Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology - Protein Synthesis
Biology - Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
japeshshah300 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageBiology - Protein Synthesis
Biology - Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
japeshshah30Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
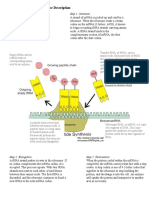
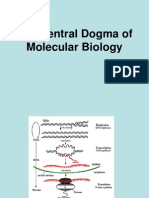
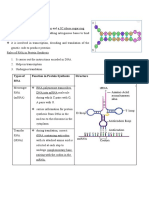
The first stage of protein synthesis is called transcription.
This involves using basis to make a strand
RNA. an enzyme called RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA in front of a gene in a non coding
region. The enzyme then separates the DNA strands. the enzyme now moves along one strand
adding complementary RNA nucleotides. These complementary base pairs are the same accept
uracil replaces thymine which pairs with adenine. The second stage of protein synthesis is called
translation which the bases are red three at a time( a codon). the mRNA strand attaches to a
ribosome in the cytoplasm. The tRNA recognises the correct corresponding codon it binds with the
other codon. when this happens the tRNA transfers the appropriate amino acid to the end of the
amino acid chain. as a represents move along it joins the amino acids from the tRNA together
forming a polypeptide( a chain of amino acids). The polypeptide chain made up of amino acids then
folds up to form a protein with a specific shape
You might also like
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDocument65 pagesQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument29 pagesGene ExpressionZainab Jamal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisEverly Joy JingcoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- Bio 1110 Lecture On Protein SynthesisDocument30 pagesBio 1110 Lecture On Protein SynthesisNokutenda KamtsetaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisMangetsu HozukiNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisShivani SriramNo ratings yet
- AziyatDocument7 pagesAziyatASHFAQ AHMADNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Section 4: Andrew BurtsfieldAndrew BurtsfieldNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisAbigailNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 (4TH Quarter) - Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 (4TH Quarter) - Protein SynthesisJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- Quiz DiscussionDocument4 pagesQuiz DiscussionIyaNo ratings yet
- Transcription of DNA To RNADocument2 pagesTranscription of DNA To RNAReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- Paper TwoDocument21 pagesPaper TwoSafder AliNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionmohammedNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument22 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisEdward GanggangNo ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument8 pagesTranscription & TranslationDr DapperNo ratings yet
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument21 pagesProtein BiosynthesisMyrrh Tagurigan TrainNo ratings yet
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesDocument40 pages2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- What Is Step 1 of Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesWhat Is Step 1 of Protein SynthesisJennifer JavedNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis: Transcription and TranslationaleksNo ratings yet
- 3.05 - DNA ReplicationDocument3 pages3.05 - DNA ReplicationGaurav Chaudhuri100% (1)
- Lesson 5 Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Protein SynthesisMarc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocument26 pages05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument14 pagesProtein SynthesisOginda MokoroNo ratings yet
- Bio Quiz # 2Document1 pageBio Quiz # 2Salma BashaNo ratings yet
- Dna ProcessesDocument28 pagesDna Processesvivas.kznne.9No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein SynthesisAvaniNo ratings yet
- DNA HomeworkDocument5 pagesDNA HomeworkZachary MorganNo ratings yet
- Ribosomes - Protein Construction Teams: RibosomeDocument2 pagesRibosomes - Protein Construction Teams: RibosomeIs SianNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: A Stepwise Description: Step 1: InitiationDocument1 pageProtein Synthesis: A Stepwise Description: Step 1: InitiationAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: InstructorDocument17 pagesCell Biology: Instructorahmed mediaNo ratings yet
- Chap 17 From Gene To Protein FixDocument30 pagesChap 17 From Gene To Protein FixRizaldi Al FauzanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document5 pagesUnit 4Jehitha CNo ratings yet
- Protien Synth 11thDocument3 pagesProtien Synth 11thtewoldeNo ratings yet
- Translation 1Document9 pagesTranslation 1akarshsingh111111No ratings yet
- Video Nomor 3Document3 pagesVideo Nomor 3M Restu HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- From Dna To ProteinDocument6 pagesFrom Dna To ProteinMadona BadoevNo ratings yet
- The Nucleus (Transcription & RNA Processing)Document13 pagesThe Nucleus (Transcription & RNA Processing)Rocelyn VillegasNo ratings yet
- Transcription: Protein Biosynthesis Is The Process by Which BiologicalDocument4 pagesTranscription: Protein Biosynthesis Is The Process by Which BiologicalAnand RajNo ratings yet
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument7 pagesProtein BiosynthesisOlusola OtasanyaNo ratings yet
- FROM Gene To Protein  Translation1cDocument41 pagesFROM Gene To Protein  Translation1cTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- S5 Biology (Protein Synthesis)Document9 pagesS5 Biology (Protein Synthesis)Mwesigwa HannahNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein SynthesismarielleanneNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein SynthesisEvans MogakaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL: DNA BIOLOGY and TECHNOLOGY 1. Describe The Biochemical CompositionDocument6 pagesTUTORIAL: DNA BIOLOGY and TECHNOLOGY 1. Describe The Biochemical Compositionaesha89No ratings yet
- 3.10 Protein-SynthesisDocument20 pages3.10 Protein-SynthesisPratika MNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument58 pagesGene ExpressionJunirose PanesNo ratings yet
- Script Assignment BioDocument2 pagesScript Assignment BioWAN NUR ALEEYA TASNIM BINTI WAN MOHAMED HAZMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- BIO G12 Unit 3 Short NotesDocument12 pagesBIO G12 Unit 3 Short NotesAmanuel AyalewNo ratings yet
- Transcription & Translation-G10Document11 pagesTranscription & Translation-G10CHALENE CLAIR PARONDO BAROTASNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDocument3 pagesPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument15 pagesCentral DogmaJean Rene100% (1)
- TranslationDocument7 pagesTranslationFathimaNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein SynthesisAshwarya ChandNo ratings yet
- Grade - 12 Biology: Oromia Education Bureau in Collaboration WithDocument79 pagesGrade - 12 Biology: Oromia Education Bureau in Collaboration Withmmree yyttNo ratings yet