A Cognitive-Behavioral Approach: Patricia Furer, PHD John R. Walker, PHDFlory23ibc23No ratings yet
- Drug Study RifampicinDocument1 pageDrug Study RifampicinEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 pagesDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- Naproxen Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageNaproxen Sodium Drug StudyKarl Lourenz Deysolong100% (1)
- Drug Study PyrazinamideDocument1 pageDrug Study PyrazinamideEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal ToothbrushDocument6 pagesProject Proposal ToothbrushARLENE AQUINONo ratings yet
- Drug-Study OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug-Study OmeprazoleBeverly Datu71% (7)
- Mfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMfe, Ferrous Sulfate, Calcium Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole - DSDocument1 pageOmeprazole - DSEnoch LabianoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ob WardDocument6 pagesDrug Study Ob WardSareno PJhēaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHoney BeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (First Meet - RLE)Document5 pagesDrug Study (First Meet - RLE)Pauline AñesNo ratings yet
- NCPDrugStudy UnfiDocument7 pagesNCPDrugStudy UnfiJULLIANNE DANIELLE A. MASNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies For Muscular and Lymphatic SystemDocument6 pagesDrug Studies For Muscular and Lymphatic SystemLili M.No ratings yet
- Gantala Drug Stusy-TabhsoDocument8 pagesGantala Drug Stusy-TabhsoHey it's FerdyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Anemia PTDocument3 pagesDrug Study Anemia PTLex CatNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJay Ann Joy PerudaNo ratings yet
- Metaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyDocument8 pagesMetaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document9 pagesDrug Study 2John Michael M. RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyhsiriaNo ratings yet
- D. PharmaDocument45 pagesD. PharmaShivam Das, Tehsil KulpaharNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Indication Side EffectsDocument18 pagesGeneric Name: Indication Side EffectsEunice MañalacNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studychandria0026No ratings yet
- Clover Cheese-LoverDocument1 pageClover Cheese-LoverArnold Christian QuilonNo ratings yet
- KETOROLACDocument1 pageKETOROLACJugen Gumba Fuentes AlquizarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - AcetamenophinDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY - AcetamenophinChenime AñanaNo ratings yet
- Austria - Drug Study - ObDocument1 pageAustria - Drug Study - ObRiczhelle AustriaNo ratings yet
- Drugs and NCPDocument4 pagesDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNo ratings yet
- Pan Trop Razo LeDocument2 pagesPan Trop Razo LeBeatrizz P GellaNo ratings yet
- AlteredDocument7 pagesAlteredDENNROSE DECLARONo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-Omeprazole 2Document3 pagesDRUG-STUDY-Omeprazole 2Froo KeruNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyAda Eloisa AloveraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyanon_168410816No ratings yet
- Medicines Affecting The Male Reproductive OrgansDocument11 pagesMedicines Affecting The Male Reproductive OrgansKristine Las GregorioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ranitidine, Citicoline, Enalapril, Aspilet, Cefuroxime Etc)Document9 pagesDrug Study (Ranitidine, Citicoline, Enalapril, Aspilet, Cefuroxime Etc)gino_23_28No ratings yet
- Medication Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesMedication Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsAnne CamilleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJEWEL DEEN VILLARMENTE OQUIANANo ratings yet
- Drug Study Mefenamic Acid SHEEDocument1 pageDrug Study Mefenamic Acid SHEEKristine CastilloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyDimple SumarcaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraNo ratings yet
- Medication Route, Dosage & Frequency Mechanism Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CNS: VertigoDocument4 pagesMedication Route, Dosage & Frequency Mechanism Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: CNS: VertigoLaxy214No ratings yet
- Dopamine Antagonist: Generic Name: Chemical EffectDocument2 pagesDopamine Antagonist: Generic Name: Chemical EffectMajeed AlzahraniNo ratings yet
- Med Ward - Drug Study - LaoDocument3 pagesMed Ward - Drug Study - LaoLady Nadjma M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Euro Pharma FurosemideDocument2 pagesEuro Pharma Furosemideashleiy17No ratings yet
- Drug Study - AlfuzosinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AlfuzosinKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRanitidine - Drug StudyBolasoc, HazelNo ratings yet
- DRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDocument1 pageDRUG ANALYSIS - AcetaminophenDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document2 pagesDrug Study 2HeavenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: 10cc/1vialDocument2 pagesDrug Study: 10cc/1vialJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Liver CirrhosisDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Liver CirrhosisBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument1 pageOmeprazole Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- RanitidineDocument2 pagesRanitidineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Ryrey A. Pacamana BSN 3C Drug StudyDocument8 pagesRyrey A. Pacamana BSN 3C Drug StudyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument2 pagesDrug Study TemplateMary hope DomalaonNo ratings yet
- MA Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMA Drug StudyJane Decenine CativoNo ratings yet
- Uep - Edu.ph: Generic NameDocument13 pagesUep - Edu.ph: Generic NameKenneth JazminNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MBDocument29 pagesDrug Study MBk4jggjtnz5No ratings yet
- Drug Analysis OB WardDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis OB WardTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drugs 2Document6 pagesDrugs 2Elyse Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- JDentResRev83194-5251648 143516Document6 pagesJDentResRev83194-5251648 143516Harnoor GhumanNo ratings yet
- Manoj Kumar Airconditioner: Airconditioner Jw-Q18WuzaDocument2 pagesManoj Kumar Airconditioner: Airconditioner Jw-Q18WuzaManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Metals (PB, HG, MN, CD, As, Ni, CR)Document49 pagesMetals (PB, HG, MN, CD, As, Ni, CR)Йеша Маниш МираниNo ratings yet
- Crohn 1 EspDocument8 pagesCrohn 1 EspRomina GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Design and Evaluation of Allium Sativum GelDocument3 pagesDesign and Evaluation of Allium Sativum GelInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology - Intro - 11Document58 pagesEpidemiology - Intro - 11Tin WannNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Infertility ProjectDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Infertility ProjectSOUMYADEEP BHUINYA100% (1)
- Toliongco vs. CADocument17 pagesToliongco vs. CAAnonymous KaNu0py71No ratings yet
- G7 OrthopedicImpairments BEEDDocument23 pagesG7 OrthopedicImpairments BEEDHazel BayerNo ratings yet
- Hazard Report Form SampleDocument2 pagesHazard Report Form Samplewelly1980okNo ratings yet
- Ziac (Bisoprolol+HCT)Document21 pagesZiac (Bisoprolol+HCT)San-Clin-Eq LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- Solar Powered Automatic Wash Hand Basin SystemDocument5 pagesSolar Powered Automatic Wash Hand Basin SystemEngr. Najeem Olawale AdelakunNo ratings yet
- Symptom Flow Chart: Vaginal DischargeDocument2 pagesSymptom Flow Chart: Vaginal DischargeJeff ZhouNo ratings yet
- For Reaction Paper Per GroupDocument26 pagesFor Reaction Paper Per GroupvinzNo ratings yet
- Lower Leg Fasciotomy: Presented By: Albert Advisor: Dr. Dewi Kurniati P., M.Kes SP - OTDocument20 pagesLower Leg Fasciotomy: Presented By: Albert Advisor: Dr. Dewi Kurniati P., M.Kes SP - OTAlbert LiangNo ratings yet
- Fcps Past Papers ExamplesDocument93 pagesFcps Past Papers ExamplesBilal Muhammad100% (1)
- Strategies in Chronic Disease - Sakanti Maulida Firjatullah - Namayanja SumayiyahDocument12 pagesStrategies in Chronic Disease - Sakanti Maulida Firjatullah - Namayanja SumayiyahNamayanja SumayiyahNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 AI Applications Part III Feb07 2022Document23 pagesLecture8 AI Applications Part III Feb07 2022CjdjkekNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Drug Therapy of GoutDocument81 pagesPharmacology: Drug Therapy of GoutYousef JafarNo ratings yet
- HAND WASHING Content FinalDocument5 pagesHAND WASHING Content Finalsrimalathi100% (1)
- Drug Study: Therapeutic Class: Antilipemics Pharmacologic Class: Hmg-CoaDocument8 pagesDrug Study: Therapeutic Class: Antilipemics Pharmacologic Class: Hmg-CoaEden Marie FranciscoNo ratings yet
- DEFEAT THE DRAGON by DRDocument203 pagesDEFEAT THE DRAGON by DRjose de jesusNo ratings yet