Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MKTG Notes Pt. 9
Uploaded by
adelaida130702Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MKTG Notes Pt. 9
Uploaded by
adelaida130702Copyright:
Available Formats
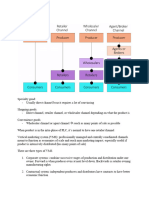
Licensing- selling rights of brand
- Used often in apparel, children’s products
- Name and character licensing is growing includes people too
- Used for foreign market entry strategy
Multi product branding/corporate branding
- Name and brand are identical
- Pros:
o Capitalize on brand equity
o Transfer of positive feelings from one product to next
o Increased adoption rate of product
- Cons
o If negative feelings are held, it will transfer too
Multi brands: 2 or more competing products are owned by the same firm under 2 different
unrelated brands
- Pros
o appeals to different customers
o Take up more shelf room
o Larger market
- Cons
o each brand may have small unprofitable market share
Private labels: are available only at specific retailers
- Pros
o higher profits,
o less pressure to lower price,
o differentiate, substitute available to consumers
o If manufacture of national brand drops them, customer loyalty increased because
tied to retailer
national brand/manufacture brand
pros
attract customer, store prestige, rapid delivery and take up less inventory
co-branding
two different brands on one product
pro
can expand brand into hard to reach category
another segment reached
easier to introduce new product
higher sales
cons
legal
marketing coordination
trust in each partner to take care of partner brand
brand vs product
positioning is rational – how company is portrayed using role and relevance
branding is emotional – how company is portrayed using words, tones, sounds, colour ,images
and pictures
brand provides loyalty to company and consumer search process
manufacturer, private-label, or generic brands
Chapter 10: Pricing
Price can have many names
Setting price policy:
1- Constraints and objectives?
2- Demand and revenue estimates
3- Cost, relationship between volume and profit
4- Determine price level (pricing strategy)
5- List or quoted price
6- Adjustments
Pricing objectives:
- Profit max - Specific number of productions
- Sales max - Survival
- Market share - Responsibility or sustainable pricing
Examples of constraints
- Demand - External trends
- Stage in PLC
- Is it a single product or a line?
- Production cost
- Financial objectives
You might also like
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionFrom EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Problem Set #2: ECO380 Markets, Competition, and StrategyDocument7 pagesProblem Set #2: ECO380 Markets, Competition, and StrategyChristina ZhangNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Product ManagementDocument17 pagesFundamentals of Product ManagementKarthik Nagendra0% (1)
- Brand-Product RelationshipDocument17 pagesBrand-Product RelationshipRitika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Building Strong Brands (Review and Analysis of Aaker's Book)From EverandBuilding Strong Brands (Review and Analysis of Aaker's Book)No ratings yet
- Consulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesFrom EverandConsulting Interview Case Preparation: Frameworks and Practice CasesNo ratings yet
- Lululemon Accounting AssignmentDocument20 pagesLululemon Accounting AssignmentBilal AlamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 11 Notesnate729No ratings yet
- Products and MarketsDocument43 pagesProducts and MarketsRahi Pathan KhanNo ratings yet
- Product, Services and Branding StrategyDocument6 pagesProduct, Services and Branding StrategyDeath StrokeNo ratings yet
- BMChapter 11Document23 pagesBMChapter 11Rabbi RahmanNo ratings yet
- Major Product DecisionsDocument4 pagesMajor Product DecisionsBaraaNo ratings yet
- Global Marketing & R&D CH 15Document16 pagesGlobal Marketing & R&D CH 15Quazi Aritra ReyanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledYassineNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix: Product Price Place Promotion Technology and The Marketing MixDocument39 pagesMarketing Mix: Product Price Place Promotion Technology and The Marketing MixAndrei PrunilaNo ratings yet
- Marketing 1Document3 pagesMarketing 1Vimansa JayakodyNo ratings yet
- Product & Brand Management: Dr. Bikash Banerjee Mobile: 9820183718Document248 pagesProduct & Brand Management: Dr. Bikash Banerjee Mobile: 9820183718pari bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Imc 40Document11 pagesImc 40Bella BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Marketing 3Document3 pagesMarketing 3Vimansa JayakodyNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Dela Cruz, Janella T. Masters in Business AdministrationDocument21 pagesSubmitted By: Dela Cruz, Janella T. Masters in Business AdministrationAngelica AnneNo ratings yet
- 2-Product DecisionDocument27 pages2-Product DecisionAKSHITA SOODNo ratings yet
- PositioningDocument18 pagesPositioningPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2012 - 2 Col Cheat Sheet For MidtermDocument4 pages2012 - 2 Col Cheat Sheet For MidtermShyamal VermaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Experience: Product and Brand MarketingDocument12 pagesConsumer Experience: Product and Brand MarketingMarwa LaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Marketing DefinitionsDocument5 pagesUnit 4 - Marketing DefinitionsAlbert GilNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Lecture Pricing Costs and RevenueDocument4 pagesWeek 9 Lecture Pricing Costs and Revenuecbenn0001No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Strategic Marketing Analysis and BudgetingDocument5 pagesTopic 2 - Strategic Marketing Analysis and BudgetingJoseph VillartaNo ratings yet
- Product and Brand Management: Submitted By: Megha Omshree Kumawat Kalpana Silawat Namrata KothariDocument33 pagesProduct and Brand Management: Submitted By: Megha Omshree Kumawat Kalpana Silawat Namrata KothariarpitakumawatNo ratings yet
- Consulting CasesDocument10 pagesConsulting Caseshds200302No ratings yet
- B 2 BDocument12 pagesB 2 BlauraNo ratings yet
- Managing Products and Brands Course 5Document33 pagesManaging Products and Brands Course 5Georgiana GNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - MarketingDocument16 pagesUnit 4 - Marketingadriana zugastiNo ratings yet
- Product Strategies: Branding & Packaging DecisionsDocument17 pagesProduct Strategies: Branding & Packaging Decisionsyeschowdhary6722No ratings yet
- ISB - Co2014 Consulting Case Book - FrameworksDocument24 pagesISB - Co2014 Consulting Case Book - Frameworksanshul suryanNo ratings yet
- Text+Romacafe 2Document7 pagesText+Romacafe 2yenes rafaelNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Product Life Cycle (PLC) & Marketing Strategies by Dr.J.R.Das Associate Professor SOA UniversityDocument19 pagesA Presentation On Product Life Cycle (PLC) & Marketing Strategies by Dr.J.R.Das Associate Professor SOA UniversitySantosh kumar sahooNo ratings yet
- Marketi ResumoDocument38 pagesMarketi ResumoCaroline DutraNo ratings yet
- Designing and Implementing Branding StrategiesDocument51 pagesDesigning and Implementing Branding StrategiesLalNo ratings yet
- Promotion and Branding 1.2Document6 pagesPromotion and Branding 1.2Vidaisbae 12No ratings yet
- Approaches To StaffingDocument31 pagesApproaches To StaffingVidaisbae 12No ratings yet
- Brand Extension: Sarwar Ahmed Syngenta Bangladesh Limited July 2010Document22 pagesBrand Extension: Sarwar Ahmed Syngenta Bangladesh Limited July 2010Md. Mufidul HassanNo ratings yet
- Global Marketing, R & DDocument31 pagesGlobal Marketing, R & DJayant KhatwaniNo ratings yet
- Brand Is A Product, Service, or Concept That Is Publicly Distinguished From Other ProductsDocument7 pagesBrand Is A Product, Service, or Concept That Is Publicly Distinguished From Other ProductsZarin EshaNo ratings yet
- What Is Marketing?Document38 pagesWhat Is Marketing?tarungupta7688No ratings yet
- Enterprise Customer Market SegmentationDocument3 pagesEnterprise Customer Market SegmentationHut LluragNo ratings yet
- Market Segmentation & TargetingDocument16 pagesMarket Segmentation & TargetingALINo ratings yet
- Product: Any Good or Service That Services To Satisfy The Needs or Wants of Customers Product Life CycleDocument2 pagesProduct: Any Good or Service That Services To Satisfy The Needs or Wants of Customers Product Life CyclejjkjljNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix & Product Life CycleDocument32 pagesMarketing Mix & Product Life CycleJayRavasa100% (1)
- Best Product Foor Market NeedDocument45 pagesBest Product Foor Market NeedAr-jay RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 SummaryDocument7 pagesChap 5 SummaryThục Nhi Lê VũNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument8 pagesMidtermAlex TalloNo ratings yet
- BUS - Paper 1 RevisionDocument61 pagesBUS - Paper 1 Revisionitzm3hasnainNo ratings yet
- Competitive AnalysisDocument38 pagesCompetitive AnalysisGravin LeoNo ratings yet
- Session - 5: Dealing With The CompetitionDocument68 pagesSession - 5: Dealing With The CompetitionAkshey ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Important Terems From CIPDocument3 pagesImportant Terems From CIPSai Tapaswi ChNo ratings yet
- 4.3.1 Strategic Brand Management Module-I Instructor:-Dr.M.Kethan Dept. of MBA KimsDocument39 pages4.3.1 Strategic Brand Management Module-I Instructor:-Dr.M.Kethan Dept. of MBA KimsBibin NinanNo ratings yet
- Introducing and Naming New Products and Brand ExtensionsDocument30 pagesIntroducing and Naming New Products and Brand ExtensionsLalNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument22 pagesBusiness Environmentgetcultured69No ratings yet
- Brand EquityDocument26 pagesBrand Equitygastro8606342No ratings yet
- MK TheoryDocument41 pagesMK TheoryVarun AnandNo ratings yet
- MR SafetyDocument3 pagesMR SafetyPaul BernardNo ratings yet
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)From EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)No ratings yet
- MKTG Notes Pt. 12Document1 pageMKTG Notes Pt. 12adelaida130702No ratings yet
- MKTG Notes Pt. 7Document3 pagesMKTG Notes Pt. 7adelaida130702No ratings yet
- MKTG Notes Pt. 6Document2 pagesMKTG Notes Pt. 6adelaida130702No ratings yet
- MKTG Notes Pt. 10Document3 pagesMKTG Notes Pt. 10adelaida130702No ratings yet
- CH 16Document23 pagesCH 16Renee100% (1)
- 2 Insurance F PDFDocument42 pages2 Insurance F PDFbambhroliya urvishaNo ratings yet
- Whose Car Is That? - It's Bill'sDocument14 pagesWhose Car Is That? - It's Bill'sMohammad JunidNo ratings yet
- PrzysuskiM BerryRatioPaperDocument10 pagesPrzysuskiM BerryRatioPapersuperandrosaNo ratings yet
- Maximum Value Functions and The Envelope TheoremDocument10 pagesMaximum Value Functions and The Envelope TheoremS mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 6 Baye PDFDocument34 pagesCapitulo 6 Baye PDFDiego Vigueras Quijada100% (1)
- Management Information CLASS (L-05 & 06) : Prepared By: A.K.M Mesbahul Karim FCADocument30 pagesManagement Information CLASS (L-05 & 06) : Prepared By: A.K.M Mesbahul Karim FCASohag KhanNo ratings yet
- The Value Pitch The Importance of Team Management v3Document30 pagesThe Value Pitch The Importance of Team Management v3Caio Sadao TamezavaNo ratings yet
- Pre BoardDocument7 pagesPre BoardRAJ RUPALINo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ModuleDocument8 pagesChapter 5 ModuleJane GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics - An Oxymoron or NotDocument4 pagesBusiness Ethics - An Oxymoron or NotDong West100% (1)
- Business Studies PDFDocument327 pagesBusiness Studies PDFsgangwar2005sg100% (1)
- Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesImportant QuestionsabhaybittuNo ratings yet
- Capitalism: The Principles of Capitalism Is As FollowingDocument2 pagesCapitalism: The Principles of Capitalism Is As FollowingUmair AdnanNo ratings yet
- ABM Applied Economics Module 4 Determining The Implications of Market Pricing On Economic Decision Making 2Document24 pagesABM Applied Economics Module 4 Determining The Implications of Market Pricing On Economic Decision Making 2Althea100% (1)
- Duality and Modern Economics - Cornes PDFDocument304 pagesDuality and Modern Economics - Cornes PDFAustin S. HooeNo ratings yet
- CRUX Casebook 2020Document133 pagesCRUX Casebook 2020Nitya BahlNo ratings yet
- ACT23 Exam FinalsDocument9 pagesACT23 Exam FinalsLim JugyeongNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument14 pagesManagerial EconomicsKuldip PardeshiNo ratings yet
- CAMA Theory and Numericals PDFDocument272 pagesCAMA Theory and Numericals PDFVanshika SoniNo ratings yet
- Chuong 3. Hoạt động marketing trong môi trường kỹ thuật số (p2)Document110 pagesChuong 3. Hoạt động marketing trong môi trường kỹ thuật số (p2)Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- Metabical Case Analysis PDFDocument7 pagesMetabical Case Analysis PDFAnonymous NlSTX4WANo ratings yet
- 2017ies Exam Question Paper-1Document5 pages2017ies Exam Question Paper-1AnjaliPuniaNo ratings yet
- Profitability ControlDocument30 pagesProfitability Controlhasmukh19840% (1)
- BSC Oxford Brookes Acca Thesis TopicsDocument7 pagesBSC Oxford Brookes Acca Thesis Topicsafcnoxdhv100% (2)
- Competitive FirmDocument34 pagesCompetitive FirmZe RomeNo ratings yet
- Cournot-Bertrand Model For Homogenous GoodsDocument3 pagesCournot-Bertrand Model For Homogenous GoodsAnurag RastogiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Causal Loop DiagramDocument10 pagesAssignment Causal Loop DiagramHasful FathoniNo ratings yet