Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Composition and Structure of Meat
Uploaded by
Lerma Canuel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesMeat is composed of muscle fibers that contain the proteins actin and myosin, which enable animal movement. Meat also contains connective tissue including collagen and elastin, which attach muscles to bones and allow stretching. The composition of meat includes water, protein, fat, and carbohydrates. Water makes up 70% of muscle tissue, protein 20%, and fat 5%. The fat and protein contribute to meat's juiciness, tenderness, and flavor. Carbohydrates aid in browning reactions that develop meat's appearance and taste during cooking methods like roasting and broiling.
Original Description:
Original Title
Composition and structure of Meat
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMeat is composed of muscle fibers that contain the proteins actin and myosin, which enable animal movement. Meat also contains connective tissue including collagen and elastin, which attach muscles to bones and allow stretching. The composition of meat includes water, protein, fat, and carbohydrates. Water makes up 70% of muscle tissue, protein 20%, and fat 5%. The fat and protein contribute to meat's juiciness, tenderness, and flavor. Carbohydrates aid in browning reactions that develop meat's appearance and taste during cooking methods like roasting and broiling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesComposition and Structure of Meat
Uploaded by
Lerma CanuelMeat is composed of muscle fibers that contain the proteins actin and myosin, which enable animal movement. Meat also contains connective tissue including collagen and elastin, which attach muscles to bones and allow stretching. The composition of meat includes water, protein, fat, and carbohydrates. Water makes up 70% of muscle tissue, protein 20%, and fat 5%. The fat and protein contribute to meat's juiciness, tenderness, and flavor. Carbohydrates aid in browning reactions that develop meat's appearance and taste during cooking methods like roasting and broiling.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
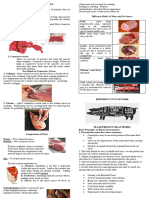
Composition and structure of Meat
Meat is a term used for the muscle of animal flesh.
These muscles that enable the living animal to
move. These muscle fibers contain two proteins:
myosin and actin.
Structure of Meat
1. Connective tissue - is composed of the two
proteins: collagen and elastin.
Muscles are attached to bones by tendons.
Tendons are made up of mostly collagen. Collagen
is creamy white in color.
Ligaments are made up of mostly elastin.
Elastin can stretch and return to its original shape.
Elastin is yellow in color.
2.Muscle fiber- lean meat is composed of long, thin
muscle fibers bound together in bundles.
3. Fine- grained meat is composed of small fibers
bound in small fibers.
4. Course- textured meat has large fibers.
Composition of Meat
1.Water-70% of muscle tissue
2.Protein- 20% of muscle tissue. Protein coagulates
when it is heated. It becomes firm and loses
moisture. When protein has coagulated to the
desired degree, the meat is said to be done.
3.Fat- 5% of the muscle tissue. The fat in meat
contributes to:
A. Juiciness
Marbling is fat that is deposited within the muscle
tissue. Surface fats protect the meat from drying out
during cooking. Adding surface fat is called
barding.
B. Tenderness
Marbling separates muscle fibers, making meat
easier to chew.
C. Flavor
Fat is the main source of flavor in meat.
4.Carbohydrates
It plays a necessary part in the complex reaction,
mallard reaction, which takes place when the meats
are browned by roasting, broiling or sauteing.
Without carbohydrates, desirable flavor-appearance
of browned meats would not be achieved.
You might also like
- Composition of MeatDocument9 pagesComposition of MeatStephanie MirandaNo ratings yet
- Module MeatDocument2 pagesModule Meatpio.barrettoNo ratings yet
- Cookero MeatDocument1 pageCookero MeatMiaNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture Introductionand Structure of Muscle TissuesDocument4 pages1st Lecture Introductionand Structure of Muscle TissuesHamnaNo ratings yet
- Week 1&2 CookeryDocument33 pagesWeek 1&2 CookeryJonabel DacilloNo ratings yet
- Module Quarter 4 CompiledDocument16 pagesModule Quarter 4 CompiledJoevic SuyodNo ratings yet
- Meat HygieneDocument50 pagesMeat HygieneberiNo ratings yet
- Meat Technology (1) WDocument68 pagesMeat Technology (1) WfaisalNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Meat - Lesson 1Document25 pagesIntroduction of Meat - Lesson 1Ella Cagadas PuzonNo ratings yet
- Meat Theory InsightDocument19 pagesMeat Theory InsightBonophool BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10: Quarter 4 Las Number 1Document8 pagesCookery 10: Quarter 4 Las Number 1Edison Manuel91% (11)
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 4 LAS Number 1 Weeks 1Document8 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 4 LAS Number 1 Weeks 1Leila Madelene LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet (Las) : Cookery 10Document8 pagesLearning Activity Sheet (Las) : Cookery 10criselda desistoNo ratings yet
- 4 A 1 A 4 A 46 Ade 4Document62 pages4 A 1 A 4 A 46 Ade 4Ken ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Cookery10 Q4 Week1 v4Document10 pagesCookery10 Q4 Week1 v4Maria Rose Tariga Aquino100% (4)
- FSTC 105 B All Aboit MeatDocument27 pagesFSTC 105 B All Aboit MeatElijah Heart BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Prepare Meat DishesDocument10 pagesModule 6 Prepare Meat DishesGilbert LoredoNo ratings yet
- AT10 Meat Tech 1Document20 pagesAT10 Meat Tech 1Reubal Jr Orquin Reynaldo100% (1)
- 4th Grading LESSON 2 Kinds and Composition of MeatDocument17 pages4th Grading LESSON 2 Kinds and Composition of MeatRenzoNo ratings yet
- Tle 1o q4 ModuleDocument22 pagesTle 1o q4 ModuleRhea AnselmoNo ratings yet
- LO1PPTGR10Document53 pagesLO1PPTGR10Ashly AragonNo ratings yet
- Q4 Module1 G10 CookeryDocument9 pagesQ4 Module1 G10 CookeryfishguadagraceNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ReportDocument14 pagesGroup 2 ReportNoire LeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Prepare Meat Dishes NotesDocument2 pagesLesson 3 - Prepare Meat Dishes Notesabejarm7No ratings yet
- 1st Demo CookeryDocument68 pages1st Demo CookeryStephanie Shane ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Cookery10 Week1-2 Q4Document5 pagesCookery10 Week1-2 Q4StephanieNo ratings yet
- Tle - 9 - Prepare and Cook MeatDocument7 pagesTle - 9 - Prepare and Cook MeatJeff Ubana PedrezuelaNo ratings yet
- Meat StructureDocument29 pagesMeat StructureJonyBlessingNo ratings yet
- Beef Poultry and EggsDocument17 pagesBeef Poultry and EggsAira RamonNo ratings yet
- Class 3 Online PDFDocument34 pagesClass 3 Online PDFG.M.Tasnimul KarimNo ratings yet
- Las 1 q4 Perform Mise en PlaceDocument6 pagesLas 1 q4 Perform Mise en PlaceDump McDumpNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Meat Lesson 1Document4 pagesReviewer Meat Lesson 1Rose Lynn100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Prepare and Cook Meat Meat: Than BeefDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Prepare and Cook Meat Meat: Than BeefFranz Russell TalosigNo ratings yet
- Meat ChapterDocument16 pagesMeat ChapterAyesha RasheedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Meat DishesDocument20 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Meat DishesRuby Esmeralda AndayaNo ratings yet
- Q4 HE Cookery 10 Week1Document4 pagesQ4 HE Cookery 10 Week1Chiesa Arellano100% (2)
- Meat Technology 1Document30 pagesMeat Technology 1Rameen ShahidNo ratings yet
- TleDocument5 pagesTleBianca MontalboNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Cook MeatDocument65 pagesPrepare and Cook MeatARLENE MORADA100% (1)
- Las Cookery 4TH Quarter - 083850Document19 pagesLas Cookery 4TH Quarter - 083850umlijamieeeNo ratings yet
- Cookery10-Week1-7 (4th)Document27 pagesCookery10-Week1-7 (4th)mary grace manalang100% (2)
- The Lesson Structure Module No. and Title: Module 1: Introduction To Animal Meat andDocument11 pagesThe Lesson Structure Module No. and Title: Module 1: Introduction To Animal Meat andMaidan SultanNo ratings yet
- TLE10-This Is MeatDocument18 pagesTLE10-This Is MeatJoy April Aguilar DeGuzmanNo ratings yet
- Culinary Mudule 10Document41 pagesCulinary Mudule 10Karen FlorendoNo ratings yet
- BHCM-2 - Unit-4 (Meat) .: Lamb/MuttonDocument26 pagesBHCM-2 - Unit-4 (Meat) .: Lamb/MuttonSangeeta GotameNo ratings yet
- Meat Analysis 2021Document113 pagesMeat Analysis 2021hossamali7272No ratings yet
- Quarter 4 TLE 10 L 1Document34 pagesQuarter 4 TLE 10 L 1Kennard GundranNo ratings yet
- 7 Meat 2020Document22 pages7 Meat 2020jobbangelobelandresNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Cookery Hand Outs 2 A.Y 2023 2024Document40 pagesGrade 10 Cookery Hand Outs 2 A.Y 2023 2024Ryan Joseph BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- FNS 201 PresentationDocument7 pagesFNS 201 PresentationMyless MukendiNo ratings yet
- TLE LAS Cookery 10 Quarter 4 Week 1Document8 pagesTLE LAS Cookery 10 Quarter 4 Week 1Edgar RazonaNo ratings yet
- Cookery Q4 Week 2 LAS 2Document1 pageCookery Q4 Week 2 LAS 2Ian Grace Dolar FabianiaNo ratings yet
- The Flesh CompositionDocument18 pagesThe Flesh CompositionMuhammad Irwan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Media Ajar DagingDocument9 pagesMedia Ajar Dagingni putu merry oktarianiNo ratings yet
- Science FolioDocument12 pagesScience FolioNG chaoshenNo ratings yet
- Composition of MeatDocument22 pagesComposition of MeatGene Rose YlaganNo ratings yet
- Cook 10 1Document8 pagesCook 10 1Jhoana Paula EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Food Science December NotesDocument13 pagesFood Science December NotesKiandra SundayNo ratings yet
- Bone Broth Recipes for Weight Loss, Smooth Skin, and No More CelluliteFrom EverandBone Broth Recipes for Weight Loss, Smooth Skin, and No More CelluliteNo ratings yet