Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wound Culture and Gram Stain
Uploaded by
Nicodeme SodeaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wound Culture and Gram Stain
Uploaded by
Nicodeme SodeaCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Dept: Microbiology/Virology
Test Name: WOUND CULTURE AND GRAM STAIN
General Information
Lab Order Codes: WDC
Synonyms: Culture, Wound
CPT Codes: 87070 – Culture, bacterial; any other source except urine, blood or
stool, with isolation and presumptive identification of isolates
87205 – Smear, primary source with interpretation; Gram or Giemsa
stain for bacteria, fungi or cell types
The following testing may be added if appropriate based on findings for
organism identification (multiple additions are possible if more than one
organism is identified) and to aid in patient treatment management.
87076 – Anaerobic isolate, additional methods required for definitive
identification of isolates
87077 – Aerobic isolate, additional methods required for definitive
identification, each isolate (if appropriate)
87106 – Culture, fungi, definitive identification, each organism, yeast (if
appropriate)
87107 – Culture, mold, definitive identification, each organism, mold (if
appropriate)
87147 – Culture, typing; immunologic method, other than
immunofluorescence (e.g., agglutination grouping), per antiserum (if
appropriate)
87184 – Susceptibility studies, disk method, per plate (if appropriate)
87185 – Enzyme detection (eg, beta lactamase), per enzyme (if
appropriate)
87186 – Susceptibility studies, microdilution or agar dilution, each multi-
antimicrobial, per plate (if appropriate)
87206 – Smear, primary source with interpretation, fluorescent and/or
acid fast stain for bacteria, fungi or cell types (if appropriate)
Test Includes: Gram stain and culture for aerobes and less fastidious anaerobes if
appropriate. All aerobic organisms will be identified. Anaerobic
organisms will be characterized or identified depending on the nature of
the culture.
Logistics
Lab Testing Sections: Microbiology
Phone Numbers: MIN Lab: 612-813-5866
STP Lab: 651-220-6555
Test Availability: Daily, 24 hours
Turnaround Time: Preliminary report available at 1 day, final report within 2 - 5 days.
Special Instructions: ● Specimen site and date/time of collection are required for
specimen processing.
● Indicate organisms suspected and diagnosis. If a Mycobacterium
species (AFB, TB) or fungus is suspected, request AFB Culture or
Fungal Culture.
Specimen
Specimen Type: Pus or other material properly obtained from a wound. Aspirated
material is superior to a swab specimen. If a swab must be used, collect
two, one for culture and one for Gram stain.
Container: Swab transport medium or sterile container
Anaerobic transport system (available from Materials Management,
Storeroom item #14536):
a. Store in dark at room temperature.
b. Discard if media turns pink/purple.
c. Discard after expiration date.
Volume: 0.5 mL pus preferred or swab in appropriate medium
Collection: Bite Wounds:
Do not culture fresh bites, as infectious agents may not be recovered.
1. Remove surface exudate by wiping with 70% alcohol.
2. Aspirate pus from the wound, or obtain it at the time of incision,
drainage or debridement of infected wound.
3. Transfer material into sterile container or anaerobic transport system.
Deep Wounds:
1. Disinfect the surface with 70% alcohol and then with 2% tincture of
iodine.
2. Aspirate the deepest portion of the lesion or pass a swab deep into
the lesion, firmly sampling the lesion’s leading edge. Avoid
contamination by the wound surface.
3. If collection is done at surgery, a portion of the abscess wall should
also be sent for culture.
4. Transfer material into a sterile container or anaerobic transport
system.
5. Remove tincture of iodine with 70% alcohol to prevent burn.
Soft Tissue Aspirate:
1. Disinfect the surface with 70% alcohol and then with 2% tincture of
iodine.
2. Aspirate the deepest portion of the lesion or sinus tract or pass a
swab into the lesion, firmly sampling the lesion’s edge. Avoid
contamination by the wound surface.
3. Transfer material into a sterile container or anaerobic transport
system.
Transport/Storage: Onsite collections: Transport to the Microbiology Laboratory
immediately at room temperature. Do not refrigerate. Refrigeration
may inhibit the viability of anaerobic organisms.
Offsite collections: Specimens must be promptly transported to the
laboratory, with the next available courier, not to exceed 24 hours from
the time of collection.
● Transport aerobic swab or aspirate refrigerated.
● Transport anaerobic swab at room temperature.
Sample Rejection: Improperly labeled specimen; specimens with prolonged transit (see
Transport/Storage for requirements); insufficient volume; external
contamination. If an unacceptable specimen is received, the physician
or nursing station will be notified and another specimen will be
requested before the specimen is discarded.
Interpretive
Reference Range: No growth
Alert Value: ● Gram-negative rods identified as ESBL or Carbapenemase producers
will be called to the physician or patient’s nurse. Infection Prevention
will be notified.
● If MRSA is isolated for the first time, and the patient location is not
Emergency department, the result will be called to the physician or
patient’s nurse.
● Any culture positive for potential agents of Bioterrorism – Bacillus
anthracis, Brucella, Burkholderia mallei/pseudomallei, Franciscella
tularensis, or Yersinia pestis will be called to Infectious Disease and/or
Infection Prevention.
● If any acid-fast bacilli is isolated, the result will be called to the
physician or patient’s nurse.
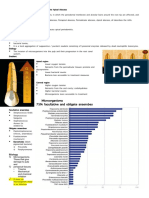
Limitations: Specimens are routinely screened for rapid growing anaerobes (e.g.,
Bacteroides fragilis group, Clostridium perfringens, Fusobacterium, and
anaerobic gram-positive cocci). Fastidious anaerobes may not be
recovered despite significant efforts to collect and properly submit a
specimen. If fastidious anaerobes are suspected, specifically order
Anaerobic Culture.
Any specimen submitted for microbial culture can be contaminated with
colonizing organisms that are not contributing to disease. Organisms
most likely to contaminate specimens of this type include, but are not
limited to, Corynebacterium sp. and coagulase-negative staphylococci.
However, these organisms may be pathogenic in certain settings.
Slow-growing Mycobacterium sp. or Nocardia sp. will not be recovered
in routine bacterial cultures even if present, since extended incubation
periods or special media are necessary for their isolation. Cultures for
these organisms should be specifically requested.
Methodology: Culture
References: Cook, JH, and M Pezzlo (1992). Specimen receipt and accessioning.
Section 1. Aerobic bacteriology, 1.2.1-4. In HD Isenberg (ed) Clinical
Microbiology Procedures Handbook. American Society for Microbiology,
Washington DC
Miller, J Michael (1999) A Guide To Specimen Management in Clinical
Microbiology, American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC
Miller, J Michael, and HT Holmes (1999) Specimen Collection,
Transport, and Storage In PR Murray et al, (ed), Manual of Clinical
Microbiology, 7th edition, American Society for Microbiology,
Washington DC, pp 33-104
Updates: 3/23/2010: CPT Updates
3/7/2011: CPT Updates
6/20/2012: Addition of Alert Value
11/11/2014: Addition of Offsite collection information
You might also like
- Practical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesFrom EverandPractical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesNo ratings yet
- Lab Dept/Section: Microbiology/Virology Test Name: Sputum Culture and Gram StainDocument4 pagesLab Dept/Section: Microbiology/Virology Test Name: Sputum Culture and Gram StainAdn crnNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection and ProcessingDocument18 pagesSpecimen Collection and ProcessingShopee PremiumismeNo ratings yet
- PL-Microbiology Specimen Collection Guidelines (2020.07.22)Document14 pagesPL-Microbiology Specimen Collection Guidelines (2020.07.22)Anonymous fgRHAEIMrHNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 6 Specimen Management TranscriptDocument10 pagesTOPIC 6 Specimen Management TranscriptShayne Mata TeranteNo ratings yet
- Lab Policies Culture Wounds Lab 3115Document7 pagesLab Policies Culture Wounds Lab 3115Marj MendezNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collections in The Medical Microbiology and parasitologyNOTESDocument43 pagesSpecimen Collections in The Medical Microbiology and parasitologyNOTESPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection, Transport and Processing: Julius T. Capili, RMT, MPH, PHDDocument38 pagesSpecimen Collection, Transport and Processing: Julius T. Capili, RMT, MPH, PHDRica Rebadomia100% (2)
- 3.6.9 SOP - Urine CultureDocument3 pages3.6.9 SOP - Urine CultureSemeeeJunior100% (2)
- Specimen Preparation in Clinical LaboratoryDocument6 pagesSpecimen Preparation in Clinical LaboratoryRed Bernaldez NiniNo ratings yet
- Specimen ManagementDocument2 pagesSpecimen ManagementGlenn BanlaygasNo ratings yet
- Instruction For Collection of Microbiology PDFDocument8 pagesInstruction For Collection of Microbiology PDFAbu KaramNo ratings yet
- Lab 9. Sample CollectionDocument23 pagesLab 9. Sample CollectionSuzan AbdNo ratings yet
- Cb1 - Specimen Handling, Transport and ProcessingDocument7 pagesCb1 - Specimen Handling, Transport and ProcessingAngelic AngelesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledRana zaatrehNo ratings yet
- Principles of Diagnostic Medical MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Diagnostic Medical MicrobiologyTarequl Islam NishadNo ratings yet
- Lecture PKDocument69 pagesLecture PKrajyurafNo ratings yet
- Common Microorganisms Cause Wound Infections: Possible Pathogens Gram Positive ExamplesDocument8 pagesCommon Microorganisms Cause Wound Infections: Possible Pathogens Gram Positive Examplesعبدالحكيم النهديNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologySampleCollectionandTransport PDFDocument16 pagesMicrobiologySampleCollectionandTransport PDFWINDA YANINo ratings yet
- Specimens CollectionDocument10 pagesSpecimens CollectionMatthews NjobvuNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory MethodsDocument70 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology and Laboratory MethodsArulmany SelliahNo ratings yet
- Uid 1776Document12 pagesUid 1776IsaacJ22No ratings yet
- Fungal Cultivation and Identification (Side Notes)Document8 pagesFungal Cultivation and Identification (Side Notes)Reca Marie FRIAS100% (1)
- MLS 422 Diagnostic MicrobiologyDocument50 pagesMLS 422 Diagnostic MicrobiologyMayowa OgunmolaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Proper Collection of SpecimensDocument26 pagesMicrobiology Proper Collection of SpecimensAndre NajealNo ratings yet
- Micro NoeDocument63 pagesMicro NoejoseNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection & ProcessingDocument23 pagesSpecimen Collection & ProcessingRobie LeañoNo ratings yet
- Lecture11 MicrobiologyDocument62 pagesLecture11 MicrobiologyVenomNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Specimen Collection, Handling & ProcessingDocument4 pagesNOTES - Specimen Collection, Handling & ProcessingOdette G. TanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Specimen Collection GuidelinesDocument16 pagesMicrobiology Specimen Collection Guidelines1DaddictNo ratings yet
- BSC 204 Notes MidtermsDocument25 pagesBSC 204 Notes MidtermsWil LynNo ratings yet
- Gram StainDocument3 pagesGram StainJennipher pamaNo ratings yet
- Koh PrepDocument4 pagesKoh PrepIndhumathiNo ratings yet
- Hai & Infection Control PracticesDocument134 pagesHai & Infection Control PracticesAnna 964250No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Introduction To VirologyDocument20 pagesLesson 6 Introduction To VirologyNOR-FATIMAH BARATNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection Guidelines 2015PDFDocument22 pagesSpecimen Collection Guidelines 2015PDFandiramasNo ratings yet
- 3.6.5 SOP - Sputum CultureDocument3 pages3.6.5 SOP - Sputum CultureSemeeeJunior50% (2)
- Specimen Collection in Infectious DiseasesDocument72 pagesSpecimen Collection in Infectious DiseasesFadi KhaizaranNo ratings yet
- Appropriate Clinical Specimens Collection and Transport For Diagnostic VirologyDocument48 pagesAppropriate Clinical Specimens Collection and Transport For Diagnostic Virologylong thomNo ratings yet
- Ova and Parasite Examination StoolDocument5 pagesOva and Parasite Examination StoolNazaqat FarooqNo ratings yet
- Haemorrhagic SepticemiaDocument14 pagesHaemorrhagic Septicemiadrdsingh11100% (1)
- Microbiology & Parasitology: Khrizlynne SoberanoDocument5 pagesMicrobiology & Parasitology: Khrizlynne SoberanoNicoleVillamorNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions Microbio Phase II UpdatedDocument10 pagesInterview Questions Microbio Phase II UpdatedSonny Francisco Jr.No ratings yet
- ENG PAHO MPX Laboratory Guidelines May2022Document12 pagesENG PAHO MPX Laboratory Guidelines May2022Julia QuadrosNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Culture CollectionDocument3 pagesAnaerobic Culture CollectionADINo ratings yet
- Sputum CollectionDocument4 pagesSputum CollectionBELIGANIO JOHANNANo ratings yet
- Unit II. 2 Bio 43, General Microbiology Lecture ClassDocument20 pagesUnit II. 2 Bio 43, General Microbiology Lecture ClassBubbles GQPNo ratings yet
- Ear Cultures Principle: 3.6.12 Sop: Ear Culture Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEar Cultures Principle: 3.6.12 Sop: Ear Culture Page 1 of 2SemeeeJuniorNo ratings yet
- lab diagnosis of infect diseases يكالوريوسDocument22 pageslab diagnosis of infect diseases يكالوريوسkasilat574No ratings yet
- Mycology SOP 2nd Ed 2019Document144 pagesMycology SOP 2nd Ed 2019Deepak Muralidhara NadigNo ratings yet
- Pus and WoundDocument16 pagesPus and WoundArmilyn Garcia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Appropriate Specimens For Anaerobic Cultures: (Phil J Microbiol Infect Dis 1998 27 (2) :71-73)Document4 pagesAppropriate Specimens For Anaerobic Cultures: (Phil J Microbiol Infect Dis 1998 27 (2) :71-73)u_niz_058038No ratings yet
- Prevalence of ESKAPE Pathogens in Hospitalized Patients of Tertiary Level Hospitals - ADocument25 pagesPrevalence of ESKAPE Pathogens in Hospitalized Patients of Tertiary Level Hospitals - AKailash MoryaNo ratings yet
- Specimen Collection GuidelinesDocument5 pagesSpecimen Collection GuidelineskmrfromNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENTDocument58 pagesEXPERIMENTYriel GuilaranNo ratings yet
- Role of Specimen CollectionDocument72 pagesRole of Specimen Collectiontummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (4)
- ROUTINE DIAGNOSTICS VCLINICS101 - Cabandi, Raso, Resano, TobosoDocument19 pagesROUTINE DIAGNOSTICS VCLINICS101 - Cabandi, Raso, Resano, TobosoDominique Joy Gayares RasoNo ratings yet
- Topic II - Collection, Handling and Processing of SpecimensDocument15 pagesTopic II - Collection, Handling and Processing of SpecimensGrace CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Sample Collection&TransportationDocument6 pagesSample Collection&TransportationGuna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Eye Culture 1. Principle: 3.6.11 SOP: Eye Cultures Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesEye Culture 1. Principle: 3.6.11 SOP: Eye Cultures Page 1 of 2SemeeeJuniorNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea New Edited 2Document82 pagesDiarrhea New Edited 2bharathNo ratings yet
- STAT 2300 Test 1 Review - S19Document19 pagesSTAT 2300 Test 1 Review - S19teenwolf4006No ratings yet
- Oxymixer High Flow Without Monitor - BrochureDocument6 pagesOxymixer High Flow Without Monitor - BrochureochaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument13 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDamarys PatriciaNo ratings yet
- Construction Site Housekeeping ChecklistDocument3 pagesConstruction Site Housekeeping ChecklistMuhammad Zarul Aziri Bin MaamurNo ratings yet
- Kepelbagaian Budaya (Individual Assignment)Document6 pagesKepelbagaian Budaya (Individual Assignment)Yusran RosdiNo ratings yet
- Your Attitude Can Make or Break Your CareerDocument29 pagesYour Attitude Can Make or Break Your CareerAarshabh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Jas08 4Document3 pagesJas08 4krishna saiNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Specialty Is Constantly ChangingDocument3 pagesThe Radiology Specialty Is Constantly ChangingLiora SochenNo ratings yet
- TemplateDocument15 pagesTemplateJogie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Mind and Emotions: A Universal Treatment For Emotional DisordersDocument9 pagesMind and Emotions: A Universal Treatment For Emotional DisordersNew Harbinger Publications100% (7)
- Skil Lab EBMDocument6 pagesSkil Lab EBMYahya Darmais FaridNo ratings yet
- NRP - Lesson 1 Foundation NRPDocument21 pagesNRP - Lesson 1 Foundation NRPShariti DeviNo ratings yet
- Emotional Body Pain Chart: How It WorksDocument3 pagesEmotional Body Pain Chart: How It Worksdaniel50% (2)
- Household Services 7 Q4 - Week 3 4Document11 pagesHousehold Services 7 Q4 - Week 3 4Christian LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Colisage ProduitsDocument6 pagesColisage ProduitsBerriche MohamedNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument70 pagesResearchMagud, Jemverick Jan Leonard O.No ratings yet
- Minimal Invasive Dentistry-A Comprehensive ReviewDocument9 pagesMinimal Invasive Dentistry-A Comprehensive ReviewKarissa NavitaNo ratings yet
- Histology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Apical AbscessDocument4 pagesHistology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Apical AbscessPrince AmiryNo ratings yet
- Youth Camp Registration Form-2022Document1 pageYouth Camp Registration Form-2022FlerkNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Trends in The Design of Hospital Ward PDFDocument16 pagesContemporary Trends in The Design of Hospital Ward PDFPreethi NandagopalNo ratings yet
- 5) Sequence of Donning and Doffing of PPE For COVID-19 MOH. Update Version (2) 17.11.2020Document27 pages5) Sequence of Donning and Doffing of PPE For COVID-19 MOH. Update Version (2) 17.11.2020Amalina RazinNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement About Your MotherDocument5 pagesThesis Statement About Your MotherSarah Brown100% (2)
- Strauman BLX Product Catalog - 450.012-A-En - LowDocument22 pagesStrauman BLX Product Catalog - 450.012-A-En - LowDiyaa SakrNo ratings yet
- Documenting and ReportingDocument3 pagesDocumenting and ReportingGLADYS GARCIANo ratings yet
- 10 Reasons Why Good Sleep Is ImportantDocument10 pages10 Reasons Why Good Sleep Is ImportantHoang Minh HangNo ratings yet
- A Review On Dental Implant ImpressionsDocument4 pagesA Review On Dental Implant ImpressionsAnonymous AyxIccS4aXNo ratings yet
- General Survey - Nursing AssessmentDocument2 pagesGeneral Survey - Nursing AssessmentDanielle TorresNo ratings yet
- Neumann 1990Document13 pagesNeumann 1990Hai My NguyenNo ratings yet
- Urinary CatheterizattionDocument85 pagesUrinary Catheterizattionbajaoc100% (6)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)