Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement Questions
Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement Questions
Uploaded by
M charan X COriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement Questions
Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement Questions
Uploaded by
M charan X CCopyright:
Available Formats
Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement Chemistry Questions with
Solutions
Q1. What is the name of the first molecular rearrangement identified by chemists?
(a) Beckmann rearrangement
(b) Curtius rearrangement
(c) Claisen rearrangement
(d) Pinacole pinacolone rearrangement
Answer: (d), Pinacol pinacolone rearrangement is the first molecular rearrangement identified by
chemists.
Q2. What is a rearrangement reaction?
Answer: A rearrangement reaction is a comprehensive class of organic reactions where an organic
substituent migrates from one atom to another in the same or different species, resulting in a structural
isomer of the original molecule.
For example, alkene on heating with a strong acid yields isomeric alkene.
Q3. What is a pinacol?
Answer: Pinacol is a white solid organic diol compound. It consists of two hydroxy groups (-OH) on
vicinal carbon atoms. The simplest member of this group is 2,3- dimethyl- 2,3- butanediol.
Structure of Pinacol:
Q4. How can you synthesise a pinacol?
Answer: Pinacol can be synthesised by a pinacol coupling reaction of acetone. Foremost we heat a
ketone with the magnesium amalgam, which is then reduced with water.
Q5. Which intermediate carbocation is more stable in pinacol pinacolone rearrangement?
(a) 1o carbocation
(b) 2o carbocation
(c) 3o carbocation
(d) 4o carbocation
Answer: ©, 3o carbocation is more stable in pinacol pinacolone rearrangement.
Q6. What is a pinacolone?
Answer: Pinacolone is a colourless liquid ketone with a molecular formula of C6H12O. It has a
peppermint or camphor-like odour.
Structure of pinacolone:
Q7. What is the IUPAC name of the simplest pinacolone?
Answer: The IUPAC name of simplest pinacolone is 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone.
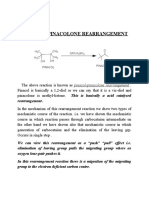
Q8. What is pinacol pinacolone rearrangement?
Answer: The pinacol pinacolone rearrangement is an approach to convert a 1,2-diol to a carbonyl
compound. It takes place under acidic conditions. The name of the reaction derives from the
rearrangement of pinacol to pinacolone.
Q9. Who discovered the pinacol pinacolone rearrangement?
(a) Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig
(b) Louis Pasteur
(c) Alfred Nobel
(d) Marie Curie
Answer: (a), The pinacol pinacolone rearrangement was discovered by Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig.
Q10. What is the IUPAC name of the simplest pinacol?
Answer: The IUPAC name of the simplest pinacol is 2,3- dimethyl- 2,3- butanediol.
Q11. How can you synthesise a pinacolone?
Answer: When pinacol is treated with dilute or moderately concentrated sulphuric acid, a
rearrangement reaction occurs, leading to the formation of ketone called pinacolone. The
rearrangement is known as pinacol-pinacolone or pinacolic rearrangement.
Q12. What are the applications of pinacolone?
Answer: Pinacolone plays an essential role in pharmaceutical industries.
● Pinacolone is useful in manufacturing pesticides, herbicides, fungicides and fertilisers.
● Pinacolone is useful in manufacturing stiripentol drugs.
● Pinacolone is useful in manufacturing cyanoguanidine drugs.
● Pinacolone is useful in the retrosynthetic analysis of vibunazole.
Q13. Explain pinacol pinacolone rearrangement in detail.
Answer: Pinacol is a white solid organic diol compound. It consists of two hydroxy groups (-OH) on
vicinal carbon atoms. In contrast, Pinacolone is a colourless liquid ketone with a molecular formula of
C6H12O. It has a peppermint or camphor-like odour.
The pinacol pinacolone rearrangement is an approach to convert a 1,2-diol (pinacol) to a carbonyl
compound (pinacolone). It takes place under acidic conditions. The name of the reaction derives from
the rearrangement of pinacol to pinacolone.
The reaction proceeds via the formation of a positively charged intermediate, and then the methyl group
migrates from one carbon centre to another leading to the formation of pinacolone.
Q14. What is migratory aptitude?
Answer: The ease with which any group undergoes nucleophilic 1,2 shift is known as its migratory
aptitude. All the groups do not migrate with equal ease in 1,2 nucleophilic rearrangement.
Q15. What is the order of migratory aptitude of different groups?
Answer: The ease with which any group undergoes nucleophilic 1,2 shift is known as its migratory
aptitude. All the groups do not migrate with equal ease in 1,2 nucleophilic rearrangement.
The migratory aptitude of the phenyl group is more than hydrogen, which is more than the alkyl group.
However, we can not apply it to unsymmetrical pinacol substrates. The most stable cation controls the
reaction pathway in an unsymmetrical pinacol.
Practise Questions on Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement
Q1. Explain the mechanism of pinacol pinacolone rearrangement?
Answer: The Pinacol Pinacolone rearrangement mechanism proceeds through four steps. Each of
these steps is explained below.
Step 1: Protonation: Foremost, the oxygen atom being electron-rich, shares its pair of electrons with
an electron-deficient proton.
Step 2: Loss of Water: Oxygen would try to retain its stability since the positive charge on oxygen is
highly unstable. Thus leading to the elimination of water.
Step 3: Rearrangement of Carbocation: Rearrangement will occur since tertiary carbocation is more
stable than secondary carbocation.
Step 4: Deprotonation: Oxygen, being electron-rich, will donate its electron pairs to an
electron-deficient carbon atom and lose a proton.
Q2. Enlist the factors that affect the formation of pinacolone.
Answer: The factors that affect pinacolone formation are enlisted below.
● Stability of carbocation
● Migratory Aptitude of the group
● Steric Hindrance
Q3. Explain pinacol-like rearrangement of the epoxide.
Answer: Some epoxides open their ring in an acidic medium forming carbocations. As these
carbocations look exactly the same as carbocation in the pinacol rearrangement, they can undergo a
similar mechanistic pattern leading to the formation of a carbonyl compound which is known as
pinacol-like rearrangement of the epoxide.
Q4. What is semi-pinacol rearrangement?
Answer: Semi-pinacol rearrangement is just like pinacol pinacolone rearrangement. In it, the reactant
specie is alcohols which have a very good leaving group at the carbon centre. The leaving groups may
be an iodo group, diazo group or tosyl group. However, the best result is obtained with the tosyl group.
Q5. Predict the products of the pinacol rearrangement of 2,3- dipheny| - 2,3- butanediol and 3-phenyl
-1.2- propanediol. Give the name of a simple chemical test that would show whether your prediction
was correct or not.
Answer: The products of the pinacol rearrangement of 2,3- dipheny| - 2,3- butanediol and 3-phenyl
-1.2- propanediol are shown below.
Iodoform test can show whether the prediction of the product is correct or not.
You might also like
- Chemistry of Reactive Intermediate FinalDocument38 pagesChemistry of Reactive Intermediate FinalTefera100% (1)
- Joining Kit - Editable V3Document30 pagesJoining Kit - Editable V3yash khitouliaNo ratings yet
- Physical Organic Chemistry—Ii: Specially Invited Lectures Presented at the Second IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry Held at Noordwijkerhout, Netherlands, 29 April–2 May 1974From EverandPhysical Organic Chemistry—Ii: Specially Invited Lectures Presented at the Second IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry Held at Noordwijkerhout, Netherlands, 29 April–2 May 1974Th. J. De BoerNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFDocument13 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFSahil Kalra100% (1)
- Exodontia Instrumentation PDFDocument6 pagesExodontia Instrumentation PDFRongJuneNo ratings yet
- Pip Pnsmv004Document12 pagesPip Pnsmv004Ricardo Zárate GodinezNo ratings yet
- Experimental Organic Chemistry Post-Lab 6 Benzopinacolone SynthesisDocument5 pagesExperimental Organic Chemistry Post-Lab 6 Benzopinacolone Synthesisapi-235187189100% (5)
- Memorandum of Agreement PtaDocument5 pagesMemorandum of Agreement PtaBarangay Pangil100% (1)
- Community Health NursingDocument21 pagesCommunity Health Nursingkaycelyn jimenez100% (2)
- Aerosols in AyurvedaDocument13 pagesAerosols in AyurvedaDr ajayNo ratings yet
- 311 Pinacol Pinacolone RearrangementDocument9 pages311 Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangementayesha sanaNo ratings yet
- RearrangementsDocument22 pagesRearrangementsVipul Newaskar100% (1)
- 148 16SCCCH8 2020062412102615Document25 pages148 16SCCCH8 2020062412102615Jawad MughalNo ratings yet
- Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement 1274Document14 pagesPinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement 1274Ayu RlNo ratings yet
- Junaid and ImranDocument29 pagesJunaid and ImranJunaid KhanNo ratings yet
- RearrangementsDocument64 pagesRearrangementsBandita Datta50% (2)
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenole and EthersDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenole and EthersNitin ChahalNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument34 pagesExercisesamaraamin2020No ratings yet
- Pinacol-Pinacolone RearrangementDocument10 pagesPinacol-Pinacolone RearrangementSubhro ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Orgchem FinalmanglicmotDocument8 pagesPortfolio in Orgchem FinalmanglicmotrlpmanglicmotNo ratings yet
- Aknowledgement: "Photochemistry of Carbonyl Compounds" Which Helped Me To GainDocument24 pagesAknowledgement: "Photochemistry of Carbonyl Compounds" Which Helped Me To GainSmitaNo ratings yet
- Pinacol RearrangementDocument2 pagesPinacol RearrangementkarinadegomaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument19 pagesChapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersNaina SinghNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Cambridge As-Level SummaryDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Cambridge As-Level SummaryReynaldi BozzNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenole and EthersDocument20 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Alcohols Phenole and EthersPundir DeeptiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Chemistry - Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument75 pagesClass 12 - Chemistry - Alcohols, Phenols and EthersFlash in AshishNo ratings yet
- Umyu CHM 4207Document14 pagesUmyu CHM 4207bangysmashiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 12th Class 1Document22 pagesChapter 11 12th Class 1Nisha vankhadeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument32 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersVIJAYNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument32 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersRiya NarangNo ratings yet
- Carbonium Ion Rearrangements-24-1Document7 pagesCarbonium Ion Rearrangements-24-1maheen aurangzaibNo ratings yet
- A Portion of The: 0 CBHB-CH-CH CSHJ - CH - CH Vi1 Vi11 - Ch-C&IDocument3 pagesA Portion of The: 0 CBHB-CH-CH CSHJ - CH - CH Vi1 Vi11 - Ch-C&IJaime GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Aldehida Dan KetonDocument88 pagesAldehida Dan KetonSITI FARAS RAHMAWATI 2021No ratings yet
- Chemistry Presentation.Document5 pagesChemistry Presentation.Bushra PervaizNo ratings yet
- Organic Aldehyde - Isothiocyanate ChemistryDocument244 pagesOrganic Aldehyde - Isothiocyanate Chemistrycarlosazucena1100% (2)
- Arenes and Aromaticity: Example: Alkyl BenzenesDocument24 pagesArenes and Aromaticity: Example: Alkyl BenzenesSteveNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheets Class 12 On Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Worksheet With Answer Set 3.docx 1Document7 pagesChemistry Worksheets Class 12 On Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Worksheet With Answer Set 3.docx 1Ayush RajputNo ratings yet
- 2 18KP1CH02 2020120403254999Document92 pages2 18KP1CH02 2020120403254999Sunny ProjectNo ratings yet
- Benzilic Acid RearrangementDocument4 pagesBenzilic Acid Rearrangementachyuta.1433No ratings yet
- Named ReactionDocument21 pagesNamed ReactionVijaya RajuNo ratings yet
- State University: From TheDocument6 pagesState University: From ThesergiosanuelmpNo ratings yet
- AS/A2 - Chemistry: 2021-23 CurriculumDocument41 pagesAS/A2 - Chemistry: 2021-23 CurriculumenderothNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument32 pagesPhenolchithiraikumar83No ratings yet
- CarbonylDocument89 pagesCarbonylSuhas PalaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 - Aldehydes-Ketones-and-Carboxylic-Acids Important QuestionDocument13 pagesChapter-12 - Aldehydes-Ketones-and-Carboxylic-Acids Important QuestionPonuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants PDFAdityaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols PDFDocument33 pagesAlcohols PDFDINESH DHANUSH KODINo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument25 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersMedicah Simon Peligrino100% (5)
- 125 A Mid 2 Chemistry-1Document24 pages125 A Mid 2 Chemistry-1syeda ruqaiyah ashfaqNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Reactions of AlkenesDocument39 pagesWeek 3 Reactions of AlkenesKate Arianne CabreraNo ratings yet
- 06photosynthesis 12Document35 pages06photosynthesis 12Anne CuadernoNo ratings yet
- ch#11Document9 pagesch#11JasNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument21 pagesAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsAnupam 4622No ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers - Board QuestionsDocument7 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, Ethers - Board QuestionsIron ManNo ratings yet
- Microreview: Oleg KulinkovichDocument13 pagesMicroreview: Oleg KulinkovichSangvenkatNo ratings yet
- Natural Products Lecture No. 08Document32 pagesNatural Products Lecture No. 08Rafia BatoolNo ratings yet
- (Chem 31) LE2 Samplex + AnsKey (1-1920)Document10 pages(Chem 31) LE2 Samplex + AnsKey (1-1920)Glyzen GaleonNo ratings yet
- 1455785668CHE P9 M19 EtextDocument17 pages1455785668CHE P9 M19 EtextAuwal ShehuNo ratings yet
- Selected Topic in ChemistryDocument12 pagesSelected Topic in ChemistryPatel EktaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane and Haloarenes by Aditya Sir ChemDocument19 pagesHaloalkane and Haloarenes by Aditya Sir Chempranav.padhle6No ratings yet
- Chapter # 11 "Organic Chemistry"Document5 pagesChapter # 11 "Organic Chemistry"Shahzaib AhmadNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 - Hydrocarbons - .Document19 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 - Hydrocarbons - .SaiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers - Board QuestionsDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols, Ethers - Board QuestionsIron ManNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13Document21 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13Anil GautamNo ratings yet
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- COOKE SP3 SpecificationDocument1 pageCOOKE SP3 SpecificationroiezaguiNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document3 pagesHW 5Mansi JainNo ratings yet
- Shipyard Individual Assignment 1Document19 pagesShipyard Individual Assignment 1subhaNo ratings yet
- Nikita Bhadula: ABES Institute of Technology, GHAZIABADDocument2 pagesNikita Bhadula: ABES Institute of Technology, GHAZIABADNikita BhadulaNo ratings yet
- A1657810355 - 23435 - 24 - 2019 - PEA 306 Time and WorkDocument87 pagesA1657810355 - 23435 - 24 - 2019 - PEA 306 Time and WorkRakesh MoparthiNo ratings yet
- Funk LoadDocument19 pagesFunk LoadPedro AraújoNo ratings yet
- Partial Derivative ReviewerDocument5 pagesPartial Derivative ReviewerErvin MogarNo ratings yet
- Business Policy Chapter 7 SlidesDocument32 pagesBusiness Policy Chapter 7 SlidesAsadChishtiNo ratings yet
- Economics 11th Edition by Slavin ISBN Test BankDocument27 pagesEconomics 11th Edition by Slavin ISBN Test Bankamber100% (26)
- Aluminium - Handling, Storage, Maintenance and CleaningDocument7 pagesAluminium - Handling, Storage, Maintenance and CleaningKiran KarthikNo ratings yet
- How To Repair WMI On A Windows XP System - EhowDocument2 pagesHow To Repair WMI On A Windows XP System - EhowMwawiNo ratings yet
- The Rizal Bill of 1956 - John Schumacher (2011) PDFDocument27 pagesThe Rizal Bill of 1956 - John Schumacher (2011) PDFWinsleth DizonNo ratings yet
- ORAL COM - Q1 - WEEK 3 - Communication Breakdown RevisedDocument4 pagesORAL COM - Q1 - WEEK 3 - Communication Breakdown RevisedCamille P. SantilecesNo ratings yet
- RHP - Catálogo de Rodamientos de Super Precisión PDFDocument24 pagesRHP - Catálogo de Rodamientos de Super Precisión PDFljcmexNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Developmental Disorders of The Oral CavityDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Developmental Disorders of The Oral CavityArafat Masud NiloyNo ratings yet
- I.T Unit 1Document9 pagesI.T Unit 1Gowtham R GowthamNo ratings yet
- Staffing: Definition: According To Koontz and O'DonnellDocument8 pagesStaffing: Definition: According To Koontz and O'DonnellNajeeb khanNo ratings yet
- Dust Work QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesDust Work QuestionnaireHykidNo ratings yet
- FINAL LAVCA Startup Heatmap Presentation 10.29.18Document11 pagesFINAL LAVCA Startup Heatmap Presentation 10.29.18Thomas HeilbornNo ratings yet
- Be A Perfect Person in Just Three Days Level NDocument6 pagesBe A Perfect Person in Just Three Days Level NEdward MarkNo ratings yet
- Third World Approaches To International Law: Dr. Juliee SharmaDocument9 pagesThird World Approaches To International Law: Dr. Juliee SharmaNeha MakeoversNo ratings yet
- Saes S 020Document28 pagesSaes S 020dissanayake90kanishkaNo ratings yet
- TD of EdtDocument28 pagesTD of EdtOussama SouidNo ratings yet
- CSVZXVZZXVZVZVDocument9 pagesCSVZXVZZXVZVZVGamex 23No ratings yet