Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module Meat
Uploaded by
pio.barrettoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module Meat
Uploaded by
pio.barrettoCopyright:
Available Formats
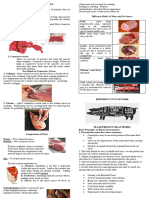
Meat - This a term for the flesh of cattle (beef and veal), sheep (lamb) and pigs (pork).
Meat comprises
water, protein, fat, and various amounts of minerals and vitamins.
Beef - This divided into large sections called primal cuts. These beef primal cuts or primal are then
broken down further into individual steak and other retail cuts.
A side of beef is literally one side of the beef carcass that is split through the backbone. Each side is then
halved between the 12th and 13th ribs into sections called the forequarter and hindquarter.
Pork is divided into large sections called primal cuts. These primal cuts are then broken down further
into individual retail cuts.
Sheep meat - This is also a staple food in some parts of the world and is consumed in many regions.
Sheep meat is otherwise known as mutton (meat of mature sheep) or lamb (immature sheep) also
classified as red meat.
Composition of Meat
1.WATER-75% of muscle tissue.
2. PROTEIN-20% of muscle tissue
Protein coagulates when it is heated. It becomes firmer and loses moisture. When protein has coagulated
to the desired degree, the meat is said to be done.
3. Fat – 5% of the muscle tissue.
The fat in meat contributes to:
a. Juiciness-Marbling is fat that is deposited within the muscle tissue. Surface fats protect the meat
from drying out during cooking.
Adding surface fat is called barding.
b. Tenderness-Marbling separates muscle fibers, making meat easier to chew.
c. Flavor- Fat is the main source of flavor in meat.
4. Carbohydrates- 5% of meat composition
It plays a necessary part in the complex reaction called Maillard reaction, which takes place when meats
are browned by roasting, broiling or sautéing. Without carbohydrates, desirable flavor-appearance of
browned meats would not be achieved.
Structure of Meat
1. Muscle Fiber - Lean meat is composed of long, thin muscle fibers bound together in bundles. -
These determine the texture or grain of a piece of meat.
Fine – grained meat is composed of small fibers.
Course – textured meat has large fibers.
2. Connective Tissue These are network of proteins that bind the muscle fibers together.
Connective tissue is tough.
Meats are high in connective tissue if the muscles are more exercised like meat from legs and the
meat comes from older animals.
Two Kinds of Connective Tissue
a. Collagen – (Fr. Greek kolla: “glue”) White connective tissue that dissolves or breaks down by
long, slow cooking with liquid.
Moist-heat cooking methods at low temperature are not effective for turning a meat high in
connective tissue into a tender, juicy finished product.
b. Elastin – AKA Silver skin (late 19th century: from elastic) Yellow connective tissue and is not
broken down in cooking.
Tenderizing can be accomplished only by removing the elastin, by pounding, and by slicing and
grinding.
Written Activity
Answer on ¼ sheet of paper please pass it on Tuesday, April 16, 2024.
Identify the following terms. Answer only.
_____1. This a term for the flesh of cattle (beef and veal), sheep (lamb) and pigs (pork).
_____2. A cut is divided into large sections.
_____3.
_____4. White connective tissue that dissolves or breaks down by long, slow cooking with liquid.
_____5.This is yellow connective tissue and is not broken down in cooking.
_____6.These are networks of proteins that bind the muscle fibers together.
_____7. This is composed of long, thin muscle fibers bound together in bundles.
_____8. Textured meat has large fibers.
You might also like
- Prepare and Cook MeatDocument62 pagesPrepare and Cook MeatSthepanie Badillo75% (8)
- Wake Up Lean: 10-Day Flat Belly BlueprintDocument65 pagesWake Up Lean: 10-Day Flat Belly BlueprintElber Andrew96% (23)
- TLE LAS Cookery 10 Quarter 4 Week 1Document8 pagesTLE LAS Cookery 10 Quarter 4 Week 1Edgar RazonaNo ratings yet
- Tle - 9 - Prepare and Cook MeatDocument7 pagesTle - 9 - Prepare and Cook MeatJeff Ubana PedrezuelaNo ratings yet
- Delish - Keto Made EasyDocument98 pagesDelish - Keto Made EasyStefan H100% (5)
- Bo de Kiem Tra Lop 4 - Bui Van VinhDocument13 pagesBo de Kiem Tra Lop 4 - Bui Van VinhPhương Thu Vũ ThịNo ratings yet
- Meat BasicsDocument97 pagesMeat BasicsPrincess Joy MoralesNo ratings yet
- Material Submittal Arch (Pro-Kitchen)Document193 pagesMaterial Submittal Arch (Pro-Kitchen)NADEEM100% (1)
- Meatcuts 1Document23 pagesMeatcuts 1annaliza barondaNo ratings yet
- Tle 1o q4 ModuleDocument22 pagesTle 1o q4 ModuleRhea AnselmoNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10: Quarter 4 Las Number 1Document8 pagesCookery 10: Quarter 4 Las Number 1Edison Manuel100% (9)
- Learning Activity Sheet (Las) : Cookery 10Document8 pagesLearning Activity Sheet (Las) : Cookery 10criselda desistoNo ratings yet
- Q4 HE Cookery 10 Week1Document4 pagesQ4 HE Cookery 10 Week1Chiesa Arellano100% (2)
- Prepare and Cook MeatDocument65 pagesPrepare and Cook MeatARLENE MORADA100% (1)
- Week 1&2 CookeryDocument33 pagesWeek 1&2 CookeryJonabel DacilloNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Meat - Lesson 1Document25 pagesIntroduction of Meat - Lesson 1Ella Cagadas PuzonNo ratings yet
- Cookery10-Week1-7 (4th)Document27 pagesCookery10-Week1-7 (4th)mary grace manalang100% (2)
- Tle 10 Reporting ?Document20 pagesTle 10 Reporting ?BiZayangAmaZona100% (1)
- Module Quarter 4 CompiledDocument16 pagesModule Quarter 4 CompiledJoevic SuyodNo ratings yet
- Cookery - 10 Quarter 4 Week 1Document13 pagesCookery - 10 Quarter 4 Week 1CYRILNo ratings yet
- Meat and PoultryDocument26 pagesMeat and PoultryCyd BenitoNo ratings yet
- Cookery10 Q4 Week1 v4Document10 pagesCookery10 Q4 Week1 v4Maria Rose Tariga Aquino100% (4)
- Reviewer Meat Lesson 1Document4 pagesReviewer Meat Lesson 1Rose Lynn100% (1)
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 4 LAS Number 1 Weeks 1Document8 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 4 LAS Number 1 Weeks 1Leila Madelene LoyolaNo ratings yet
- LO1PPTGR10Document53 pagesLO1PPTGR10Ashly AragonNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Cookery Hand Outs 2 A.Y 2023 2024Document40 pagesGrade 10 Cookery Hand Outs 2 A.Y 2023 2024Ryan Joseph BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- Las 1 q4 Perform Mise en PlaceDocument6 pagesLas 1 q4 Perform Mise en PlaceDump McDumpNo ratings yet
- TleDocument5 pagesTleBianca MontalboNo ratings yet
- Beef Poultry and EggsDocument17 pagesBeef Poultry and EggsAira RamonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Prepare and Cook Meat Meat: Than BeefDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Prepare and Cook Meat Meat: Than BeefFranz Russell TalosigNo ratings yet
- 4th Grading LESSON 2 Kinds and Composition of MeatDocument17 pages4th Grading LESSON 2 Kinds and Composition of MeatRenzoNo ratings yet
- Q4 Module1 G10 CookeryDocument9 pagesQ4 Module1 G10 CookeryfishguadagraceNo ratings yet
- Las Cookery 4TH Quarter - 083850Document19 pagesLas Cookery 4TH Quarter - 083850umlijamieeeNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document12 pagesWeek 1KISHANo ratings yet
- Composition and Structure of MeatDocument2 pagesComposition and Structure of MeatLerma CanuelNo ratings yet
- BHCM-2 - Unit-4 (Meat) .: Lamb/MuttonDocument26 pagesBHCM-2 - Unit-4 (Meat) .: Lamb/MuttonSangeeta GotameNo ratings yet
- Red Meat and Variety CutsDocument6 pagesRed Meat and Variety CutsTayapad, Irene C.No ratings yet
- Chapter No.1 Meat CookeryDocument15 pagesChapter No.1 Meat CookeryKrishna Chaudhary0% (1)
- Module 6 Prepare Meat DishesDocument10 pagesModule 6 Prepare Meat DishesGilbert LoredoNo ratings yet
- 4 A 1 A 4 A 46 Ade 4Document62 pages4 A 1 A 4 A 46 Ade 4Ken ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Composition of MeatDocument9 pagesComposition of MeatStephanie MirandaNo ratings yet
- 10 Cookerylas 1Document3 pages10 Cookerylas 1Althea RejaeNo ratings yet
- FSTC 105 B All Aboit MeatDocument27 pagesFSTC 105 B All Aboit MeatElijah Heart BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Cookery10 Week1-2 Q4Document5 pagesCookery10 Week1-2 Q4StephanieNo ratings yet
- 1st Demo CookeryDocument68 pages1st Demo CookeryStephanie Shane ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Culinary Mudule 10Document41 pagesCulinary Mudule 10Karen FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Cookero MeatDocument1 pageCookero MeatMiaNo ratings yet
- PHT 2Document49 pagesPHT 2Juliet Cayao SajolNo ratings yet
- The Flesh CompositionDocument18 pagesThe Flesh CompositionMuhammad Irwan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Feng 3008-Food Technology I-Week 2Document71 pagesFeng 3008-Food Technology I-Week 2Zülal Sıla BaştürkNo ratings yet
- BSC HS Sem V Adv Food Prod Sys HS 301 Chapter 1Document13 pagesBSC HS Sem V Adv Food Prod Sys HS 301 Chapter 1Krystil Mae D BoncolmoNo ratings yet
- TLE10-This Is MeatDocument18 pagesTLE10-This Is MeatJoy April Aguilar DeGuzmanNo ratings yet
- Meat and PoultryDocument8 pagesMeat and PoultryAman KeltaNo ratings yet
- Poultry AND Game: Prepared By: Cherry G - GamboaDocument44 pagesPoultry AND Game: Prepared By: Cherry G - GamboaAmore AcademyNo ratings yet
- 4-Red Meat PDFDocument13 pages4-Red Meat PDFمحمد بركاتNo ratings yet
- WU - 2020 - F&BP - II Course MaterialDocument51 pagesWU - 2020 - F&BP - II Course Materialtebebe solomonNo ratings yet
- Weeks 31 and 32Document59 pagesWeeks 31 and 32G3 ODL Kim Angela BernardoNo ratings yet
- Meat CookeryDocument30 pagesMeat CookeryPadmanaaban PrabhuNo ratings yet
- TLE Group 2Document23 pagesTLE Group 2Janet C. RamosNo ratings yet
- Meat Tle Group2Document12 pagesMeat Tle Group2Klyd Troy PeralesNo ratings yet
- Cook 10 1Document8 pagesCook 10 1Jhoana Paula EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Prepare Meat Dishes NotesDocument2 pagesLesson 3 - Prepare Meat Dishes Notesabejarm7No ratings yet
- Tiếng Anh 7 ISW - Semester 1 - Final TestDocument4 pagesTiếng Anh 7 ISW - Semester 1 - Final Testlan AnhNo ratings yet
- Istiana Maulidah Soal UTS BINGDocument15 pagesIstiana Maulidah Soal UTS BINGIstiana MaulidahNo ratings yet
- Oliva Travel CakeDocument2 pagesOliva Travel CakeAshNo ratings yet
- The Acceptability of Kangkong Polvoron in Dominic Institute of Science and TechnologyDocument5 pagesThe Acceptability of Kangkong Polvoron in Dominic Institute of Science and TechnologynoblesalametchpatriceNo ratings yet
- 100 Ways of Cooking EggsDocument136 pages100 Ways of Cooking EggsRandomUserNo ratings yet
- SOAL BAHASA INGGRIS Ujian Madrasah Atau Sekolah Jenjang MTS, SMP SederajatDocument8 pagesSOAL BAHASA INGGRIS Ujian Madrasah Atau Sekolah Jenjang MTS, SMP Sederajatpreman ilmuNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Meal PlanningDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Meal Planningashenafihailemariam43No ratings yet
- KOP BP 27 HO Stages in Sugar BoilingDocument1 pageKOP BP 27 HO Stages in Sugar BoilingsamismithNo ratings yet
- CS HUM G111 Input and Output 5Document20 pagesCS HUM G111 Input and Output 5YasminNo ratings yet
- Seasonal Plants - Planting ScheduleDocument1 pageSeasonal Plants - Planting ScheduleEd ChambersNo ratings yet
- DLP About Coco Water VinegarDocument11 pagesDLP About Coco Water VinegarJosh GandelaNo ratings yet
- Inspection 3 and Inspection 4Document2 pagesInspection 3 and Inspection 4Md Ali RazuNo ratings yet
- MENU Durango Cantina 50123Document3 pagesMENU Durango Cantina 50123Farley ElliottNo ratings yet
- The Twelve Principles of Sentient MealsDocument1 pageThe Twelve Principles of Sentient MealsDivyajyoti DevaNo ratings yet
- Ol Manahan Ad Cleanliness Cookery 1 1Document8 pagesOl Manahan Ad Cleanliness Cookery 1 1api-651109143No ratings yet
- Cooking ProposalDocument3 pagesCooking ProposalMarco RegunayanNo ratings yet
- German Bread Recipe - Official Masala TV Breakfast RecipesDocument2 pagesGerman Bread Recipe - Official Masala TV Breakfast RecipesMohammad Hisham Bhawpal0% (1)
- Harmony FoodbookDocument32 pagesHarmony FoodbookSamNo ratings yet
- Super Nachos RecipeDocument2 pagesSuper Nachos RecipeCloonyNo ratings yet
- Inbound 6254766050680619910Document1 pageInbound 6254766050680619910Lisa AmahleNo ratings yet
- Tle 7 Week 3Document4 pagesTle 7 Week 3DIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- Stock Opname KitchenDocument3 pagesStock Opname Kitchenofficial.ashroriNo ratings yet
- Food Exchange (1) .DaitoyDocument17 pagesFood Exchange (1) .DaitoyElla Mae AbutinNo ratings yet
- ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VOICE FinalDocument23 pagesACTIVE AND PASSIVE VOICE FinalAllaiza Eve NovioNo ratings yet
- Surat DCDocument11 pagesSurat DCWayan Pandy PerdanaNo ratings yet
- FSM 100: Meal Management: Activity 1 in Types of Table ServicesDocument2 pagesFSM 100: Meal Management: Activity 1 in Types of Table ServicesRomina MolenillaNo ratings yet