Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BC FL Inflammation 592301
Uploaded by
georgescumirelaligiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BC FL Inflammation 592301
Uploaded by
georgescumirelaligiaCopyright:
Available Formats
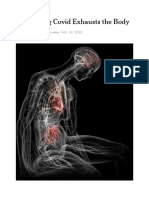
How Inflammation Impacts the Body
As the cellular and molecular mechanisms
behind various diseases are uncovered,
scientists are gaining a better understanding BRAIN
of inflammation’s complex role in disease
pathogenesis. When the immune system THYROID
functions correctly, inflammation is one HEART
of the many steps the body can take to rid
itself of unwanted pathogens, however,
when the immune system mistakenly LUNGS
STOMACH
attacks the body’s healthy tissues or organs,
the results are often debilitating. PANCREAS
We recently compiled examples of how
LIVER
inflammation can impact specific tissues
and organs, plus some of the accumulating KIDNEYS
research revealing the cellular mechanisms
behind these processes. Keep reading to
better understand how inflammation can INTESTINES BLADDER
manifest in the body and its role in certain
diseases and disorders.
BRAIN
Since the 1970s, brain inflammation has been linked to diseases like Alzheimer’s and
Parkinson’s, but new research efforts, particularly those assisted by imaging, have
allowed scientists to observe these processes at greater detail than ever before. In March
2022, researchers investigated how neuroinflammation impacts neuronal proliferation
and healthy cognition in mice. Their work provides evidence that brain inflammation is a
key neuropathological pathway of interest in the cognitive loss associated with AD.
LUNGS
Lung disease, an all-encompassing term including asthma, COPD,
influenza, pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung cancer, and many other breathing
problems, is frequently characterized by lung inflammation. In 2021, a
review paper suggested some strategies for advancing treatments.
THYROID
Thyroiditis, typically a result of unusually high or low levels of thyroid hormones in
the blood, is broken into three primary phases of thyroiditis: acute, euthyroid, and
hypothyroid. Hypothyroidism becomes permanent in 5-15% of patients. In 2022,
researchers investigated how COVID-19 impacts thyroid function and inflammation
in 174 patients with PCR-confirmed patients with SARS-CoV-2. In general, they
found that 80.46% of evaluated patients displayed abnormalities in thyroid function
tests at least once throughout the scientists’ observation.
INTESTINES
While there is no cure for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there have been
promising findings, such as those from UTSW researchers in 2022, discovering
new drug targets for inflammatory bowel disease. In the study, the team identified
a protein, Pak2, that interacts with inflammatory molecules in the gut. When
the researchers blocked Pak2 in mice, the animals lost weight, had more colon
inflammation, and showed other symptoms of IBD, including diarrhea and blood in
their stools. In the presence of Pak2, however, the IBD-like inflammation eased.
HEART
Inflammation in the heart can lead to irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), heart failure,
coronary heart disease, and more. In 2021, scientists published a paper discussing the
recent advances in cardiac tissue engineering for managing myocardium. While there
has been previous work testing microfluidic devices with stem cells, the team suggests
a hydrogel-based system with both encapsulated stem cells and biocompatible patches
loaded with cells and applied at the site of infarction.
KIDNEYS
Kidney inflammation, or nephritis, is most commonly caused by autoimmune
diseases or infections. Lupus nephritis occurs when lupus autoantibodies
affect structures within the kidneys that filter out waste. In 2020, researchers
in Japan investigated the network of inflammatory mechanisms behind lupus
nephritis, with findings suggesting that blocking JAK/STAT and TIM-1/TIM-4
signaling pathways may help develop novel therapeutic agents.
PANCREAS
Chronic pancreatitis (CP) can lead to irreversible damage to exocrine and endocrine
pancreatic parenchyma. Though there is still no cure for chronic pancreatitis other
than removal of the pancreas, scientists have suggested that gene therapy and cystic
fibrosis conductance regulator (CFTR) potentiators show potential as possible new
treatments for chronic pancreatitis.
BLADDER
Inflammation of the bladder, or cystitis, usually occurs after a bacterial infection.
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic disorder characterized by an inflamed or irritated
bladder wall. In 2022, researchers investigated gender differences in interstitial
cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS), and discovered differences in both symptom
profiles and patient experiences of symptoms and their impact.
LIVER
In 2018, researchers looked at the role of inflammation in liver disease and
clarified the role of inflammasomes in the aggravation of liver disease, as
well as how selectively blocking this pathway may be a valuable strategy to
delay fibrosis progression in liver diseases.
STOMACH
Gastritis is an umbrella term for several conditions, all including inflammation of the
stomach’s lining. Severe cases can occur due to major surgeries, infections, medication,
or autoimmune disorders. Scientists took a closer look at chronic gastritis in 2015,
discovering that, in addition to the risks of malignancy and peptic ulcer, severe forms of
gastritis may associate with failures in the absorption of essential vitamins, like vitamin
B12, micronutrients (like iron, calcium, magnesium and zinc), diet and medicines.
www.biocompare.com
You might also like
- Summary of Andrew J. Wakefield's Waging War On The Autistic ChildFrom EverandSummary of Andrew J. Wakefield's Waging War On The Autistic ChildNo ratings yet
- Immunobiology of the Complement System: An Introduction for Research and Clinical MedicineFrom EverandImmunobiology of the Complement System: An Introduction for Research and Clinical MedicineGordon D. RossRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Enteropathic Spondyloarthritis: From Diagnosis To Treatment: Clinical and Developmental Immunology January 2013Document13 pagesEnteropathic Spondyloarthritis: From Diagnosis To Treatment: Clinical and Developmental Immunology January 2013Miki MausNo ratings yet
- Causes and Treatments For Long Haul CovidDocument4 pagesCauses and Treatments For Long Haul Covidandrogynus100% (1)
- Insulitis en La DMT1Document6 pagesInsulitis en La DMT1Psico AstralNo ratings yet
- Reference 1Document12 pagesReference 1Mirzania Mahya FathiaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Inflammageing Chronic Inflammation in Ageing, Cardiovascular Disease, and FrailtyDocument39 pages2018 Inflammageing Chronic Inflammation in Ageing, Cardiovascular Disease, and FrailtyJuanPablo Pino GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Gut Disc Axis: A Cause of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Low Back Pain?Document9 pagesGut Disc Axis: A Cause of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Low Back Pain?Cecunat TepotzotlánNo ratings yet
- Probiotics Improve Long Covid PDFDocument9 pagesProbiotics Improve Long Covid PDFSANTA HILDEGARDA DE BINGEN100% (1)
- Ijms 24 01526 v2Document25 pagesIjms 24 01526 v2della.ps2310No ratings yet
- How Long Covid Exhausts The BodyDocument9 pagesHow Long Covid Exhausts The BodyAjaybpa100% (1)
- Li2022 Article Gut-discAxisACauseOfInterverteDocument9 pagesLi2022 Article Gut-discAxisACauseOfIntervertemireliNo ratings yet
- Clinical Evidence On The Potential Beneficial Effects ofDocument12 pagesClinical Evidence On The Potential Beneficial Effects ofDyane VatriciaNo ratings yet
- Interstitial Lung Disease 2021 3Document11 pagesInterstitial Lung Disease 2021 3Khanh Ha NguyenNo ratings yet
- Periodontitis and Alzheimer S DiseaseDocument6 pagesPeriodontitis and Alzheimer S DiseaseDINI LARASATINo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument8 pagesUlcerative ColitispipotoNo ratings yet
- Elife 79397 v2Document21 pagesElife 79397 v2lata.pauccaraNo ratings yet
- Old and New Therapeutic Strategies in Systemic SclerosisDocument6 pagesOld and New Therapeutic Strategies in Systemic SclerosisJosé Javier Morales NúñezNo ratings yet
- TUBERCULOSISDocument18 pagesTUBERCULOSISPabloNo ratings yet
- InterleukinnnDocument29 pagesInterleukinnnNeike OctaryNo ratings yet
- Aspectos ClinicosDocument21 pagesAspectos ClinicosVictor ValarezoNo ratings yet
- Review Explores The Involvement of The Endothelium As An Important Underpinning of Long COVIDe28099s PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesReview Explores The Involvement of The Endothelium As An Important Underpinning of Long COVIDe28099s PathophysiologyMatias Garcia MilaNo ratings yet
- Chronic and Degenerative Diseases Obesity, Inflammation and The Immune SystemDocument7 pagesChronic and Degenerative Diseases Obesity, Inflammation and The Immune SystemAlexNo ratings yet
- Gut Dysfunction and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver DiseaseDocument9 pagesGut Dysfunction and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver DiseaseAshwiniNo ratings yet
- 1678 9849 RSBMT 56 E0260 2022Document7 pages1678 9849 RSBMT 56 E0260 2022Walter Huamani AlvitesNo ratings yet
- Molecular Pathobiology of Scleritis and Its Therapeutic ImplicationsDocument13 pagesMolecular Pathobiology of Scleritis and Its Therapeutic ImplicationsApriansyah Arfandy AzisNo ratings yet
- Mediterranean - Diet - Endothelial - Function - and - Vascular - Inflammatory - Markers 2018 PDFDocument4 pagesMediterranean - Diet - Endothelial - Function - and - Vascular - Inflammatory - Markers 2018 PDFPaulo CardosoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Griese Etiologic Classification of DiffuseDocument19 pages2022 Griese Etiologic Classification of DiffuseUnggul YudhaNo ratings yet
- Histologic Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesDocument14 pagesHistologic Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesDiego Fernando Ortiz TenorioNo ratings yet
- Solving The Puzzle Molecular Research in Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesDocument206 pagesSolving The Puzzle Molecular Research in Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesLiceul Teoretic Mihail KogalniceanuNo ratings yet
- Is There A Causal Link Between Inflammation and DementiaDocument7 pagesIs There A Causal Link Between Inflammation and DementiaFiterman AdrianNo ratings yet
- WJG 20 Anniversary Special Issues (3) : Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument10 pagesWJG 20 Anniversary Special Issues (3) : Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDeril RidwanNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence As A Possible Signal of Neuromuscular Toxicity During Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment - Case Report and Retrospective Pharmacovigilance StudyDocument10 pagesUrinary Incontinence As A Possible Signal of Neuromuscular Toxicity During Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment - Case Report and Retrospective Pharmacovigilance StudyRA Tri Retno WulanNo ratings yet
- 2003 Probiotic and IBDDocument5 pages2003 Probiotic and IBDsujata sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1-2017 Research HighlightsDocument8 pages1-2017 Research Highlightsonco learnNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Crohn's Disease: April 2015Document19 pagesPathogenesis of Crohn's Disease: April 2015Jimena Panti BriceñoNo ratings yet
- The Ceylon Medical JournalDocument3 pagesThe Ceylon Medical JournalAnonymous fOcbAtNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease Can Be Spared by Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory DrugsDocument4 pagesAlzheimer's Disease Can Be Spared by Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory DrugsAra Runa ConstellatiaNo ratings yet
- 10 Current Research Articles Related To Our SystemDocument11 pages10 Current Research Articles Related To Our Systemhomework solutionNo ratings yet
- RetrieveDocument12 pagesRetrievei.ch.lampropoulosNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kel. 2Document11 pagesJurnal Kel. 2ho himmaNo ratings yet
- 4.the Pathogenesis of Psoriatic ArthritisDocument12 pages4.the Pathogenesis of Psoriatic ArthritisstuckinbedNo ratings yet
- Cytokine Storm and Leukocyte Changes in Mild Versus SevereDocument25 pagesCytokine Storm and Leukocyte Changes in Mild Versus SevereRaffaharianggaraNo ratings yet
- Artículo 2 InmunoDocument20 pagesArtículo 2 InmunoEmmanuel UriosoNo ratings yet
- PoncetsdiseaseDocument5 pagesPoncetsdiseasep81483145No ratings yet
- Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy For Coronavirus Disease 2019 - Which? When? and How Much?Document14 pagesMesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy For Coronavirus Disease 2019 - Which? When? and How Much?diana.alyNo ratings yet
- Organising PneumoniaDocument12 pagesOrganising PneumoniaA. RaufNo ratings yet
- The Kidney in Auto-Immune and Auto-Inflammatory Processes Definitions, Mechanisms, and BiomarkersDocument12 pagesThe Kidney in Auto-Immune and Auto-Inflammatory Processes Definitions, Mechanisms, and BiomarkersIndra kusuma mardiaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis-Pathophysiology and Therapeutic ConceptsDocument22 pagesSepsis-Pathophysiology and Therapeutic ConceptsJuan ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Immunology Science and Public Health TheDocument1 pageImmunology Science and Public Health ThezishidayatullahbatamNo ratings yet
- The Role of Nutrition in InflammationDocument11 pagesThe Role of Nutrition in Inflammationsq6qmtd26kNo ratings yet
- Zozulinska, 2006Document5 pagesZozulinska, 2006wanda oktariaNo ratings yet
- VaccinesDocument12 pagesVaccinesPriscila SelingardiNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Research Reviews - 2022 - Liu - Inflammatory Bowel Disease BiomarkersDocument32 pagesMedicinal Research Reviews - 2022 - Liu - Inflammatory Bowel Disease BiomarkersDiego Fernando Ortiz TenorioNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S120197122030031X Main PDFDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S120197122030031X Main PDFJoana MirandaNo ratings yet
- OccupMedLond 2015 Noone 262 3Document3 pagesOccupMedLond 2015 Noone 262 3Danang Adhi SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Disease An Evidence Based Approach To DiaDocument6 pagesKawasaki Disease An Evidence Based Approach To DiaJustine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture ModulatesDocument12 pagesAcupuncture ModulatesAdán LópezNo ratings yet
- Reviews: Immunity, Microbiota and Kidney DiseaseDocument12 pagesReviews: Immunity, Microbiota and Kidney DiseaseEss liNo ratings yet
- Infectious Connections: How Short-Term Foodborne Infections Can Lead to Long-Term Health ProblemsFrom EverandInfectious Connections: How Short-Term Foodborne Infections Can Lead to Long-Term Health ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Belo. Nur 192. Session 13 LecDocument3 pagesBelo. Nur 192. Session 13 LecTam BeloNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesType 2 Diabetes MellitusCadiz Etrama Di RaizelNo ratings yet
- HeartburnDocument76 pagesHeartburnRock ArtadiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Companies in DelhiDocument10 pagesPharmaceutical Companies in DelhiAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Borda2018 PDFDocument48 pagesBorda2018 PDFlarasNo ratings yet
- Tumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708Document3 pagesTumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708CitrusNo ratings yet
- ApheresisDocument5 pagesApheresisGRK BIOMEDNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Manisha Chichani 29032023 064453 PMDocument1 pageMrs. Manisha Chichani 29032023 064453 PMManisha ChichaniNo ratings yet
- Guided Prep Pack - Neet Mds 2021-22Document13 pagesGuided Prep Pack - Neet Mds 2021-22Annu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Pharmacotherapy Pearls For Emergency Neurological Life Support PDFDocument26 pages01 - Pharmacotherapy Pearls For Emergency Neurological Life Support PDFawinsyNo ratings yet
- FREE PRINTABLE CNA Practice ExamDocument12 pagesFREE PRINTABLE CNA Practice Examheartandhandstraining_com91% (57)
- General Format For Orthopedic AssessmentDocument27 pagesGeneral Format For Orthopedic AssessmentMegha Patani100% (7)
- Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment MarketDocument3 pagesGlobal Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment MarketiHealthcareAnalyst, Inc.No ratings yet
- Efficacy of Glimepiride/metformin Combination Versus Glibenclamide/ Metformin in Patients With Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesEfficacy of Glimepiride/metformin Combination Versus Glibenclamide/ Metformin in Patients With Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitusfannia nabillaNo ratings yet
- Shark Cartilage MonographDocument4 pagesShark Cartilage MonographWalter Sanhueza BravoNo ratings yet
- CotrimoxazoleDocument3 pagesCotrimoxazolecsy123No ratings yet
- Delayed Vs Immediate Umbilical Cord ClampingDocument37 pagesDelayed Vs Immediate Umbilical Cord ClampingAndi DeviriyantiNo ratings yet
- Rog Final MDDocument5 pagesRog Final MDSaiNo ratings yet
- A Childbirth Cheat Sheet For Dads-To-be - Baby CenterDocument3 pagesA Childbirth Cheat Sheet For Dads-To-be - Baby CenterDrhtrth AsdfghsfgNo ratings yet
- LINKSERVE Training MaterialsDocument15 pagesLINKSERVE Training MaterialslisingynnamaeNo ratings yet
- Hypernatremia PediatricsDocument7 pagesHypernatremia PediatricsJOHANNESKIFENDINo ratings yet
- Hospital Statistics Report On 8.5.2020Document4 pagesHospital Statistics Report On 8.5.2020vaideeswari kumarNo ratings yet
- NCP Case PresDocument5 pagesNCP Case Pressyd19No ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument31 pagesGastric CancerHarleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Onco-Critical Care An Evidence-Based ApproachDocument539 pagesOnco-Critical Care An Evidence-Based ApproachZuriNo ratings yet
- Patient Delivery Receipt: Product Delivery Location: FacilityDocument1 pagePatient Delivery Receipt: Product Delivery Location: FacilityPat Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PartografDocument31 pagesPartografrovi wilmanNo ratings yet
- Causes, Severity and Outcome of Neonatal Thrombocytopenia in Hi-Tech Medical College and Hospital, BhubaneswarDocument4 pagesCauses, Severity and Outcome of Neonatal Thrombocytopenia in Hi-Tech Medical College and Hospital, BhubaneswarInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Biology Final Exam Grade 9Document2 pagesBiology Final Exam Grade 9Yesha Shah100% (1)
- Gwen Watego (New)Document3 pagesGwen Watego (New)Duan Tian0% (1)