Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3) Assurance
Uploaded by
kasimranjhaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3) Assurance
Uploaded by
kasimranjhaCopyright:
Available Formats
Assurance
It is an engagement when one party appoints another party to provide the
satisfaction (confidence) to another party in order to increase the confidence
of another party and reducing the level of risk.
NOTE:-
Assurance and Audit 1 By:- Haris Hanif
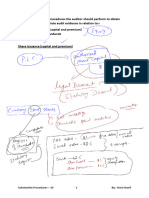
5 Elements of Assurance Engagement
(1) Three Parties
- Intended User:
The individual or class of individual who need the assurance.
- Responsible party:
The party whose work is being assessed by the practitioner.
- Practitioner:
The one who provides the assurance to the intended user and should be independent and
expert in the relevant field.
(2) Subject Matter
This involves any data which is being evaluated by the practitioner for the purpose of
assurance to the intended user.
(3) Criteria
These are the parameter (or Standards/criteria) against which the subject matter is being
evaluated by the practitioner.
(4) Evidence
These are all the information and explanation collected by the practitioner by applying
suitable procedures on the given subject matter and those evidences should be
sufficient (Quantity) and appropriate (Quality).
(5) Assurance Report
This is the written report by the practitioner containing the assurance (opinion) on the
subject matter, being addressed to the intended user.
Assurance and Audit 2 By:- Haris Hanif
International Standards
• IAS (International Accounting Standards)
• IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards)
• ISAE (International Standards on Assurance Engagement)
• ISA (International Standards on Audit)
• ISRE (International Standards on Review Engagement)
Levels of Assurance
ISAE (International Standards on Assurance Engagement)
• Absolute Assurance (Guarantee)
• Reasonable Assurance
• Limited/Moderate Assurance
Reasonable Assurance
Limited/Moderate Assurance
Assurance and Audit 3 By:- Haris Hanif
Examples of Reports
POSITIVE REPORT
• In our opinion, _____________ gives True and Fair View.
• In our opinion, _____________ do NOT give True and Fair View.
NEGATIVE REPORT
Nothing has come to our attention which causes us to believe that __________ is NOT True and Fair.
EXTERNAL AUDIT
Assurance and Audit 4 By:- Haris Hanif
5 Elements of AUDIT Engagement
(1) Three Parties
- Intended User:
- Responsible party:
- Practitioner:
(2) Subject Matter
(3) Criteria
(4) Evidence
(5) Assurance Report
Assurance and Audit 5 By:- Haris Hanif
Advantages of Audit
• It provides satisfaction to shareholders.
• It adds credibility in the financial statements.
• It also assist other stakeholders in making the economical decision, based on the financial
statements.
• It enables the auditor to give constructive advice to the management on the system
improvements.
Limitations of Audit
• There is limited time to do audit.
• Auditor works on sample basis and possible chances are that the sample which is ignored
may contain the misstatements.
• Evidences may be persuasive, rather than conclusive.
• Audit is not the objective work, judgements have to be made and auditors’ judgement may
not be appropriate sometimes.
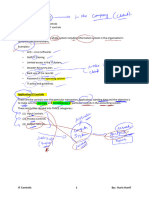
ASSURANCE
AUDIT Engagement REVIEW Engagement
Assurance and Audit 6 By:- Haris Hanif
Review Engagement
It is the voluntary exercise in which a practitioner is engaged to evaluate the subject matter
other than financial statements (like internal controls) and applied limited procedures
mainly Inquiry and Analytical procedures and expresses the limited assurance in the form of
Negative report.
TYPES OF REVIEW ENGAGEMENT
(1) Direct Engagement
This is the engagement in which the practitioner evaluates the subject matter with the
limited procedures and then concludes the opinion.
(2) Attestation Engagement
This is the engagement in which the practitioner does NOT evaluate the subject matter, but
the practitioner ensures whether the information is free from material misstatements and
then grid the stamp as attested.
Non – Assurance Engagement
This is the engagement, in which the practitioner is engaged but NO ASSURANCE is
provided.
(1) Agreed upon procedures
This is the engagement in which practitioner is engaged to collect the facts and figures on
certain subject matter with some agreed procedures, but NO OPINION will be given, the
users will draw the opinion by themselves.
(2) Compilation Engagement
This is the engagement in which the practitioner is engaged to compile the information, but
NO ASSURANCE is given.
Example, Tax return compilation.
Assurance and Audit 7 By:- Haris Hanif
You might also like
- 1-Ch 1 & 2-A&a-Overview & Profession-7eDocument30 pages1-Ch 1 & 2-A&a-Overview & Profession-7eLuke MorganNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Overview of Audit AssuranceDocument54 pagesIntroduction and Overview of Audit Assurancesyed rahmanNo ratings yet
- CH #1 AssuranceDocument7 pagesCH #1 AssuranceIqraNo ratings yet
- F8 ACCA Summary + Revision Notes 2017Document148 pagesF8 ACCA Summary + Revision Notes 2017Arbab JhangirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document20 pagesLecture 2FiruzaNo ratings yet
- Assurance Engagement - ISAE 3000Document19 pagesAssurance Engagement - ISAE 3000Daniel DadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Assurance EngagementsDocument31 pagesChapter 1 Assurance EngagementsOmer UddinNo ratings yet
- AssuranceDocument39 pagesAssuranceLinh MaiNo ratings yet
- Assurance EngagementDocument19 pagesAssurance EngagementAbdulkarim Hamisi KufakunogaNo ratings yet
- Audit and AssuranceDocument53 pagesAudit and Assuranceattaullah_niazi93No ratings yet
- AT Quiz 1 - B1Document15 pagesAT Quiz 1 - B1AMNo ratings yet
- Summary NotesDocument11 pagesSummary NotesAhmad Noainy AntapNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Assurance 1Document6 pagesIntroduction To Assurance 1nurmaisarahnurazim1No ratings yet
- Auditing Theory Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesAuditing Theory Lecture NoteskæsiiiNo ratings yet
- Business AssuranceDocument38 pagesBusiness AssuranceRAQIB 2025No ratings yet
- Assurance Ch-1-7Document14 pagesAssurance Ch-1-7tusher pepolNo ratings yet
- AA Summary NotesDocument184 pagesAA Summary NotesMohamed Alpha JallohNo ratings yet
- Auditing - Review Material 1Document23 pagesAuditing - Review Material 1KathleenNo ratings yet
- Summary NotesDocument183 pagesSummary Noteschet2019budhaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 AaaDocument5 pagesTopic 1 AaaIsaac OsoroNo ratings yet
- Apiag Audit Theory Reviewer DraftDocument70 pagesApiag Audit Theory Reviewer DraftDanilo ApiagNo ratings yet
- Audit NotesDocument3 pagesAudit NotesGurveer SNo ratings yet
- Assurance Engagements in The PHDocument4 pagesAssurance Engagements in The PHChristine Jayne MarceloNo ratings yet
- File 2023-03-02 06-33-26 PDFDocument51 pagesFile 2023-03-02 06-33-26 PDFHamd ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Aaa Topic 1Document8 pagesAaa Topic 1Cindy ClollyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Assurance and AuditDocument43 pagesIntro To Assurance and AuditGrace GamboaNo ratings yet
- AUDIT - EvidenceDocument12 pagesAUDIT - EvidenceCostancia rwehaburaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory: Elements of An Assurance Engagement 1.) Suitable CriteriaDocument14 pagesAuditing Theory: Elements of An Assurance Engagement 1.) Suitable CriteriaIm NayeonNo ratings yet
- Degree of Confidence: Auditing Theory Review NotesDocument103 pagesDegree of Confidence: Auditing Theory Review NoteskNo ratings yet
- Audit 1Document9 pagesAudit 1emc2_mcv100% (1)
- Auditing and Assurance Principles PDFDocument7 pagesAuditing and Assurance Principles PDFTine GriegoNo ratings yet
- Acc701 Auditing: Overview of Auditing, Assurance, and The Auditing ProfessionDocument4 pagesAcc701 Auditing: Overview of Auditing, Assurance, and The Auditing ProfessionUshra KhanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Slides Topic No 1 - Purpose and Scope of An AuditDocument24 pages2022 Slides Topic No 1 - Purpose and Scope of An Auditd2gsknj9qvNo ratings yet
- Attestation Services 2Document8 pagesAttestation Services 2sana olNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.auditing Princples and Tools RevDocument122 pagesChapter 3.auditing Princples and Tools RevyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Assurance EngagementDocument6 pagesAssurance EngagementEmmaNo ratings yet
- 2) Chapter 1 Assurance EngagementsDocument27 pages2) Chapter 1 Assurance Engagementsazone accounts & audit firmNo ratings yet
- BodyDocument13 pagesBodyAzizul AviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Assurance & Other Related ServicesDocument5 pagesChapter 12 - Assurance & Other Related ServicesellieNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five 5. Audit EvidenceDocument11 pagesChapter Five 5. Audit EvidenceAbrha636No ratings yet
- Assurance Audit of Financial StatementsDocument40 pagesAssurance Audit of Financial StatementsnabilaqurotaNo ratings yet
- Audit & Assurance PowerPointDocument26 pagesAudit & Assurance PowerPointDavid JohnNo ratings yet
- Aud Theo NotesDocument149 pagesAud Theo NotesJohn Joshua LeonardoNo ratings yet
- WK 1 Ugbs 2020 Natue and Scope of AuditDocument29 pagesWK 1 Ugbs 2020 Natue and Scope of AuditSTALLONE KOMLA NYAVORNo ratings yet
- Audit Approach PDFDocument12 pagesAudit Approach PDFfaisal gaziNo ratings yet
- FOURDocument4 pagesFOURRandy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Explanation of Audit Report of Grameenphone LTDDocument19 pagesExplanation of Audit Report of Grameenphone LTDtaohid khanNo ratings yet
- Acct 151Document44 pagesAcct 151Justin RoisNo ratings yet
- Assurance Auditing and Related ServicesDocument182 pagesAssurance Auditing and Related Servicesmoon2fielNo ratings yet
- Handout in Auditing and AssuranceDocument20 pagesHandout in Auditing and AssuranceJessa Mae LavadoNo ratings yet
- AUDITING ALL SLIDES ..... Anthony & BrainDocument316 pagesAUDITING ALL SLIDES ..... Anthony & BrainAnita SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Aud TheoDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Aud TheoCamille MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Accp 301 FinalsDocument16 pagesAccp 301 Finalsnerissa belloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AudDocument14 pagesChapter 5 AudMoti BekeleNo ratings yet
- AT Compiled Reports (Prelims-Midterms)Document38 pagesAT Compiled Reports (Prelims-Midterms)AMNo ratings yet
- Chapt 1Document63 pagesChapt 1Dinaol TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Philippine Standards On Auditing (PSA)Document19 pagesPhilippine Standards On Auditing (PSA)Erica DaprosaNo ratings yet
- Audit Engagement Strategy (Driving Audit Value, Vol. III): The Best Practice Strategy Guide for Maximising the Added Value of the Internal Audit EngagementsFrom EverandAudit Engagement Strategy (Driving Audit Value, Vol. III): The Best Practice Strategy Guide for Maximising the Added Value of the Internal Audit EngagementsNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Effective Internal Management System Audits: Implementing internal audits as a risk management toolFrom EverandA Guide to Effective Internal Management System Audits: Implementing internal audits as a risk management toolRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- 56) EthicsDocument14 pages56) EthicskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 41) Risk and Response Question KangarooDocument2 pages41) Risk and Response Question KangarookasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 26) Substantive Procedures - 7Document4 pages26) Substantive Procedures - 7kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 22) Substantive Procedures - 3Document4 pages22) Substantive Procedures - 3kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 29) Substantive Procedures - 10Document4 pages29) Substantive Procedures - 10kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 23) Substantive Procedures - 4 - Gooseberry CoDocument6 pages23) Substantive Procedures - 4 - Gooseberry CokasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 39) Understanding Client Entity and Its Environment - IsA 315Document2 pages39) Understanding Client Entity and Its Environment - IsA 315kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 40) Materiality - IsA 320Document4 pages40) Materiality - IsA 320kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 27) Substantive Procedures - 8Document4 pages27) Substantive Procedures - 8kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 42) Analytical Procedures - IsA 520Document4 pages42) Analytical Procedures - IsA 520kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 37) Audit Risk and Risk ResponseDocument5 pages37) Audit Risk and Risk ResponsekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 19) Audit EvidenceDocument6 pages19) Audit EvidencekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 34) Assertions Specific SubstantiveDocument4 pages34) Assertions Specific SubstantivekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 2) IntroductionDocument7 pages2) IntroductionkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 4) Internal ControlsDocument5 pages4) Internal ControlskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 6) Inventory SystemDocument4 pages6) Inventory SystemkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 7) IT ControlsDocument2 pages7) IT ControlskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- ACCA F8 - AUDIT RISK by Alan Biju Palak ACCADocument5 pagesACCA F8 - AUDIT RISK by Alan Biju Palak ACCAkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Standard On Auditing 120Document7 pagesPhilippine Standard On Auditing 120Zach RiversNo ratings yet
- Homework - Attestation ServicesDocument2 pagesHomework - Attestation ServicesMycah AliahNo ratings yet
- Ican Journal June 2011Document80 pagesIcan Journal June 2011casarokarNo ratings yet
- AT Quizzer 1 Overview of Auditing Answer Key PDFDocument11 pagesAT Quizzer 1 Overview of Auditing Answer Key PDFKimyMalaya100% (5)
- 2001 Audit Charter-CISADocument7 pages2001 Audit Charter-CISAdeeptimanneyNo ratings yet
- Assurence QuestionDocument82 pagesAssurence QuestionSakib Ahmed AnikNo ratings yet
- Testbank AuditingDocument57 pagesTestbank AuditingJane Gavino100% (1)
- Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsDocument5 pagesPhilippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsAdan EveNo ratings yet
- Summary of Code of EthicsDocument30 pagesSummary of Code of EthicsMJNo ratings yet
- Agenda Item 5-B: International Framework For Assurance EngagementsDocument21 pagesAgenda Item 5-B: International Framework For Assurance Engagementskelvin mkweshaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsDocument15 pagesPhilippine Framework For Assurance EngagementsAnonymous LC5kFdtcNo ratings yet
- ACP 314 Auditing and Assurance Principles Week 1 - 3Document80 pagesACP 314 Auditing and Assurance Principles Week 1 - 3Rain Lerog0% (1)
- F8 Notes by Sir ZiaDocument262 pagesF8 Notes by Sir ZiaSubrat AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Isae 3000Document19 pagesIsae 3000muhammad taufikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Solution ManualDocument13 pagesChapter 20 - Solution ManualjuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Test BankDocument25 pagesChapter 16 Test BankDiane CabiscuelasNo ratings yet
- Acc 411 - AssuranceDocument9 pagesAcc 411 - AssurancemildredNo ratings yet
- Guidance For StakeholdersDocument25 pagesGuidance For StakeholderssjmpakNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics CPAR Manila ReviewerDocument14 pagesCode of Ethics CPAR Manila ReviewerJudith GabuteroNo ratings yet
- MIA By-Laws On Professional Ethics (As at 20 May 2020)Document294 pagesMIA By-Laws On Professional Ethics (As at 20 May 2020)Nurul Hannani SazaliNo ratings yet
- Advanced Auditing & AssuranceDocument239 pagesAdvanced Auditing & AssuranceJohn Kimiri Njoroge100% (1)
- At 1 Theory Palang With Questions 1Document12 pagesAt 1 Theory Palang With Questions 1Sharmaine JoyceNo ratings yet
- Journal 1Document6 pagesJournal 1Sittie Ainna A. UnteNo ratings yet
- SKANS F8 Revision Notes 2018Document178 pagesSKANS F8 Revision Notes 2018WsxQaz86% (7)
- Auditing and Assurance Services in Australia by Gay TEST BANKDocument15 pagesAuditing and Assurance Services in Australia by Gay TEST BANKEdward YangNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Assurance Principles CparlDocument56 pagesTest Bank Assurance Principles Cparlcherry padreNo ratings yet
- Quality Control GuideDocument98 pagesQuality Control GuideyonportesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Auditing Theory and ProblemsDocument65 pagesReviewer Auditing Theory and ProblemsJerome MorenoNo ratings yet
- Intthry at Long Quiz 1 Answer Key 012718Document12 pagesIntthry at Long Quiz 1 Answer Key 012718Racel DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Adcanced Auditing and Professional Ethics Vol. 1Document828 pagesAdcanced Auditing and Professional Ethics Vol. 1Mayank Jain100% (8)