Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amazon Case Ib Expert
Uploaded by
hiepnq22408c0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesAmazon Case Ib Expert
Uploaded by
hiepnq22408cCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS
ASSIGNMENT 2: AMAZON IN EMERGING MARKETS
TEAM: IB EXPERT
NUMBE STUDENT LEVEL OF
NAME
R CODE COMPLETION
1 NGUYEN MAU TRUNG TRONG K224081098 100%
2 NGUYEN QUANG HIEP K224081070 100%
3 HO MINH QUYEN K224081085 100%
4 LE THI CHAU THUY K224081090 100%
5 TRAN THI TU MY K224081078 100%
1. What is the strategic positioning of Amazon?
Strategic Position Analysis of Amazon in the Indian Market:
Amazon entered the Indian market with a clear understanding of the regulatory
environment, including FDI restrictions, import taxes, and adjusting its business model to
operate optimally. In a highly competitive market like India, Amazon has endeavored to
create differentiation, including:
For product distribution: Amazon recognized early on the challenges of
distribution in India, thus investing significantly in building fulfillment centers and a
logistics network to ensure timely delivery, including offering next-day delivery services.
By providing the "Fulfillment by Amazon" program, the company offered sellers a
convenient solution for storage and delivery, addressing a major pain point for e-
commerce businesses in India. After Amazon introduced next-day delivery, Flipkart
announced they would provide "Guaranteed Same Day" delivery. Subsequently, both
companies began offering same-day delivery services in some cities if orders were placed
within a certain timeframe.
Additionally, Amazon introduced various customer-friendly policies: To
compensate for difficulties in address positioning and ensuring timely delivery for sellers,
Agarwal added PIN codes (similar to ZIP codes in the US) and milestone fields on the
delivery information page, reaching 21,000 PIN codes compared to 12,000 of other
retailers, offering incentives for sellers when signing a two-year membership contract
with the first year free, providing a trial service called "Mainstreaming Sellers/SMEs" to
guide them on online transactions, product listing, and accepting online payments.
With the increasing number of Internet users in India, to attract buyers, Piacentini
and Agarwal offered many incentives for customer referrals or purchases from
Amazon.in. In the early stages of operation in India, Amazon offered free shipping
services, attracting buyers by replicating the cash-on-delivery payment option provided in
China. In addition to online payment options such as credit cards, debit cards, and bank
transfers, cash-on-delivery payment methods allowed Amazon customers to pay for their
goods at the time of delivery.
To support sellers, Amazon provided benefits such as free membership in the first
year and support and training on platform usage. Initiatives like "Mainstreaming
Sellers/SMEs" aimed to attract small retailers with little or no experience in online
selling, thereby expanding the seller base on Amazon.in.
Strategic Position Analysis of Amazon in the Chinese Market:
Amazon's strategic positioning in China has been a complex and challenging endeavor.
Despite being the largest Internet-based retailer in the world, Amazon faced difficulties in
establishing a strong presence in the Chinese market.
Initial Entry and Challenges: Amazon entered the Chinese market in 2004 by
acquiring Joyo, the largest online book seller in China at the time. However, Amazon
struggled to replicate its success in the United States and faced strong competition from
local players like Alibaba and JD.com.
Strategic Missteps: Amazon made strategic missteps in China by attempting to fit its
working business model from the United States into the Chinese market. However, the
Chinese consumer market demanded something different, and Amazon failed to adapt
effectively.
Competition with Local Giants: Alibaba and JD.com, two prominent Chinese e-
commerce giants, employed strong local strategies that posed significant challenges to
Amazon's market share in China. These local players had well-established platforms and
better understanding of Chinese consumer preferences.
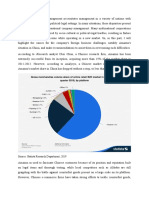
Market Share Decline: Despite initially making inroads, Amazon's market share in
China declined over the years. In 2008, Amazon China held 15.4% of the country's
eCommerce market share, but by 2015, it had dwindled to just 1.1%. During this period,
T-Mall dominated with a 58.6% share, followed by Jingdong at 22.8%.
Shift in Strategy: In 2019, Amazon made the decision to shut down its domestic e-
commerce marketplace business in China. Instead, the company focused on "cross-
border" selling to Chinese consumers, targeting opportunities in the Asia/Pacific region
while leaving the Chinese market to local leaders Alibaba and JD.com.
Lessons Learned: Amazon's experience in China served as a valuable lesson in the
complexities of engaging a foreign market with well-established local players. The
company redirected its energies and invested significantly in expansion efforts in India, a
market it deemed more conducive to long-term success
Strategic Position Analysis of Amazon in the Brazilian Market:
Amazon applied a different strategy in Brazil, focusing on enhancing customer
experience.
Amazon focused on the e-book market by introducing only the Kindle Store
instead of the large e-commerce market because by 2013, over half of Brazil's population
used the Internet and most were interested in reading books. Amazon officially signed
contracts with over 30 book publishers, increasing the number of titles in the national
language of Brazil, introducing e-readers.
When Amazon penetrated the Brazilian market, it faced a series of challenges such
as the tax identification number system, labor laws, backend challenges, and strong
competition from longstanding e-commerce companies. This includes complex tax
systems (In 2014, Brazil ranked 116th in the World Bank's "Ease of Doing Business"
ranking, ranked 159th out of 189 countries in terms of tax availability.), expensive labor
costs (employers must pay for food, transportation, health insurance, 30 days of annual
leave, and mandatory bonuses for their employees.), and especially underdeveloped
transportation infrastructure (69% of roads in Brazil are still poor, narrow, and scattered -
"The World Economic Forum ranks Brazil 104th out of 142 countries measured in
overall infrastructure quality.") Not only that, with high import taxes making the price of
e-books twice as high as in the United States, making it difficult to compete with
domestic e-commerce companies.
Amazon adjusted its strategy to attract customers. Due to high import prices,
Amazon collaborated with 30 domestic publishers to print books, allowing the Kindle
installment payment option for up to 12 months, as Brazilian consumers often use
payment plans for expensive products and provide free delivery for their Kindle products.
2. What international business strategy does Amazon employ in emerging markets
(India, China, and Brazil)? Explain?
Amazon's strategy in emerging markets like India, China, and Brazil shows both
adaptation and core principles:
Adapting to Local Needs:
Mobile-First Approach: Unlike developed markets where desktops reign supreme,
Amazon prioritizes mobile apps for a more internet-savvy, smartphone-using population.
Logistics and Infrastructure: Building a robust delivery network is crucial. Amazon
invests heavily in local warehousing and fulfillment centers to ensure fast and reliable
deliveries, even in areas with complex infrastructure.
Seller Enablement: Programs like Amazon Tatkal in India help small businesses get
online quickly, addressing their concerns and easing the transition to e-commerce.
Core Customer-Centric Principles:
Seamless Online Experience: A user-friendly website and app with local languages and
payment options are essential.
Competitive Prices: Amazon leverages its global scale to offer competitive pricing and
deals, attracting budget-conscious consumers.
Wide Selection: A vast product catalog catering to a variety of needs, along with local
favorites, is a key element.
Learning from Experience: China Example: Unlike its approach in the US, Amazon in
China initially struggled by directly controlling inventory and logistics. They've since
adapted to a more marketplace-focused model.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions: Partnering with local players and acquiring
established businesses gives Amazon a foothold in the market and local expertise.
By combining these elements, Amazon tailors its strategy to each market's unique
characteristics while staying true to its core principles of customer focus and wide
selection. This adaptability has been key to their success in emerging markets.
You might also like
- Amazon Marketing Strategy PlanDocument18 pagesAmazon Marketing Strategy Planmegan75% (4)
- The Shopping Revolution, Updated and Expanded Edition: How Retailers Succeed in an Era of Endless Disruption Accelerated by COVID-19From EverandThe Shopping Revolution, Updated and Expanded Edition: How Retailers Succeed in an Era of Endless Disruption Accelerated by COVID-19No ratings yet
- Amazon in Emerging MarketsDocument43 pagesAmazon in Emerging MarketsAiman KhanNo ratings yet
- Amazon in China and IndiaDocument14 pagesAmazon in China and IndiaKapileswar Mallick100% (1)
- Best Practices Final S4HANA 2020Document934 pagesBest Practices Final S4HANA 2020Sandeep Reddy MuskulaNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS Amazon Go FinalDocument19 pagesCASE ANALYSIS Amazon Go FinalNikhil MohanNo ratings yet
- MGMT 415 P1&2Document20 pagesMGMT 415 P1&2UsmanNo ratings yet
- Amazon Strategic ManagementDocument17 pagesAmazon Strategic ManagementAssignment WriterNo ratings yet
- Amazon CaseDocument5 pagesAmazon CaseSravan KumarNo ratings yet
- Amazon Case Study-Strategic ManagementDocument7 pagesAmazon Case Study-Strategic ManagementMihaela Medina100% (1)
- Socio-Cultural and Political-Legal Barriers For Amazon in ChinaDocument5 pagesSocio-Cultural and Political-Legal Barriers For Amazon in Chinaphuc hauNo ratings yet
- Amazon SWOT 2021 - SWOT Analysis of Amazon - Business Strategy HubDocument18 pagesAmazon SWOT 2021 - SWOT Analysis of Amazon - Business Strategy HubFUNTV5No ratings yet
- Amazon ProjectDocument25 pagesAmazon ProjectParth100% (3)
- Retail CaseDocument7 pagesRetail Casekhazima UmairNo ratings yet
- Amazon's Foray Into India - ReportDocument21 pagesAmazon's Foray Into India - ReportSomdeb BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 47 Branch AccountsDocument53 pages47 Branch AccountsShivaram Krishnan70% (10)
- Kshitij Negi Semester 4 (Csit)Document10 pagesKshitij Negi Semester 4 (Csit)Kshitij NegiNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering: Name: Yarrapureddy Akhileswar Reddy USN: 1RV19CV125Document8 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering: Name: Yarrapureddy Akhileswar Reddy USN: 1RV19CV125Adnan KhanNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument15 pagesAmazonKrishna Vishwakarma100% (1)
- E CommerceDocument25 pagesE CommerceANURAG AJMERANo ratings yet
- Case Study On Amazon 1Document9 pagesCase Study On Amazon 1MUNSIF JAWEEDNo ratings yet
- IB2 GroupworkDocument30 pagesIB2 GroupworkNguyen Linh GiangNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument3 pagesAmazonAnshik YadavNo ratings yet
- Strategy Report: AmazonDocument19 pagesStrategy Report: AmazonNadia RiazNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Consumer Customers Seller Customers Developer CustomersDocument5 pagesIntroduction: Consumer Customers Seller Customers Developer CustomersDiana GicanNo ratings yet
- Amazon Case StudyDocument8 pagesAmazon Case StudyHuy Trần100% (1)
- Digital Marketing - End Term Question PaperDocument6 pagesDigital Marketing - End Term Question PaperPragya Singh BaghelNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesLiterature ReviewZoyeb Iqbal SIDDIQUINo ratings yet
- A Study About Remarketing To Consumers Abandoning Carts at E-Commerce Sites With Respect To Women in Pune City Reference - Amazon (Target Group-Women's in Pune)Document7 pagesA Study About Remarketing To Consumers Abandoning Carts at E-Commerce Sites With Respect To Women in Pune City Reference - Amazon (Target Group-Women's in Pune)Virat KohliNo ratings yet
- Majority Stake in Flipkart $1.4 Billion Paytm Mall: I Analyze Trends and Current Events in Technology, Marketing and AIDocument5 pagesMajority Stake in Flipkart $1.4 Billion Paytm Mall: I Analyze Trends and Current Events in Technology, Marketing and AIAninda DuttaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Business Plan Amazon: Assessment 2Document14 pagesEntrepreneurship: Business Plan Amazon: Assessment 2SteffNo ratings yet
- Ann Adham MBA Midterm Case StudyDocument8 pagesAnn Adham MBA Midterm Case Studyomarshrief84No ratings yet
- AmazonDocument3 pagesAmazonSaidmurod XNo ratings yet
- Amazon: ContentDocument6 pagesAmazon: ContentDiana GicanNo ratings yet
- WWW - Ugb.Ro/Etc: Andreea Nicoleta Donici, PHD Student, Andreea Maha PHD StudentDocument7 pagesWWW - Ugb.Ro/Etc: Andreea Nicoleta Donici, PHD Student, Andreea Maha PHD StudentSandeep ChiluveruNo ratings yet
- HRM Project On AmazonDocument17 pagesHRM Project On AmazonFalaq Khowaja100% (2)
- Amazon 2021 - Chantelle Monica RochesterDocument7 pagesAmazon 2021 - Chantelle Monica RochesterChantelle RochesterNo ratings yet
- SMGroup - Section H - Aditi Singh - Tanvi ChoudharyDocument12 pagesSMGroup - Section H - Aditi Singh - Tanvi ChoudharyTANVI CHOUDHARY PGP 2021-23 BatchNo ratings yet
- Amazon Case StudyDocument4 pagesAmazon Case Studyvaish100% (1)
- Amazon StrategyDocument9 pagesAmazon StrategySaradha Devi GrandhiNo ratings yet
- Web Marketing Strategy A Study On Amazon PDFDocument12 pagesWeb Marketing Strategy A Study On Amazon PDFIrfan IdreesNo ratings yet
- Marketing 361 Phase 2Document9 pagesMarketing 361 Phase 2api-378050784No ratings yet
- Benchmark Practices of Amazon Adopted in IndiaDocument8 pagesBenchmark Practices of Amazon Adopted in IndiaAbhishek Abhi50% (2)
- Amazon Prime - 1 - REVISEDDocument17 pagesAmazon Prime - 1 - REVISEDnyan hein aungNo ratings yet
- Impact of Changing Consumer BehaviorDocument9 pagesImpact of Changing Consumer BehaviorANUSHKA BISWAS 20212106No ratings yet
- Industry Consulting-Arnab MitraDocument11 pagesIndustry Consulting-Arnab Mitraarnab.mtrNo ratings yet
- Ajay's Case Study On AmazonDocument7 pagesAjay's Case Study On AmazonRashika guptaNo ratings yet
- Presented By: GROUP 1Document32 pagesPresented By: GROUP 1Rishabh ThapaNo ratings yet
- FNCE481 - Securities Analysis Assignment 4.1Document18 pagesFNCE481 - Securities Analysis Assignment 4.1pierrrgeneNo ratings yet
- Case Study AMAZONDocument8 pagesCase Study AMAZONrahul maneNo ratings yet
- Amazon Written Assignment - 2018Document2 pagesAmazon Written Assignment - 2018francess gideonNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment OMDocument13 pagesIndividual Assignment OMThe Shelby BoyNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of Amazon (2016)Document10 pagesSWOT Analysis of Amazon (2016)Poulomi Roy100% (2)
- FIN 330 Final Project IDocument9 pagesFIN 330 Final Project ISarai SternzisNo ratings yet
- Amazon in Financial Services 1614482166Document49 pagesAmazon in Financial Services 1614482166Yogendra RathoreNo ratings yet
- AMAZON Marketing Strategies Tarun Jain (21BC372) Tutorial - I41 BCom (Hons) Semester - 5Document13 pagesAMAZON Marketing Strategies Tarun Jain (21BC372) Tutorial - I41 BCom (Hons) Semester - 5tarunjain1505No ratings yet
- AmazonDocument12 pagesAmazonHassaan Qazi100% (1)
- BUSI3005 - Supply Chain and Logistics Management: in Class Assignment1Document6 pagesBUSI3005 - Supply Chain and Logistics Management: in Class Assignment1Gurleen KourNo ratings yet
- Amazon in India Research Report 1Document25 pagesAmazon in India Research Report 1Thu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy of AmazonDocument51 pagesMarketing Strategy of AmazonObisike Emezi100% (1)
- Option 1: Amazon Australia Student's Name Institutional AffiliationDocument8 pagesOption 1: Amazon Australia Student's Name Institutional AffiliationJoshua OrangaNo ratings yet
- Amazon Business: A Comprehensive Guide for B2B ProcurementFrom EverandAmazon Business: A Comprehensive Guide for B2B ProcurementNo ratings yet
- Recruitment by M/s Cloud Analogy: Manish SharmaDocument2 pagesRecruitment by M/s Cloud Analogy: Manish SharmaUtkarsh Tripathi72No ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument2 pagesInvoiceAbirami EkambaramNo ratings yet
- 5a - Valuation of Bonds and DebenturesDocument19 pages5a - Valuation of Bonds and DebenturesSudha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Clarify and Standardize Heineken Brand Image WorldwideDocument9 pagesClarify and Standardize Heineken Brand Image WorldwideclovicNo ratings yet
- 2chapter TwoDocument38 pages2chapter TwoEbsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- Ranked #8 in The World: Mba, MSC and LLMDocument70 pagesRanked #8 in The World: Mba, MSC and LLMIanNo ratings yet
- 1A. Vendor Offer KIEKENS-DSH - Code2Document15 pages1A. Vendor Offer KIEKENS-DSH - Code2vivekanandakuwaitNo ratings yet
- Hard Facts About RMP Infotec Pvt. LTDDocument12 pagesHard Facts About RMP Infotec Pvt. LTDRavi Indian100% (1)
- Adam Horticulture Farm PLCDocument82 pagesAdam Horticulture Farm PLCHabtu AsratNo ratings yet
- BIA Email Brochure - Data Science & Business Analytics - 2023Document4 pagesBIA Email Brochure - Data Science & Business Analytics - 2023Yojit ChavhanNo ratings yet
- Systematic Methods of Community Action in Understanding Community Background Information For LearnersDocument2 pagesSystematic Methods of Community Action in Understanding Community Background Information For Learnersapollo100% (3)
- TA Universal Analysis ManualDocument346 pagesTA Universal Analysis ManualSayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- PriceAction's Candlestick Cheat SheetDocument17 pagesPriceAction's Candlestick Cheat SheetJesus HerrnandezNo ratings yet
- Udyog Aadhaar Registration Certificate PDFDocument1 pageUdyog Aadhaar Registration Certificate PDFnishant kumarNo ratings yet
- Market Cap To GDP RatioDocument8 pagesMarket Cap To GDP RatiokalpeshNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 11th Edition by MishkinDocument13 pagesTest Bank For The Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 11th Edition by Mishkinordainer.cerule2q8q5g100% (39)
- Lazada VietnamDocument17 pagesLazada Vietnamthuannd2223No ratings yet
- 1 - 1 - 1 - 2 - PF Loan Application FormDocument2 pages1 - 1 - 1 - 2 - PF Loan Application FormDEBABRATA SASMALNo ratings yet
- Bitcoin To PaypalDocument10 pagesBitcoin To PaypalRobiulNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Typhoon Urduja To The Tourism Development of The Municipality of NavalDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Typhoon Urduja To The Tourism Development of The Municipality of NavalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Pupil's Entry Monitoring System With SMS NotificationDocument83 pagesPupil's Entry Monitoring System With SMS NotificationMio Betty J. MebolosNo ratings yet
- OPEMANA - Wegman's CaseDocument8 pagesOPEMANA - Wegman's CaseDennyseOrlidoNo ratings yet
- 01 Samss 051Document14 pages01 Samss 051ArshadNo ratings yet
- 1,000 Cases of Exam Paper Leak Reported - FIA Informs NA Body - Pakistan - Business RecorderDocument2 pages1,000 Cases of Exam Paper Leak Reported - FIA Informs NA Body - Pakistan - Business RecorderahmedlakhanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Azure For Java Developers D.Document361 pagesMicrosoft Azure For Java Developers D.EfrailegNo ratings yet
- Print Reciept RequestDocument1 pagePrint Reciept RequestMuhd AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- BE955 Coursework 2022-2023 SpringDocument4 pagesBE955 Coursework 2022-2023 Springwaqas aliNo ratings yet
- CRS WFCS 594092 ADocument4 pagesCRS WFCS 594092 ADiego Rosa de OliveiraNo ratings yet