Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parabolic Curves!
Uploaded by
BryanHarold BrooOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parabolic Curves!
Uploaded by
BryanHarold BrooCopyright:
Available Formats
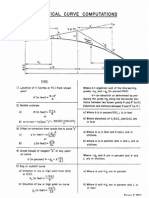
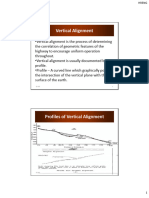
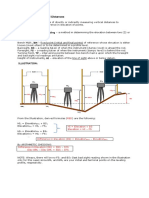
PC = point of curvature, also known as BVC (beginning of vertical curve)
PT = point of tangency, also known as EVC (end of vertical curve)
PI = point of intersection of the tangents, also called PVI (point of vertical intersection)
L = length of parabolic curve, it is the projection of the curve onto a horizontal surface which
corresponds to the plan distance.
S1 = horizontal distance from PC to the highest (lowest) point of the summit (sag) curve
S2 = horizontal distance from PT to the highest (lowest) point of the summit (sag) curve
h1 = vertical distance between PC and the highest (lowest) point of the summit (sag) curve
h2 = vertical distance between PT and the highest (lowest) point of the summit (sag) curve
g1 = grade (in percent) of back tangent (tangent through PC)
g2 = grade (in percent) of forward tangent (tangent through PT)
A = change in grade from PC to PT
a = vertical distance between PC and PI
b = vertical distance between PT and PI
H = vertical distance between PI and the curve
FORMULAS OF A VERTICAL PARABOLIC CURVE:
Slope = Rise/Run; rise = Run x slope (*it is very important to know these property of a triangle)
Determining values of “a” and “b”:
a= g L b= g L
Determining distance of highest point from PC (S1) and PT (S2)
S = S =
Squared Property of Parabola (SPP) *very important (derived from your analytic geometry)
( )
= Where: H =
A = Algebraic change in slope direction = |g1 – g2| *take absolute value
4
Sources: Traffic & Highway Engineering by Garber& Hoel
google.com
You might also like
- Vertical Parabolic CurveDocument5 pagesVertical Parabolic CurveHarvey Jusay CarableNo ratings yet
- Paraolic CurveDocument3 pagesParaolic CurveJohn Carlo DomanaisNo ratings yet
- Surveying 3Document33 pagesSurveying 3Raymund PertudoNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical Prabolic Summit Curve PDFDocument17 pagesSymmetrical Prabolic Summit Curve PDFRenzo Formanes100% (1)
- Vertical Parabolic CurvesDocument12 pagesVertical Parabolic Curvesnicole.galvezNo ratings yet
- Parabolic CurveDocument16 pagesParabolic CurveharabassNo ratings yet
- Parabolic CurveDocument16 pagesParabolic CurveAnonymous KUNMyMBEENo ratings yet
- Vertcal Curve CalculationsDocument1 pageVertcal Curve CalculationsScridbparshuNo ratings yet
- Appendix A4Document5 pagesAppendix A4Jegan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Vertical Parabolic CurveDocument5 pagesVertical Parabolic CurveRonwell De LeonNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Exam Solution GuideDocument11 pagesAP Physics 1 Exam Solution GuideBUG67% (3)
- Conversion - Geographic To CartesianDocument2 pagesConversion - Geographic To CartesianKellyNo ratings yet
- Separation DimensionDocument30 pagesSeparation DimensionJyotishKhannaNo ratings yet
- Common Equations For AreaDocument4 pagesCommon Equations For AreaATHULNo ratings yet
- Volume Formulas: Shape Volume Formula VariablesDocument2 pagesVolume Formulas: Shape Volume Formula VariablesaomineNo ratings yet
- Crossant - Conic-Sections FormulaDocument1 pageCrossant - Conic-Sections Formulaalireza katebiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Geometric Design of Highways AnnotatedDocument80 pagesLecture 6-Geometric Design of Highways AnnotatedAntonio RojasAcunaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design of HighwaysDocument74 pagesGeometric Design of HighwaysJoshua Tirao100% (1)
- Symmetrical Parabolic CurveDocument8 pagesSymmetrical Parabolic CurveRalph Castillo0% (1)
- 1.basic Maths (Theory) (1-9)Document9 pages1.basic Maths (Theory) (1-9)Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Measurement of DistancesDocument10 pagesMeasurement of DistancesewqewqeNo ratings yet
- Module 18 - Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Parabolic CurvesDocument5 pagesModule 18 - Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Parabolic CurvesGerovic ParinasNo ratings yet
- Job #5 To Layout The Vertical Curve by Using Tangent Correction Method. ApparatusDocument5 pagesJob #5 To Layout The Vertical Curve by Using Tangent Correction Method. ApparatusAbid Ali100% (1)
- Formula Reference Sheet: Shape Formulas For Area (A) and Circumference (C)Document2 pagesFormula Reference Sheet: Shape Formulas For Area (A) and Circumference (C)Ben HillNo ratings yet
- Elev FactDocument10 pagesElev FactJason AgbotNo ratings yet
- Shape Formulas For Area (A) and Circumference (C)Document2 pagesShape Formulas For Area (A) and Circumference (C)Vincent CruzNo ratings yet
- AIDocument7 pagesAIAmit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 1521702258divyani Digi Photogrammetry (2Document20 pages1521702258divyani Digi Photogrammetry (2Bhanupratap Singh SodhaNo ratings yet
- CE 201 Vertical Curves B 2Document7 pagesCE 201 Vertical Curves B 2Noelle Reese AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Vertical Parabolic CurvesDocument4 pagesVertical Parabolic CurvesMarc Dared Cagaoan100% (5)
- CG Multiple QuestionsDocument5 pagesCG Multiple QuestionssuwaskarkiNo ratings yet
- Shape Formulas For Area (A) and Circumference (C) : A BH X Base X Height A LW Length X WidthDocument16 pagesShape Formulas For Area (A) and Circumference (C) : A BH X Base X Height A LW Length X WidthDominic G. Casinto100% (1)
- MECG1022 Handout Equations For Involute Curve On The Surface of The Base CircleDocument3 pagesMECG1022 Handout Equations For Involute Curve On The Surface of The Base CircleEstephany Nathaly Adrian ErazoNo ratings yet
- Notes PDFDocument8 pagesNotes PDFchai tea latteNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument1 pageSurveyingAnele CatayasNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Searching: A Search: Nazmul HasanDocument5 pagesHeuristic Searching: A Search: Nazmul HasanInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- IA 16heights Distances (79 85)Document3 pagesIA 16heights Distances (79 85)eamcetmaterials75% (4)
- Bulletin Of The Serbian Geographical Society Година 2015. Свеска Xcv-Бр. 4 YEAR 2015 Tome Xcv - N 4Document22 pagesBulletin Of The Serbian Geographical Society Година 2015. Свеска Xcv-Бр. 4 YEAR 2015 Tome Xcv - N 4Bojan KojovicNo ratings yet
- Distance Transforms of Sampled FunctionsDocument15 pagesDistance Transforms of Sampled FunctionsHuy Nguyễn BảoNo ratings yet
- Shape Factors Depth Factors Inclination Factors Other FactorsDocument4 pagesShape Factors Depth Factors Inclination Factors Other FactorsManikumar CheboluNo ratings yet
- Precalculus: Prepared By: Calculus TeacherDocument6 pagesPrecalculus: Prepared By: Calculus TeacherJohn Aaron EugenioNo ratings yet
- Area & Volume FormulasDocument10 pagesArea & Volume FormulasIsmail100% (1)
- Heights and Distances: Angle of ElevationDocument3 pagesHeights and Distances: Angle of ElevationHarsh VyasNo ratings yet
- Projection Slice TheoremDocument15 pagesProjection Slice Theoremjajohns1No ratings yet
- 2d GeometryDocument21 pages2d GeometrybalachandarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PPT 3rd Year SurevyDocument24 pagesChapter 1 PPT 3rd Year SurevyHenok AsmamawNo ratings yet
- 15-5 Directional DerivativesDocument5 pages15-5 Directional DerivativesPooj PNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Plane: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedDocument10 pagesMotion in A Plane: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedAnchitBansalNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formula SheetDocument2 pagesGeometry Formula SheetNilesh Godse100% (1)
- AO Search AlgorithmsDocument5 pagesAO Search Algorithmsrakshita rajappaNo ratings yet
- c1 PDFDocument52 pagesc1 PDFMuhammad Naseer 1965-FBAS/MSCMA/F19No ratings yet
- Basic Geometric Principles of Aerial PhotographyDocument12 pagesBasic Geometric Principles of Aerial PhotographyDeepankar DuttaNo ratings yet
- Heights & DistancesDocument3 pagesHeights & DistancesMahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- Mensuration-Ii: H D H D H H DDocument0 pagesMensuration-Ii: H D H D H H DBalabhadruni SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections Formula SheetDocument1 pageConic Sections Formula SheetPrasad DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal ReviewerDocument9 pagesPre Cal ReviewerradazamarkedNo ratings yet
- Computer GraphicsDocument460 pagesComputer GraphicsvipanaroraNo ratings yet
- Earthworks 01Document6 pagesEarthworks 01BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- SettlementDocument57 pagesSettlementBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- HRENG05 - Vertical Alignment - F2FDocument15 pagesHRENG05 - Vertical Alignment - F2FBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Notes On Mohrs Circlesand Shear StrengthDocument18 pagesNotes On Mohrs Circlesand Shear StrengthBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- HRENG SyllabusDocument6 pagesHRENG SyllabusBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Eu 2-Cold Water SystemDocument1 pageEu 2-Cold Water SystemBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- TRANSPOENG Module 0.0 - Classroom Orientation & Leveling of ExpectationsDocument15 pagesTRANSPOENG Module 0.0 - Classroom Orientation & Leveling of ExpectationsBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- 7 AREA by DMD and DPDDocument4 pages7 AREA by DMD and DPDBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Taking Charge of Ones HealthDocument123 pagesTaking Charge of Ones HealthBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength NotesDocument8 pagesShear Strength NotesBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- TRANSPOENG Module 1.0 - Introduction To Transportation EngineeringDocument19 pagesTRANSPOENG Module 1.0 - Introduction To Transportation EngineeringBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- How To Become A Better Student and Setting Goals Quiz PDFDocument5 pagesHow To Become A Better Student and Setting Goals Quiz PDFBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 1 Unit 1 (Principles of Statics)Document14 pagesMech 1 Module 1 Unit 1 (Principles of Statics)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Horizontal DIstancesDocument20 pagesMeasurement of Horizontal DIstancesBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- ConcreteDocument46 pagesConcreteBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Hreng03 Isd Odl PDFDocument14 pagesHreng03 Isd Odl PDFBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 4 Unit 1 (Method of Joints)Document19 pagesMech 1 Module 4 Unit 1 (Method of Joints)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 4 Unit 2 (Method of Sections)Document15 pagesMech 1 Module 4 Unit 2 (Method of Sections)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 5 Unit 3 (Centroids of Composite Figures)Document14 pagesMech 1 Module 5 Unit 3 (Centroids of Composite Figures)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 5 Unit 1 (Center of Gravity of A Flat Plate) and Unit 2 (Centroids of Areas and Lines)Document14 pagesMech 1 Module 5 Unit 1 (Center of Gravity of A Flat Plate) and Unit 2 (Centroids of Areas and Lines)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Angle and DirectionsDocument3 pagesAngle and DirectionsBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- 4 Three-Wire LevelingDocument3 pages4 Three-Wire LevelingBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Errors and COrrectionsDocument12 pagesErrors and COrrectionsBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- CMT Laboratory 6 Unit Weight of Coarse AggregatesDocument6 pagesCMT Laboratory 6 Unit Weight of Coarse AggregatesBryanHarold Broo0% (1)
- 3 Differential LevelingDocument4 pages3 Differential LevelingBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 2 Unit 1 (Forces and Components)Document16 pagesMech 1 Module 2 Unit 1 (Forces and Components)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 1 Unit 2 (Parallelogram Law) and Unit 3 (Triangle Law)Document7 pagesMech 1 Module 1 Unit 2 (Parallelogram Law) and Unit 3 (Triangle Law)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- CMT Laboratory 7 Specific Gravity of Coarse AggregatesDocument6 pagesCMT Laboratory 7 Specific Gravity of Coarse AggregatesBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- CMT Laboratory 4 Sieve Analysis of Fine AggregatesDocument6 pagesCMT Laboratory 4 Sieve Analysis of Fine AggregatesBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Mech 1 Module 2 Unit 2 (Moment of A Force)Document9 pagesMech 1 Module 2 Unit 2 (Moment of A Force)BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyFrom EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsFrom EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlFrom EverandLees' Process Safety Essentials: Hazard Identification, Assessment and ControlRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignFrom EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Troubleshooting Vacuum Systems: Steam Turbine Surface Condensers and Refinery Vacuum TowersFrom EverandTroubleshooting Vacuum Systems: Steam Turbine Surface Condensers and Refinery Vacuum TowersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3From EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsFrom EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Distillation Design and Control Using Aspen SimulationFrom EverandDistillation Design and Control Using Aspen SimulationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- The Perfumed Pages of History: A Textbook on Fragrance CreationFrom EverandThe Perfumed Pages of History: A Textbook on Fragrance CreationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Coupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsFrom EverandCoupled CFD-DEM Modeling: Formulation, Implementation and Application to Multiphase FlowsNo ratings yet
- A New Approach to HAZOP of Complex Chemical ProcessesFrom EverandA New Approach to HAZOP of Complex Chemical ProcessesNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Carbon : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Carbon : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Cosmetic Science: An Introduction to Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Cosmetic Science: An Introduction to Principles and ApplicationsH. W. HibbottRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Fun Facts about Hydrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Hydrogen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Coulson and Richardson’s Chemical Engineering: Volume 2B: Separation ProcessesFrom EverandCoulson and Richardson’s Chemical Engineering: Volume 2B: Separation ProcessesAjay Kumar RayNo ratings yet
- Pulp and Paper Industry: Emerging Waste Water Treatment TechnologiesFrom EverandPulp and Paper Industry: Emerging Waste Water Treatment TechnologiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bioinspired Materials Science and EngineeringFrom EverandBioinspired Materials Science and EngineeringGuang YangNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena in Heat and Mass TransferFrom EverandTransport Phenomena in Heat and Mass TransferJ.A. ReizesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Stress Analysis of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Vessel Components: International Series of Monographs in Mechanical EngineeringFrom EverandThe Stress Analysis of Pressure Vessels and Pressure Vessel Components: International Series of Monographs in Mechanical EngineeringS. S. GillRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Fundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersFrom EverandFundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersNo ratings yet