0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views2 pagesELPL-Final Copy 2016
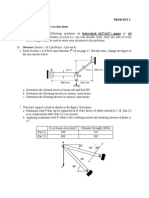
The document is a mechanical engineering exam covering elasticity and plasticity theory. It contains 5 questions, the first two covering elasticity with sub-questions on stress and strain tensors, principal stresses, and failure theories. The third question derives strain-displacement relations for a stretched bar. Questions four and five cover plasticity, comparing yield criteria, deriving flow rules, and discussing elastoplastic relations and sources of nonlinearity.
Uploaded by
Mohamed AbdelazizCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views2 pagesELPL-Final Copy 2016
The document is a mechanical engineering exam covering elasticity and plasticity theory. It contains 5 questions, the first two covering elasticity with sub-questions on stress and strain tensors, principal stresses, and failure theories. The third question derives strain-displacement relations for a stretched bar. Questions four and five cover plasticity, comparing yield criteria, deriving flow rules, and discussing elastoplastic relations and sources of nonlinearity.
Uploaded by
Mohamed AbdelazizCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd