Professional Documents
Culture Documents
In Context: Subject Area: Organic Chemistry Level: 14-16 Years (Foundation) Topic: Alkenes Source: RSC - li/3jI6P77
In Context: Subject Area: Organic Chemistry Level: 14-16 Years (Foundation) Topic: Alkenes Source: RSC - li/3jI6P77
Uploaded by
AteamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
In Context: Subject Area: Organic Chemistry Level: 14-16 Years (Foundation) Topic: Alkenes Source: RSC - li/3jI6P77
In Context: Subject Area: Organic Chemistry Level: 14-16 Years (Foundation) Topic: Alkenes Source: RSC - li/3jI6P77
Uploaded by
AteamCopyright:
Available Formats
In context
Subject area: Organic chemistry Level: 14–16 years (Foundation)
Topic: Alkenes Source: rsc.li/3jI6P77
1. Many fresh fruit and vegetables produce ethene.
This gas may then ripen other fruit which is unripe.
The table below shows how much ethene (in cm 3) is produced
from 1 kg of fruit each hour.
Name of fruit or vegetable Volume of ethene produced
by 1 kg of fruit in 1 hour (in
cm3)
Apricot 30
Avocado 150
Rhubarb 0.25
Banana 3.2 Source: Envato Elements
Pineapple 1.2 × 10–3
Passion fruit 235
Pear 85
a) Write the volume of ethene produced by 1 kg of pineapple per hour as a normal
number (that is, one not in standard form).
b) Place the fruit in order of the volume of ethene they produce each hour, smallest
first.
c) Calculate the volume of ethene produced by the following masses of fruit.
Remember to give units in your answers.
i) 2 kg of bananas in 1 hour
ii) 200 g of apricots in 1 hour
iii) 4 kg of pears in 2 hours
Organic chemistry in context: © Royal Society of Chemistry
Alkenes (F) edu.rsc.org Page 1 of 4
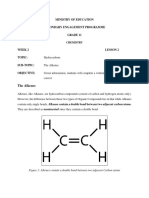
d) Ethene has the molecular formula C2H4.
Draw the structure of an ethene molecule showing the chemical bonds.
e) Ethene is described as an unsaturated hydrocarbon, define each term in the table
below.
Unsaturated
Hydrocarbon
f) State the name of a chemical substance that could be used to show that ethene is
unsaturated.
g) Give the result of the test when using the substance in part f).
Organic chemistry in context: © Royal Society of Chemistry
Alkenes (F) edu.rsc.org Page 2 of 4
2. This question is about the two molecules in the table below.
a) Complete the table.
Molecule 1 Molecule 2
Homologous series
General formula of
homologous series
Name of substance
Molecular formula
Burns with smoky
flame (Y/N)
b) Give the name of a substance that would change molecule 2 into molecule 1.
c) Which of the molecules is the more reactive?
Give a reason.
Parts d) and e) are about the molecule shown.
d) What is the name of this molecule?
Organic chemistry in context: © Royal Society of Chemistry
Alkenes (F) edu.rsc.org Page 3 of 4
e) Which molecule in the table (molecule 1 or molecule 2) is this molecule most
similar to?
Give a reason for your answer.
Organic chemistry in context: © Royal Society of Chemistry
Alkenes (F) edu.rsc.org Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- How To Eat To Live by Elijah MuhammadDocument71 pagesHow To Eat To Live by Elijah MuhammadShaheed Jennings87% (23)
- Module 5 OrgchemDocument9 pagesModule 5 OrgchemJHUNNTY LOZANONo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Grade 10 Life Sciences November Paper 2Document10 pagesInstructions: Grade 10 Life Sciences November Paper 2JustinCase199167% (3)
- Vegans Prevent & Heal Tooth DecayDocument11 pagesVegans Prevent & Heal Tooth DecayAline BragaNo ratings yet
- Stardew Valley Community Center ChecklistDocument7 pagesStardew Valley Community Center Checklistpauchanmnl100% (2)
- 5.5.1 PracticeDocument12 pages5.5.1 PracticeSid MathurNo ratings yet
- Class LKG 2021 22Document27 pagesClass LKG 2021 22Nafisa AhmadNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Active Recreation (Street & Hip-Hop Dances)Document18 pagesPhysical Education: Quarter 3 - Module 1: Active Recreation (Street & Hip-Hop Dances)Mary Cris Go100% (2)
- National 5 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature's ChemistryDocument18 pagesNational 5 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature's ChemistryDoraNo ratings yet
- Natural Sciences Content Manual Grade 8 Final 2023 Version 1677504822Document76 pagesNatural Sciences Content Manual Grade 8 Final 2023 Version 1677504822SAMANTHA SMITHNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Poster - Introduction and RubricDocument7 pagesEcosystem Poster - Introduction and Rubricapi-271661638No ratings yet
- In Context: Subject Area: Organic Chemistry Level: 14-16 Years (Foundation) Topic: Alkenes Source: RSC - li/3jI6P77Document4 pagesIn Context: Subject Area: Organic Chemistry Level: 14-16 Years (Foundation) Topic: Alkenes Source: RSC - li/3jI6P77Dũng PhạmNo ratings yet
- Csalkeneshigherstudentv1 213227Document4 pagesCsalkeneshigherstudentv1 213227AteamNo ratings yet
- AlkeneDocument5 pagesAlkeneAli r24No ratings yet
- Knowledge Check: 1. This Question Is About The Molecules in The TableDocument4 pagesKnowledge Check: 1. This Question Is About The Molecules in The TableDũng PhạmNo ratings yet
- MIC 201 - Prac Paper 2 - June 2022Document6 pagesMIC 201 - Prac Paper 2 - June 2022Lucas LuluNo ratings yet
- In ContextDocument4 pagesIn ContextLanbin CuiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Life ScienceDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Life ScienceAndevie Balili IguanaNo ratings yet
- Science Allen SQPDocument48 pagesScience Allen SQPloda lassunNo ratings yet
- Directions: Follow The Step-By-Step Instructions For This Exercise Found On The Worksheet Below and in The Virtual Lab and Record YourDocument4 pagesDirections: Follow The Step-By-Step Instructions For This Exercise Found On The Worksheet Below and in The Virtual Lab and Record YourTiara WilliamsNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersDocument12 pagesAQA GCSE Bioenergetics AnswersJoeNo ratings yet
- Ecology Study Guide 4 - EcosystemsDocument6 pagesEcology Study Guide 4 - EcosystemsJoeNo ratings yet
- Biology Class XDocument4 pagesBiology Class Xneha singhNo ratings yet
- Bio Class XDocument2 pagesBio Class Xneha singhNo ratings yet
- 4.5.3 Test (TST) - Teacher-Scored Unit TestDocument15 pages4.5.3 Test (TST) - Teacher-Scored Unit TestMia Isabella San InocencioNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Learner Support DocumentDocument36 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 Learner Support DocumentLiezel100% (1)
- In ContextDocument4 pagesIn ContextRajlaxmi JainNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2 Final Exam - Semester 2 Exam (Test)Document20 pages5.1.2 Final Exam - Semester 2 Exam (Test)joonseo81No ratings yet
- Bio 14 LAB Exercise 9 EcologyDocument13 pagesBio 14 LAB Exercise 9 EcologyBarbara Jane CambasNo ratings yet
- LIF101 Mid Semester ExaminationDocument6 pagesLIF101 Mid Semester ExaminationPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Ecology (You May Either Add The Answers and Notes On This Worksheet or Use Additional Sheets)Document9 pagesTopic 4 Ecology (You May Either Add The Answers and Notes On This Worksheet or Use Additional Sheets)한서현No ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument10 pagesEcosystemHelmi Hirman AnugrahNo ratings yet
- In Context: Subject Area: Organic Chemistry Level: 14-16 Years (Foundation) Topic: Alcohols Source: RSC - Li/3NtocpmDocument6 pagesIn Context: Subject Area: Organic Chemistry Level: 14-16 Years (Foundation) Topic: Alcohols Source: RSC - Li/3NtocpmRizki HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chemistry Week 2 Lesson 2Document4 pagesGrade 11 Chemistry Week 2 Lesson 2RealGenius (Carl)No ratings yet
- KZN LFSC Grade 11 Step Ahead Learner Support Document2023Document49 pagesKZN LFSC Grade 11 Step Ahead Learner Support Document2023akwandengcobo5No ratings yet
- Learner Guide 2019Document47 pagesLearner Guide 2019Andrew NaleNo ratings yet
- Ecology Study Guide 4 - EcosystemsDocument6 pagesEcology Study Guide 4 - EcosystemsJoeNo ratings yet
- Energy and Matter Study GuideDocument3 pagesEnergy and Matter Study GuideNorlijun HilutinNo ratings yet
- NS 2018-Bundle-All-Grade-8-Natural-Sciences-Exams-And-MemosDocument37 pagesNS 2018-Bundle-All-Grade-8-Natural-Sciences-Exams-And-MemosEstelle EsterhuizenNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsDocument8 pagesAqa Gcse Bioenergetics Graspit - QuestionsJoeNo ratings yet
- PTS 2019 GS Test 10 QP PDFDocument11 pagesPTS 2019 GS Test 10 QP PDFashish choudharyNo ratings yet
- Nabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursDocument10 pagesNabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursCecilia KhaombiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science - EcosystemDocument25 pagesEnvironmental Science - EcosystemtashNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 20171Document14 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 20171Pretentious WreackerNo ratings yet
- Activity Worksheet 2.2.Document10 pagesActivity Worksheet 2.2.hestiaNo ratings yet
- Primary Productivity and Energy Dynamics Manuel TzulDocument7 pagesPrimary Productivity and Energy Dynamics Manuel Tzulapi-323831182No ratings yet
- 1.3.5 Practice - Matter and Energy in The Biosphere (Practice)Document2 pages1.3.5 Practice - Matter and Energy in The Biosphere (Practice)jjtobin81redNo ratings yet
- SPM Bio Perlis 2009 Serta SkemaDocument96 pagesSPM Bio Perlis 2009 Serta Skemahilmi72100% (1)
- Science 2015 PDFDocument15 pagesScience 2015 PDFashwaniNo ratings yet
- Energy Photosynthesis Respiration TestDocument30 pagesEnergy Photosynthesis Respiration Testapi-237801056No ratings yet
- Energy End Thermo PDFDocument31 pagesEnergy End Thermo PDFssfoodtechNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1 SLDocument3 pagesBiology Paper 1 SL刘宇杰No ratings yet
- Quiz Heart GR 9 (C)Document1 pageQuiz Heart GR 9 (C)Marwa IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Biology Set - 1 KeyDocument13 pagesBiology Set - 1 Keyroyal ghostNo ratings yet
- 14.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages14.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistrygoverotaropafadzwaNo ratings yet
- 14.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages14.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistryNqobile SingojwanaNo ratings yet
- Tinashe 20Document17 pagesTinashe 20Nqobile SingojwanaNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences P2 Feb-March 2011 EngDocument21 pagesPhysical Sciences P2 Feb-March 2011 EngMmabatho VilakaziNo ratings yet
- 14.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages14.0 Introduction To Organic ChemistryNqobile SingojwanaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Gr11 Notes PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesLife Sciences Gr11 Notes PhotosynthesisseakaneoNo ratings yet
- KZN LFSC Grade 11 Step Ahead Teacher Support Document 2023Document40 pagesKZN LFSC Grade 11 Step Ahead Teacher Support Document 2023nomvulamathipaNo ratings yet
- Nabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursDocument10 pagesNabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursCecilia KhaombiNo ratings yet
- Eco SystemDocument8 pagesEco SystemanoopstudieNo ratings yet
- Primary Productivity and Energy Dynamics-RennelDocument6 pagesPrimary Productivity and Energy Dynamics-Rennelapi-323831182No ratings yet
- Agriculture Fill in The BlanksDocument2 pagesAgriculture Fill in The BlanksDaksh bhallaNo ratings yet
- Farm To TableDocument12 pagesFarm To TableJacquelynKosNo ratings yet
- English BookDocument48 pagesEnglish BookajiNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in AgricultureDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in AgricultureReajean EscosaisNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Underutilized Fruit Crops in Hot Semi-Arid Regions: Developments and Challenges - A ReviewDocument9 pagesCultivation of Underutilized Fruit Crops in Hot Semi-Arid Regions: Developments and Challenges - A ReviewJitendra singh shivranNo ratings yet
- Fruits and Vegetables: ReferencesDocument1 pageFruits and Vegetables: ReferencesGuillermo William PiañarNo ratings yet
- Cookies Poudre D'orangeDocument7 pagesCookies Poudre D'orangeimene boulaalouaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Little Steps Level 2 Student S Book Zapiain Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesCambridge Little Steps Level 2 Student S Book Zapiain Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFwilliam.orsborn826100% (14)
- Soal B.ing Kls 3Document3 pagesSoal B.ing Kls 3Ini AkiNo ratings yet
- Family Menu ProjectDocument20 pagesFamily Menu ProjectRavenNo ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 3Document11 pagesCropSci101 Module 3Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Parentline DescriptionDocument1 pageParentline DescriptionAgricultura de campoNo ratings yet
- Guide 7, Preparing and Canning Jams and JelliesDocument10 pagesGuide 7, Preparing and Canning Jams and Jelliesanton_428No ratings yet
- Seed Harvesting, Processing and StorageDocument6 pagesSeed Harvesting, Processing and StorageSheeba KausarNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Plant and Fungal Diversity: Chapter ObjectivesDocument15 pagesThe Evolution of Plant and Fungal Diversity: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- List of VocabularyDocument17 pagesList of VocabularyMaskur SyuaibNo ratings yet
- Food-Where Does It Come From PPT Part 1Document22 pagesFood-Where Does It Come From PPT Part 1charliecharliestoryNo ratings yet
- 21 PDFDocument8 pages21 PDFPrincess BernardinoNo ratings yet
- CatalogueDocument76 pagesCatalogueramsringarNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument24 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsNalla Raghuram ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Carrefour - Procurement Grocery List - 15oct2019 - RevDocument24 pagesCarrefour - Procurement Grocery List - 15oct2019 - RevAnonymous ZMjBEWNo ratings yet
- Plants Adaptations NotesDocument14 pagesPlants Adaptations NotessmedificationNo ratings yet
- Practical Project: Production of Mango Powder From MangoDocument12 pagesPractical Project: Production of Mango Powder From MangoTakreem SindhuNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 2Document11 pagesExercise No. 2MA. NECOLE JEREMIAH GONZALESNo ratings yet
- 7 Day Juicing PlanDocument4 pages7 Day Juicing PlanBernhard MaschkeNo ratings yet