Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learners With Learning Disability
Uploaded by
Matias, Emie Rose Q.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learners With Learning Disability
Uploaded by
Matias, Emie Rose Q.Copyright:
Available Formats
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
Foundation on Special and Inclusive Education
First Semester, A.Y. 2023-2024
MODULE 7:
LEARNERS WITH LEARNING DISABILITY
Your bright future starts here (075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
LESSON 1: DESCRIPTION OF LEARNING DISABILITIES
Introduction
Let us together journey in understanding fully the definition and concepts of
learning disabilities. It is important to determine what is learning disability is
so that you can manage the child's needs, behavior, and appropriately utilize
educational intervention
A learning disability is a neurological disorder. In simple terms, a learning
disability results from a difference in the way a person's brain is "wired."
Children with learning disabilities are as smart as or smarter than their peers.
But they may have difficulty reading, writing, spelling reasoning, recalling
and/or organizing information if left to figure things out by themselves or if
taught in conventional ways.
A learning disability can't be cured or fixed; it is a lifelong issue. With
the right support and intervention, however, children with learning disabilities
can succeed in school and go on to successful, often distinguished careers
later in life. Parents can help children with learning disabilities achieve such
success by encouraging their strengths, knowing their weaknesses,
understanding the educational system, working with professionals and
learning about strategies for dealing with specific difficulties.
In the United States and Canada, the term learning disability is used to refer
to psychological and neurological conditions that affect a person's
communicative capacities and potential to be taught effectively. The term
includes such conditions as:
dysgraphia - writing disorder, dyslexia - reading disorder, mathematics
disorder developmental aphasia.
In the United Kingdom, the term learning disability is used more generally to
refer to developmental disability.
Someone with a learning disability does not necessarily have low or high
intelligence, nor any innate inability to learn. It just means this individual has
an impairment to their ability due to a processing disorder, such as auditory
processing or visual processing, that is detrimental to normal teaching
methods. Learning disabilities are usually identified by school psychologists
through testing of intelligence, academics and processes of learning.
Your bright future starts here (075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
LESSON 2: CATEGORIES OF LEARNING DISABILITIES
Introduction
Learning disabilities are due to genetic and/or neurobiological factors that
alter brain functioning in a manner which affects one or more cognitive
processes related to learning. These processing problems can interfere with
learning basic skills such as reading, writing and/or math. They can also
interfere with higher level skills such as organization, time planning, abstract
reasoning, long or short-term memory and attention. It is important to
realize that learning disabilities can affect an individual’s life beyond
academics and can impact relationships with family, friends and in the
workplace.
1. ADHD
A disorder that includes difficulty staying focused and paying attention,
controlling behavior and hyperactivity.
2. DYSCACULIA
A specific learning disability that affects a person’s ability to understand
numbers and learn math facts.
3. DYSGRAPHIA
A specific learning disability that affects a person’s handwriting ability and fine
motor skills.
4. DYSLEXIA
A specific learning disability that affects reading and related language-based
processing skills.
5. DYSPRAXIA
A disorder which causes problems with movement and coordination, language
and speech.
6. EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONING
Affects, planning, organization, strategizing, attention to details and managing
time and space.
7. NON-VERBAL LEARNING DISABILITIES
Has trouble interpreting nonverbal cues like facial expressions or body
language and may have poor coordination.
8. Oral / Written Language Disorder and Specific Reading
Comprehension Deficit
Your bright future starts here (075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
Learning disabilities that affect an individual’s understanding of what they
read or of spoken language. The ability to express one’s self with oral
language may also be impacted.
LESSON 3: CAUSES OF LEARNING DISABILITIES
1.Heredity
Often, learning disabilities run in the family, so it's not uncommon to find that
people with learning disabilities have parents or other relatives with similar
difficulties
2.Problems during pregnancy and birth
Learning disabilities may be caused by illness or injury during or before birth.
It may also be caused by low birth weight, lack of oxygen, drug and alcohol
use during pregnancy, and premature or prolonged labor.
3.Incidents after birth
Head injuries, nutritional deprivation, and exposure to toxic substances (i.e.
lead) can contribute to learning disabilities.
4.Acquired trauma
Presumes to be due to central nervous - dysfunction. When the brain is
developing before, during, or after birth.
5.Biochemical Imbalance
it was once theorized that biochemical disturbances within a child's body
caused
learning disabilities. For example, Feingold (1975, 1976) claimed that artificial
colorings and flavorings in many of the food’s children eat can cause learning
disabilities and hyperactivity.
6.Environmental Factors/Poor Instruction
Although very difficult to document as primary causes of learning disabilities,
environmental factors- particularly impoverished living conditions early in a
child's life and poor instruction, probably contribute to the achievement
deficits experienced by many children in this special education category.
Children cannot learn if they have not been properly taught. Quality schools
and excellent teachers count. Oftentimes children who have received
lowquality schooling are misdiagnosed with learning.
Your bright future starts here (075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
LESSON 4: TEACHING STRATEGIES
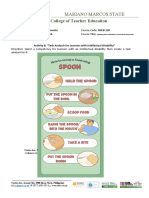
1. Break tasks into smaller steps
Don't try to teach everything at once. That doesn't work right for anyone at
all.
Especially those with learning disabilities have a lesser attention span, hence
you
have to make it both short and captivating. Thus, breaking the information
into smaller bite-sized chunks is an effective teaching strategy.
2. Present information in ways they can best adapt
Each one has a different learning style. Especially those with learning
difficulties have certain senses that are stronger than the others for them.
And as a teacher, you should work on identifying those and tutor your
students via the same These can be through 3 major learning styles that are,
visual, auditory or kinesthetic. And as per their stronger traits, you can alter
your teaching strategies, like helping them via graphics and videos, podcasts,
or by giving them small tasks and helping them with hands- on experience.
3. Probe regularly to ensure understanding
Once you have covered the topic do not leave it at that, get back to it and
check whether or not they remember it correctly. Revisions and reminders are
important for each one, and in this case too only practice will make perfect.
Many make it a strategy to revise with an online class every other day after
they take an offline session. This way they would be in touch with the topic
and also get familiar with
different learning platforms. (So make sure to invest in a good online teaching
app.)
4. Encourage independent practice
Allow them to experiment and learn on their own. Do not spoon-feed
everything. Once you familiarize them with certain topics or techniques, give
them some time and space to try them out on their own. Experimentation will
make things more interesting for them, and inculcate the trait of patience.
5. Model what you want students to do
Remember that influence outweighs everything else. What you do and show
them will stay with them for longer than what you instruct them to do. Like
it's rightly said, actions speak louder than words. Do things with them. Have
them contribute while showing them that you are with them on this ride.
6. Incorporate mnemonics
Another effective teaching strategy is to do it via mnemonics. This learning
method increase retention and retrieval with the help of varied cues to make
Your bright future starts here (075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
it easy. Though, as an educator, you have to make sure that the memory
tricks that you choose are actually easy for them to remember.
Your bright future starts here (075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
(075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
Your bright future starts here ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
(075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
Your bright future starts here ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
URDANETA CITY College of
UNIVERSITY
Owned and operated by the City Government of Urdaneta
Teacher Education
(075) 600 - 1507
San Vicente West, Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
Your bright future starts here ucu.edu.ph | univpresidentofficial@gmail.com
You might also like
- How To Overcome Negative ThoughtsDocument18 pagesHow To Overcome Negative Thoughtsdushtt100% (1)
- Q1 Wk4 DLP - HousekeepingDocument4 pagesQ1 Wk4 DLP - Housekeepingmarissa clatero100% (1)
- Sip Pes PDFDocument196 pagesSip Pes PDFPatricia Ann MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report On Child-Friendly SchoolDocument2 pagesAccomplishment Report On Child-Friendly SchoolRachelle Annie Tagam100% (2)
- Definition, Goals, and Scope of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument7 pagesDefinition, Goals, and Scope of Special and Inclusive EducationMaia Gabriela100% (1)
- INOCENTE Activity 10 Task AnalysisDocument2 pagesINOCENTE Activity 10 Task AnalysisTiffany InocenteNo ratings yet
- I Year M.Sc. Nursing Psychiatric Nursing. YEAR 2011-2013Document20 pagesI Year M.Sc. Nursing Psychiatric Nursing. YEAR 2011-2013Archana YadavNo ratings yet
- ISEPST-0136 Full PaperDocument14 pagesISEPST-0136 Full PaperNormalia SageNo ratings yet
- Attitude of Teachers Towards Children With Disabilities in Early Childhood Centres in The Sissala West DistrictDocument7 pagesAttitude of Teachers Towards Children With Disabilities in Early Childhood Centres in The Sissala West DistrictInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Kinnlee Thesis Final 1111Document17 pagesKinnlee Thesis Final 1111MatricaRoseNo ratings yet
- Aashita Varma - A54 (2) - Aashita VarmaDocument12 pagesAashita Varma - A54 (2) - Aashita VarmaAnwesha RayNo ratings yet
- Special Education (SPED)Document3 pagesSpecial Education (SPED)Anonymous YwtZrxpNo ratings yet
- IzelDocument13 pagesIzelJustine Rage SarmientoNo ratings yet
- MARCH 30, 2023 - ACTIVITY 2 - Early Child.Document2 pagesMARCH 30, 2023 - ACTIVITY 2 - Early Child.Ciara kaye JarabeseNo ratings yet
- Teaching Students With Impairments-My Emotional ReactionsDocument6 pagesTeaching Students With Impairments-My Emotional ReactionsElijah0% (1)
- Reading Impairment ReflectionDocument4 pagesReading Impairment ReflectionJinky OmboyNo ratings yet
- A Phenomenological Study On The Lived Experiences of Pre-School Teachers Educating Special ChildrenDocument28 pagesA Phenomenological Study On The Lived Experiences of Pre-School Teachers Educating Special ChildrenIrish Mae JovitaNo ratings yet
- Reflection 1Document4 pagesReflection 1ANNALIZA FIECASNo ratings yet
- University Urdaneta City: Learning Activity # 5 Planning, Assessing, & Reporting Learners ProgressDocument1 pageUniversity Urdaneta City: Learning Activity # 5 Planning, Assessing, & Reporting Learners ProgressMark Kenneth CeballosNo ratings yet
- Senior High School: Valeriano E. Fugoso Memorial SchoolDocument8 pagesSenior High School: Valeriano E. Fugoso Memorial SchoolRoxanne GruezoNo ratings yet
- Natasha Meseldzija - Educ4720 Assignment 3Document9 pagesNatasha Meseldzija - Educ4720 Assignment 3api-476696603No ratings yet
- Teaching Students With Disabilities: Intellectual DisabilitiesDocument3 pagesTeaching Students With Disabilities: Intellectual DisabilitiesPhuong Uyen DoanNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of SPED Education For Students Diagnosed With Autism Spectrum Disorder CheckedDocument3 pagesThe Effectiveness of SPED Education For Students Diagnosed With Autism Spectrum Disorder CheckedDebz CayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document8 pagesChapter 7niroannabellaNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Education AnswerDocument4 pagesInclusive Education AnswerClaudia BanicoNo ratings yet
- The Solution To Absenteeism: in Grade 7 Student of Abuyog National High SchoolDocument4 pagesThe Solution To Absenteeism: in Grade 7 Student of Abuyog National High SchoolAilen Lagula CervantesNo ratings yet
- Visual Impaired StudentsDocument13 pagesVisual Impaired Studentskrezyl Mae LagayadaNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and Studies: Science, Technology, Engineering, and MathematicsDocument8 pagesReview of Related Literature and Studies: Science, Technology, Engineering, and MathematicsJan Mico AriasNo ratings yet
- Original Research Paper - 040417Document26 pagesOriginal Research Paper - 040417thrishamaecaidoyNo ratings yet
- EPortfolio-SIQUIG, BUENAFLOR, CAMALESDocument72 pagesEPortfolio-SIQUIG, BUENAFLOR, CAMALESCherryl SiquigNo ratings yet
- Research SampleDocument40 pagesResearch SampleJm seNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document31 pagesLecture 7joiannagcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Chikwature Oyedele Ganyani2016Document12 pagesChikwature Oyedele Ganyani2016Florentina LucanNo ratings yet
- Challenges Experiencedby Visually Impaired Studentsin EducationDocument16 pagesChallenges Experiencedby Visually Impaired Studentsin EducationPrincess PacpacNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Kompetensi Guru Sekolah Luar Biasa Dalam Asesmen Potensi Dan Komunikasi KedukaanDocument7 pagesPengembangan Kompetensi Guru Sekolah Luar Biasa Dalam Asesmen Potensi Dan Komunikasi KedukaanIsnainiNo ratings yet
- Reducing Student's Tardiness Through SSIP (Students Success Intervention Program)Document6 pagesReducing Student's Tardiness Through SSIP (Students Success Intervention Program)Psychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Summary ReportDocument2 pagesSummary Report121954No ratings yet
- JPSP - 2023 - 4Document7 pagesJPSP - 2023 - 4Jayra Marie Guiral ChavezNo ratings yet
- Audio Books As Teaching Media To Blind Students in Learning EflDocument9 pagesAudio Books As Teaching Media To Blind Students in Learning EflAkhmad JuhairiNo ratings yet
- Reflection Ri 2Document2 pagesReflection Ri 2Lory YcoyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1,2 and 3Document28 pagesCHAPTER 1,2 and 3Mark Gaberiel FelominaNo ratings yet
- Aman (Manpreet B 9)Document16 pagesAman (Manpreet B 9)Anonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH Ghgfffyfi - Docx..bak11Document23 pagesRESEARCH Ghgfffyfi - Docx..bak11MASTERfun GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Alternative Learning System Senior High SchoolDocument9 pagesAlternative Learning System Senior High Schoolemeemarieson.belvisNo ratings yet
- 91-Article Text-641-3-10-20221116Document5 pages91-Article Text-641-3-10-20221116Nafilah Rizqy HasanahNo ratings yet
- Gifted Learners ReflectionDocument2 pagesGifted Learners ReflectionJinky OmboyNo ratings yet
- 189180-Article Text-480489-1-10-20190821 PDFDocument12 pages189180-Article Text-480489-1-10-20190821 PDFElisa FekaduNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness and Efficiency of Blended Learning To The Students of Saint Vincent School Maddela Quirino IncorporatedDocument27 pagesThe Effectiveness and Efficiency of Blended Learning To The Students of Saint Vincent School Maddela Quirino Incorporatedjenielyn madarangNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Module 1 Prof ED 103 Study Guide Module 1 Prof ED 103Document10 pagesStudy Guide Module 1 Prof ED 103 Study Guide Module 1 Prof ED 103Clyrien RayeNo ratings yet
- Jessel C. Yara Final ExaminationDocument5 pagesJessel C. Yara Final ExaminationJessel YaraNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument27 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesLianne Grace Basa BelicanoNo ratings yet
- Arh Mental SDHCP Activity DesignDocument4 pagesArh Mental SDHCP Activity Designerik francis laurenteNo ratings yet
- Proofread Manuscript 10-18-17Document110 pagesProofread Manuscript 10-18-17chicken skenNo ratings yet
- Research-1 (1) 1Document13 pagesResearch-1 (1) 1Jay-Ar Cruz Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Module 1 Prof ED 103Document7 pagesStudy Guide Module 1 Prof ED 103Darlene Dacanay DavidNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Module 1 Foundations of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument7 pagesStudy Guide Module 1 Foundations of Special and Inclusive Educationreyes alvarezNo ratings yet
- Profed Sir Patrick Inclusive 1-4Document26 pagesProfed Sir Patrick Inclusive 1-4smileydaintyNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report SpedDocument5 pagesAccomplishment Report SpedRose Ann Cunanan GallevoNo ratings yet
- ED 205 ReviewerDocument13 pagesED 205 ReviewerPrince Eugene NunezNo ratings yet
- Navigating Reading: A Guide for Teaching Children with DyslexiaFrom EverandNavigating Reading: A Guide for Teaching Children with DyslexiaNo ratings yet
- BADMINTON 3rd and 4th Discussion 1Document31 pagesBADMINTON 3rd and 4th Discussion 1Matias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- The-name-Beowulf-mean 20230904 195934 0000Document27 pagesThe-name-Beowulf-mean 20230904 195934 0000Matias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- GEOMETRY Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesGEOMETRY Lesson PlanMatias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- Art App ReviewerDocument19 pagesArt App ReviewerMatias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 The Indigenous ArtDocument2 pagesChapter 17 The Indigenous ArtMatias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- University Urdaneta City: Activity 1Document3 pagesUniversity Urdaneta City: Activity 1Matias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 MultigradeDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 4 MultigradeMatias, Emie Rose Q.No ratings yet
- Text AnalysisDocument47 pagesText AnalysisyasserNo ratings yet
- Birdsong and Human Language - Website - VersionDocument2 pagesBirdsong and Human Language - Website - VersiongabbyNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Connections Between Thoughts, Feelings, and Behavior What's in "Thoughts, Feelings, and Actions" What Happened?Document4 pagesUnderstanding The Connections Between Thoughts, Feelings, and Behavior What's in "Thoughts, Feelings, and Actions" What Happened?Thea Louise GarciaNo ratings yet
- Psychometric Test Psychometric Test & AssessmentDocument7 pagesPsychometric Test Psychometric Test & AssessmentVAIBHAV SANGALENo ratings yet
- Compilation UtsDocument158 pagesCompilation Utshatdog hatdogNo ratings yet
- gr7 Science Week 1-2Document4 pagesgr7 Science Week 1-2Czz ThhNo ratings yet
- Distinguish Between Ways To Access Money, Including Borrowing, Saving, and Working To Earn MoneyDocument2 pagesDistinguish Between Ways To Access Money, Including Borrowing, Saving, and Working To Earn Moneyemilio fer villaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument2 pagesTheoretical FrameworkJessica Jasmine MajestadNo ratings yet
- FDP On Critical Thinking For Problem SolvingDocument3 pagesFDP On Critical Thinking For Problem SolvingBonnie guptaNo ratings yet
- Creating A Classroom Environment: That Promotes Positive BehaviorDocument43 pagesCreating A Classroom Environment: That Promotes Positive BehaviorFeñoRomanSuazoNo ratings yet
- Sample Portfolio STUDENT-TEACHING 2022Document15 pagesSample Portfolio STUDENT-TEACHING 2022Cid PonienteNo ratings yet
- Howell - Designing Explicit Vocabulary Instruction 1 - MergedDocument10 pagesHowell - Designing Explicit Vocabulary Instruction 1 - Mergedapi-668162105No ratings yet
- Robotics QAME FormsDocument42 pagesRobotics QAME FormsAlbert Corsame UmbacNo ratings yet
- Information Gathering For Everyday Life UsageDocument2 pagesInformation Gathering For Everyday Life UsageGirli JoseeNo ratings yet
- Delm 215 Instructional Models For Improving Student AchievementDocument3 pagesDelm 215 Instructional Models For Improving Student Achievementarmand resquir jrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Eliciting RequiremnetsDocument61 pagesChapter 3 - Eliciting RequiremnetsKhairul Faris Bin OmarNo ratings yet
- HBMS4303 Planning The Teaching of MusicDocument166 pagesHBMS4303 Planning The Teaching of MusicraravviaNo ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 4 - Module 2: Preparing A Personal Health CareerDocument29 pagesHealth: Quarter 4 - Module 2: Preparing A Personal Health CareerWindel DarulloNo ratings yet
- ACTFLPerformance Descriptors-Interpretive PDFDocument2 pagesACTFLPerformance Descriptors-Interpretive PDFsarah guoNo ratings yet
- DLL-English 8 Q3L16Document2 pagesDLL-English 8 Q3L16Wen J. BuelaNo ratings yet
- BAT Assignment.Document6 pagesBAT Assignment.Melanie NdlovuNo ratings yet
- Backround IntroductionDocument3 pagesBackround Introductionmanilyn dacoNo ratings yet
- Eng-3-Q1Wk2 Writing A Short Descriptive ParagraphDocument4 pagesEng-3-Q1Wk2 Writing A Short Descriptive Paragraphagnes villamentoNo ratings yet
- Module-4 (Te2)Document12 pagesModule-4 (Te2)Joanne LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Rti Full Ws C05u01s02e03 01 QwoiDocument1 pageRti Full Ws C05u01s02e03 01 QwoiPhuc TangNo ratings yet
- CompleteDocument55 pagesCompleteOlalekan MichaelNo ratings yet
- How Anticipatory Information Shapes Subsequent Emotion RegulationDocument7 pagesHow Anticipatory Information Shapes Subsequent Emotion RegulationASNo ratings yet
- 5 PD Lecture Self EsteemDocument18 pages5 PD Lecture Self EsteemZain AbroNo ratings yet