Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Https:Www.cdc.Gov:Hepatitis:Hbv:Pdfs:Hepbgeneralfactsheet
Uploaded by
tinosan3Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Https:Www.cdc.Gov:Hepatitis:Hbv:Pdfs:Hepbgeneralfactsheet
Uploaded by
tinosan3Copyright:
Available Formats
HEPATITIS B
General Information
What is hepatitis? How is Hepatitis B spread?
“Hepatitis” means inflammation of the liver. The liver The Hepatitis B virus is spread when blood, semen, or
is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the other body fluids from an infected person enters the
blood, and fights infections. When the liver is body of someone who is not infected. The virus can
inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. be spread through:
Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and • Sex with an infected person. Among adults,
certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. Hepatitis B is often spread through sexual contact.
However, hepatitis is most often caused by a virus. In
the United States, the most common types of viral • Injection drug use. Sharing needles, syringes, and
hepatitis are Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C. any other equipment to inject drugs with someone
infected with Hepatitis B can spread the virus.
• Outbreaks. While uncommon, poor infection
control has resulted in outbreaks of Hepatitis B in
The only way to know if healthcare settings.
you have Hepatitis B is to • Birth. Hepatitis B can be passed from an infected
get tested. mother to her baby at birth. Worldwide, most
people with Hepatitis B were infected with the virus
as an infant.
What is Hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is not spread through breastfeeding,
sharing eating utensils, hugging, kissing, holding
Hepatitis B can be a serious liver disease that results hands, coughing, or sneezing. Unlike some forms of
from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. Acute hepatitis, Hepatitis B is also not spread by
Hepatitis B refers to a short-term infection that contaminated food or water.
occurs within the first 6 months after someone is
infected with the virus. The infection can range in
severity from a mild illness with few or no symptoms What are the symptoms of
to a serious condition requiring hospitalization. Some Hepatitis B?
people, especially adults, are able to clear, or get rid
of, the virus without treatment. People who clear the Many people with Hepatitis B do not have symptoms
virus become immune and cannot get infected with and do not know they are infected. If symptoms occur,
the Hepatitis B virus again. they can include: fever, feeling tired, not wanting to eat,
upset stomach, throwing up, dark urine, grey-colored
Chronic Hepatitis B refers to a lifelong infection with stool, joint pain, and yellow skin and eyes.
the Hepatitis B virus. The likelihood that a person
develops a chronic infection depends on the age at
which someone becomes infected. Up to 90% of infants When do symptoms occur?
infected with the Hepatitis B virus will develop a chronic If symptoms occur with an acute infection, they
infection. In contrast, about 5% of adults will develop usually appear within 3 months of exposure and can
chronic Hepatitis B. Over time, chronic Hepatitis B can last up to 6 months. If symptoms occur with chronic
cause serious health problems, including liver Hepatitis B, they can take years to develop and can be
damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. a sign of advanced liver disease.
Continued on next page
How would you know if you How is Hepatitis B treated?
have Hepatitis B? For those with acute Hepatitis B, doctors usually
recommend rest, adequate nutrition, fluids, and
The only way to know if you have Hepatitis B is to get close medical monitoring. Some people may need
tested. Blood tests can determine if a person has to be hospitalized. People living with chronic
been infected and cleared the virus, is currently Hepatitis B should be evaluated for liver problems
infected, or has never been infected. and monitored on a regular basis. Treatments are
available that can slow down or prevent the effects
of liver disease.
Who should get tested for
Hepatitis B and why? Can Hepatitis B be prevented?
Yes. The best way to prevent Hepatitis B is by getting
CDC develops recommendations for testing based vaccinated. The Hepatitis B vaccine is typically given
upon a variety of different factors. Here is a list of as a series of 3 shots over a period of 6 months. The
people who should get tested. The results will help entire series is needed for long-term protection.
determine the next best steps for vaccination or
medical care.
Who should get vaccinated
All pregnant women are routinely tested for
Hepatitis B. If a woman has Hepatitis B, timely against Hepatitis B?
vaccination can help prevent the spread of the All infants are routinely vaccinated for Hepatitis B
virus to her baby. at birth, which has led to dramatic declines of new
Household and sexual contacts of people with Hepatitis B cases in the US and many parts of the
Hepatitis B are at risk for getting Hepatitis B. world. The vaccine is also recommended for people
Those who have never had Hepatitis B can benefit living with someone infected with Hepatitis B,
from vaccination. travelers to certain countries, and healthcare and
public safety workers exposed to blood. People with
People born in certain parts of the world that high-risk sexual behaviors, men who have sex with
have increased rates of Hepatitis B. Testing helps men, people who inject drugs, and people who have
identify those who are infected so that they can certain medical conditions, including diabetes,
receive timely medical care. should talk to their doctor about getting vaccinated.
People with certain medical conditions should
be tested, and get vaccinated if needed. This
includes people with HIV infection, people who For more information
receive chemotherapy and people on Talk to your doctor, call your health department, or
hemodialysis. visit www.cdc.gov/hepatitis.
People who inject drugs are at increased risk for
Hepatitis B but testing can tell if someone is
infected or could benefit from vaccination to
prevent getting infected with the virus.
Men who have sex with men have higher rates
of Hepatitis B. Testing can identify unknown
infections or let a person know that they can
benefit from vaccination.
June 2016
www.cdc.gov/hepatitis
You might also like
- Hepatitis B CasestudyDocument2 pagesHepatitis B CasestudyG-0294-18 RAMANGNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B FactsDocument2 pagesHepatitis B Factsmilan salvaNo ratings yet
- The Complete Guide to Hepatitis B: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Hepatitis B: Symptoms, Risks, Diagnosis & TreatmentsNo ratings yet
- I'M Positive, Now What?: Hepatitis BDocument2 pagesI'M Positive, Now What?: Hepatitis BKishor SinghNo ratings yet
- He PB When Someone CloseDocument2 pagesHe PB When Someone Closesheila dewantyNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B virus: Definition, causes, transmission, signs, prevention and screeningDocument10 pagesHepatitis B virus: Definition, causes, transmission, signs, prevention and screeningSamafale channelNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers: Hepatitis BDocument4 pagesQuestions and Answers: Hepatitis BRain NakagoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Hepatitis B 2018ADocument9 pagesGroup 1 Hepatitis B 2018ADewi PandjukangNo ratings yet
- Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factors: Hepatitis A Hepatitis C Hepatitis DDocument41 pagesCauses, Incidence, and Risk Factors: Hepatitis A Hepatitis C Hepatitis DAmber ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis PresentationDocument15 pagesHepatitis Presentationkaren.cotejo10No ratings yet
- Hepatitis B BrochureDocument16 pagesHepatitis B BrochureTrebor SantosNo ratings yet
- HepBPerinatal ProtectWhenPregnant BWDocument2 pagesHepBPerinatal ProtectWhenPregnant BWKhalidatunnur Andrianie NasihinNo ratings yet
- 4rth Clinical JamalDocument10 pages4rth Clinical JamalSardar Luqman BashirNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis: Information For Gay/Bisexual MenDocument2 pagesViral Hepatitis: Information For Gay/Bisexual MenPatrick RamosNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis 101 A Thru C - FINAL 04-30-2014Document3 pagesViral Hepatitis 101 A Thru C - FINAL 04-30-2014ipcsafetyofficerNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Facts: 400 Million People Live with Chronic HBVDocument8 pagesHepatitis B Facts: 400 Million People Live with Chronic HBVNika AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument61 pagesHepatitis BMichael AmandyNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B (HepB Vaccine)Document6 pagesHepatitis B (HepB Vaccine)Desiree EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B FAQsDocument4 pagesHepatitis B FAQsImtiax LaghariNo ratings yet
- Your Liver Is The Largest Organ Inside Your Bod1Document14 pagesYour Liver Is The Largest Organ Inside Your Bod1Rrhandy Mae dela CruzNo ratings yet
- HepB VaccinationDocument2 pagesHepB VaccinationmdNo ratings yet
- Hep BDocument2 pagesHep Bapi-435620975No ratings yet
- Hepatitis B - Beyond The BasicsDocument7 pagesHepatitis B - Beyond The BasicsYong Fang YueNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument6 pagesHepatitis B: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentHazel Anne FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C in Pregnancy: The American College of Obstetricians and GynecologistsDocument3 pagesHepatitis B and Hepatitis C in Pregnancy: The American College of Obstetricians and GynecologistsYuliana WiralestariNo ratings yet
- Vaccination BDocument1 pageVaccination BAsh Clinical553800No ratings yet
- Topic OverviewDocument4 pagesTopic OverviewipcsafetyofficerNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment: Submitted By: Maham Ahmed (01-171182-013) Class: BS Psychology Date: 23 Submitted To: Sir Kashif AliDocument6 pagesBiology Assignment: Submitted By: Maham Ahmed (01-171182-013) Class: BS Psychology Date: 23 Submitted To: Sir Kashif Alihurricane2010No ratings yet
- HepCGeneralFactSheet PDFDocument2 pagesHepCGeneralFactSheet PDFMakkatul HikmahNo ratings yet
- He PC General Fact SheetDocument2 pagesHe PC General Fact SheetAnonymous CY0zKsNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B InfectionDocument8 pagesHepatitis B Infectionto van quyenNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: What Is It?Document2 pagesHepatitis B: What Is It?DrBertram ForerNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A: Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesDocument4 pagesHepatitis A: Questions and Answers: Information About The Disease and VaccinesSodiqa Strida SaSi TwinzNo ratings yet
- He Pa General Fact SheetDocument2 pagesHe Pa General Fact SheetNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- Patient Education - Hepatitis B (Beyond The Basics) - UpToDateDocument14 pagesPatient Education - Hepatitis B (Beyond The Basics) - UpToDatekesavanNo ratings yet
- Hep B VaccineDocument2 pagesHep B VaccineGilang Hadi FNo ratings yet
- Faq 125 GedDocument3 pagesFaq 125 GedAchmad Deddy FatoniNo ratings yet
- LiverDocument26 pagesLiverDinesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyMargarita Limon BalunesNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A Fact SheetDocument2 pagesHepatitis A Fact SheetKUER NewsNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis VirusAround 4% of Indian Population Affected by Hepatitis VirusDocument2 pagesHepatitis VirusAround 4% of Indian Population Affected by Hepatitis Virusvvan1980No ratings yet
- Immunization of Hepatitis BDocument33 pagesImmunization of Hepatitis BibrahimNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy HepBDocument2 pagesPregnancy HepBJonah CarloNo ratings yet
- Key Facts: Geographical DistributionDocument4 pagesKey Facts: Geographical DistributiondenyNo ratings yet
- The A, B, Cs of Viral HepatitisDocument7 pagesThe A, B, Cs of Viral HepatitishawllatyNo ratings yet
- Microorganism Assigned (Name) : Hepatitis B VirusDocument6 pagesMicroorganism Assigned (Name) : Hepatitis B VirusmaeNo ratings yet
- FactSheet HepBFamilyDocument1 pageFactSheet HepBFamilyConny Noor AfifaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B OverviewDocument8 pagesHepatitis B OverviewAnnieElizabethNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Project-NikkiDocument10 pagesInfectious Disease Project-Nikkiuglyghost0514No ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument28 pagesHepatitis BLex DgtNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Project-NikkiDocument10 pagesInfectious Disease Project-Nikkiuglyghost0514No ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument3 pagesHepatitis BChinhNo ratings yet
- What Is Hepatitis?: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis CDocument10 pagesWhat Is Hepatitis?: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis CCheska CruzNo ratings yet
- HEPA B and PIDDocument40 pagesHEPA B and PIDNica PinedaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E.group1Document34 pagesHepatitis A, B, C, D, E.group1R الالمعيNo ratings yet
- seminar hep BDocument38 pagesseminar hep Bdeeptiraut62No ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: Your Doctor. DR Michael Jones, Medical EditorDocument9 pagesHepatitis B: Your Doctor. DR Michael Jones, Medical Editormmbrelvi2757No ratings yet
- What Is Hepatitis BDocument2 pagesWhat Is Hepatitis BVanetNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B: A Silent InfectionDocument11 pagesHepatitis B: A Silent InfectionMalar MuthiahNo ratings yet
- Https:Www.moh.Gov.sa:En:Awarenessplateform:VariousTopics:Documents:Hepatitis CDocument3 pagesHttps:Www.moh.Gov.sa:En:Awarenessplateform:VariousTopics:Documents:Hepatitis Ctinosan3No ratings yet
- Runny Nose HDocument1 pageRunny Nose HTalal AwanNo ratings yet
- The Differential Diagnosis of Rhinorrhea - YmaiDocument4 pagesThe Differential Diagnosis of Rhinorrhea - YmaiNur Wahdania PutriNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0085253815518541 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0085253815518541 MainaripNo ratings yet
- Https:Www.nottsapc.nhs.Uk:Media:Mtqjk4pd:Dental AbscessDocument2 pagesHttps:Www.nottsapc.nhs.Uk:Media:Mtqjk4pd:Dental Abscesstinosan3No ratings yet
- 304 TextsetlessonDocument18 pages304 Textsetlessonapi-506887728No ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Teaching Learning 1Document4 pagesQuestionnaire On Teaching Learning 1Sonia Agustin100% (1)
- Questão 13: Technology Anticipates Fast-Food Customers' OrdersDocument3 pagesQuestão 13: Technology Anticipates Fast-Food Customers' OrdersOziel LeiteNo ratings yet
- Theory of Multiple Intelligences and WhyDocument7 pagesTheory of Multiple Intelligences and WhyEveNo ratings yet
- CH 7b - Shift InstructionsDocument20 pagesCH 7b - Shift Instructionsapi-237335979100% (1)
- Pump Foundation Analysis and Design ReportDocument18 pagesPump Foundation Analysis and Design ReportArchana ArchuNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Modelling With Deep Learning A ReviewDocument6 pagesAir Pollution Modelling With Deep Learning A ReviewliluNo ratings yet
- XDM-100 IOM SDH A00 4-5 enDocument334 pagesXDM-100 IOM SDH A00 4-5 endilipgulatiNo ratings yet
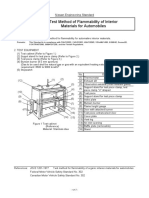
- Test Method of Flammability of Interior Materials For AutomobilesDocument17 pagesTest Method of Flammability of Interior Materials For AutomobilesKarthic BhrabuNo ratings yet
- Adding Rows Dynamically in A Table Using Interactive Adobe FormsDocument5 pagesAdding Rows Dynamically in A Table Using Interactive Adobe Formsbharath_sajjaNo ratings yet
- 2010 ATRA Technical SeminarDocument35 pages2010 ATRA Technical Seminartambache69100% (1)
- Dissertation Conflit Israelo PalestinienDocument7 pagesDissertation Conflit Israelo PalestinienPaySomeoneToWriteAPaperForMeUK100% (2)
- Passive Voice PDFDocument5 pagesPassive Voice PDFJohan FloresNo ratings yet
- Cancer Registry Standard Operating ProceduresDocument3 pagesCancer Registry Standard Operating ProceduresAnan AghbarNo ratings yet
- Quintin Kynaston School Wikipedia.Document3 pagesQuintin Kynaston School Wikipedia.John_Adam_St_Gang_QKNo ratings yet
- Corporation optional standard deduction and individual deductionsDocument6 pagesCorporation optional standard deduction and individual deductionsKenneth Bryan Tegerero Tegio100% (1)
- Lethal Dose TableDocument1 pageLethal Dose TableRochie DiezNo ratings yet
- The Blender InterfaceDocument22 pagesThe Blender InterfaceacocancerNo ratings yet
- How My Brother Leon Brought Home A WifeDocument16 pagesHow My Brother Leon Brought Home A Wifefusha23No ratings yet
- Why Students Choose ABM CoursesDocument6 pagesWhy Students Choose ABM CoursesJhas MinNo ratings yet
- CMS-855B - 04052021Document49 pagesCMS-855B - 04052021Sheldon GunbyNo ratings yet
- SAP On ASE Development UpdateDocument16 pagesSAP On ASE Development Updatebetoy castroNo ratings yet
- Density and Unit Weight ReportDocument71 pagesDensity and Unit Weight ReportGayan Indunil JayasundaraNo ratings yet
- Packing Lists AbroadDocument9 pagesPacking Lists AbroadAdit PinheiroNo ratings yet
- EUROLAB Cook Book Doc 19 - Impartiality ConfidentialityDocument2 pagesEUROLAB Cook Book Doc 19 - Impartiality ConfidentialityMariam KhanNo ratings yet
- 05 N141 31673Document21 pages05 N141 31673priya thakurNo ratings yet
- Afternoon Quiz Set 4Document66 pagesAfternoon Quiz Set 4pchakkrapani100% (1)
- 2006 Estes Model Rocketry CatalogDocument44 pages2006 Estes Model Rocketry CatalogMisesWasRightNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo de Ingles Grado 4 PrimariaDocument37 pagesCuadernillo de Ingles Grado 4 PrimariaMariaNo ratings yet
- Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry - Hormonal Control in Signal TransductionDocument18 pagesHarper's Illustrated Biochemistry - Hormonal Control in Signal TransductionDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaNo ratings yet