Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tool Engineering - Tut. Sheet 2 2022-23
Uploaded by
chaurasia.nikhil2001Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tool Engineering - Tut. Sheet 2 2022-23
Uploaded by
chaurasia.nikhil2001Copyright:
Available Formats
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
B. Tech. VI Semester (Production & Industrial Engineering)
TOOL ENGINEERING
TUTORIAL SHEET- 2 (Jigs and Fixtures Design, and Gauge Design)
1. State the purpose of gauges. Discuss the design of i) snap gauge, ii) plug gauge, iii) flush
pin gauge, iv) thread gauge, and v) angle gauge
2. Sketch and explain
a) pilot plug gauge b) taper plug gauge c) snap gauge
3. Draw and sketch a snap gauge to check shaft of diameter 210-0.03
4. Design and sketch a flush pin gauge to measure a hole depth of 50 ± 0.10 mm. with diameter
varying from 25 mm to 18 mm, in a mild steel workpiece of outer rectangular shape of 100
mm × 50 mm.
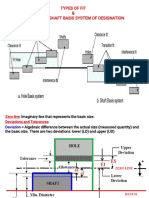
5. A hole and shaft system has the following dimensions:
60 mmH8/c8
The standard tolerance is given by
I 0.453 D 0.001D
Where D= Diameter of geometric mean of steps, mm
I = standard tolerance, micron
The multiplier for grade 8 is 25. The fundamental deviation for shaft c for D>40 is given by
-(95 +0.8D)
The diameter range lies between 50 to 80 mm. Sketch the fit and show on it the actual
dimensions of hole and shaft. Name the class of fit. Also, design the suitable gauges to
check the hole and the shaft.
6. A limit gauge is required to check the hole 50 +0.339 mm (50 H8). The depth of hole is 200
mm. Design the gauge and sketch it with dimensions.
7. Design a centre distance gauge to measure a centre distance of 52 mm between two holes in
a mild steel component. The two holes have the diameter of 15 H9 and 14 H10.
8. Explain the technical supply conditions for gauges?
9. Discuss the various materials used for gauge manufacture.
0.04 0.05
10. The rectangular hole of width 70 mm and breadth 90 mm
0.00 0.00
0.04 0.05
inside a rectangular workpiece of size 100 mm × 120 mm × 30 mm
0.00 0.00
is to be checked.
Design the suitable gauges based on Taylor’s principle.
11. Whether the gauges should be cared for before and after use? Explain.
12. What is the difference between a limit gauge and a non-limit gauge (standard gauge).
13. Describe the essential characteristics of an indexing jig.
14. Explain the function of each basic element of a fixture. Which material is referred for each
element; give reasons for your choice.
15. A hole of 50 mm is to be drilled in a 100 mm diameter rod which has a tolerance of ±0.25
mm. V-block fixture is to be used. Determine the possible variations from the centre line of
the drill bushing when: i) 90o V-block is used, ii) 70o V-block is used, iii) 120o V-block is
used. Sketch the fixture.
16. Describe welding fixture by giving suitable example.
17. List various types of quick acting clamps.
18. Write a note on classification of tools.
You might also like
- Assignment 4Document1 pageAssignment 4utkarshtyagi2307No ratings yet
- Manual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsFrom EverandManual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Metrology and Surface Engineering: Unit - IDocument8 pagesMetrology and Surface Engineering: Unit - Isatyanarayana19No ratings yet
- Tutorials Printed VersionDocument22 pagesTutorials Printed VersionNjabulo NgobeseNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Subject:Tool Engineering/Tool Design Q.No QuestionDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank: Subject:Tool Engineering/Tool Design Q.No QuestionhemendraNo ratings yet
- Bill of QuantityDocument4 pagesBill of Quantityeng-ashraf abdullahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1. - Probability and StatisticsDocument1 pageAssignment 1. - Probability and StatisticsTejo NathNo ratings yet
- Cedrick JoshuaDocument7 pagesCedrick JoshuaRommel TayactacNo ratings yet
- Me2308 Set2Document4 pagesMe2308 Set2kaliappan454900% (1)
- METROLOGYDocument5 pagesMETROLOGYGangadhar TallaNo ratings yet
- Design of Jigs QP Upto 2010Document20 pagesDesign of Jigs QP Upto 2010Naresh Dharma100% (1)
- Tutorial 4 Sheet Metal WorkingDocument2 pagesTutorial 4 Sheet Metal WorkingSawai PariharNo ratings yet
- D.desmaan Machining & Manufacturing Lab ReportDocument11 pagesD.desmaan Machining & Manufacturing Lab ReportD.DesmaanNo ratings yet
- MMM QuestionsDocument5 pagesMMM QuestionsAshok MallNo ratings yet
- Workshop - and - Machine - Shop ManualDocument96 pagesWorkshop - and - Machine - Shop ManualBenjie flor CalayegNo ratings yet
- GATE Metrology QuestionsDocument14 pagesGATE Metrology QuestionsWilson Kumar33% (3)
- Metrology and Quality Control PracticalDocument53 pagesMetrology and Quality Control PracticalDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE75% (4)
- VQC PDFDocument24 pagesVQC PDFBhargav AS SeeramNo ratings yet
- Conduct Experiment On Lathe 100Document9 pagesConduct Experiment On Lathe 100balakaleesNo ratings yet
- International Institute of Managemant & Technical Studies: Machine DrawingDocument2 pagesInternational Institute of Managemant & Technical Studies: Machine DrawingyekahNo ratings yet
- Metrology & Instrumentation Course File1Document112 pagesMetrology & Instrumentation Course File1harshith pondeNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document4 pagesModule 4sathiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 Introduction LimitSystemsDocument3 pagesTutorial1 Introduction LimitSystemsSanthosh AmaraNo ratings yet
- Measuring Pin Catalogue: Measuring Pins Measuring Pin Sets Storage Cases Test Certificates Magnetic Measuring PinsDocument12 pagesMeasuring Pin Catalogue: Measuring Pins Measuring Pin Sets Storage Cases Test Certificates Magnetic Measuring PinsManh PhamNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2019-20 MEE2001 ELA VL2019201005431 Reference Material II 12-Jul-2019 Conventional TolerancingDocument22 pagesFALLSEM2019-20 MEE2001 ELA VL2019201005431 Reference Material II 12-Jul-2019 Conventional TolerancingNikhil VermaNo ratings yet
- MEC 112 Lectures 20182019Document54 pagesMEC 112 Lectures 20182019vargas100% (3)
- Thread Cutting and Knurling To Make Nut and BoltDocument3 pagesThread Cutting and Knurling To Make Nut and BoltHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Mukul SardanaNo ratings yet
- By The End of The Lesson, Students Should Be Able ToDocument33 pagesBy The End of The Lesson, Students Should Be Able ToMichael Castro AbuduNo ratings yet
- 006 Assignment Hung Chi HouDocument27 pages006 Assignment Hung Chi HouchillichilliNo ratings yet
- UOW - Lecture 2 Measuring ToolsDocument9 pagesUOW - Lecture 2 Measuring ToolsVinnoth SrikumarNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksDocument3 pagesTime: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksAnonymous ZB6qyhD6No ratings yet
- Vibrant NDT Services PVT LTD Chennai: Sr. No. Description Picture Binny Rate Alco Rates Vibrant Rate 1 Ultrasonic BlocksDocument4 pagesVibrant NDT Services PVT LTD Chennai: Sr. No. Description Picture Binny Rate Alco Rates Vibrant Rate 1 Ultrasonic BlocksGovindKrishnanNo ratings yet
- MartikáDocument6 pagesMartikálaboratorioNo ratings yet
- Doweling, Fastening and Locking Plates Operation SheetDocument4 pagesDoweling, Fastening and Locking Plates Operation SheetPolarcheif 01No ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurement & Metrology Jan 2014Document2 pagesMechanical Measurement & Metrology Jan 2014Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- 8.1.12 Programming Example: Milling: ComponentDocument1 page8.1.12 Programming Example: Milling: ComponentmuhdqasimNo ratings yet
- ME8513 & Metrology and Measurements LaboratoryDocument3 pagesME8513 & Metrology and Measurements LaboratorySakthivel KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- ME3201Document4 pagesME3201Md. Tariqul Islam MunnaNo ratings yet
- rr320302 MetrologyDocument8 pagesrr320302 MetrologySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Hand Tools - Metal: Marking Out, Measurement, Fitting & AssemblyDocument16 pagesHand Tools - Metal: Marking Out, Measurement, Fitting & Assemblytarmizy100% (1)
- 35232chapter 3 Linear MeasurementDocument14 pages35232chapter 3 Linear Measurementk.ghanemNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Fitter QuestionDocument6 pagesMicrosoft Word - Fitter QuestionVikashKumarNo ratings yet
- PipeworkDocument5 pagesPipeworkTAPIZ ACMVNo ratings yet
- ToleranceDocument21 pagesTolerancemonikeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 6Document4 pagesAssignment No. 6NARENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Test Project Sheet MetalDocument10 pagesTest Project Sheet MetalSyed Idrus Syed OmarNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Dial GaugeDocument21 pagesCalibration of Dial GaugeAnthony Burns82% (11)
- 4 Hours / 100 MarksDocument7 pages4 Hours / 100 MarkswarekarNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-29 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-29 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering Assignment Thapar UniversityDocument5 pagesManufacturing Engineering Assignment Thapar UniversitySaurav Kumar0% (1)
- Tool Engineering - Tutorial Sheet 3 - 2022 - 2023Document1 pageTool Engineering - Tutorial Sheet 3 - 2022 - 2023chaurasia.nikhil2001No ratings yet
- May 2014Document3 pagesMay 2014Arun Prakash NatesanNo ratings yet
- Important Questions MetrologyDocument5 pagesImportant Questions Metrologyswathi_ipe100% (1)
- Metal ReinforcementDocument9 pagesMetal ReinforcementMaria Kharissa BalingNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Project ProposalDocument5 pagesSupply Chain Project Proposalchaurasia.nikhil2001No ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument3 pagesArtificial Intelligencechaurasia.nikhil2001No ratings yet
- BGMI FixtureDocument3 pagesBGMI Fixturechaurasia.nikhil2001No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentchaurasia.nikhil2001No ratings yet
- Light Engineering (Nut, Bolt, Washer, Rivets, Etc.) : 2. MarketDocument4 pagesLight Engineering (Nut, Bolt, Washer, Rivets, Etc.) : 2. Marketashwini wadhaveNo ratings yet
- Dremel Attachment Compatibility ChartDocument1 pageDremel Attachment Compatibility Chartcamilo fonsecaNo ratings yet
- Deutz Ba 8M 816Document1 pageDeutz Ba 8M 816MOHD NAJMAN BIN MUDA50% (2)
- Woodturning 4 April (2014)Document108 pagesWoodturning 4 April (2014)Jiri BunataNo ratings yet
- 50 Wood Carving Patterns For Beginners-Compressed July 2021Document99 pages50 Wood Carving Patterns For Beginners-Compressed July 2021whitou100% (3)
- General Tool List (700vym) : 2 (Width 3, 5mm) 2 (#0, #2)Document4 pagesGeneral Tool List (700vym) : 2 (Width 3, 5mm) 2 (#0, #2)JackNo ratings yet
- Ch-23 Jig and FixturesDocument51 pagesCh-23 Jig and FixturesrajaNo ratings yet
- 1Bhk Apartment Interior DesignDocument4 pages1Bhk Apartment Interior DesignChandni Thadani100% (1)
- Non Conventional System of ConstructionDocument4 pagesNon Conventional System of ConstructionPeach CreamNo ratings yet
- Jig Fixture DesignDocument66 pagesJig Fixture DesignSimont3100% (1)
- Lithic Stone Tool Typology PDFDocument6 pagesLithic Stone Tool Typology PDFMohitNo ratings yet
- Assembly Drawing Tail Stock 2Document12 pagesAssembly Drawing Tail Stock 2Syech Maulana Malik100% (1)
- CIR VS Arnoldus Carpentry and CTADocument2 pagesCIR VS Arnoldus Carpentry and CTAPalangkikay WebNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Book Artisan Level 1Document47 pagesPlumbing Book Artisan Level 1Patrick Macharia100% (4)
- 2 Stories BuildingDocument24 pages2 Stories BuildingAndrew ArahaNo ratings yet
- TimberDocument80 pagesTimberYooganNo ratings yet
- Drilling Log: Bore Profile Core Description Standard Penetration Test " N " Value (Blows/Feet) DepthDocument6 pagesDrilling Log: Bore Profile Core Description Standard Penetration Test " N " Value (Blows/Feet) DepthAlex SudrajatNo ratings yet
- List of MachinesDocument1 pageList of MachinesVasske VasovićNo ratings yet
- MACHDocument3 pagesMACHGeoffrey CasanaNo ratings yet
- 2nd MCQ FLEXIBLE MANUFACTURING SYSTEMSDocument11 pages2nd MCQ FLEXIBLE MANUFACTURING SYSTEMSGaurav RajputNo ratings yet
- Material Price ListDocument4 pagesMaterial Price ListPraveen Varma VNo ratings yet
- Tap Drill SizesDocument2 pagesTap Drill SizesManvendra KumarNo ratings yet
- 26 Machine ViceDocument19 pages26 Machine ViceFajri HamdanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Objectives: To Develop An Understanding ofDocument24 pagesLecture Objectives: To Develop An Understanding ofMuhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- HarnamDocument4 pagesHarnamEngr SobiaNo ratings yet
- At SchoolDocument2 pagesAt SchoolNghanNo ratings yet
- Andert Egger Hanggi Leitner City DirectoriesDocument52 pagesAndert Egger Hanggi Leitner City Directoriesapi-327987435No ratings yet
- Assignment No.1 SolutionDocument4 pagesAssignment No.1 SolutionHazem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Casing ScrapperDocument2 pagesCasing ScrapperJOGENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Pipe and Installation Tools: Wall ChaserDocument12 pagesPipe and Installation Tools: Wall ChaserSamy El-BeheryNo ratings yet
- FreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsFrom EverandFreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Autodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersFrom EverandAutodesk Inventor 2020: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate UsersNo ratings yet
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchFrom EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- SketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyFrom EverandSketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Product Manufacturing and Cost Estimating using CAD/CAE: The Computer Aided Engineering Design SeriesFrom EverandProduct Manufacturing and Cost Estimating using CAD/CAE: The Computer Aided Engineering Design SeriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)From EverandAutodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- FreeCAD | Design Projects: Design advanced CAD models step by stepFrom EverandFreeCAD | Design Projects: Design advanced CAD models step by stepRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Contactless Vital Signs MonitoringFrom EverandContactless Vital Signs MonitoringWenjin WangNo ratings yet