Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Audit Reviewer
Uploaded by
Angelly Esguerra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesAudit Reviewer
Uploaded by
Angelly EsguerraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
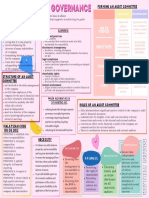
Assurance Independent & objective assurance &
and Advice advice to promote continuous
CHAPTER 1: improvements
IA IN THE ORGANIZATION Achieved through fully resources
a. The Big Picture View: Three Lines Model independent internal audit function that
operates in accordance with international
b. Governance, Risk Management, Internal Control
standards.
c. Ensuring Internal Audit Value to the Organization
Principle 2: GOVERNING BODY RULES
THREE MODEL LINES
Ensures appropriate structures & processes are in
place for effective governance
Ensures objectives & activities are aligned
delegates responsibility & provides resources to
management to achieve the objectives while ensuring
legal, regulatory, & ethical expectations are met
Establishes & oversees an independent, objective,
and competent internal audit function to provide
clarity & confidence
Principle 3: MANAGEMENT AND FIRST- AND
SECOND-LINE ROLES
Management’s responsibility comprises both first- and
second-line roles
- Help organizations understand and organize the various First Line Roles
activities and responsibilities that make up governance, - Directly aligned with the delivery of products or
risk management and control services to clients
- Responsibility shared across different functions, it is - Includes the roles of support functions
important to have a clear picture to avoid confusion, - Managing risk
overlap, and gaps Second Line Roles
- Provide assistance with managing risk, assigned
to specialists
- Focus on specific objectives of risk management
- A broader responsibility for risk management
Principle 4: THIRD LINE ROLES
- IA (& EA may consider) provides independent and
objective assurance and advice through competent
application of systematic and discipline processes to
promote & facilitate continuous improvement.
PRINCIPLE 5: THIRD LINE INDEPENDENCE
- IA’s independence is critical to its objectivity,
authority, and credibility by establishing accountability
Principle 1: BASIC ELEMENTS OF GOVERNANCE to the G.B.; unfettered access to people resources, &
data needed to complete its work; freedom from bias or
Accountabilit Achieved through transparent oversight, interference in audit services.
y integrity
Governing bodies must ensure PRINCIPLE 6: CREATING AND PROTECTING VALUE
disclosures are accurate, timely, reliable,
comprehensive, and in compliance with Alignment of activities is achieved through
legislative & regulatory requirements, & communication, cooperation, and collaboration.
ethical norms Ensures the reliability, coherence, and transparency
Action Reliable & well-informed action needed for risk-based decision making.
Critical to achieving the objectives
Management must provide direction and
ensure analysis, planning, monitoring, FOUR OVERLAPPING & COMPLEMENTARY ROLES
risk oversight, & reporting back to the
G.B. 1. LEADERSHIP & OVERSIGHT Governing Bodies
2. STRATEGY EXECUTION Management First External - Satisfy legislative to protect the
Lines Assurance interest of stakeholders
3. SUPPORT, GUIDANCE, & CONTROL Provides - Satisfy request by management
Management Second Lines and G.B. to complement internal
4. OBJECTIVES ASSURANCE & ADVICE sources of assurance
Independent IA
GOVERNANCE, RISK MANAGEMENT, CONTROLS
Leadership & Must have measures to ensure that G.B.
Oversight directs:
- In accordance with Stakeholders’ Governance the combination of processes &
interests/needs structures implemented by the board to inform,
- Within requirements of direct, manage and monitor toward the
law/regulations achievement of its objectives.
Governing THE KEY ROLES IN THE THREE Risk management is a process to identify, assess,
Bodies LINE MODELS manage, and control potential events to provide
- Oversights the organization reasonable assurance.
- Monitor stakeholder’s interest Internal Control any action to manage risk and
- Promotes ethical behavior
increase likelihood that established objectives &
- Establishes structures & processes
goals.
for governance
- Delegates responsibility and
provides resources GRC: Drivers of Organizational Sustainability
- Determines risks & exercises
oversight of risk management Governance
Strategy - Responsible of executing strategy
Execution - Includes support functions, even Surround all activities
those outsourced Vision, Mission Values
Management - Leads & directs action (including Ensure needs of key stakeholders are met
First Lines managing risk) & application of
resources Risk Management
- Maintain a continuous reports with
Identify & manage risks (what could go wrong)
the G.B.
- Establishes and maintains Exploit opportunities that enables success (what
structures for operations & risks should go right)
- Ensures compliance Operates within direction of governance structure
Support, - Develop, monitor, & continuously
Guidance, improve policies Control
Control - Supporting management policies, Subset & integral part of broader RM activities
setting goals for implementation
Risk response to execute RM strategies
Management - Provides complementary expertise,
Second Lines support, monitoring and challenge Geared to achievement
to risks
- Provides analysis & reports on the
adequacy & effectiveness of risk
management & internal control
Objectives - Enhance and protect organizational
Assurance & value
Advice: - Does not replace the
INTERNAL management’s obligation to
AUDIT monitor performance & report
to the G.B.
Internal Audit - Maintains primarily accountability
& independence
- Communicates independent
assurance and advice to the
management and the G.B. on the
effectiveness of governance and
risk management
- Reports impairment to the G.B.
and implements safeguards as
required
You might also like
- Chapter 11Document14 pagesChapter 11Willma PaladaNo ratings yet
- CombinepdfDocument25 pagesCombinepdfW-304-Bautista,PreciousNo ratings yet
- 47 67Document3 pages47 67an scNo ratings yet
- Principles of Auditing: Topic 3 - Part 1Document7 pagesPrinciples of Auditing: Topic 3 - Part 1Khánh Đoan NgôNo ratings yet
- Three Lines Model UpdatedDocument13 pagesThree Lines Model UpdatedJose David Pardo SalazarNo ratings yet
- Aud1206 Operations Auditing Finals ReviewerDocument3 pagesAud1206 Operations Auditing Finals ReviewerJazmine Arianne DalayNo ratings yet
- Internal Control, Internal Auditor & Risk ManagementDocument58 pagesInternal Control, Internal Auditor & Risk ManagementWagimin SendjajaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management and Internal AuditorDocument58 pagesRisk Management and Internal AuditorAnanda rizky syifa nabilahNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditing 02 IA OverviewDocument3 pagesInternal Auditing 02 IA OverviewSummer FitzNo ratings yet
- Internal ControlsDocument5 pagesInternal ControlsAya PulidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-8Document10 pagesChapter 6-8DeyNo ratings yet
- Rodriguez Zyra-Denelle 16 JournalDocument10 pagesRodriguez Zyra-Denelle 16 JournalDaena NicodemusNo ratings yet
- The IIA's Three Lines ModelDocument13 pagesThe IIA's Three Lines ModelOSAMA ABUSKARNo ratings yet
- Sistem Pengendalian InternalDocument18 pagesSistem Pengendalian InternalElizabeth PutriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Internal Control and Risk ManagementDocument50 pagesLesson 4 Internal Control and Risk ManagementAngelica PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Romney Ais13 PPT 01Document42 pagesRomney Ais13 PPT 01Chesya Bintang CarolineNo ratings yet
- Development of The Profession of IADocument1 pageDevelopment of The Profession of IAatien_azNo ratings yet
- 4 - AIS ReviewerDocument1 page4 - AIS ReviewerAira Jaimee GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in GBRC PRELIMDocument2 pagesReviewer in GBRC PRELIMJhernel SuaverdezNo ratings yet
- 4 5850471109056532140Document59 pages4 5850471109056532140Yehualashet MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of The Operation.: AuditsDocument4 pagesEffectiveness of The Operation.: AuditsAllia AntalanNo ratings yet
- Internal Control Assessment PDFDocument9 pagesInternal Control Assessment PDFRomlan D.No ratings yet
- Internal Control AssessmentDocument8 pagesInternal Control AssessmentRomlan D.No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Internal ControlsDocument5 pagesLesson 6 - Internal ControlsAllaina Uy BerbanoNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditings Role in Corporate Governance (IIA)Document4 pagesInternal Auditings Role in Corporate Governance (IIA)Vidya IntaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Internal ControlDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Internal ControlCazia Mei JoverNo ratings yet
- Audit Internal Chapter 6Document34 pagesAudit Internal Chapter 6Fitri NoviaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 1: Introduction To Cost AccountingMộng ThuýNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 and 11 - GovernanceDocument1 pageChapter 10 and 11 - GovernanceAnonymous ReaderNo ratings yet
- Governance Summary 1 9Document9 pagesGovernance Summary 1 9Ivy Claire SemenianoNo ratings yet
- CIA Part 1, Unit 1-1Document35 pagesCIA Part 1, Unit 1-1Ahmed AzaziNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Evaluasi Manajemen Risiko - YLYDocument16 pagesPresentasi Evaluasi Manajemen Risiko - YLYOPERASIONALNo ratings yet
- Implementing The Five Key Internal Controls: PurposeDocument6 pagesImplementing The Five Key Internal Controls: PurposeRia GabsNo ratings yet
- Advanced Audit and Assurance - Chapter 5 - Quality ControlDocument42 pagesAdvanced Audit and Assurance - Chapter 5 - Quality Controlady.mighty003No ratings yet
- Intro To Internal Auditing Ch. 1, 2, and 3 Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesIntro To Internal Auditing Ch. 1, 2, and 3 Flashcards - QuizletIman NessaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance MIND MAPDocument1 pageCorporate Governance MIND MAPnormalasaliminNo ratings yet
- GBERMICDocument3 pagesGBERMICAnnyeong AngeNo ratings yet
- Internal Auditings Role in Corporate GovernanceDocument4 pagesInternal Auditings Role in Corporate GovernanceJawadNo ratings yet
- Control Financiero y CalidadDocument6 pagesControl Financiero y CalidadRamón G. PachecoNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint PresentationDocument15 pagesPowerPoint PresentationMOHAMAD AMIRUL AINAN BIN BASHIR AHMAD MoeNo ratings yet
- Aud Chapter 3Document7 pagesAud Chapter 3Klo MonNo ratings yet
- NOTES - GOVBUSMAN - Chapter 1Document2 pagesNOTES - GOVBUSMAN - Chapter 1Bundalian, Louisse Nicole A.No ratings yet
- Defition of TermsDocument5 pagesDefition of TermssrachylNo ratings yet
- Internal Control Toolkit 2-lmgtDocument22 pagesInternal Control Toolkit 2-lmgtPablo AzierNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Internal Control System Part 1 StudentDocument7 pagesTopic 3 Internal Control System Part 1 Studentnnmnghi1409No ratings yet
- CHP 5Document14 pagesCHP 5ali iqbalNo ratings yet
- Bussiness Ethics Chapter 12Document3 pagesBussiness Ethics Chapter 12Ian Farouk Ahmad EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Consideration of Internal ControlDocument43 pagesConsideration of Internal ControlDebbie Grace Latiban LinazaNo ratings yet
- Auditing Chapter 11Document15 pagesAuditing Chapter 11Joseph LomboyNo ratings yet
- Tema: Control Interno: Auditoría Financiera IDocument16 pagesTema: Control Interno: Auditoría Financiera IPablo GarzonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in MGT3Document5 pagesReviewer in MGT3Dave ManaloNo ratings yet
- Walden Slides PresentationDocument30 pagesWalden Slides PresentationNguyễn Trọng KhaNo ratings yet
- Final OAP Practice Guide Dec 2011Document29 pagesFinal OAP Practice Guide Dec 2011Pramod AthiyarathuNo ratings yet
- Aca 312B NotebookDocument13 pagesAca 312B NotebookErika Joy Casimero ColasteNo ratings yet
- SIA Kel 3 FinishDocument25 pagesSIA Kel 3 FinishNugraha HaritsNo ratings yet
- The Three Lines of Defence: Audit Committee InstituteDocument4 pagesThe Three Lines of Defence: Audit Committee InstituteDigong SmazNo ratings yet
- COSO Framework 7 PillarDocument1 pageCOSO Framework 7 PillarEddo LatievaryaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - SU 1 Foundations of Internal AuditingDocument86 pagesPart 1 - SU 1 Foundations of Internal Auditingintern.hmdsNo ratings yet
- Institue of Internal Auditors, Definition of Internal Auditing (2013)Document7 pagesInstitue of Internal Auditors, Definition of Internal Auditing (2013)sara sibumaNo ratings yet
- Second Chapter Humans' Attitude Towards Nature: Storehouse of MaterialsDocument35 pagesSecond Chapter Humans' Attitude Towards Nature: Storehouse of MaterialsnheneNo ratings yet
- NVC Games Package English Version WebDocument36 pagesNVC Games Package English Version WebThiago RaydanNo ratings yet
- The Stanford Prison ExperimentDocument3 pagesThe Stanford Prison Experimentbutch jastinNo ratings yet
- Final AgreementDocument15 pagesFinal AgreementAzrina NurichoNo ratings yet
- Analytical School of JurisprudenceDocument5 pagesAnalytical School of JurisprudenceAniket RajNo ratings yet
- Jodhpur Escorts Service Call Ravina 9509259176 Sexy Call Girls in JodhpurDocument27 pagesJodhpur Escorts Service Call Ravina 9509259176 Sexy Call Girls in Jodhpursoniya sharmaNo ratings yet
- join Illuminati 666 brotherhood here //Brief on Illuminati society 2020 whats-app on +22371926246 and join us for wealthy benefits. HOW TO JOIN ILLUMINATI,WHERE CAN I JOIN ILLUMINATI/WHAT IS ILLUMINATI/I WANT TO JOIN ILLUMINATI/ I WANT TO JOIN THE BROTHERHOOD FRATERNITY, I WANT TO JOIN ILLUMINATI BROTHERHOOD/I WANT TO JOIN ILLUMINATI IN MY COUNTRY/ WHERE CAN I JOIN ILLUMINATI IN MY COUNTRY, I WANT TO JOIN THE SECRET SOCIETY OF ILLUMINATI/ I WANT TO JOIN ILLUMINATI CULT,OCCULT,/ WHERE CAN I FINE ILLUMINATI AND JOIN FOR MONEY/POWER/FAME/PROMOTIONS/MAGIC. 666 lucifer.Document2 pagesjoin Illuminati 666 brotherhood here //Brief on Illuminati society 2020 whats-app on +22371926246 and join us for wealthy benefits. HOW TO JOIN ILLUMINATI,WHERE CAN I JOIN ILLUMINATI/WHAT IS ILLUMINATI/I WANT TO JOIN ILLUMINATI/ I WANT TO JOIN THE BROTHERHOOD FRATERNITY, I WANT TO JOIN ILLUMINATI BROTHERHOOD/I WANT TO JOIN ILLUMINATI IN MY COUNTRY/ WHERE CAN I JOIN ILLUMINATI IN MY COUNTRY, I WANT TO JOIN THE SECRET SOCIETY OF ILLUMINATI/ I WANT TO JOIN ILLUMINATI CULT,OCCULT,/ WHERE CAN I FINE ILLUMINATI AND JOIN FOR MONEY/POWER/FAME/PROMOTIONS/MAGIC. 666 lucifer.illuminati brotherhoodNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Ethical Dilemmas and Decisions in Criminal Justice 9th Edition PDFDocument42 pagesOriginal PDF Ethical Dilemmas and Decisions in Criminal Justice 9th Edition PDFpatricia.morrison594100% (29)
- Practical Research 1: Prelim ExaminationDocument6 pagesPractical Research 1: Prelim ExaminationJac PolidoNo ratings yet
- P1 Revision Mock B Answers D17Document16 pagesP1 Revision Mock B Answers D17Meyly LingNo ratings yet
- Endline Evaluation PDFDocument12 pagesEndline Evaluation PDFJayden YoonNo ratings yet
- Management of Business Triat Thoery PresentationDocument17 pagesManagement of Business Triat Thoery PresentationOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- The Rape JokeDocument6 pagesThe Rape Jokeagustin cassinoNo ratings yet
- Friendships Adventurer (ISFP) Personality 16personalitiesDocument1 pageFriendships Adventurer (ISFP) Personality 16personalitiesronghui009No ratings yet
- m4m A Level PrepDocument26 pagesm4m A Level PrepSumaiyaNo ratings yet
- Bpops Accomplishment Report 2022Document7 pagesBpops Accomplishment Report 2022Acel Cuyat100% (1)
- Ganda Ka A Philosophical, Historical, and Cultural Exploration of Beauty Standards in The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesGanda Ka A Philosophical, Historical, and Cultural Exploration of Beauty Standards in The PhilippinesysblnclNo ratings yet
- Maxims For Public Servants: Chapter - IvDocument4 pagesMaxims For Public Servants: Chapter - IvLalithNo ratings yet
- Desmond and The Very Mean Word Teachers Guide PDFDocument3 pagesDesmond and The Very Mean Word Teachers Guide PDFAuburn HouseNo ratings yet
- Module No. 1: ST NDDocument2 pagesModule No. 1: ST NDErwil AgbonNo ratings yet
- Family WisdomDocument5 pagesFamily WisdomJankiNo ratings yet
- Joan Poliner Shapiro - Jacqueline A. Stefkovich, Joan Poliner Shapiro, Jacqueline A. Stefk - Ethical Leadership and Decision Making in Education - Applying Theoretical Perspectives To Complex DilemmasDocument199 pagesJoan Poliner Shapiro - Jacqueline A. Stefkovich, Joan Poliner Shapiro, Jacqueline A. Stefk - Ethical Leadership and Decision Making in Education - Applying Theoretical Perspectives To Complex DilemmasNOURDINE EZZALMADINo ratings yet
- Bajaj ElectricDocument13 pagesBajaj Electricamisha jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Roles and Responsibilities of Table Tennis OfficialsDocument3 pagesRoles and Responsibilities of Table Tennis OfficialsHans Mosqueda100% (1)
- Villarama Vs NLRC G.R. No. 106341Document7 pagesVillarama Vs NLRC G.R. No. 106341Graile Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Business Law MidtermsDocument11 pagesBusiness Law MidtermsMary Jescho Vidal AmpilNo ratings yet
- I Am Not Your Asian StereotypeDocument3 pagesI Am Not Your Asian StereotypeソンギョウゼンNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 3 - Lit ChartDocument13 pagesStudy Guide 3 - Lit ChartSouren KhedeshianNo ratings yet
- Khalsa College For Women, Ludhiana: Admission Form (2023-24) Application / Form No: 12951-14753Document4 pagesKhalsa College For Women, Ludhiana: Admission Form (2023-24) Application / Form No: 12951-14753SONU SNo ratings yet
- Ethical Leadership in The Age of Corporate Social Responsibility: A Comparative Study of Multinational CorporationsDocument17 pagesEthical Leadership in The Age of Corporate Social Responsibility: A Comparative Study of Multinational CorporationsPushpender SinghNo ratings yet