Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NPSH
Uploaded by
sasi636974Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NPSH
Uploaded by
sasi636974Copyright:
Available Formats
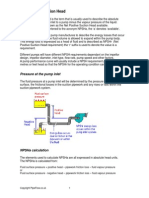
NPSH - NPSH stands for **Net Positive Suction Head** and it is a measure of how close the fluid at a
given point is to flashing, and so to cavitation. is a measure of the pressure experienced by a fluid on
the suction side of a centrifugal pump.
There are two types of NPSH: **Available NPSH (NPSH A)** and **Required NPSH (NPSH R)
NPSH-R is a pump property . NPSH-R is a minimum suction pressure that must be exceeded for the
pump to operate correctly and minimise flashing and cavitation. is quoted by pump manufacturers as
a result of extensive testing under controlled conditions. NPSH-R is defined as the value at which the
discharge pressure is reduced by 3% because of the onset of cavitation .NPSH R is the NPSH required
by the pump to operate without cavitation.
NPSH-A is a system property. Net Positive Suction Head Available is calculated from the suction-side
system configuration. A measure of how close the fluid at a given point is to flashing, and so to
cavitation. It is essentially the suction-side pressure less the vapour pressure of the pumped fluid at
that point . Technically it is the absolute pressure head minus the vapour pressure of the liquid.
To avoid cavitation, NPSH A must be greater than NPSH R.
The purpose of NPSH is to identify and avoid the operating conditions which lead to vaporisation of
the fluid as it enters the pump – a condition known as flashing.
To increase NPSH available, you need to increase the pressure at the pump inlet. Here are some
ways to do that:
Lower the pump level.
Raise the reservoir level.
Reduce motor RPM if possible.
Reduce minor losses upstream of the pump.
Reduce major losses upstream of the pump.
You can also improve the NPSHa by either increasing the elements that add energy to the
liquid or by reducing the elements that subtract energy from the liquid.
You might also like
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Operator’S Guide to Centrifugal Pumps, Volume 2: What Every Reliability-Minded Operator Needs to KnowFrom EverandOperator’S Guide to Centrifugal Pumps, Volume 2: What Every Reliability-Minded Operator Needs to KnowNo ratings yet
- NPSH and Specific SpeedDocument16 pagesNPSH and Specific SpeedmyravganacNo ratings yet
- Net Positive Suction HeadDocument2 pagesNet Positive Suction Headanwerosama0% (1)
- Pid Presentation 1Document11 pagesPid Presentation 1SahilNo ratings yet
- InstallationOperationMaintenance 3620 PT BRDocument5 pagesInstallationOperationMaintenance 3620 PT BREdson França RodriguesNo ratings yet
- A Look at Centrifugal Pump Suction Hydraulic - Part 1Document4 pagesA Look at Centrifugal Pump Suction Hydraulic - Part 1Said Ahmed SalemNo ratings yet
- Pump Suction CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesPump Suction Characteristicsvermaakash22No ratings yet
- NPSH For Metering PumpsDocument7 pagesNPSH For Metering PumpsRahul S. ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- NPSHDocument1 pageNPSHssabih75No ratings yet
- 7 - Pumps (Part 2)Document27 pages7 - Pumps (Part 2)AmpNo ratings yet
- Melab Act2Document2 pagesMelab Act2Theo AlapanNo ratings yet
- NPSH1Document8 pagesNPSH1koyasrujanaNo ratings yet
- NPSHDocument7 pagesNPSHsateesh chandNo ratings yet
- NPSH Pump OperatingDocument4 pagesNPSH Pump OperatingJanneth Herrera FloresNo ratings yet
- Pup CalDocument18 pagesPup Calsklahiri.cheNo ratings yet
- 10 Pump Cavitation TenDocument27 pages10 Pump Cavitation TenAbdallah MansourNo ratings yet
- Understanding Net Positive Suction Head of Centrifugal PumpDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Net Positive Suction Head of Centrifugal PumpJohn RajNo ratings yet
- Useful Information On NPSH, NPSHA and NPSHRDocument8 pagesUseful Information On NPSH, NPSHA and NPSHRpietroNo ratings yet
- Pump Classifications:: Transportation of FluidsDocument2 pagesPump Classifications:: Transportation of FluidsAvinash GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- GPM RevDocument138 pagesGPM RevJuan Cortes TorizNo ratings yet
- Me151 MidtermsDocument18 pagesMe151 MidtermsJohnNo ratings yet
- Net Positive Suction HeadDocument7 pagesNet Positive Suction HeadNenad MutavdzicNo ratings yet
- Pumpe I Ventilatori - KavitacijaDocument3 pagesPumpe I Ventilatori - KavitacijaTvrtko CrepuljaNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Pump CatalogDocument109 pagesReciprocating Pump Catalogmetasoniko2014100% (2)
- Understanding Net Positive Suction Head - Short Notes For GATE Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Net Positive Suction Head - Short Notes For GATE Mechanical EngineeringBharat BhushanNo ratings yet
- Considering NPSH When Making A Pump SelectionDocument8 pagesConsidering NPSH When Making A Pump SelectionMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Pump ReportDocument12 pagesPump ReportHesham Zaghloul100% (1)
- NPSH Note Piping Easy23764Document6 pagesNPSH Note Piping Easy23764Samuel OlonadeNo ratings yet
- Pumps OverviewDocument12 pagesPumps OverviewHesham ZaghloulNo ratings yet
- Net Positive Suction Head Analysis For Testing The Condition of A Centrifugal Pump PDFDocument6 pagesNet Positive Suction Head Analysis For Testing The Condition of A Centrifugal Pump PDFJaime Andrés HuertasNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump (Advanced)Document9 pagesCentrifugal Pump (Advanced)Việt Đặng XuânNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps - Piping Installation Design & Hydraulic System Calculation by AFT Fathom and PIPE-FLO SoftwareDocument84 pagesCentrifugal Pumps - Piping Installation Design & Hydraulic System Calculation by AFT Fathom and PIPE-FLO SoftwareHadi VeyseNo ratings yet
- NPSH Is An: Acronym Hydraulic Vapor PressureDocument5 pagesNPSH Is An: Acronym Hydraulic Vapor PressureSantosh Yellappa SulebhavikarNo ratings yet
- PC PumpDocument5 pagesPC Pumpphantanthanh100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pumps CavitationDocument34 pagesCentrifugal Pumps CavitationAhlem BrahimNo ratings yet
- LNG Pumps, CMDocument11 pagesLNG Pumps, CMRachitNo ratings yet
- Net Positive Suction Head or NPSHDocument4 pagesNet Positive Suction Head or NPSHSathish LingamNo ratings yet
- WCB Pumps Centrifugal C-Series Curve Instruction CentDocument4 pagesWCB Pumps Centrifugal C-Series Curve Instruction CentMuhammad Hardes Elfar WandiNo ratings yet
- Solving Pump Inlet ProblemsDocument4 pagesSolving Pump Inlet ProblemsterracesNo ratings yet
- Chapter Fluid Machinery - PART 2Document27 pagesChapter Fluid Machinery - PART 2Winter NaiNo ratings yet
- Pumps Design and PerformanceDocument27 pagesPumps Design and PerformanceJefferson SmithNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps NPSHDocument6 pagesCentrifugal Pumps NPSHSubrata MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps CavitationDocument34 pagesCentrifugal Pumps CavitationJose Jesus Arboledas HerranzNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump Sizing, Selection and Design Practices (Hay)Document77 pagesCentrifugal Pump Sizing, Selection and Design Practices (Hay)Scribd_del75% (8)
- Cavitation PDFDocument16 pagesCavitation PDFIsmail SakrNo ratings yet
- Pump NPSHa and Suction and Delivery Line Head Loss CalculationDocument6 pagesPump NPSHa and Suction and Delivery Line Head Loss CalculationSugar Technology100% (1)
- ME Lab Activity 2 FinalsDocument3 pagesME Lab Activity 2 FinalsTheo AlapanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document15 pagesChapter 14Hamza AliNo ratings yet
- A Look at Centrifugal Pump Suction Hydraulic - Part 2Document3 pagesA Look at Centrifugal Pump Suction Hydraulic - Part 2Said Ahmed SalemNo ratings yet
- NPSHDocument5 pagesNPSHmbakhshi2No ratings yet
- NPSHR & Impeller TrimDocument2 pagesNPSHR & Impeller Trimdk4monjureNo ratings yet
- RP Technical Paper NPSH Reciprocating Pumps v2 PDFDocument4 pagesRP Technical Paper NPSH Reciprocating Pumps v2 PDFbalaji100% (1)
- NPSH - Net Positive Suction HeadDocument9 pagesNPSH - Net Positive Suction Headlokeshjaddu6No ratings yet
- How To Predict CavitationDocument7 pagesHow To Predict CavitationrkssNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machine Problems - cavitation&NPSHDocument3 pagesFluid Machine Problems - cavitation&NPSHOstwald GarciaNo ratings yet
- Natalie Portmans Shaved Head Glossary of Firefighting Equipment#n Talk PageDocument34 pagesNatalie Portmans Shaved Head Glossary of Firefighting Equipment#n Talk PageMikelaNo ratings yet
- Process Engineering Manual 005 IIDocument29 pagesProcess Engineering Manual 005 IImuktaanand100% (12)
- Sucker-Rod Pumping Handbook: Production Engineering Fundamentals and Long-Stroke Rod PumpingFrom EverandSucker-Rod Pumping Handbook: Production Engineering Fundamentals and Long-Stroke Rod PumpingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)