0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views5 pagesUnderstanding Conditional Probability
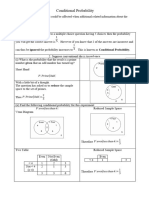
The document discusses conditional probability and provides examples and formulas to calculate conditional probability. It also includes sample probability questions and exercises for students to practice calculating conditional probability.
Uploaded by
mohamad.elali01Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Probability Theory,
- Statistical Problems,
- Mathematical Probability,
- Event Outcomes,
- Probability Concepts,
- Probability Models,
- Probability Frameworks,
- Probability Assessment,
- Mathematical Relationships,
- Even Numbers
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views5 pagesUnderstanding Conditional Probability
The document discusses conditional probability and provides examples and formulas to calculate conditional probability. It also includes sample probability questions and exercises for students to practice calculating conditional probability.
Uploaded by
mohamad.elali01Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Topics covered
- Probability Theory,
- Statistical Problems,
- Mathematical Probability,
- Event Outcomes,
- Probability Concepts,
- Probability Models,
- Probability Frameworks,
- Probability Assessment,
- Mathematical Relationships,
- Even Numbers