Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hav Mapping Slide 2
Hav Mapping Slide 2
Uploaded by
marioOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hav Mapping Slide 2
Hav Mapping Slide 2
Uploaded by
marioCopyright:
Available Formats
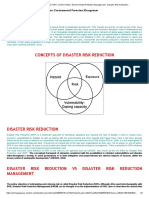
Slide 2: What is HAV Mapping?
HAV Mapping, or Hazard, Asset, and Vulnerability Mapping, represents a
sophisticated and methodical approach employed to dissect the intricate dynamics
of risk within a specific geographical area. It operates as a structured framework
designed to identify, analyze, and visualize the various elements that contribute to
the overall risk landscape.
At its essence, HAV Mapping entails a systematic inventory and assessment of
hazards, assets, and vulnerabilities present within the designated region. Hazards
encompass a diverse range of potential threats, including natural disasters like
earthquakes, floods, and wildfires, as well as human-made hazards such as industrial
accidents or chemical spills. By meticulously identifying and characterizing these
hazards, stakeholders gain critical insights into the types, frequencies, and severities
of risks that communities may face.
Assets, on the other hand, constitute the invaluable resources and infrastructure
within the area, including but not limited to buildings, transportation networks,
healthcare facilities, and natural resources. Asset mapping entails not only identifying
the physical components but also assessing their economic, social, and
environmental significance. Understanding the spatial distribution and vulnerabilities
of these assets is paramount for effective risk management and disaster response.
Vulnerability mapping forms the third pillar of HAV Mapping, delving into the
susceptibility of communities, infrastructure, and ecosystems to various hazards. This
involves evaluating factors such as population density, socio-economic status, land
use patterns, and environmental fragility. By pinpointing areas of heightened
vulnerability, decision-makers can prioritize interventions and allocate resources
where they are most needed.
Ultimately, HAV Mapping serves as a powerful tool for enhancing risk awareness,
facilitating evidence-based decision-making, and fostering resilience in the face of
uncertainty. By comprehensively assessing hazards, assets, and vulnerabilities,
stakeholders can develop targeted strategies to mitigate risks, strengthen
preparedness, and build adaptive capacities within communities.
You might also like
- Unit-4 Risk Analysis Technigues PDFDocument25 pagesUnit-4 Risk Analysis Technigues PDFShashank S RNo ratings yet
- Transportation Risk ManagementDocument16 pagesTransportation Risk ManagementlugbishNo ratings yet
- Hav Mapping Slide 1Document1 pageHav Mapping Slide 1marioNo ratings yet
- Territorial Vulnerability Assessment Frame in Colombia: Disaster Risk ManagementDocument15 pagesTerritorial Vulnerability Assessment Frame in Colombia: Disaster Risk ManagementDiego RamirezNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument6 pagesReflection Paperhanzpastorfide7No ratings yet
- Hav Mapping Slide 3Document1 pageHav Mapping Slide 3marioNo ratings yet
- Ijgi 07 00068 v2 PDFDocument23 pagesIjgi 07 00068 v2 PDFMuchamad DafipNo ratings yet
- DRRM Module2Document7 pagesDRRM Module2Jessa Eraldin OriginesNo ratings yet
- Desaster AssignmentDocument3 pagesDesaster Assignmentrana72aliNo ratings yet
- UNISDR Science and Technology Conference On The Implementation of The Sendai Framework For Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030Document12 pagesUNISDR Science and Technology Conference On The Implementation of The Sendai Framework For Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030Bebing LuyasNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2212420918303662 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S2212420918303662 MainPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Natasha - Kapai - MT20UPL022 - Assignment 1 - UDRRDocument9 pagesNatasha - Kapai - MT20UPL022 - Assignment 1 - UDRRNatasha KapaiNo ratings yet
- DM Mad 16Document3 pagesDM Mad 16GOUTHAM GOUTHAMNo ratings yet
- A Geospatial Analysis of Multi-Hazard Risk in DharDocument25 pagesA Geospatial Analysis of Multi-Hazard Risk in Dhartest testNo ratings yet
- Present Trends in Landsliding ControlDocument6 pagesPresent Trends in Landsliding ControlOanaNo ratings yet
- A Qualitative or QuantitativeDocument1 pageA Qualitative or QuantitativeMa. Karyl Ashrivelle CarreonNo ratings yet
- Vulnerability& Capacity AssessmentDocument14 pagesVulnerability& Capacity AssessmentGOUTHAM GOUTHAMNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Culher 2016 05 007Document13 pages10 1016@j Culher 2016 05 007Diana C.No ratings yet
- Risk N VulnerabilityDocument15 pagesRisk N VulnerabilityGOUTHAM GOUTHAMNo ratings yet
- Geoforum: SciencedirectDocument15 pagesGeoforum: SciencedirectRakibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk ReductionDocument3 pagesDisaster Risk ReductionNiña YastoNo ratings yet
- Community - Based Disaster Risk ManagementDocument40 pagesCommunity - Based Disaster Risk ManagementLouray Jean BereberNo ratings yet
- CRA MechanicsDocument5 pagesCRA MechanicsRonin BeltranNo ratings yet
- The UN Global Level 2020Document9 pagesThe UN Global Level 2020FlavioNo ratings yet
- DRM Week2Document9 pagesDRM Week2Lalaine LuzaNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument26 pagesDisaster ManagementHajarathbanu BagawanNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Learning General Emergency Life Support 2 - Scenario 2 Group 6BDocument4 pagesProblem Based Learning General Emergency Life Support 2 - Scenario 2 Group 6BFriedrich Rabin SitumorangNo ratings yet
- DRRR Notes 1Document2 pagesDRRR Notes 1Jaicheene C. LaronNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2212420919310398 MainDocument34 pages1 s2.0 S2212420919310398 MainFish FriedNo ratings yet
- Climate: Flood Vulnerability Analysis in Urban Context: A Socioeconomic Sub-Indicators OverviewDocument18 pagesClimate: Flood Vulnerability Analysis in Urban Context: A Socioeconomic Sub-Indicators OverviewFarahnaaz BagwanNo ratings yet
- Indicators For Disaster Risk Management: I I P D R MDocument38 pagesIndicators For Disaster Risk Management: I I P D R MIvy SuquibNo ratings yet
- Unit V Disaster Management - Applications and Case StudiesDocument54 pagesUnit V Disaster Management - Applications and Case StudiesAravindhan RNo ratings yet
- AssessmentsDocument28 pagesAssessmentsanubha guptaNo ratings yet
- Disaster MGTDocument30 pagesDisaster MGTojuNo ratings yet
- Ahtar Alam Sir LupDocument17 pagesAhtar Alam Sir LupMuneeb Yaqoob 01No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Concept, Goal and Products, Tools and IssuesDocument85 pagesRisk Assessment: Concept, Goal and Products, Tools and IssuesPravita Arvyn DirgantariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1& 2 Disaster MGTDocument32 pagesUnit 1& 2 Disaster MGTAarti SainiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 VulnerabilityDocument20 pagesUnit-1 Vulnerabilityabhishek sudheerNo ratings yet
- DRRMDocument6 pagesDRRMEl lenNo ratings yet
- Model Framework: DraftDocument14 pagesModel Framework: DraftJitendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Combining Hazard, Social Vulnerability and Resilience To Provide A Proposal For Seismic Risk AssessmentDocument18 pagesCombining Hazard, Social Vulnerability and Resilience To Provide A Proposal For Seismic Risk AssessmentMilena ZainotteNo ratings yet
- The Vulnerability To Water Hazards of UrDocument12 pagesThe Vulnerability To Water Hazards of UrDeliaRobuNo ratings yet
- Sat Imagery Interpretation Guide3Document24 pagesSat Imagery Interpretation Guide3Alliyah AporNo ratings yet
- Resilience Is The Ability of A SystemDocument3 pagesResilience Is The Ability of A SystemAbel AssefaNo ratings yet
- g13 SafetyDocument12 pagesg13 SafetyKean Ahlbrix GaspeNo ratings yet
- Colombia Urban Level 2017Document12 pagesColombia Urban Level 2017FlavioNo ratings yet
- Exposure and Physical Vulnerability Indicators To Assess Seismic Risk in Urban Areas A Step Towards A Multi Hazard Risk AnalysisDocument25 pagesExposure and Physical Vulnerability Indicators To Assess Seismic Risk in Urban Areas A Step Towards A Multi Hazard Risk Analysisscri_kkNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 12 07355 v2Document22 pagesSustainability 12 07355 v2Deba RoyNo ratings yet
- TA1-RiskReductionMeasuresforDams 508Document13 pagesTA1-RiskReductionMeasuresforDams 508Asad IqbalNo ratings yet
- A Quantitative Flood Risk Analysis Methodology For Urban Areas With Integration of Social Research DataDocument21 pagesA Quantitative Flood Risk Analysis Methodology For Urban Areas With Integration of Social Research Datanur syafiqaNo ratings yet
- Shivamogga District Disaster Management Plan 2019-2020Document238 pagesShivamogga District Disaster Management Plan 2019-2020Monika AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Terms Ra 10121Document4 pagesTerms Ra 10121Arlly Faena AbadNo ratings yet
- TIEMS 2008 Bernd Rohrmann KeynoteDocument10 pagesTIEMS 2008 Bernd Rohrmann KeynoteAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Vulnerability AssessmentDocument3 pagesVulnerability AssessmentfarihafairuzNo ratings yet
- PM 211 Module 2 - SPDocument11 pagesPM 211 Module 2 - SPLouray JeanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk ManagementDocument72 pagesDisaster Risk ManagementDoctor Oliver RyneNo ratings yet
- Redefining Community and Vulnerability in The Context of Emergency ManagementDocument6 pagesRedefining Community and Vulnerability in The Context of Emergency ManagementVimala NunavathNo ratings yet
- DRRR 110Document7 pagesDRRR 110Alexa Nicole PamaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Disaster& Risk Management Submitted By: Ezza Ahmad Butt Submitted To: Ma'Am Shumaila Submission Date: 24 SPET 2021 Semester 7Document5 pagesAssignment 1 Disaster& Risk Management Submitted By: Ezza Ahmad Butt Submitted To: Ma'Am Shumaila Submission Date: 24 SPET 2021 Semester 7Shumaila MajeedNo ratings yet
- Constructing Risk: Disaster, Development, and the Built EnvironmentFrom EverandConstructing Risk: Disaster, Development, and the Built EnvironmentNo ratings yet