Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Chapter Feasibility Analysis
Uploaded by
xowof70509Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Chapter Feasibility Analysis
Uploaded by
xowof70509Copyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|22853254
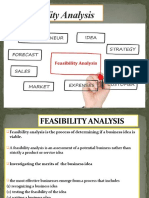
Chapter 3: Feasibility analysis
Feasibility analysis
Is the process of determining if a business idea is viable
Figure 3.1 page 99: Testing Proposed business venture in: (if yes in all areas then
proceed with idea)
o Product/service feasibility,
o Industry/Target market feasibility,
o Organisational feasibility,
o Financial feasibility
It is an investigative process and should critique the merits of a proposed business.
Failure to investigate can leads to:
o blinding an entrepreneur from risks associated with the business.
o “everything about my opportunity is wonderful”
Primary research: collected by the person conducting the analysis (taking to
prospective costumers, feedback from industry experts)
Secondary research: probes data that is already collected (industry studies, info from
internet or library)
Product/Service Feasibility Analysis
Assessment of the overall appeal of the product or service
1. Product/Service Desirability:
o Questions to ask: Is it reasonable?
o Does it serve a need in the marketplace?
o Is it something real customers would buy?
o Is it solving a problem or gains support from any environmental trend?
o Is it a good time to introduce it to the market?
o Fatal flaws in the first design?
Don’t take final conclusions from these questions rather ask potential costumers (Tool:
“Get out of the building”)
Concept test:
o Preliminary description of a product or service idea (=concept statement,1 A4)
Contains: description of product or service
The intended target market (list of customers)
The benefits of the product or service (how it ads value or solves a
problem)
How product will be positioned in relation to competitors
About management team
o Show the concept statement to industry experts and to potential customer to
solicit their feedback
o Example of concept statement from “New venture fitness drinks” (picture)
o Common reason for failure: Not large enough market for product
Online tools for completing feasibility analysis
o 3D printing services
o A/B Split testing
o Feedback on business ideas (examples: Quirky, Founder suite)
Downloaded by Imtiaz Sultan (helloawan103@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|22853254
o Landing pages (launch rock)
o Surveys
o Market research
o Q&A sites
2. Product/Service demand:
o Method 1: Talking face to face method with potential customers
Potential customers and relevant players
Find people by contacting trade associations and attend industry trade
shows
o Method 2: Utilizing online tools, such as google AdWords and landing pages to
assess demand.
Buy keywords on google search to place your ad (Ad is linked to your
landing page)
On your landing page you provide a field to enter your email if
interested in product. The scale of demand depends on how many
people are interested and enter their email.
o Method 3: Library, Internet and Gumshoe research
Researching secondary data from prospective customers and industry-
related data
IBIS Worlds provides industry reports
Example: selling Toys: beneficial to browse through toy stores,
volunteer at a care center, talk to the care center owner
Industry/Target Market Feasibility Analysis
Assessment of the appeal of the target market and the industry
A firm’s industry: group of firms producing similar products or services
A firm’s target market is just the part of the industry which it wants to appeal to
Most companies select a certain target market out of an industry
1. Component: Industry Attractiveness: (Characteristics)
o Characteristics: Young rather than old
o Early life cycle
o Are fragmented rather than concentrated
o Growing
o Selling “must have” rather than “want to have”
o Not Crowded
o High rather than low operating margins
o Independent from low prices of for example raw material
o Environmental, social, economic trends favor the industry
Get an understand if an industry is a good or a poor one for start-ups: IBIS World,
Mintel, Bizminer
2. Component: Target Market Attractiveness
o Start ups usually choose to sell to a narrower group of customers within a
market segment (=Target Market)
o Start-ups usually introduce either a new product into a new market or a new
market for an existing product, but not both. (too expensive)
Downloaded by Imtiaz Sultan (helloawan103@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|22853254
o Finding a good market: a market large enough for the new venture but small
enough not to attract larger competitors, study other markets related to your
market (are they growing or shrinking)
Organizational Feasibility Analysis
Does the proposed business have enough management experience,
organisational competence and resources to successfully launch? Main issues:
Management Prowess:
o The ability of it’s initial management team
o The main factors of the self-assessment of the management team or
solo entrepreneur are their passion and the extent to which they
understand the market in which the firm will participate
o Extensive professional and social networks are beneficial
o Crucial to know what type of new-venture team they can assemble
o A new-venture team: a group of founders, key employees and advisers
that can support a venture in it’s start-up years.
o Highly capable individuals, that would be part of the new-venture
team, identified by the founders, give credibility to the organizational
feasibility.
o Frequently it comes out after of assessing the organisational feasibility
that partners are beneficial.
Resource sufficiency:
o Assessment if the company can obtain enough resources (in this case
nonfinancial resources)
o Identify the most important nonfinancial resources and see if they are
available (for example: are there enough fitting employees available in
the community that the company wants to launch)
o To test resource sufficiency: List 6 to 12 most critical nonfinancial
resources
o Types of nonfinancial resources:
Affordable office space
Lab space, manufacturing space, or space to launch new
businesses
Contract manufacturers or service providers
Key management employees
Key support personnel
Key equipment
Ability to obtain intellectual property protection on key
aspects of the business
Support of local governments and state governments
Ability to form favorable business partnerships
Financial Feasibility Analysis
A preliminary financial assessment is usually sufficient
Most important issues at the beginning of a business:
o Start-up cash
o Financial performance of similar businesses
o Overall financial attractiveness of the proposed venture
Downloaded by Imtiaz Sultan (helloawan103@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|22853254
Total Start-Up Cash Needed
Total cash needed to prepare a business to make it’s first sale
Reasonable plan how to cover the start-up costs and how to repay the borrowed
money should be made
Over estimate costs because things will go wrong
Financial Performance of Similar Businesses
This assessment is done by comparing the proposed Start-Up to other similar
businesses. Ways of doing that:
Financial reports of thousands of companies is available online. Find a small
comparable firm. Useful pages: IBISWorld, BizStats, BizMiner
Ask the business owner of a similar company to share sales and income data
Observation and legwork to obtain data from similar businesses
Overall Financial Attractiveness of the Proposed Venture
These evaluations are based primarily on a new venture’s projected sales and rate of
return
More precise estimation of cash flow, income statements and balance sheets (=pro
forma financial statements) usually applicable in the business planning stage.
To Assess the start-Up’s projected rate of return should be weighted against the
following factors:
o The amount of capital invested
o The risks assumed in launching the business
o The existing alternatives for the money being invested
o The existing alternatives for the entrepreneur’s time and efforts
A Feasibility Analysis Template
The feasibility stage should be seen as something fluid and while doing the first screen
of the feasibility with the template, suggestions might come up to make the business
more feasible.
Downloaded by Imtiaz Sultan (helloawan103@gmail.com)
You might also like
- The Innovator's Solution (Review and Analysis of Christensen and Raynor's Book)From EverandThe Innovator's Solution (Review and Analysis of Christensen and Raynor's Book)No ratings yet
- Venture Catalyst (Review and Analysis of Laurie's Book)From EverandVenture Catalyst (Review and Analysis of Laurie's Book)No ratings yet
- Consulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesFrom EverandConsulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Feasibility AnalysisDocument24 pagesChapter 3 - Feasibility AnalysisUmar MasoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 COMM 320Document5 pagesChapter 3 COMM 320kosta georgalosNo ratings yet
- Summary and Analysis of The Innovator's Dilemma: When New Technologies Cause Great Firms to Fail: Based on the Book by Clayton ChristensenFrom EverandSummary and Analysis of The Innovator's Dilemma: When New Technologies Cause Great Firms to Fail: Based on the Book by Clayton ChristensenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Only the Paranoid Survive (Review and Analysis of Grove's Book)From EverandOnly the Paranoid Survive (Review and Analysis of Grove's Book)No ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Creation of New VenturesDocument53 pagesChapter 02 Creation of New Venturesኢትኤል ኢትዮጵNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship TheoryDocument39 pagesEntrepreneurship TheoryŁeejLa INo ratings yet
- "Elevate Your Entrepreneurial Journey Unleashing the Power of Startup Success": BusinessFrom Everand"Elevate Your Entrepreneurial Journey Unleashing the Power of Startup Success": BusinessNo ratings yet
- The Silicon Valley Way (Review and Analysis of Sherwin Jr.'s Book)From EverandThe Silicon Valley Way (Review and Analysis of Sherwin Jr.'s Book)No ratings yet
- Feseability AnalysisDocument41 pagesFeseability Analysistester accountNo ratings yet
- 02 Idea Assessment Feasibility Analysis Business ModelDocument4 pages02 Idea Assessment Feasibility Analysis Business ModelImaan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Feasibility AnalysisDocument48 pagesLecture 3 - Feasibility Analysissamiah ahmedNo ratings yet
- Week 8 (Learning Materials)Document9 pagesWeek 8 (Learning Materials)CHOI HunterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. E Ship - PPTX 11Document32 pagesChapter 2. E Ship - PPTX 11abebeyonas88No ratings yet
- Roadmap to Entrepreneurial Success (Review and Analysis of Price's Book)From EverandRoadmap to Entrepreneurial Success (Review and Analysis of Price's Book)No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document18 pagesChapter 2Yosef KetemaNo ratings yet
- BUS 311 Recognising and Exploiting Business OpportunitiesDocument5 pagesBUS 311 Recognising and Exploiting Business OpportunitiesAdeleye AdetunjiNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Feasibility of A New Venture 1.1 Assessment and Evaluation of Entrepreneurial OpportunitiesDocument13 pagesAssessing The Feasibility of A New Venture 1.1 Assessment and Evaluation of Entrepreneurial OpportunitiesBereket Desalegn100% (1)
- Feasibility AnalysisDocument5 pagesFeasibility AnalysisAida GanituenNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Analysis (2023)Document45 pagesFeasibility Analysis (2023)Noman ZafarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Conducting A Feasibility Analysis and Designing A BusinessDocument29 pagesLecture 3 Conducting A Feasibility Analysis and Designing A BusinessDaniyal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)From EverandDealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Industrial Management ExamDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Industrial Management ExamKawsar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Jagran Lakecity University: Jagran School of Commerce & EconomicsDocument11 pagesJagran Lakecity University: Jagran School of Commerce & EconomicsvibhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document35 pagesChapter 3ademe tamiruNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - AnswerDocument6 pagesUNIT 3 - AnswerJessica PillaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To EntrepreneurshipDocument16 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To EntrepreneurshipMichael Di MonacoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Ch.2Document27 pagesEntrepreneurship Ch.2Joseph KinfeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 LessonDocument32 pagesWeek 3 LessonJheonology FernandoNo ratings yet
- PME Unit-2 NOTESDocument7 pagesPME Unit-2 NOTESPRATHAM PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Assignment BriefDocument6 pagesUnit 9 Assignment BriefSuwaiba IftikharNo ratings yet
- Overview of EntrepreneurshipDocument34 pagesOverview of EntrepreneurshipMary June Jabian SumonodNo ratings yet
- 06 Handout 1Document5 pages06 Handout 1Ashley LaosantosNo ratings yet
- A Study On Problem Faced by Startup Companies in BangaloreDocument6 pagesA Study On Problem Faced by Startup Companies in BangaloreAnand AanuNo ratings yet
- Environmental Analysis: Business Opportunity IdentificationDocument27 pagesEnvironmental Analysis: Business Opportunity IdentificationShane Barles100% (1)
- Chapter 3Document23 pagesChapter 3Cedie Garbo MonteroNo ratings yet
- C Tme CGR 6 Eq KVB Vsre Puy Wdoqg 5 M8 AODocument29 pagesC Tme CGR 6 Eq KVB Vsre Puy Wdoqg 5 M8 AOVanessa ElliviaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Ch.2Document27 pagesEntrepreneurship Ch.2Amanuel AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Checklist: Plan your way to business successFrom EverandBusiness Plan Checklist: Plan your way to business successRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Audit your Intellectual Property (IP)From EverandHow to Audit your Intellectual Property (IP)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Applied Eco - Industry and Environmental Analysis Business Opportunity IdentificationDocument5 pagesApplied Eco - Industry and Environmental Analysis Business Opportunity IdentificationGarnet RigorNo ratings yet
- Startup Business Success Blueprint: Navigating Your First Year As An EntrepreneurFrom EverandStartup Business Success Blueprint: Navigating Your First Year As An EntrepreneurNo ratings yet
- How to Grow When Markets Don't (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Wise's Book)From EverandHow to Grow When Markets Don't (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Wise's Book)No ratings yet
- Reading Business PlanningDocument26 pagesReading Business PlanningBence CzuforNo ratings yet
- Entrep Tos CoverageDocument4 pagesEntrep Tos CoverageSandro OpenioNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Corporate Entrepreneurship-Is The Conceptualization of Entrepreneurship at TheDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurship: Corporate Entrepreneurship-Is The Conceptualization of Entrepreneurship at TheMahmudul Hasan100% (1)
- 4a CREATING AND STARTING THE VENTUREDocument22 pages4a CREATING AND STARTING THE VENTUREIsha SinghNo ratings yet
- Summary: A Good Hard Kick in the Ass: Review and Analysis of Adams' BookFrom EverandSummary: A Good Hard Kick in the Ass: Review and Analysis of Adams' BookNo ratings yet
- Leading the Revolution (Review and Analysis of Hamel's Book)From EverandLeading the Revolution (Review and Analysis of Hamel's Book)No ratings yet
- 2nd QuarterDocument40 pages2nd QuarterSayme WPNo ratings yet
- Revisions EntrepreneurshipDocument4 pagesRevisions EntrepreneurshipVincent Mjk ChapelainNo ratings yet
- Summary: Disciplined Entrepreneurship: Review and Analysis of Aulet's BookFrom EverandSummary: Disciplined Entrepreneurship: Review and Analysis of Aulet's BookNo ratings yet
- R&D Productivity: How to Target It. How to Measure It. Why It Matters.From EverandR&D Productivity: How to Target It. How to Measure It. Why It Matters.No ratings yet
- Operation ManagementDocument4 pagesOperation Managementxowof70509No ratings yet
- Chap007 FDIDocument32 pagesChap007 FDIxowof70509No ratings yet
- Chap 03Document38 pagesChap 03xowof70509No ratings yet
- International Business: by Charles W.L. HillDocument34 pagesInternational Business: by Charles W.L. HillAnonymous rWn3ZVARLgNo ratings yet
- Chap 004Document30 pagesChap 004italo_ramirez_5No ratings yet
- Chap 006Document25 pagesChap 006ht1205No ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesEntrepreneurshipxowof70509No ratings yet
- Paper Naiz ShakirDocument6 pagesPaper Naiz Shakirxowof70509No ratings yet
- RPPT FinalDocument8 pagesRPPT FinalArpann DekaNo ratings yet
- Cs-Supertrends 22 Eng RGBDocument47 pagesCs-Supertrends 22 Eng RGBWildan AriefNo ratings yet
- Job AppliedDocument12 pagesJob Appliedsandeep mauryaNo ratings yet
- Understanding The 4P'sDocument2 pagesUnderstanding The 4P'sLeeLing BettyNo ratings yet
- Wallstreetjournal 20161231 The Wall Street JournalDocument44 pagesWallstreetjournal 20161231 The Wall Street JournalstefanoNo ratings yet
- Mapi Lending Investors Inc.: Member Loan Ledger UnitDocument2 pagesMapi Lending Investors Inc.: Member Loan Ledger UnitMhine MhineNo ratings yet
- Pyq Fin250Document3 pagesPyq Fin250shfirdaus044No ratings yet
- Proforma Ata#119 7 02 2022Document32 pagesProforma Ata#119 7 02 2022Jamir FloresNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development Notes 2022FDocument44 pagesEntrepreneurship Development Notes 2022FAlvin MoraraNo ratings yet
- Cleaner Engineering and TechnologyDocument15 pagesCleaner Engineering and TechnologyAsyraf YazidNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Business CombinationDocument22 pagesUNIT I Business CombinationDaisy TañoteNo ratings yet
- một số câu hỏi bài tập tiếng anhDocument21 pagesmột số câu hỏi bài tập tiếng anhNam chính Chị củaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of CostsDocument14 pagesConcepts of CostsMughees Ahmed100% (1)
- Emirates Plane Ticket Template 17Document3 pagesEmirates Plane Ticket Template 17Shafik PatelNo ratings yet
- March 2021 Payslip CPSDocument41 pagesMarch 2021 Payslip CPSWjz WjzNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics - CH9 - Analysis of Competitive MarketsDocument53 pagesMicroeconomics - CH9 - Analysis of Competitive MarketsRuben NijsNo ratings yet
- BCHDE5311 - Regular MORNINGDocument10 pagesBCHDE5311 - Regular MORNINGDhruv ShahNo ratings yet
- BGG Hansa Rule enDocument12 pagesBGG Hansa Rule enRafael Iglesias de la RochaNo ratings yet
- Solution Chapter 6 Financial Statements Pre Adjustments 1Document8 pagesSolution Chapter 6 Financial Statements Pre Adjustments 1IsmahNo ratings yet
- Bos 050121 Interp 4Document214 pagesBos 050121 Interp 4samartha umbare100% (1)
- Snapshot Checklist - Vendor - SPA Without TitleDocument7 pagesSnapshot Checklist - Vendor - SPA Without TitleAdhariahNo ratings yet
- ानम् "That which is not different from knowledge which arises spontaneously."Document1 pageानम् "That which is not different from knowledge which arises spontaneously."Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- C 4 C 00 D 37Document12 pagesC 4 C 00 D 37alyaa rabbaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plan REM311 Oct 22 - MFMDocument4 pagesLecture Plan REM311 Oct 22 - MFMSITI MARIAM MAILNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Human ResourcesDocument2 pagesProblem Sets Human ResourcesHiếu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Hire Purchase Law RevisedDocument46 pagesHire Purchase Law RevisedBilliee ButccherNo ratings yet
- Taxguru - In-Guide To Set Off Carry Forward of Losses Under Each Head of IncomeDocument4 pagesTaxguru - In-Guide To Set Off Carry Forward of Losses Under Each Head of Incomeanudeepb1604No ratings yet
- Ch06 Cash and ReceivablesDocument62 pagesCh06 Cash and ReceivablesCerekiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 BelardoDocument8 pagesChapter 7 BelardoAndrea BelardoNo ratings yet
- Blaw Prelims ReviewerDocument17 pagesBlaw Prelims ReviewerVanessa dela Torre0% (1)