0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views10 pagesGraphing Quadratic Functions Guide
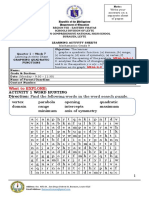
The document provides instructions on graphing quadratic functions by identifying key points like the vertex and creating a table of x and y values, then plotting the points. It includes examples of graphing quadratic functions given in vertex form or by matching a graph. The objectives are to correctly graph quadratic functions and identify how changing a, h, and k values affect the graph.
Uploaded by
mary joy buliagCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views10 pagesGraphing Quadratic Functions Guide
The document provides instructions on graphing quadratic functions by identifying key points like the vertex and creating a table of x and y values, then plotting the points. It includes examples of graphing quadratic functions given in vertex form or by matching a graph. The objectives are to correctly graph quadratic functions and identify how changing a, h, and k values affect the graph.
Uploaded by
mary joy buliagCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd