Professional Documents
Culture Documents
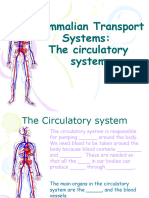
Blood Circulation (Word)
Uploaded by
Technical Nihal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Blood Circulation(Word)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesBlood Circulation (Word)
Uploaded by
Technical NihalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Blood BLOOD
Describe Structure and function of.
a) Red Blood cells. (Erythrocytes).
Struchire!
Red blood cells are minute,
biconcare dises, Consist of spongy cytoplasm in an elastic membrane. They have no nuclei. In their
cytoplasm,
a red pigment haemoglobin is present. They are made in the red bone-marrão of the short bones such
as sternum, ribs and
Vertebrae.
Function: ) Haemoglobin contains iren in its molecule.
and readily It has an affinity for oxygen Combines to form cxy-haemoglobin. This property makes it most
efficient in transporting oxygen from the lungs to the tissues 2) Break down of red blood cells occurs
after four months. It causes formation of bile in the liver. Bile is used in fat digestion.
b) White Blood cells. (Leucocytes)
round,
6) Granulocytes white blood cellshare, irregular in shape. They have lobed nucleus. They are made in
the bone marrow, the lymph nodes or in the spleen Granules are present in the cytoplason,
They can move by a flowing
flowing action of their cytoplasm and can pass out of blood? capillaries by squeening between the cells
of the capillary wall. They ingest and destroy bacteria and deadedly other pathogens by the flowing
action of cytoplesom.
Lymphocytes are round in structure, with smooth cell membranx
Nucleus round but granules absent in the Cytoplasm Function, They seerche antibody, which acts on
antigen thus it provides by flowing round, engulfing and digesting them. 3) Lymphocytes: ???
Platelets.
immunity.
Platelets are cell fragments budded
off from special, very large cells in the red
bone marrow
They play
an
important part in the
clotting action of the blood.
Plasma
G
7
The liquid part of the blood is called solution in water of the plasma, which is many compounds. Some of
the most importent cof these compounds are sodium chloride, Sodium hydrogen carbonate, glucose,
amino acids and is proteins including albumin, fibrinogen and the globulin antibodies, hormones, urea
and Other nitrogenous compounds.
1007
ces
In the plasma digested food carbon it dioxide, and excretory products are carried round the body.
Aries
ces
LYMPHOCYES MEMORY CELLS
[Lymphocytes are relatively small white
blood cells, with
a nucleus which readily,
takes up the stains used to make blood
small amount of cytoplasia] films and with only
formed from cells in the bone marrow
They are
Called stem cells.
[Lymphocytes are classified into two types according to the way they develop. These are B Lymphocytes
and T Lymphocytes I
Blymphocytes secrete antibodies into body fluids T Lymphocytes helps her to destroy antigens inside
body cells, and so their role in the immune response is known cell-mediated response ]
as
the
which
XB Lymphocyte produced antibody. to be detectable in the blood. During this line the microorganism
carrying the antigen set off this response able to form a large
person
ill. Eventually enough population to make a however, the antibodies may get the upper hand, destroying
the micro-organisms and allowing the symptoms of illness to subside
0LB Lymphocyte meet an antigen for the first time. called the primary response- of the same antigen
invades body on a second Occasion, a much faster response occurs which
produces a much larger quantities of the appropriate antibody, and this is called a Secondary response.
It happens because when the B lymphocytes divided during the primary response, some of them
stopped dividing and secreting antibody and became memory cells. One Quite large numbers
are
of
these cells each capable of secreting the antibody specific for that partienter anligen remain in the body
for a long time after the first infection. They capable of responding very quickly if the Same antigen
appears again. The response is often so fast and so effective that the a person is quite unaware as the
micro- - organism entered in the body']
Blood
Describe how the circulatory system helps to
Stop bacteria entering
a cut in the skin.
a cut in the skin and Ans. When there is
an envyme known as blood vessels are damaged, thrombe kinase is released. Thrombokinase Converts
the protein prothrombin to thrombin in the presence of calcium. Thrombin then catalyses the conversion
of the soluble protein fibrinogen to a meshwork of insoluble threads of fibrin. These fibrin threads
entangle the blood corpuscles and the whole mass clot. The clotting of blood seals the cul- forms
preventing bacteria from entering the blood stream. Q Explain, with named examples, how essential
substances Carried in the blood capillaries reach the cytoplasm of the body cells
Contain
2
Ans. The minute spaces between tissue cells
a colourless liquid, the tissue fluid. This tissue fluid carries substances in solution between the body cells
and the blood capillaries,
Oxygen is carried in the red blood cells as Oxyhemoglobin. When blood passes through oxygen- pook
tissues, cxygen is liberated. It then diffuses out of the blood capillary wall. Dissolved food substances
also diffuse out of the thin walls of the blood capillaries into the tissue fluid. From there, these
substances diffuse into the cytoplasm of the cells.
IS
Q. Describe and explain the flow of blood through the heart from the time that it arrives at vena cava to
the time that it leaves at aorta.
Ans:
Deoxygenated blood from the head, neck and arms is returned to the right atrium by the superior vena
cava. When the right atrium Contracts, blood flows in to the right ventricle via the tricuspid valve which
separates the atrium from the ventride and prevents the back flow of blood from the ventride to the
atrium. Blood leaves the right ventricle when it contracts by the pulmonary arch which subsequently
divides into Huot two pulmonary arteries, one to each lung. Backflow of blood into the right ventricle is
prevented by semi-lunar valves in the pulmonary
arch.
Oxygenated blood from the lungs are returned to the left atrium by the pulmonary veins when the left
atrium contracts, blood is forced into the left ventricle via the bicuspid valve which prevents the back flow
of blood into the atrium. When the left ventricle contracts, the blood flows into the aorta and is then
distributed to all parts of the body except the lungs. The aorta also contains semi-lunare Valves to
prevent the back flow of blood into the left ventricle.
Q. a
Bleed.
Describe how o molecule of digested food from the gut enters the blood stream.
Ans. A molecule of digested feed e.g. glucose which is broken down from carbohydrates in the mouth
and stomach pass along the gut by peristalsis until they reach the small intestine. The walls of the
intestine are made up of numerous finger-like projections called villi which project into the intestinal
cavity. The villi are rich supplied with blood and lymphatic vessels to carry away the food substances.
The glucose molecule is absorbed by the villi and the glucose passes across the walls of the blood
vessels and into the blood stream.
Q. Describe the pathway by which the glucose molecule eventually reaches calls in the hand. Ans. The
blood leaving the small intestine with glucose molecule enters the hepatic portal vein. This pauses
through the liver and via the hepatic vein and ! posterior vena cava, the deoxygenated blood reaches the
heart. The heart pumps this blood to the lungs which then, after that, flows back to the heart.
Now the blood with, the glucose is then pumped out of the heart via the north. The aort branches into the
sub-clarian artery and the dorsal aorta. The arm,
//
67401
weed cel
being
fore-limb is supplied with blood from m heart via the sub-clavian artery. As the blood passes" the tissues
in the hand, the molecule of food i.e. glucase passes out from the blood capillaries and to the calls of the
hand.
Q. What is meant by a double circulation? Ans. In double circulation, blood passes through the heart
twice: from the main circulation of the body to the heart, then to the lungs and back to the heart again
before the blood is pumped into the
main circulation.
6. How do the tive parts afada circulation differ from
One another?
Ans. The pulmonary circulation links the lungs to the heart. Pulmonary arteries carry the blood to the
lungs; oxygenated blood is returned to the heart by the pulmonary veins.
Systemic circulation is the main circulation. Oxygenated blood is distributed to all parts of the body, and
veins carry the blood from all parts of the body back to the heart.
Vena cara
Semilunan valve Right atrium
Tricuspid valve
Right-ventricle
Con
Pulmonary artery
402
-Aohla
Wall
-Pulmonary vein
B. Left ventricle -Left atrium -Bicuspid valve
·Tendon
Left ventricle
•Cardige muscle.
Section of Heart-
Lumen.
Elastic muscle fibre
Section of artery
Non elastic muscle fibre.
Wall
section of vein Sectional Blood capillary
(7 47
You might also like
- 6.4 Circulatory System PresentationDocument27 pages6.4 Circulatory System Presentation0mar AlshamsiNo ratings yet
- Lymph Health: The Key to a Strong Immune SystemFrom EverandLymph Health: The Key to a Strong Immune SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Circulatory SystemDocument14 pagesCirculatory Systemsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesCirculatory SystemccparangueNo ratings yet
- Transport Systems and Mechanism SS2 (Autosaved)Document11 pagesTransport Systems and Mechanism SS2 (Autosaved)ImCosmoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Topic-1Body Fluidsquick ReviewDocument13 pagesCirculatory System: Topic-1Body Fluidsquick ReviewAppyNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Transport in Humans SummaryDocument63 pagesIGCSE Biology Transport in Humans SummaryClarissa Muliawan100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of DengueDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Dengueciarkai_18No ratings yet
- Class-12 (RBSE) Biology-Ch-24 Blood Circulatory System PDFDocument7 pagesClass-12 (RBSE) Biology-Ch-24 Blood Circulatory System PDFIshansi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System and Gas Exchange Powerpoint CUMMULATIVEDocument55 pagesCirculatory System and Gas Exchange Powerpoint CUMMULATIVEAjay N. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Summary Vet Quiz (Cvs-Heart)Document3 pagesSummary Vet Quiz (Cvs-Heart)Deeza Joice CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System in MammalsDocument8 pagesCirculatory System in MammalsObiora Ekene HilaryNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyRamon PerroneNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument18 pagesCardio Vascular SystemjeniferNo ratings yet
- Lesson No 18Document8 pagesLesson No 18Moideen MoideenvtmsNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesBlood Anatomy and PhysiologyRao Asad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: The Mammalian Transport System: SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 8: The Mammalian Transport System: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument9 pagesBloodCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument5 pagesBody Fluids and CirculationSheehan MathurNo ratings yet
- Transport in HumansDocument6 pagesTransport in HumansJason Ng100% (5)
- 11 Biology Notes Ch18 Body Fluids and CirculationDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes Ch18 Body Fluids and CirculationKambaska Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Module 12 The Composition and Function of BloodDocument11 pagesModule 12 The Composition and Function of BloodMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 9 HBDocument8 pages9 HBMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument34 pagesHuman PhysiologyMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Bio Chap 8 Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesBio Chap 8 Circulatory SystemJyoti AmbwaniNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Body Fluids and CirculationDocument7 pagesNcert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulationmehrahani03No ratings yet
- BloodDocument7 pagesBloodNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemSaadNo ratings yet
- 550 ICSE ClassX Biology TheCirculatorySystem RNDocument14 pages550 ICSE ClassX Biology TheCirculatorySystem RNHarshitNo ratings yet
- Circulatory - System EditedfocusssnoteDocument136 pagesCirculatory - System Editedfocusssnoteamir kingNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals o Level2018Document12 pagesTransport in Animals o Level2018MuneebNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemSharafatNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezNo ratings yet
- 07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFDocument27 pages07 Human Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014 PDFJohn DeHans100% (2)
- Excellup Class TenDocument3 pagesExcellup Class TenHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemWayneNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System2Document9 pagesCirculatory System2Wajeeha AsifNo ratings yet
- Life Process Part 2 2Document32 pagesLife Process Part 2 2Anin BertNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory System L2.2Document53 pagesHuman Circulatory System L2.2SUBSCRIBE TO PewDiePieNo ratings yet
- Blood Anatomy Physiology HandoutsDocument6 pagesBlood Anatomy Physiology HandoutsKids JangNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Ch-9 Transportation of Materials Q's - AnsDocument4 pagesCh-9 Transportation of Materials Q's - AnsTaksh GautamNo ratings yet
- Riding On The Red RoadDocument4 pagesRiding On The Red RoadSandra MeruNo ratings yet
- Circulatory MechanismDocument8 pagesCirculatory MechanismGresia FalentinaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals 1Document6 pagesTransport in Animals 1makah2711No ratings yet
- Blood and Blood Vessels Module 3Document16 pagesBlood and Blood Vessels Module 3Jenevieve Tungcul SimanganNo ratings yet
- 11S HSB Notes The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pages11S HSB Notes The Circulatory SystemTenika RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument5 pagesBiology Reviewer13l4nk17No ratings yet
- GCSE Mammalian Transport System - VesselsDocument104 pagesGCSE Mammalian Transport System - Vesselspranavsantosh13No ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Parts of The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesLymphatic System: Parts of The Circulatory Systemdownfree28No ratings yet
- Blood and Its FunctionsDocument5 pagesBlood and Its FunctionsAgustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemGennelle GabrielNo ratings yet
- Blood and CirculationDocument7 pagesBlood and CirculationFarhan HossenNo ratings yet
- Iii. Patient and His Illness A. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIii. Patient and His Illness A. Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 42 Reading GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 42 Reading GuideCaleb SchantzNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 18 (PDF)Document11 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 18 (PDF)Nilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 10Document9 pagesBiology Chapter 10wongchengen2006No ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculatoinDocument34 pagesBody Fluids and CirculatoinPrasmita BeheraNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument5 pagesBiologyorlaconn3No ratings yet
- Case Study-Cereal PartnersDocument5 pagesCase Study-Cereal PartnersTariq MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Indiga Indiga: Tech TechDocument32 pagesIndiga Indiga: Tech Techsunny100% (1)
- Snowflake Schema - JennyDocument2 pagesSnowflake Schema - JennyJennyNo ratings yet
- Caps Fet Physical Science WebbbbDocument170 pagesCaps Fet Physical Science WebbbbWonder Bee NzamaNo ratings yet
- Catalogue For TubingDocument1 pageCatalogue For Tubingprabhakaran.cNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Montenegrin LanguageDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Montenegrin LanguageSanja MacutNo ratings yet
- Giki Students Hand Book 08Document75 pagesGiki Students Hand Book 08Jawad Rasheed Sheikh100% (1)
- Rack & Pinion DesignDocument9 pagesRack & Pinion Designmannu057No ratings yet
- QQQQ PDFDocument484 pagesQQQQ PDFSagor Saha100% (1)
- Wilkerson Case Study FinalDocument5 pagesWilkerson Case Study Finalmayer_oferNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 1b Make Your Idea A Reality Unit 3 Critical Thinking QuestionsDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurship 1b Make Your Idea A Reality Unit 3 Critical Thinking QuestionsNastech ProductionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12.1.2 Respiratory Substrates and RQDocument30 pagesChapter 12.1.2 Respiratory Substrates and RQnie20060301No ratings yet
- Inkubator TransportDocument8 pagesInkubator TransportYassarNo ratings yet
- Bba-Mq Tias 2023-24Document2 pagesBba-Mq Tias 2023-24Chris PresleyNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Motherboard SchematicsDocument49 pages3.3 Motherboard SchematicsJoanna WęgielNo ratings yet
- INST240 Sec4Document127 pagesINST240 Sec4bhanu6212No ratings yet
- 02 RgebDocument1,168 pages02 Rgebprožnik100% (3)
- PIRCHLDocument227 pagesPIRCHLapi-3703916No ratings yet
- CRC Ace Far 1ST PBDocument9 pagesCRC Ace Far 1ST PBJohn Philip Castro100% (1)
- KV Admission EnclosureDocument1 pageKV Admission EnclosureLaishram PilotNo ratings yet
- Cancer Registry Standard Operating ProceduresDocument3 pagesCancer Registry Standard Operating ProceduresAnan AghbarNo ratings yet
- Distress Manual PDFDocument51 pagesDistress Manual PDFEIRINI ZIGKIRIADOUNo ratings yet
- Real Estate License AgreementDocument2 pagesReal Estate License AgreementRocketLawyerNo ratings yet
- BCSP GuideDocument44 pagesBCSP GuideCarol Sarmiento DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Scenario - Taxation 2019 UNISA - Level 1 Test 4Document7 pagesScenario - Taxation 2019 UNISA - Level 1 Test 4Tyson RuvengoNo ratings yet
- Type Italian Characters - Online Italian KeyboardDocument3 pagesType Italian Characters - Online Italian KeyboardGabriel PereiraNo ratings yet
- Quintin Kynaston School Wikipedia.Document3 pagesQuintin Kynaston School Wikipedia.John_Adam_St_Gang_QKNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Modelling With Deep Learning A ReviewDocument6 pagesAir Pollution Modelling With Deep Learning A ReviewliluNo ratings yet
- Test Method of Flammability of Interior Materials For AutomobilesDocument17 pagesTest Method of Flammability of Interior Materials For AutomobilesKarthic BhrabuNo ratings yet
- Executive MBA Project - Self Help Allowance - FinalDocument55 pagesExecutive MBA Project - Self Help Allowance - FinalKumar SourabhNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)