Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05_Ancient Near East The world of the old -testament-
Uploaded by
Sweet Zhel NarretoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05_Ancient Near East The world of the old -testament-
Uploaded by
Sweet Zhel NarretoCopyright:
Available Formats
02 L E C
Salvation History 26
THEO 100-Prof’s name here
21O1
Ancient Near East: The world of the old -testament
OUTLINE
I Introduction ❖ Assyria
II Diagnosing Severity of Anemia
➢ The north was the land of fierce
A Moderate Anemias
B Severe Anemias warrior and kings.
III Laboratory Diagnosis of Anemia ❖ Babylon
A RBC Indices ➢ Further in the east marked the great
i capital of the ancient world
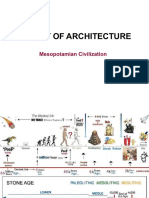
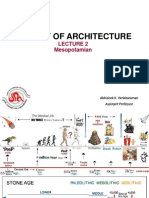
ii ❖ Sumer
➢ First cradle of human civilization
TRANS CHAP 16: ❖ Fertile crescent
➢ Such route was termed
➢ Enriched by the twin rivers of
CHAPTER THREE Mesopotamia in the east: the
Ancient Near East: The world of the old -testament Euphrates and the Tigris river, as well
as the Nile river of Egypt in western
part.
➢ More than a list of names and books, The
bible is a legacy of people, a rich testimony of 2. People and places of the ancient near east
cultures from the past and a way of life ➢ Mesopotamians/Mesopotamia
different from our own. To appreciate the ✓ Is literally referred to as “the land
bible is to discover such past, and to find the between two river
crucial nexus between experiences and ✓ The two rivers are Tigris and the
universal meanings which both bind the past Euphrate
and the present. ➢ Ubaid people: The pre-sumerian
✓ As to their traditional theory has it
that they descended from a “Semitic
1. Fertile crescent people called Amorites who had been
pressing in on the fertile crescent
❖ Canaan since late in the third millennium and
has overrun Palestine and turned
upper Mesopotamia into an Amorite
land.” (NJBC, 1990 1177)
✓ They knew how to drain the marshes
for agriculture, develop trade and
➢ The promised land to Abraham and
industries, including weaving,
his descendants
leatherwork, metalwork, masonry and
➢ Was a country located at the heart of
pottery
the ancient Near east
❖ Sumerians
❖ Egypt
✓ The sumerians took over and
➢ Southwest to canaan was the home of
pioneered the development of “city
the ancient Pharaohs and the Nile
state government” providing a model
river
of harmony, and order in ancient
BSN-2B TRANSCRIBED BY: GROUP #
societies but shifted to the way of the have influenced the Bible's story of
ruler creation, and most important, the
✓ Became greater and more powerful in concepts of God-man relationship and
the period from 3000 BC to 2400, the man's inevitable fate, death. In that
local assembly gave way to the idea of story, Gilgamesh, "a powerful king
divinely appointed kings who ruled as and hero, two-thirds divine, without a
god’s regent or deputy (1992:40) peer in the world" (Gill, 2008:124),
✓ They were credited for having became arrogant in his rule, and
developed a legal system and displeased the gods and goddesses,
inventions of pictographic Cuneiform who eventually decided to terminate
writing, the lunar calendar; water him by creating a wild and innocent
clock; sundial; the chariot; and man named Enkidu equal to him in
military phalanx; the potter’s wheel; strength (Ibid.).
the use of vault, arch, dome, column ✓ Gilgamesh, having learned the plot of
and tower in architecture, plus a the gods, used his cunning strategy,
highly developed polytheistic religion and sent whores to seduce him. It said
that had an enormous influence on all that "after six days and seven nights
the later civilization of the ancient of lovemaking, Enkidu was tamed"
world” (Gill, 2008 22). (Ibid.). Later in such account,
Gilgamesh fought Enkidu, defeated
him, and in an unexpected turn of
fate, became his only friend and ally.
From then on, Gilgamesh and Enkidu
enjoyed each other's company, and
later, decided to retaliate against the
gods: Enkidu killed the bull sent by
the goddess Ishtar but met the
inevitable consequence of death,
which was revealed to him in a
dream. The death of Gilgamesh's only
friend, Enkidu, flooded his heart with
✓ They were also famous for their
grief. After realizing that death awaits
ziggurat- a temple dedicated to the
all men as an inescapable end like
chief god or goddess of a Sumerian
Enkidu's, Gilgamesh undertook an
city-which has survived through the
epic journey of finding the fruit of
aging of time, and the passing of
immortality and seek "Utnapishtim,
history.
the only survivor, along with his
family, of the Flood, and the only man
to whom the gods had granted
everlasting life" (Ibid.,127).
Utnapishtim initially persuaded him to
✓ Central also to the Sumerian religion humbly accept the truth about the
was the concept of man and his inevitability of death but failed.
relationship to the god again, a great ❖ Akkadians
contrast of between Abraham, and ✓ With the leadership of King Sargon,
YHWH. the Akkadians subdued the
✓ In a fascinating Sumerian myth, Epic Sumerians:
of Gilgamesh, the story of a hero-king ✓ Not only did Sargon manage to
and demi-god named Gilgamesh may subdue all the Sumerian city-states,
BSN-2B TRANSCRIBED BY: GROUP #
and put an end to Sumer as a major ❖ Assyrians
political power, he and his successors ✓ The name Assyria was derived from
also took over the entire Tigris- "Ashur” which referred to “the
Euphrates basin and expanded into warrior-god of the city" (Ibid., 63). To
neighbouring countries (Gill, 2008:31) historians and archeologists, Assyria
❖ Babylonians was most remembered as a military
empire with its army as the backbone
of the nation, giving its structure and
hierarchy (Gill, 2008:72)
✓ In relation to the Bible, the prophets-
Isaiah, Micah, Zephaniah and Nahum
in the southern kingdom (Harris,
2009 65,66) warned Israel of the
danger posed by the Assyrian army,
and interpreted it as "the instrument
✓ Babylon attracted increased curiosity, of divine wrath“ due to Israel's
and greater relevance when its sinfulness In later centuries, the
contributions were unearthed and prophets were proven to be right in
known by experts and scholars. their words.
✓ For instance, its rulers forged lasting ✓ The Assyrian conquest, particularly in
legacies to human civilizations. the province of Samaria, left a painful,
✓ King Hammurabi (1728-1686 BC), who divisive scar on Israel. The Assyrians
was just a "vassal king of the Elamite brought their own citizens in Samaria
dynasty of Larsa" (McKenzio, 1965 and had inter-marriages with the local
334), rose to greater power and inhabitants (known to be the
expanded rule when he "conquered descendants of the Northern tribes of
Isin, Larsa, Eshnunna, and Mari and Israel) an event that would eventually
created an empire which extended be used to project unjustified
the Persian Gulf to the discrimination against the Samaritans,
Mediterranean" (Ibid. 334) due to their mixed blood with the
✓ Quite striking, the similarity, and the pagan Assyrians.
contrast of the Law of Hammurabi,
and the Mosaic Law are apparent. ❖ Egyptians
Hammurabi. received the Law from ✓ Land of the immortal pyramids and
the Babylonian god of justice, the great Nile river, Egypt is located
Shamash, in order to further the well- southwest of Canaan. Its history was
being of mankind' (Gill, 2008.60), complex and fascinating. Its
particularly those who are vulnerable contributions and legacies echoed the
to exploitation (Harris and Platzner, wealth and power of on ancient great
2003:43). empire.
✓ On the other hand, Moses received ✓ The Nile had its regular season of
the Decalogue, the Ten flood, allowing the Egyptian for an
Commandments from YHWH "who ample time of preparation, and
heard the cries of his people... and enabling them to set their time for
[intended] to bring the Israelites out plowing, planting, and harvest,
of Egypt" (Exodus 3.7). reflecting stability and prosperity. To
the Egyptians, the Nile was a great gift
from the gods: it brought alluvial soil
on its banks for their vegetation, and
BSN-2B TRANSCRIBED BY: GROUP #
water for their consumption, animals, everything they would need for
irrigation and farming. eternity (1997:26)
✓ Thus, the Egyptian people willingly
paid their tribute and offered
thanksgiving to their gods. Such
attitude was clearly manifested in Canaanites
their respect and allegiance to the The Canaanites were the earlier
king of Egypt, the Pharaoh, "originally settlers of Canaan, and eventually, were
meaning "great house" or "palace" replaced by Abraham, and his descendants-in
(O'Brien and Wong, 1995:36). view of YHWH's word to Abraham of the
Promised Land. In the Bible, they adhered to a
According to their belief, "kingship
religion independent from their neighbors.
was a divine institution...and formed
EL Chief God, Spouse of
part of a universal cosmic order"
Asherah, father of all
(Ibid., 36). Faithful to this view,
gods (except for Baal);
pharaoh was even described as "a god El’s epithet was the
by whose dealing one lives, the father Bull; also referred as
and mother of all men, alone by Creator/Possessor of
himself, without an equal" (Ibid., 36). Heaven and Earth.
✓ Such religious practice of worshipping
BAAL Universal god of
many gods showed sharp contrast to
fertility; also called as
the one God of Abraham and his
the Lord of Rain and
descendants. In the book of Exodus,
Dew; Baal’s
Moses, a descendant of Abraham,
epithet as the storm
was narrated both as an instrument god; also known as ‘He
and a witness of YHWH's great power who rides on the
over the Egyptian's pantheon of gods Clouds)’
when He sent plagues to the helpless
Egyptians in order to liberate his ASHERAH Consort of El and
mother of the gods;
oppressed people, the Hebrews, from
also cited as the
slavery.
consort of Baal.
✓ In addition, the Egyptians believed in
the concept of an afterlife, similar to ANATH Goddess of love and
what Christians believe today. To this war, the sister and
end, Ellis and Esler offered us a helpmate of the god of
concise Egyptian view on winning a Baal.
blissful afterlife:
✓ Belief in the afterlife affected all The practice of offering the firstborn
Egyptians, from the highest noble to as a holocaust sacrifice was uniquely
the lowest peasant. To win eternal Canaanite. Such Canaanite influence can also
life, each soul had to pass a test. be noticed in the Bible.
Osiris weighted a soul's heart against In the book of Genesis, we are told of
the feather of truth. Those he judged Abraham's test (Genesis 22) of offering his
to be sinners were fed to the firstborn, Isaac. Also, we learn the story of
crocodile shaped Eater of the Dead. Jephthah who pledged to YHWH a sacrifice of
Worthy souls entered the Happy Field the first person who will meet him upon his
of Food. Egyptians believed that the return from a victorious war-when only
brought grief and sorrow unto his heart when
afterlife would be much like life on
he saw his own daughter as the first person
Earth, so they buried the dead with
coming towards him while "playing
tambourines and dancing" (Judges 11.34).
BSN-2B TRANSCRIBED BY: GROUP #
King Cyrus was a well-accepted, and
adored leader during his day. He was a CONCLUSION
monarch, a person of mercy and compassion From experiences, it is truly a
(O'Brien and Wong, 2005:52). He issued a fundamental consideration to investigate and
decree for the release, and return of understand the historical past of a specific
foreigners from their places of origin - the people and their culture. By taking into
context that enabled the Diaspora Jews (Jews account these rich heritage, traditions, beliefs,
in exile) to return to Judah, and to start the and key leaders, we get glimpses and pieces
rebuilding of their nation, and the renewal of of their identity and significance in the world.
their faith. Such royal decree, and many other We are also humbled by these feats and
well-remembered decisions, legacies, and legacies. We are also ushered to greater
achievements of Cyrus earned him a special maturity as we became less and less
respect in the ancient Near East. judgmental of their people.
As to their religious beliefs, the
Persians, like the Israelites, were monotheists:
they believed in "Ahuramazda (the "Wise
Lord")...who brought all things into
being...and gave all humans the freedom to
choose between right and wrong" (O'Brien
and Wong, 2005:54). However, this good god
Ahuramazda was in conflict with Angra
Mainyu, the evil spirit, thereby, producing a
dualistic struggle between good and evil
(McKenzie, 1965:662)..
The Greeks, with the young Alexander
the Great as the emperor, took advantage of
the internal strife among the Persian leaders,
and put a final rest to Persian rule and
prominence in history. The young Greek
emperor "defeated the Persian king Darius III”
in 333 BCE (Porter, 2007:133), and initiated
the spread of Hellenism. In 165 BCE, the
Seleucid King Antiochus IV Epiphanes
“invaded Judaea, tried to Hellenize the Jews,
and desecrated the Second Temple in
Jerusalem" (Encyclopedia Britannica, 2010) by
placing the statue of Zeus in the Holy of REFERENCES
Holies, the most sacred place for the Jews. As
a result, the entire Jewish population was “PROF’S PPT ON QUIPPER AND LECTURE”
enraged, and furious by the very act of
desecration and insult.
BSN-2B TRANSCRIBED BY: GROUP #
BSN-2B TRANSCRIBED BY: GROUP #
You might also like
- SecretsOfTheDeadSea ScriptDocument10 pagesSecretsOfTheDeadSea ScriptDave JittaNo ratings yet
- History and Theory of Architecture 1 Week 4: Egyptian Architecture and the Architecture of DeathDocument49 pagesHistory and Theory of Architecture 1 Week 4: Egyptian Architecture and the Architecture of DeathBalqis SumayyahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 World Civilization Summer 2021 NSUDocument23 pagesLecture 5 World Civilization Summer 2021 NSUImam HossainNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - World CivilizationDocument23 pagesLecture 5 - World CivilizationTasnim Alam Piyash 1731712No ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian Civilization: SPRING 2021Document26 pagesAncient Egyptian Civilization: SPRING 2021Shitab Ashhab ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - Arch. of Ancient Egypt 1Document12 pagesCh4 - Arch. of Ancient Egypt 1aishasalmanj02No ratings yet
- Wadi El Hol SerabidDocument8 pagesWadi El Hol SerabidNatielNo ratings yet
- Historical Geography of The BibleDocument51 pagesHistorical Geography of The BibleMangkhum TonsingNo ratings yet
- Stas111 Prelims ReviewerpdfDocument16 pagesStas111 Prelims ReviewerpdfAnah NicoleNo ratings yet
- Mesopotamia and Egypt HandoutDocument3 pagesMesopotamia and Egypt HandoutEcoNo ratings yet
- 2 Writing and CitylifeDocument17 pages2 Writing and CitylifeWARRIOR FFNo ratings yet
- Pyramid TableDocument7 pagesPyramid Tableapi-350813969100% (1)
- Empires of Ancient MesopotamiaDocument153 pagesEmpires of Ancient MesopotamiaTanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: - Ancient TimesDocument6 pagesChapter 1: - Ancient TimesCJ PrettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 TargetsDocument1 pageChapter 2 TargetsDavid DuezNo ratings yet
- World History ReviewerDocument10 pagesWorld History ReviewerMark SerranoNo ratings yet
- GRP.1 (Tigris Euphrates)Document5 pagesGRP.1 (Tigris Euphrates)trinidadNo ratings yet
- H-4 Mesopotamian CivilizationDocument79 pagesH-4 Mesopotamian CivilizationVinayak RuhelaNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egypt:: "The Gift of The Nile"Document59 pagesAncient Egypt:: "The Gift of The Nile"Mizanur Rahman PeashNo ratings yet
- Petrosyan 2001 Sacred MountainDocument8 pagesPetrosyan 2001 Sacred MountainAshok PavelNo ratings yet
- Egyptian and MesopotamianDocument20 pagesEgyptian and MesopotamianAnkush BhartiNo ratings yet
- Ancient Near East Civilizations: Mesopotamia, Egypt, Aryans & MoreDocument48 pagesAncient Near East Civilizations: Mesopotamia, Egypt, Aryans & MoreJoviecca Lawas100% (1)
- Lec 10 11 - MESOPOTAMIADocument31 pagesLec 10 11 - MESOPOTAMIAAMNA NAVEED100% (1)
- Unit 9 Ancient Mesopotamia and EgyptDocument35 pagesUnit 9 Ancient Mesopotamia and Egyptbego docencia100% (2)
- Mesopotamia EgyptDocument2 pagesMesopotamia EgyptMichaela ChNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egypt: "The Gift of The Nile"Document34 pagesAncient Egypt: "The Gift of The Nile"Balavant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Persia Chart 2 River ValleysDocument3 pagesPersia Chart 2 River ValleysJason NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bronze Age Lesson Discusses Rise of Mesopotamia and EgyptDocument23 pagesBronze Age Lesson Discusses Rise of Mesopotamia and EgyptKim Depoldo MarillaNo ratings yet
- Egyptian History PresentationDocument27 pagesEgyptian History Presentationapi-335599040No ratings yet
- Mr. Hughes' Study Sheet On MesopotamiaDocument2 pagesMr. Hughes' Study Sheet On Mesopotamiaapi-26171952No ratings yet
- Topic Discussant Leizl S. LibetarioDocument22 pagesTopic Discussant Leizl S. LibetarioErman GaraldaNo ratings yet
- Werner Keller - The Bible As HistoryDocument175 pagesWerner Keller - The Bible As HistoryGiorgosby17No ratings yet
- Raoul Mclaughln - Silk TiesDocument9 pagesRaoul Mclaughln - Silk Tiesodohere1No ratings yet
- Module 3. Ancient Near EastDocument30 pagesModule 3. Ancient Near EastjullianaculalaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Human SettlementDocument79 pagesEvolution of Human Settlementshabareesh kailainathanNo ratings yet
- Miscellanea: Comnenus: Just A Little Empire On CyprusDocument28 pagesMiscellanea: Comnenus: Just A Little Empire On Cyprus12chainsNo ratings yet
- Lecture For ClassDocument97 pagesLecture For ClassRITHWIK DINESHNo ratings yet
- Reading Egyptian CivilizationDocument16 pagesReading Egyptian CivilizationC S Omi TalukderNo ratings yet
- MesopotamiaDocument48 pagesMesopotamiawhiteNo ratings yet
- BS Egypt (Assignmint-1)Document26 pagesBS Egypt (Assignmint-1)anjaliNo ratings yet
- Ancient Civilizations OriginsDocument6 pagesAncient Civilizations OriginsLoui LagareNo ratings yet
- Genesis-The World of GenesisDocument9 pagesGenesis-The World of GenesisJoao fagundes de b netoNo ratings yet
- 03-Near East ArchitectureDocument10 pages03-Near East Architectureace leeNo ratings yet
- 3 - Mesopotamian ArtDocument62 pages3 - Mesopotamian Artahmedessamaee654No ratings yet
- Writing and City Life: by Simone Khurana CLAS:XI-'F'Document14 pagesWriting and City Life: by Simone Khurana CLAS:XI-'F'rimpaNo ratings yet
- A Discourse On Phlan and Its ProblemsDocument6 pagesA Discourse On Phlan and Its ProblemsazurecobaltNo ratings yet
- VAKLADocument15 pagesVAKLAJoshua BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Sir Choc K Enc Abo 3 Lecturefor Yr AS Stude NTDocument33 pagesSir Choc K Enc Abo 3 Lecturefor Yr AS Stude NTAnonymous HumanNo ratings yet
- Midgard World Book-14Document1 pageMidgard World Book-14Daw AndradesNo ratings yet
- Phoenicians - Chapter 1Document27 pagesPhoenicians - Chapter 1James BradleyNo ratings yet
- Gerald Massey Book of Beginnings Vol.1-2 PDFDocument1,201 pagesGerald Massey Book of Beginnings Vol.1-2 PDFYohanan100% (2)
- Gog Magog and The Kingdom of The KhazarsDocument33 pagesGog Magog and The Kingdom of The KhazarsmsobhanNo ratings yet
- WHP 3-6-5 Read - The Rise of Empires Akkadians and Assyrians - 720LDocument9 pagesWHP 3-6-5 Read - The Rise of Empires Akkadians and Assyrians - 720LFaye A.No ratings yet
- H-3a EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATIONDocument74 pagesH-3a EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATIONVinayak RuhelaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument59 pagesReportDave ThreeTearsNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian Civilization: A Comprehensive OverviewDocument43 pagesAncient Egyptian Civilization: A Comprehensive OverviewKrish D.No ratings yet
- Chronicle Timeline MES WtADocument3 pagesChronicle Timeline MES WtAPreston HalcombNo ratings yet
- 2e - South of The SunDocument95 pages2e - South of The SunJohan H. P. Jr.No ratings yet
- John Willey - Chrysostom-The OratorDocument200 pagesJohn Willey - Chrysostom-The OratorfragmenteNo ratings yet
- Medieval Alchemical Book Decodes Ancient Egyptian HieroglyphsDocument9 pagesMedieval Alchemical Book Decodes Ancient Egyptian HieroglyphsGohed Braun100% (1)
- Egyptian-Literature - LOZADA, ERICA FAYE L.Document11 pagesEgyptian-Literature - LOZADA, ERICA FAYE L.Erica LozadaNo ratings yet
- Raz cqlz26 MysteryofkingtutDocument3 pagesRaz cqlz26 MysteryofkingtutSheri LeeNo ratings yet
- Lost Technologies of Ancient Egypt - by Christopher DunnDocument405 pagesLost Technologies of Ancient Egypt - by Christopher DunnCreativeFreedom100% (1)
- Library of Universal 01clarDocument438 pagesLibrary of Universal 01clarAharon Ben Ysrayl100% (1)
- From Slave To Pharaoh - The Black Experience of Ancient Egypt (PDFDrive)Document231 pagesFrom Slave To Pharaoh - The Black Experience of Ancient Egypt (PDFDrive)Paulo Haristeu De Almeida De Magalhães100% (1)
- 721 Ancient Egyption Love PoetryDocument5 pages721 Ancient Egyption Love PoetryEmrysNo ratings yet
- Mapeh: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Western Classical Art Traditions-Paintings and SculpturesDocument23 pagesMapeh: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Western Classical Art Traditions-Paintings and SculpturesPrincess Jovelyn GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 234011-The Urban Pattern City Planning and Design - TextDocument460 pages234011-The Urban Pattern City Planning and Design - TextNishani patelNo ratings yet
- A Matter of TimeDocument6 pagesA Matter of TimeAnthony E. Larson100% (1)
- 17 57 1 PBDocument8 pages17 57 1 PBKıvanç TatlıtuğNo ratings yet
- BADER, B.-Ancient - Egyptian - PotteryDocument22 pagesBADER, B.-Ancient - Egyptian - PotteryRocío Ruiz MonteroNo ratings yet
- Snowden MisconceptionsDocument24 pagesSnowden MisconceptionskkkmmmkkkNo ratings yet
- Second Intermediate Period Jewellery inDocument19 pagesSecond Intermediate Period Jewellery inAntwain UtleyNo ratings yet
- Timeline of World History PDFDocument1 pageTimeline of World History PDFMuhammad Uzair QadirNo ratings yet
- TT37 - Tomb of Harwa in Theban NecropolisDocument9 pagesTT37 - Tomb of Harwa in Theban NecropolisAhmed Tolba100% (1)
- The Complex of DjoserDocument4 pagesThe Complex of Djosersaraaaadel.3No ratings yet
- Ptolemaic Tax Farming System Reduced RiskDocument13 pagesPtolemaic Tax Farming System Reduced RiskHussein RizkNo ratings yet
- DR Naguib KanawatiDocument1 pageDR Naguib KanawatiAngela PageNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian Coffins - LowDocument60 pagesAncient Egyptian Coffins - LowAhmed Tolba100% (3)
- Ancient Egypt Wikipedia ArticleDocument1 pageAncient Egypt Wikipedia ArticleRaja DuraiNo ratings yet
- Yosef A.A. Ben-JochannanDocument14 pagesYosef A.A. Ben-JochannanHaqi Jamison100% (1)
- Gemstones in Ancient EgyptDocument26 pagesGemstones in Ancient EgyptAmber McDonald100% (1)
- Egypt Medjai Sahara: HamunaptraDocument1 pageEgypt Medjai Sahara: HamunaptraSanket PatilNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egypt NodrmDocument401 pagesAncient Egypt NodrmDaisy Bogdani100% (5)
- Handouts For Ancient ScienceDocument9 pagesHandouts For Ancient ScienceGen ArnistoNo ratings yet
- ContinueDocument2 pagesContinueMake for ItNo ratings yet
- 1st Q Western and Classical Art TraditionsDocument71 pages1st Q Western and Classical Art TraditionsReginaJoanePlejeNo ratings yet
- A Taste of Honey MNT and MDKT Vessels in PDFDocument11 pagesA Taste of Honey MNT and MDKT Vessels in PDFJohn BeratNo ratings yet
- Unit Outline Introduction The West Before 1300Document21 pagesUnit Outline Introduction The West Before 1300api-324512227No ratings yet
- Prey: Immigration, Islam, and the Erosion of Women's RightsFrom EverandPrey: Immigration, Islam, and the Erosion of Women's RightsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Secrets of Divine Love: A Spiritual Journey into the Heart of IslamFrom EverandSecrets of Divine Love: A Spiritual Journey into the Heart of IslamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (116)
- Seeking Allah, Finding Jesus: Third Edition with Bonus Content, New ReflectionsFrom EverandSeeking Allah, Finding Jesus: Third Edition with Bonus Content, New ReflectionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1058)
- Islamic History: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandIslamic History: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (81)
- The Gift of Rumi: Experiencing the Wisdom of the Sufi MasterFrom EverandThe Gift of Rumi: Experiencing the Wisdom of the Sufi MasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Bible and the Qur'an: A Comparative StudyFrom EverandThe Bible and the Qur'an: A Comparative StudyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Show Up: A Motivational Message for Muslim WomenFrom EverandShow Up: A Motivational Message for Muslim WomenRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (11)
- Rumi's Little Book of Life: The Garden of the Soul, the Heart, and the SpiritFrom EverandRumi's Little Book of Life: The Garden of the Soul, the Heart, and the SpiritRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- In the Shadow of the Sword: The Birth of Islam and the Rise of the Global Arab EmpireFrom EverandIn the Shadow of the Sword: The Birth of Islam and the Rise of the Global Arab EmpireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (137)
- Fiqh Us Seerah: Understanding the Life of Prophet MuhammadFrom EverandFiqh Us Seerah: Understanding the Life of Prophet MuhammadRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- No God but One: Allah or Jesus?: A Former Muslim Investigates the Evidence for Islam and ChristianityFrom EverandNo God but One: Allah or Jesus?: A Former Muslim Investigates the Evidence for Islam and ChristianityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (186)
- Arabic Course for English Speaking Students Madina Islamic UniversityFrom EverandArabic Course for English Speaking Students Madina Islamic UniversityNo ratings yet
- Morals and Manners in Islam: A Guide to Islamic AdabFrom EverandMorals and Manners in Islam: A Guide to Islamic AdabRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Sexual Ethics and Islam: Feminist Reflections on Qur'an, Hadith, and JurisprudenceFrom EverandSexual Ethics and Islam: Feminist Reflections on Qur'an, Hadith, and JurisprudenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The 99 Names Of Allah (Glorified And Exalted Is He) In VerseFrom EverandThe 99 Names Of Allah (Glorified And Exalted Is He) In VerseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Complete Infidel's Guide to the KoranFrom EverandThe Complete Infidel's Guide to the KoranRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (65)