Professional Documents
Culture Documents
60) Caats and Ada
60) Caats and Ada
Uploaded by
kasimranjhaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
60) Caats and Ada
60) Caats and Ada
Uploaded by
kasimranjhaCopyright:
Available Formats
CAATS & ADA
CAATS (Computerised Assisted Audit Techniques)
It is the application of audit procedures using computer as an audit tool.
NOTE:- The overall objective and scope of the audit do not change when the
audit is conducted in a computerised environment. However, the application of
audit procedures may requires the auditor to consider techniques that use the
computer as an audit tool.
CAATS
Test Data
CAATS and ADA 1 By:- Haris Hanif
Audit Software
CAATS and ADA 2 By:- Haris Hanif
Advantages of CAATS
- Larger number of items can be tested quickly and accurately and giving
assurance to the auditor.
- CAATS can be used in multiple clients for the smooth audit.
- There may be digital security to protect the details of the client’s records.
- CAATS facilitates both testing general as well as application controls.
- Auditor can test the transactions like from where it was originated in the
system rather than relying on the paper records which may be incorrect or
manipulated.
Drawbacks of CAATS
- Initial setup of CAATS may be time consuming and expensive for the audit
firm.
- Audit staff might not be well trained and that firm needs to train them and
hence training cost would have to borne by the firm.
- The system of particular client may not be compatible/supportive with
CAATS.
- Any negligency by the audit team may affect the client’s system like lost or
corruption of data, while using the CAATS.
CAATS and ADA 3 By:- Haris Hanif
DATA and BIG DATA
BIG DATA
CAATS and ADA 4 By:- Haris Hanif
NOTE:-
CAATS and ADA 5 By:- Haris Hanif
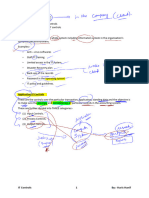
AUDIT DATA ANALYTICS (ADA)
It is a process of analysing the past data through inspection, extraction, filtering
and selecting the relevant data in order to make a pattern, deviations,
consistencies, inconsistencies, anomalies.
Audit firms use the data analytics to understand the client, performing
preliminary analytical procedures, performing TOC and substantive testing,
sampling and concluding the evidences.
How the Auditor can use Data Analytics
- Understanding the client, its nature of business, S.O.P.s, financial
statements, controls.
- Developing the expectations (by auditor) and comparing the reported
figures by client and investigate the significant variance.
- Compare the performance of client with the similar competitors in the
market to ascertain any kind of manipulation.
- Analyse the accounting figures, like aged receivable and ascertaining
the reasonableness of the provisions made for doubtful debt.
- Analysing the sales and purchase pattern for the trend of slow moving
inventory and consider whether it needs to be written off.
- Analysing the cash flows for the routes of money trail for any hint of
money laundering.
CAATS and ADA 6 By:- Haris Hanif
Data Analytics and Audit Quality
- Large sample
- More procedures can be performed and more evidences.
- Quick performing the audit procedures and low D.R.
- Detailed information analysis.
- Appropriate opinion.
- Can be used in the future audit (recurring audit)
Limitations of Data Analytics
- Time consuming to train the audit staff.
- Training cost.
- CAATs development.
- Any technical error by the audit firm may lead to loss or corruption of
client’s data.
- Issue of IT security
CAATS and ADA 7 By:- Haris Hanif
You might also like
- Sas Anti Money Laundering 105623Document4 pagesSas Anti Money Laundering 105623cheejustin0% (1)
- AML Transaction Monitoring Data GovernanceDocument17 pagesAML Transaction Monitoring Data Governancesimha117750% (2)
- Milktea System Docu Chapter 1 5Document26 pagesMilktea System Docu Chapter 1 5Innovator Adrian100% (2)
- Pov Aml Transaction Monitoring Scenarios Fine Tuning ProtivitiDocument4 pagesPov Aml Transaction Monitoring Scenarios Fine Tuning ProtivitiSam 1980No ratings yet
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessFrom EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Testing ProcessRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Differences of Curriculum in Malaysia, Indonesia and ThailandDocument7 pagesDifferences of Curriculum in Malaysia, Indonesia and ThailandNurul Afifah Mohd NorlisanNo ratings yet
- Data Analytics and The Auditor PDFDocument8 pagesData Analytics and The Auditor PDFAzeem KhanNo ratings yet
- CH8 Hunton CaatsDocument4 pagesCH8 Hunton Caatskimbavalentino100% (1)
- Auditing Extra Notes1Document9 pagesAuditing Extra Notes1Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Data Analytics and The Auditor - ACCA GlobalDocument5 pagesData Analytics and The Auditor - ACCA GlobalJasim UddinNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgD1sYm56PHRPgCcMMl5ZVdZLplwetgPn9flkODr97nA1JvYCzGRaEUz4Y3uoPI icInXbPlRHbeN0ATMBgRZTh3 u5zHfN9cnxYzQARZvphHUjGpIFt2rLeiuIjnfdH0F1Wsja-UxIdWVcODocument5 pagesACFrOgD1sYm56PHRPgCcMMl5ZVdZLplwetgPn9flkODr97nA1JvYCzGRaEUz4Y3uoPI icInXbPlRHbeN0ATMBgRZTh3 u5zHfN9cnxYzQARZvphHUjGpIFt2rLeiuIjnfdH0F1Wsja-UxIdWVcOclara san miguelNo ratings yet
- Benfords Law CAATSDocument28 pagesBenfords Law CAATSHetNo ratings yet
- Data AnalyticsDocument5 pagesData AnalyticsMayal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Continuous Audit-Retail BankingDocument24 pagesContinuous Audit-Retail BankingtharushiNo ratings yet
- Data Analytics For External Auditors: What Data Analytics Can Do and How It Contributes To Audit QualityDocument6 pagesData Analytics For External Auditors: What Data Analytics Can Do and How It Contributes To Audit QualityGeorgia VasanthaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Computer Assisted Auditing Techniques (CAAT)Document3 pages4 - Computer Assisted Auditing Techniques (CAAT)gimata kochomataNo ratings yet
- How It's Changing AuditingDocument2 pagesHow It's Changing Auditingkhushboosingh25junNo ratings yet
- Ta-Data AnalyticsDocument6 pagesTa-Data AnalyticsSubikshaa BaluNo ratings yet
- CAAT Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of RevenueDocument9 pagesCAAT Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Revenueoseng2mercon2010No ratings yet
- ComputerassistedaudittechniquesDocument7 pagesComputerassistedaudittechniquesRinokukunNo ratings yet
- Computer Audited TechniquesDocument23 pagesComputer Audited Techniquesmonica perambulyNo ratings yet
- Auditing IT (F)Document39 pagesAuditing IT (F)Abdulkarim Hamisi KufakunogaNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Project Report of DISA 3.0 CourseDocument3 pagesCertificate: Project Report of DISA 3.0 CoursePoonam JangirNo ratings yet
- Planning AAADocument5 pagesPlanning AAAena warNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2Ruiz, CherryjaneNo ratings yet
- Auditing Gray CH 10 Substantive Testing Computer Assisted Audit Techniques and Audit Programmes PDFDocument29 pagesAuditing Gray CH 10 Substantive Testing Computer Assisted Audit Techniques and Audit Programmes PDFfelianiNo ratings yet
- Reducing The Cost of AML Compliance PDFDocument24 pagesReducing The Cost of AML Compliance PDFahmedzafarNo ratings yet
- CPA Journal-Continuous AuditingDocument3 pagesCPA Journal-Continuous AuditingPaul Ryan BalonNo ratings yet
- Computer Assisted Audit Tools Chap-04Document30 pagesComputer Assisted Audit Tools Chap-04I-am KumNo ratings yet
- IT AuditDocument4 pagesIT AuditBryanNo ratings yet
- Computer-Assisted Audit Techniques (CAATs)Document5 pagesComputer-Assisted Audit Techniques (CAATs)Esther WanjukiNo ratings yet
- Data AnalyticsDocument2 pagesData AnalyticsRîzwâñ JazeelNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL FOR TOPIC 8 Auditors and ITDocument3 pagesTUTORIAL FOR TOPIC 8 Auditors and ITfrhNo ratings yet
- CISDocument21 pagesCISDaud Farook IINo ratings yet
- Audit Command LanguageDocument12 pagesAudit Command LanguageFrensarah RabinoNo ratings yet
- Computerised Information System (CIS)Document41 pagesComputerised Information System (CIS)Arsyad Noraidi100% (1)
- Data AnalyticsDocument25 pagesData AnalyticsElla GraceNo ratings yet
- Case 3Document6 pagesCase 3Ashraf ZamanNo ratings yet
- Computer Assisted Audit ToolsDocument41 pagesComputer Assisted Audit ToolsLaiza Mechelle Roxas MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Deploying Machine Learning Models in An Anti-Money Laundering (AML) ProgramDocument11 pagesDeploying Machine Learning Models in An Anti-Money Laundering (AML) ProgramjehaanmandalNo ratings yet
- CAATDocument2 pagesCAATMohammad MonirujjamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter10Document2 pagesChapter10Keanne ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- Standards That Have Been WITHDRAWNDocument41 pagesStandards That Have Been WITHDRAWNDa Yani ChristeeneNo ratings yet
- Ac220 - CaatsDocument17 pagesAc220 - CaatsChristineNo ratings yet
- A 6.4 Audit Unit 6Document8 pagesA 6.4 Audit Unit 6Gaurav MahajanNo ratings yet
- TBIT Arpit TakDocument5 pagesTBIT Arpit TakArpit TakNo ratings yet
- Accounting SystemDocument6 pagesAccounting SystemephraimNo ratings yet
- Bit006 Accounting Information Systemcontrol&Substantive TestingDocument4 pagesBit006 Accounting Information Systemcontrol&Substantive TestingGabriel PatronNo ratings yet
- Audit Sampling, Techniques & Procedures: - Abhijitsanzgiri Chartered AccountantDocument24 pagesAudit Sampling, Techniques & Procedures: - Abhijitsanzgiri Chartered AccountantajayuselessNo ratings yet
- WK 10a - IT AuditingDocument18 pagesWK 10a - IT Auditingfaisal_cseduNo ratings yet
- Continuous AuditingDocument2 pagesContinuous AuditingHasan Barlaas0% (1)
- Chapter 26 FinalDocument3 pagesChapter 26 FinalLenlen VersozaNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Systems - Integrates Business Process Functionality and Information From All of AnDocument12 pagesEnterprise Systems - Integrates Business Process Functionality and Information From All of AnShaina ObreroNo ratings yet
- Auditing Data Management Systems: Chapter 3 With Added InfoDocument54 pagesAuditing Data Management Systems: Chapter 3 With Added InfoSamonte JemimahNo ratings yet
- Cisa Module 1 Part B ExecutionDocument32 pagesCisa Module 1 Part B ExecutionREJAY89No ratings yet
- Audit ProgramDocument2 pagesAudit ProgramDyanne Yssabelle DisturaNo ratings yet
- Substantive Testing, Computer-Assisted Audit Techniques and Audit ProgrammesDocument23 pagesSubstantive Testing, Computer-Assisted Audit Techniques and Audit ProgrammesAnnaNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Using CaattsDocument38 pages10.2 Using CaattsPauline MercadoNo ratings yet
- December 2011 Quality ScanDocument1 pageDecember 2011 Quality ScanSergey ShkapovNo ratings yet
- Cisa Exam Testing Concept Online Auditing TechniquesDocument8 pagesCisa Exam Testing Concept Online Auditing TechniquesKaran MehtaNo ratings yet
- 56) EthicsDocument14 pages56) EthicskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 41) Risk and Response Question KangarooDocument2 pages41) Risk and Response Question KangarookasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 22) Substantive Procedures - 3Document4 pages22) Substantive Procedures - 3kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 26) Substantive Procedures - 7Document4 pages26) Substantive Procedures - 7kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 42) Analytical Procedures - IsA 520Document4 pages42) Analytical Procedures - IsA 520kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 27) Substantive Procedures - 8Document4 pages27) Substantive Procedures - 8kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 29) Substantive Procedures - 10Document4 pages29) Substantive Procedures - 10kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 40) Materiality - IsA 320Document4 pages40) Materiality - IsA 320kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 39) Understanding Client Entity and Its Environment - IsA 315Document2 pages39) Understanding Client Entity and Its Environment - IsA 315kasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 34) Assertions Specific SubstantiveDocument4 pages34) Assertions Specific SubstantivekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 37) Audit Risk and Risk ResponseDocument5 pages37) Audit Risk and Risk ResponsekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 2) IntroductionDocument7 pages2) IntroductionkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 23) Substantive Procedures - 4 - Gooseberry CoDocument6 pages23) Substantive Procedures - 4 - Gooseberry CokasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 6) Inventory SystemDocument4 pages6) Inventory SystemkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 4) Internal ControlsDocument5 pages4) Internal ControlskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 3) AssuranceDocument7 pages3) AssurancekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 19) Audit EvidenceDocument6 pages19) Audit EvidencekasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- 7) IT ControlsDocument2 pages7) IT ControlskasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- ACCA F8 - AUDIT RISK by Alan Biju Palak ACCADocument5 pagesACCA F8 - AUDIT RISK by Alan Biju Palak ACCAkasimranjhaNo ratings yet
- Special Topics: Dania Al - Falah Dr. Ala'Aldin AlrowwadDocument50 pagesSpecial Topics: Dania Al - Falah Dr. Ala'Aldin AlrowwadDania Al-ȜbadiNo ratings yet
- SingapuraItihaasaVaibhava Nov2021 SingapuraDocument78 pagesSingapuraItihaasaVaibhava Nov2021 Singapuradg7jg7sgn8No ratings yet
- Bnu Mba (Mini Project Giudeliness)Document12 pagesBnu Mba (Mini Project Giudeliness)lathifsyed94No ratings yet
- Template-Research Project ProposalDocument2 pagesTemplate-Research Project ProposalKarren Cassandra PalileoNo ratings yet
- Audit and GCGDocument10 pagesAudit and GCGGerry Ditan SibueaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Accounting Software in Achieving The Internationalaccounting Standard Boards Qualitative Characteristics of Financial InformationDocument13 pagesThe Influence of Accounting Software in Achieving The Internationalaccounting Standard Boards Qualitative Characteristics of Financial InformationIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Victor Vrooms Expectancy TheoryDocument6 pagesVictor Vrooms Expectancy TheoryRVKotiaN100% (1)
- Some People Say History Is One of The Most Important SubjectDocument1 pageSome People Say History Is One of The Most Important Subjecthamody662002No ratings yet
- Reflection Paper of InternshipDocument5 pagesReflection Paper of Internshipapi-473237155No ratings yet
- Interviewing TechniquesDocument15 pagesInterviewing Techniquesnikos kasiktsisNo ratings yet
- Project Synopsis of Insurance CompanyDocument4 pagesProject Synopsis of Insurance CompanySamar GhorpadeNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceAbhilash H NagarajNo ratings yet
- Students' Expectations About Their Grades Versus Course Expectations From Them - Will The Mismatch Ensure Quality EducationDocument15 pagesStudents' Expectations About Their Grades Versus Course Expectations From Them - Will The Mismatch Ensure Quality EducationAnkaNo ratings yet
- 22-PS-Using The Proportionate Extrapolation Workbook AS2 V12Document7 pages22-PS-Using The Proportionate Extrapolation Workbook AS2 V12Carlota Nicolas VillaromanNo ratings yet
- AMBA 670 Managing Strategy in The Global MarketplaceDocument3 pagesAMBA 670 Managing Strategy in The Global MarketplaceemekaobasiNo ratings yet
- What Is It? Why Is It So Important?Document20 pagesWhat Is It? Why Is It So Important?GangadharNo ratings yet
- Effect of Warm Water Foot Bath Therapy On Body Temperature Among Children With FeverDocument19 pagesEffect of Warm Water Foot Bath Therapy On Body Temperature Among Children With FeverImron BuhoriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document35 pagesLesson 1clement lesibaNo ratings yet
- Ebau Anxiety DreamsDocument4 pagesEbau Anxiety DreamsLaura Gemma Rodríguez PastorNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection Process in Castle ToyotaDocument48 pagesRecruitment and Selection Process in Castle Toyotaramkumarloi100% (3)
- Listing of STEM DisciplinesDocument1 pageListing of STEM DisciplinesIoan BilcuNo ratings yet
- SIT718 Real World Analytics Assessment Task 2: Problem Solving PurposeDocument3 pagesSIT718 Real World Analytics Assessment Task 2: Problem Solving PurposeJack PhamNo ratings yet
- Astm - d5016 - 08 (Total Sulfur in Coal and Coke Combustion Residues)Document6 pagesAstm - d5016 - 08 (Total Sulfur in Coal and Coke Combustion Residues)Dandy Rizkan100% (1)
- CEA Course Packet (Building Utilities 2)Document19 pagesCEA Course Packet (Building Utilities 2)Eli BerameNo ratings yet
- Journal of Marketing ManagementDocument18 pagesJournal of Marketing ManagementCarolina Haita100% (2)
- IJPDLM 11 2017 0348EmergingProcurementAnalyticsDocument33 pagesIJPDLM 11 2017 0348EmergingProcurementAnalyticsSUMIT JAINNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance of Artificial Beaches For The Kuwait Waterfront ProjectDocument14 pagesDesign and Performance of Artificial Beaches For The Kuwait Waterfront ProjectSujanNepalNo ratings yet
- Issues in The Social and Emotional Adjustment of Gifted ChildrenDocument12 pagesIssues in The Social and Emotional Adjustment of Gifted Childrenapi-301904910No ratings yet
- AS Psychology (Andrade - Doodling)Document18 pagesAS Psychology (Andrade - Doodling)Ana VieiraNo ratings yet